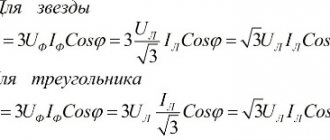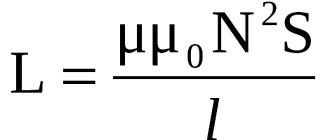What is electric power
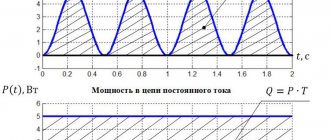
The power of an electric current refers to certain changes associated with energy. For example, transmission of electricity through wires. In this case, the line power is determined.
Or it could be a transformation, so an electric motor can perform some mechanical work, a phone converts electricity into radio waves, spends energy to operate the processor, screen, and the like. It turns out that power refers to energy consumption over a certain period of time.
But there is also a reverse process. So the generator, on the contrary, generates electricity, giving it to the consumer, and has some power. The battery can be both a source of energy and a consumer during charging. By its essence, power is a scalar quantity and is determined in a point period of time.
| Scalar – a quantity determined only by a number, without indicating the direction of movement of the electric current. |
In addition, the consumer himself can change his power depending on the task at hand. This is easier to explain using the example of a film camera.
When the camera is operating, the current consumption is the same, if photography is taken, then the power is different, and if a flash is used, then the power is already a third. And every time you can determine your energy consumption using a simple formula.
Formula for calculating power, current and voltage
the units of power included in the formula or determine what makes electrical energy capable of performing any action?
The electric charge that makes up the current must move; only in this case is it possible to manifest it, since by definition, electric current is the movement of charged particles in a closed circuit. Therefore, power directly depends on the amount of energy transferred per point in time in a certain circuit.
What makes charges move? This is the potential difference created by the power source. It is measured in Volts and is called voltage . Another thing that needs to be taken into account is the number of charges passing at this moment through the cross section of the conductor. This is called amperage and is measured in Amperes. Here are the two ingredients needed for the simplified formula.
What should be done with these components? To make it easier to understand, we will assume that voltage is responsible for the speed of movement, and current is responsible for the amount of charge. Let the voltage be equal to 1 unit and the current start with 2 charges. In this case, 2 charges will be moved per unit of time.
What if the voltage is increased to 2 units? Then the charges will be moved twice as much, since the speed of movement will be increased.
From this we conclude: to find out the power (the number of moved charges), you need to multiply the voltage by the current. Substituting the symbols, we get the power formula: P=UI;
- where P is power,
- U – voltage,
- I – current strength.
It remains to find out how electrical power is measured.
Determination of power transformer power
For the manufacture of transformer power supplies, a single-phase power transformer is required, which reduces the alternating voltage of the 220 volt mains to the required 12-30 volts, which is then rectified by a diode bridge and filtered by an electrolytic capacitor.
These transformations of electric current are necessary since any electronic equipment is assembled on transistors and microcircuits, which usually require a voltage of no more than 5-12 volts.
To assemble a power supply yourself, a novice radio amateur needs to find or purchase a suitable transformer for the future power supply. In exceptional cases, you can make a power transformer yourself. Such recommendations can be found on the pages of old books on radio electronics.
But nowadays it’s easier to find or buy a ready-made transformer and use it to make your own power supply.
Full calculation and independent production of a transformer for a beginning radio amateur is quite a difficult task. But there is another way. You can use a used but serviceable transformer. To power most home-made designs, a low-power power supply with a power of 7-15 watts is enough.
If the transformer is purchased in a store, then, as a rule, there are no special problems with selecting the right transformer. The new product has all its main parameters indicated, such as power , input voltage , output voltage , as well as the number of secondary windings, if there is more than one.
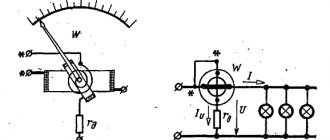
But what if you come across a transformer that has already worked in some device and you want to reuse it to design your own power supply? How to determine the power of a transformer, at least approximately? The power of the transformer is a very important parameter, since the reliability of the power supply or other device you assemble will directly depend on it. As you know, the power consumed by an electronic device depends on the current it consumes and the voltage required for its normal operation. Approximately this power can be determined by multiplying the current consumed by the device ( In) by the supply voltage of the device ( Un ). I think many are familiar with this formula from school.
,where Un – voltage in volts; Iн – current in amperes; P – power in watts.
Let's look at determining the power of a transformer using a real example. We will train on the TP114-163M transformer. This is an armor-type transformer, which is assembled from stamped W-shaped and straight plates. is worth noting that transformers of this type are not the best in terms of efficiency . But the good news is that such transformers are widespread, often used in electronics and can be easily found on the shelves of radio stores or in old and faulty radio equipment. In addition, they are cheaper than toroidal (or, in other words, ring) transformers, which have high efficiency and are used in fairly powerful radio equipment.
So, before us is the transformer TP114-163M. Let's try to roughly determine its power. As a basis for calculations, we will take recommendations from the popular book by V.G. Borisov "Young Radio Amateur".
Watt and other power units
The concept of watt was first used in 1882. Previously, power was measured in horsepower. This term was included in the international system in 1960. The designation uses the letter W in the international system and W as the Russian equivalent. The concept of power is used not only in electrical engineering; power can be:
- mechanical;
- thermal;
- electromagnetic and so on.
If you understand how current power is measured, then there are derivatives from the basic unit. The complete list is given in the table.
In everyday life, watts and kilowatts are most often used. This is where confusion can arise. When you need to find out what power is measured in, you should clarify what we are talking about. The fact is that there is another measurement - kilowatt per hour. What is the difference between kilowatt and kilowatt per hour?
The first concept indicates the power of the device, that is, the ability of the device to convert electrical energy into something else. For example, a 1 kW light bulb can consume energy equal to 1 kW in one hour.
A 100 W light bulb will consume the same energy in 10 hours. And the meter, which monitors energy consumption, takes into account the consumption of all the energy passing through it in one hour. During the same hour, several kilowatts can be consumed.
It turns out that the power of the device does not depend on the operating time, but the power consumption, on the contrary, is directly related to time. Since we are talking about alternating current, it should also be noted that not everything is so simple here.
Methodology for calculating transformer power
When calculating the power transformer of the supply substation, the average daily load and the duration of the period of maximum consumption are taken into account. In this case, the following ratio should be taken into account:
The peak consumption mode must also take into account the exposure time, since with short-term bursts (up to 1 hour), the device will operate in an underloaded mode, which is not economically profitable.
In such cases, it is necessary to take into account the overload capacity of the structure, which depends on design features, ambient temperature and cooling conditions. This is dictated by the conditions of permissible heating of the constituent elements (windings, switching circuits).
The concept of load factor defines the ratio of average daily and maximum consumption of electrical energy. The load factor is always less than one. Its value is related to the requirements for the reliability of power supply. The lower the required reliability, the more the coefficient can approach unity.
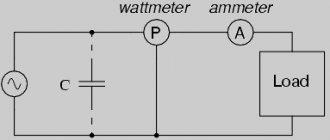
How are active, reactive and apparent power measured?
When it comes to DC current, then the above formula is applicable to the calculation. It can also be used to measure the instantaneous value of power in alternating current, but when it comes to determining power in a long-term temporary value, this formula is not applicable here. The fact is that in alternating current there are several definable powers:
- active;
- reactive;
- complete.
Let us immediately note that total power includes active and reactive power. What are these components and how is the power of each of them measured?
Reactive power, without going into complexity, consists of load power in the circuit of which inductance and (or) capacitance are included.
| Inductance is the name given to coils, with or without a core. For example, transformer, motor, choke. By capacitance we mean capacitors. |
It is determined by the formula Q=U·I·sinφ. The unit of measurement is VAR (Volt-Amp reactive) or var. The new component sinφ determines the phase shift in degrees or radians. What does it mean?
When alternating current passes through an inductance, the current begins to lag behind the changing voltage. This is due to the electromagnetic field that arises when current passes through a conductor. This field prevents you from changing direction. This shift is called positive.
Capacitance, on the contrary, acts in the opposite direction. The capacitor strives to equalize the potential difference across its plates. Therefore, the current leads the voltage. This shift is called negative.
Active power is determined by the formula P=U·I·cosφ. In a circuit with an active load, the capacitive and inductive components are very weakly expressed. Measured in Watts (W).
The apparent power is determined by the sum of the active and reactive power for the vector. Measured in Volt Amperes for SI, in Russia VA (Volt-Ampere) is used.
How to calculate correctly
Active power, how to make the correct calculation?
The power of the electric current affects how quickly the device can complete the job. For example, an expensive heater with twice the power will heat a room faster than two cheap ones with half the power. It turns out that it is more profitable to buy a unit with more power in order to heat a cold room faster. But, at the same time, such a unit will consume significantly more energy than its cheaper counterpart.
The power consumption of all appliances in the house is also taken into account when selecting wiring for installation in the house. If you do not take this into account and subsequently connect too many devices to the network, this will cause network overload. The wiring will not be able to withstand the power of the electric current of all devices, which will lead to melting of the insulation, short circuit and self-ignition of the wiring. As a result, a fire may start, which can lead to irreparable consequences.
You may be interested in this: How to find out amperage
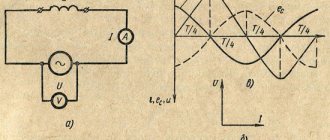
Single-phase sinusoidal current in electrical circuits is calculated by the formula P = U x I x cos φ, where υ and Ι. Their designation is encrypted as follows: the root mean square value of voltage and current, and φ is the phase angle between them.
For non-sinusoidal current circuits, the electrical capacitance is equal to the square root of the sum of the squares of the active and reactive performance. Active performance is characterized by the speed of the irreversible process of converting electrical energy into other types of energy. This capacitance can be calculated through the current, voltage and active component of the circuit resistance r or its conductivity g using the formula P = I(2) xr = U(2) x g.
Reactive Power
It should be noted that:
- The resistor consumes active power and releases it in the form of heat and light.
- inductance consumes reactive power and releases it in the form of a magnetic field.
- The capacitor consumes reactive power and releases it in the form of an electric field.
In any electrical circuit of both sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal current, the active capacity of the entire circuit is equal to the sum of the active powers of the individual parts of the circuit; for three-phase circuits, the electrical capacity is defined as the sum of the throughput of the individual phases. With the total performance S, the active one is related by the relation P = S x cos φ.
In the theory of long lines (the analysis of electromagnetic processes in a transmission line, the length of which is comparable to the length of the electromagnetic wave), the complete analogue of active power is transmitted power, which is defined as the difference between the incident power and the reflected performance.
How to find reactive apparent power through active power? This performance, which characterizes the loads created in electrical devices by fluctuations in the energy of the electromagnetic field in a sinusoidal alternating current circuit, is equal to the product of the rms values of voltage U and current I, multiplied by the sine of the phase angle φ between them: Q = U x I x sin φ (if the current lags behind the voltage, the phase shift is considered positive, if it is ahead, it is negative).
Reactive quantity designation