Instrumentation and automation engineer
Unified qualification reference book for positions of managers, specialists and other employees (US), 2021 Section “Qualification characteristics of positions of employees of nuclear energy organizations” The section was approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated December 10, 2009 N 977
Engineer for the acquisition of special products
Job responsibilities. Provides operation, maintenance and repair of instrumentation and automation equipment (CI&A) in accordance with rules, instructions and orders. Monitors the technical condition and safe operation of equipment, participates in the investigation of the causes of its failure. Keeps records and analyzes equipment failures and comments, summarizes equipment operating experience, and draws up reports. Develops measures to improve the operation, maintenance and repair of instrumentation and automation systems, draws up technical specifications and monitors its implementation. Reviews technical documentation for new instrumentation and automation systems, prepares proposals to eliminate comments. Participates in the development and implementation of technological maps, programs, labor organization projects, standards and instructions for operation, maintenance and repair of equipment. Considers rationalization proposals and inventions, generalizes and disseminates best practices in the operation and repair of instrumentation and automation equipment. Develops proposals for standards for equipment maintenance and repair. Prepares requests for spare parts, materials, tools and measuring instruments. Organizes acceptance from installation and commissioning of newly installed instrumentation and automation equipment, conducts experimental work on the equipment. Draws up schedules for maintenance and repair of instrumentation and automation systems, measuring instruments and automation. Ensures the implementation of schedules for preventive inspections and various types of repairs of instrumentation and automation equipment, takes part in checking the performance of instrumentation and automation systems. Organizes the introduction of advanced labor methods and techniques, carries out activities for certification and rationalization of workplaces. Conducts training and assists employees in mastering new instrumentation systems and measuring instruments. Participates in the pricing of work and assignment of qualification categories to workers.
Must know: laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, methodological and regulatory documents on the operation, maintenance and repair of instrumentation and automation equipment; prospects for the development of instrumentation and automation schemes and systems; fundamentals of metrology, goals and objectives of metrological support; organizing repair and maintenance of equipment; system of scheduled preventive maintenance and rational operation of instrument equipment; technical characteristics, design features, purpose and operating principles of equipment, technical operation rules; principles of maintenance and repair planning; the procedure for drawing up applications for equipment, materials, spare parts, tools; the procedure for tariffication of work and workers, provisions for remuneration; fundamentals of economics, organization of production, labor and management; basics of labor legislation; environmental regulations; labor protection and fire safety regulations; internal labor regulations.
Qualification requirements.
Instrumentation and automation engineer of category I: higher professional (technical) education and work experience as an instrumentation and automation engineer of category II for at least 3 years.
Instrumentation and automation engineer of category II: higher professional (technical) education and work experience as an instrumentation and automation engineer for at least 3 years.
Instrumentation and automation engineer: higher professional (technical) education without any work experience requirements.
GENERAL OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
1.1.
Employees who are at least 18 years old, have the necessary theoretical and practical training, have undergone a medical examination and have no contraindications for health reasons, have passed an introductory and primary workplace instructions on labor protection and training according to a special program, certified by the qualification commission and received permission to work independently.1.2. An instrumentation mechanic must periodically, at least once a year, undergo training and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements and receive permission to perform high-risk work.1.3. An instrumentation mechanic, regardless of qualifications and work experience, must undergo repeated training in labor safety at least once every three months;
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
in case of violation of labor safety requirements, as well as during a break in work for more than 30 calendar days, he must undergo unscheduled instruction.1.4. An instrumentation mechanic must undergo training and testing of knowledge of the rules and regulations for working in electrical installations and receive (confirm) an electrical safety group of at least III.1.5.
Women are not allowed to work on the repair of control and measuring instruments filled with mercury and radioactive devices.1.6. An instrumentation and automation mechanic who is allowed to work independently must know: the design, operating principle and methods of setting up the devices, mechanisms and apparatus being repaired and adjusted.
Purpose and methods of setting up control and measuring instruments. Rules, regulations and instructions for labor protection and fire safety. Rules for the use of primary fire extinguishing agents. Methods of providing first aid in case of accidents. Internal labor regulations of the organization.1.7.
An instrumentation mechanic sent to participate in work unusual for his profession must undergo targeted training on the safe performance of the upcoming work.1.8. An instrumentation mechanic is prohibited from performing work for which he is not authorized in accordance with the established procedure, as well as using tools and equipment with which he does not have the skills to handle safely.1.9.
During work, the instrumentation mechanic can be adversely affected mainly by the following dangerous and harmful production factors: - electric current, the path of which, in the event of a short circuit to the housing, can pass through the human body; - moving and rotating parts of the electromechanical devices and systems used, as well as tools, machines, equipment;
- sharp edges, burrs, roughness on the surface of tools, devices, equipment; - increased concentration of lead vapor in the air of the working area (when soldering with POS type solders); - soldering iron tip heated to a high temperature and molten solder; - flying off (for example, from spring-loaded wires) particles of molten solder;
- harmful chemicals contained in lubricants and paints and varnishes; - increased level of ionizing radiation (for example, when working with devices with sources of ionizing radiation); - insufficient illumination of the workplace.1.10. During work, an instrumentation mechanic must use special clothing and other personal protective equipment from the effects of hazardous and harmful production factors.1.11.
To prevent the possibility of a fire, the instrumentation mechanic must comply with fire safety requirements himself and prevent other workers from violating these requirements; Smoking is allowed only in specially designated areas.1.12. The instrumentation mechanic is obliged to observe labor and production discipline.1.13.
READ MORE: Encyclopedia of solutions. Purchasing methods under Law N 223-FZ, conditions for their application. Procurement Regulations
If an accident occurs with any of the employees, the victim must be given first aid, report the incident to the manager and maintain the situation of the incident, if this does not create a danger to others.1.14. An instrumentation mechanic, if necessary, must be able to provide first aid and use a first aid kit.1.15.
To prevent the possibility of illness, an instrumentation mechanic should follow the rules of personal hygiene, including washing his hands thoroughly with soap before eating.1.16. It is not allowed to perform work while intoxicated or in a state caused by the consumption of narcotic drugs, psychotropic, toxic or other intoxicating substances, as well as drink alcoholic beverages, use narcotic drugs, psychotropic, toxic or other intoxicating substances at the workplace or during work. time.1.17.
An instrumentation mechanic who violates or fails to comply with the requirements of labor protection instructions is considered a violator of production discipline and may be subject to disciplinary liability, and, depending on the consequences, to criminal liability; if the violation is associated with causing material damage, then the perpetrator may be held financially liable in the prescribed manner.
Instrumentation and automation mechanic
Instrumentation and automation mechanic is a profession of a worker who maintains, repairs and operates various instrumentation equipment and automatic control systems.
- Persons who are at least 18 years old, have secondary vocational education or vocational training, have undergone a medical examination and have no contraindications to performing this work, have been trained in safety regulations, have vocational training, and have tested their knowledge of rules for the operation of consumer electrical installations (PEEP), certification according to the rules, norms and instructions for industrial safety in the certification commission. Certification of instrumentation mechanics is carried out once a year. Repeated instruction is carried out after 6 months.
- A mechanic for instrumentation and automation is administratively subordinate to the head of the workshop, and operationally and technically to the instrumentation and automation master of the workshop or the person replacing him.
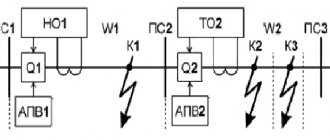
The instrumentation and automation mechanic on duty promptly reports to the production site foreman (MPU), performs commissioning work strictly in accordance with the instructions for the equipment to be connected and subsequently serviced (controllers, control panels). In the event of an emergency in the workshop, the instrumentation and control mechanic on duty acts in accordance with the order of the LPU. During work, maintains contact with operational technological personnel. The MPU is obliged to notify the MPU about any malfunctions noticed.
Education in the resume of an instrumentation mechanic
This section indicates the name of the educational institution, faculty, specialty and graduation date. Training must be confirmed by an appropriate document
. Having a diploma in your specialty is always a priority. This is your trump card, which helps you get a position even in the absence of practical experience.
For a specialist working with instrumentation, advanced training is of great importance
. The application form must include all online and offline courses, lectures, and seminars that are relevant to the position. The block indicates the name of the educational institution or organizer, the name of the course and the year of completion.
Template for filling out information about the education received:
EDUCATION
- Institution:
College of Modern Technologies - Faculty:
Educational building No. 2 “Alekseevsky”
- Speciality:
Instrumentation and automation engineer
- Year of ending:
2015
An example of filling out information about completed courses:
COURSES
- Year of ending:
2015 - Course name:
Advanced training in the field of instrumentation and automation
- Conducting organization:
Professional Training Center
- Year of ending:
2019
- Course name:
Oil and gas equipment repair
- Conducting organization:
Academy of Vocational Education
Responsibilities
- Perform all types of work provided for by the ETKS in a timely and high-quality manner in accordance with the assigned qualifications and in compliance with the rules and regulations for their safe implementation, ensuring trouble-free operation of measuring instruments.
- Perform maintenance work on measuring instruments, routine repairs of alarm and interlock circuits.
- Carry out orders and instructions for the enterprise, orders and instructions from the head of the workshop, instrumentation and automation (MPU) foreman concerning production activities.
- Comply with internal labor regulations, observe labor and production discipline.
- Use electricity, spare parts, materials economically and ensure the safety of entrusted material assets.
- Maintain a clean and tidy work area, assigned equipment and area.
- Perform the duties of a worker in accordance with the generally applicable Regulations on the industrial safety and labor protection management system at the enterprise.
- Always be at the workplace in special clothing and safety shoes, have with you the necessary protective equipment in good condition and be able to use them
- Perform only the work that is assigned to him in compliance with the requirements of the rules and instructions for their safe implementation.
- Promptly report to the instrumentation and control master about the completion of the assigned task or the reasons for its non-fulfillment, about all problems that arise and measures taken to eliminate them.
- Make entries about the results of the work performed in the operational log, passports for measuring instruments, a schedule of verifications and calibrations of measuring instruments, a plan-schedule-report of the performance of alarm and interlock circuits.
- Require installation personnel and other persons operating instrumentation and automation equipment to treat instrumentation and automation equipment and equipment with care.
What is instrumentation and automation: definition of the term and types
Most often, the installation of these devices is carried out by specialists.
For this reason, these instrumentation devices must have exceptional characteristics in terms of quality and measurement accuracy. A special group of instrumentation is formed by instruments used to measure pressure. These should be considered various models of pressure gauges, vacuum gauges, pressure meters, etc. These devices have become widespread in various fields, which include industry, boiler systems, and oil refining. Mention should also be made of control and measuring devices that measure the volume of bulk solids and liquids.
In addition to them, there are other subgroups of instrumentation, which include devices used to determine switching costs, protection devices, etc. Although there are quite a lot of these devices, thermostats, auto drives, and frequency converters are most often used.
As already mentioned, the main purpose of instrumentation and automation is to measure certain quantities.
Responsibilities of a baling specialist
When drawing up job descriptions for managers and specialists, it is necessary to take into account the general provisions for this issue of the directory and the introduction with general provisions for the first release of the directory of positions.
We draw your attention to the fact that the same and similar job titles may appear in different editions of the CEN.
instrumentation and automation) is guided by: - regulatory documents on the issues of the work being performed; - methodological materials regarding relevant issues; - the charter of the organization; - labor regulations; - orders and instructions from the head of the organization (immediate manager); - this job description.4. An instrumentation and automation engineer must know: - guidelines, regulations, instructions and methodological materials related to working with instrumentation and automation, environment communications and refrigeration equipment; - technology of production processes; - device, methods maintenance and repair of instrumentation and automation equipment, communications and refrigeration equipment; - basics of economics, organization of production, labor and management; - basics of labor legislation; - rules and regulations of labor protection and fire safety.5.
Job Description for Instrumentation and Control Engineer
Like any regulatory document, the DI contains an introductory part and mandatory sections that make up its “backbone”. Let's consider what the job description of an instrumentation and automation engineer might look like in the general case.
By the way, the above option, after making certain additions, can be used at an enterprise in any field.
So, the first mandatory section is “General Provisions”.
Its content is approximately the same for any DI, so there is no point in considering it in detail.
The second is “Tasks and Responsibilities.” An approximate list of responsibilities is already given above. Only one thing can be added to it: the activities of an engineer must comply with the requirements of the law “On Ensuring the Uniformity of Measurements.” The list of tasks, as already mentioned, is specified depending on the specifics of the enterprise. The third section that is necessarily present in the DI is “Rights”.
Basically, this section provides what
Job Description for Instrumentation and Automation Engineer (I&C)
During the absence of an instrumentation and automation engineer, his duties are performed in the prescribed manner by an appointed deputy, who bears full responsibility for their proper execution. 6. To perform the functions assigned to him, the instrumentation and automation engineer (I&C) is obliged to: 6.1. Organize work on the technical operation and repair of instrumentation and control equipment, communications equipment, refrigeration equipment and ensure their uninterrupted operation.
6.2. Draw up schedules for scheduled preventative repairs and maintenance of instrumentation and automation equipment, communications equipment, refrigeration equipment and ensure their implementation. 6.3. Organize the repair of faulty or rejected devices during state verification.
Events Quarter
(Instrumentation and automation - instrumentation and automation) General characteristics of the profession A person who first comes to the control panel of a large enterprise is amazed by the abundance of a wide variety of instrumentation, sensors, analyzers, regulators and other automatic equipment. This entire complex of instrumentation and automation provides the operator with information about the mode of the technological process.
Without well-established operation of instrumentation and automation, normal operation, high quality products, safety and accident-free work are unthinkable. An instrumentation and automation mechanic is a universal specialist who performs maintenance, repair and operation of various instrumentation equipment and automatic control systems.
An instrumentation mechanic deals with rapidly becoming more complex and improving equipment, which requires constant professional growth from him.