Full check of the diode bridge
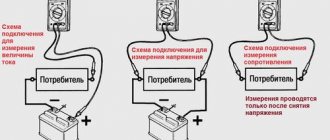
You can also check the diode bridge with a multimeter according to the following instructions:
- We set the red probe to “–”, and touch the black terminals in turn to which the alternating voltage is connected “
", in both cases there should be about 500 on the device screen. We put the black probe on “–”, touch the red terminals “
or AC”, the multimeter display shows one, which means the diodes do not conduct in the opposite direction. The first half of the diode bridge is working.
The black probe is on “+”, and with the red one we touch the AC voltage inputs, the results should be the same as in point 1. We swap the probes, repeat the measurements, the results should be the same as in step 2.
The same can be done with a “tseshka” (a Soviet-made universal measuring device). How to check a diode bridge with a dial multimeter is described in the video:
By the way, the test can be performed without a tester at all - with a battery and a test light (or LED). When the diode is turned on correctly, current will flow through the light bulb and it will light up.
In conclusion, I would like to note that diode bridges are installed everywhere: in the charger, welding machine, on the inverter, in power supplies, etc. Thanks to the described method, you can test diodes for performance at home.
It will be useful to read:
Electronics today are an integral part of any mobile gadget, household appliance or vehicle. Often the cause of a breakdown is the failure of a semiconductor - a small element of the electronic “filling”. Checking the diode allows you to understand whether this conductor is working or needs to be replaced.
You can perform such manipulations yourself at home without the involvement of a specialist. To do this, you will need knowledge of the basics of electrical engineering and a special measuring device - a multimeter. In the case where the diode cannot be removed from the circuit, you will have to be creative and create a device adapted for these conditions.
Verification procedure
Testing of the diode bridge is carried out in its disconnected state from the rest of the circuit. If the bundle is represented by a single assembly, it is soldered entirely. For a design based on an element base, they break the electrical lines with the transformer and further connected parts of the circuit. There are cases when it is easier to unsolder diodes for individual testing than to test them assembled on a board.
The principle of the definition is based on the fact that each semiconductor pn element, the basis of the bridge, passes current in one direction and blocks its movement in the opposite direction.
The multimeter is switched to ringing mode. The probes are placed in sockets - black “COM”, this will be the “negative” contact, red in “VmA” or similar, depending on the model of the device. It will be a plus. We check the first diode for current flow. To do this, touch the “−” output with a red probe, and touch the upper “~” input with a black one. The multimeter should signal the start of current flow by showing the opening voltage of the diode.
Semiconductor element number 2 is checked by touching the black probe of the second input contact “~”. The tester readings should be almost identical to the previous sample. Now we need to evaluate the performance of the pn junction for the first two elements. The probes are swapped, that is, the black one will now lie on “−”, and the red ones will touch the AC inputs in turn. In both cases, the tester should show 1, which means there is no electron movement.
Next, they move on to testing elements 3 and 4. The black probe is connected to the “+” output of the bundle and alternately touches the red inputs, previously coming from the step-down part of the circuit. The readings change and are approximately equal - both elements pass current in the same direction. The probes are swapped - red to “+”, and black to both “~”, to determine whether semiconductor elements 3 and 4 are broken through. There should be no movement of electrons in both cases.
You can speed up the check if the current passing through one element of the bundle is known. To do this, place a black probe at the “+” output, and a red one at the “−” output. The tester reading should be approximately equal to the number of millivolts of opening multiplied by two. If the value is different or absent altogether, one of the diodes of the entire bridge is faulty. The functionality of the pn junction of the common elements is checked by connecting the multimeter back. Current should not flow in the direction from the red probe to the black one.
The simplest and roughest check
We will need an indicator screwdriver. It costs pennies and should be in every home's toolbox. You just need to first touch the 220V input of the rectifier, if the indicator on the phase wire lights up, then voltage is present, if not, the problem is clearly not in the diode bridge and you need to check the cable. If there is voltage at the input, check the voltage at the positive output of the rectifier; at this point it can reach up to 310 V, the indicator will show it to you. If the indicator does not light, the diode bridge is broken.
Unfortunately, we won’t be able to find out anything else using an indicator screwdriver. You can learn how to use an indicator screwdriver from our article.
Multimeter
Testing with a tester allows you to determine the serviceability of the diode or confirm its failure. The most commonly used measuring instrument in this area is the multimeter. It is used to measure all the main parameters of electrical circuit components: current, voltage, resistance, capacitance. More expensive models are able to measure the temperature of an object, find out the gain, the capacitance of capacitors, and test the circuit for a short circuit.
Almost all modern types of multimeter can work with both constant and sinusoidal types of electric current. Among the devices on the market, digital and analog types are the most in demand. And although the first type is more popular, the second is still actively used by professionals in their work.
The main advantages of classic analog multimeters are their reliability and low cost (compared to digital ones). However, the minus manifests itself in less accuracy, allowing an error of 1.5-2%.
Digital devices are often used at home. They are more accurate (accuracy up to 0.5%), easy to operate and have greater measurement resolution.
These testers do not require calibration before each measurement and are resistant to vibration.
There is a third type whose device includes both a pointer and a digital indicator.
In addition to the main body, the tester comes with 2 probes with red and black wires.
At the bottom of the instrument panel you can see several connectors:
- “COM” - common, grounded (for black probe);
- “VΩmA” - a connector that allows you to ring the contacts, measure the current strength and frequency (for the red probe);
- “10 A” is a socket for a wire that allows you to measure current up to 10A.
The fourth “°C mA Lx” socket, present on some models, measures additional parameters (temperature, gain and capacitance).
Also on the front panel you can see a rotary disk surrounded by a scale with digital values and marks. Using this dial, you can set the required values, configure them to the desired modes or perform certain functions.
How to check without dismantling
You can diagnose the device on site without disassembling the generator or desoldering the part. To do this, unscrew all the wires on the generator and voltage regulator, set the tester to ohmmeter mode, and connect the lamp to the battery in the manner described above.
This method allows you to check the serviceability of the entire bridge and individual groups.
Short circuit
For this test, the positive electrode is applied to output 30 of the generator (“plus” of the power rectifier), and the negative electrode is applied to the housing. A resistance value of 1 indicates that the bridge is in good condition.
One end of the lamp is connected to the negative terminal of the generator, the other to the positive terminal. A lit lamp indicates a short circuit.
Negative group
The negative electrode of the tester is connected to the frame of the generator, the positive electrode is connected to one of the diode bridge mounting bolts. The negative group is operational if the resistance is infinity.
To check with a lamp, connect its minus to the generator casing, and the plus to the axle mounting bolt. The lamp lights up or flashes when there is a malfunction in the negative group of elements.
Positive
The positive probe of the multimeter is connected to the positive terminal, the negative one to the bridge mounting bolt. With a working group, the resistance is infinite.
The negative of the lamp is connected to the bridge mounting bolt, the plus is applied to the positive terminal. A lit lamp indicates a short circuit in the positive semiconductors.
Minor group
The positive electrode of the tester is pressed to terminal 61 (usually the “plus” of the additional rectifier), the negative electrode is connected to any bridge mounting bolt. The diodes are serviceable with a resistance value of 1.
The negative end of the lamp is connected to the bridge mounting bolt, and the positive end is connected to terminal 61. A lit lamp indicates a malfunction in this group.
Bridges can be made of individual diodes or made as a monolithic structure (diode assembly)
Instructions for verification
Verification is carried out using several methods. This is done with the assistance of a multimeter and a lamp. With the first method, measurements are more accurate and safe. However, if the multimeter malfunctions, you can use a flashlight lamp with a voltage of 12 volts. After choosing the measurement method and finding the diode bridge, you need to inspect the entire board.
12 volt flashlight lamp for checking the bridge
Elements must have a natural color and no charring or decay. You also need to look at the place where the soldering and tracks are located. It is important that there are no broken or sealed parts. It is also necessary to inspect electrolytic capacitor barrels. They should appear undamaged and unswollen. If a capacitor swells and explodes, it is necessary to desolder it. All the same, this part needs to be replaced and will interfere with measurements. If a capacitor explodes, after desoldering it is necessary to thoroughly wash the board with alcohol, since parts of this element are acidic electrolytes that conduct current.
You may be interested in this: How to check the mosfet (field tester)
Next, you need to carry out a continuity test of the diode bridge. It is carried out in several stages. First, on the spot without desoldering, then more precisely with desoldering the circuit from the device. As a rule, in many cases only on-site testing is required. To work, you should take a dial or digital multimeter and set the resistance measurement mode to 1 kOhm.
Note! In the case of a digital multimeter, you need to set it to diode test mode. In each case, the result of the normal voltage is as follows: up to 200 and 700 Ohms.
Checking the bridge with a multimeter
Using a generator tester
You can check the diode bridge on the generator by performing the following steps:
- Unsolder the bridge from the generator and check each diode with a multimeter at a resistance mode of 1 kOhm;
- Bring the probes to the diode edges and take a measurement;
- Apply the probes to the diode edges in the opposite order and take another measurement after 10 minutes.
In addition to the topic of how to check the diode bridge of a generator with a multimeter, it should be noted that its negative and positive contacts work properly when outputting values up to 700 Ohms. If the value is less than 500 Ohm or the infinity sign, this indicates a hardware malfunction.
Testing the bridge with a generator lamp
If you don’t have a multimeter, you can check the diode bridge using a light bulb and battery. You need to take a battery or a cassette with 12 volt batteries, as well as an incandescent lamp that matches the voltage of the batteries. It should be selected low-power. Otherwise, you can burn the diode bridge with current. A light bulb from a flashlight or sidelights may be suitable for measurement. Next, you need to act as indicated by the diode bridge test circuit.
Scheme for checking a bridge using a generator lamp
According to the diagram steps on the left, you need to install the diode in the forward direction. At this moment the light should light up. This is a key sign of normal operation. According to the right diagram, the light bulb should not light up. All you need to do is assemble the tester and probes, ring the bridge and look at the lamp.
Note! If the light comes on, this indicates low resistance. If not, then it matters a lot.
Checking a conventional diode bridge
As written above, the diode bridge consists of four separate semiconductor diodes. To check its serviceability, we need to ring each of them in two directions. We turn the multimeter into test mode (it is marked with a diode or sound icon) and select the first diode with which we will begin the test.
We find its anode (positive terminal) and cathode (negative terminal). Usually they are indicated on the diode body using a color designation or corresponding icons. First, we check the diode in direct connection; to do this, we connect the red probe (positive) to the anode, and the black probe (negative) to the cathode.
Numbers should appear on the multimeter display - the value of the voltage drop, it is indicated in millivolts. This is the minimum voltage that is needed to open the diode.
Now let's check it in reverse connection, to do this we swap the probes - red to the cathode, and black to the anode. The display should show one, which indicates to us that the PN junction has a high resistance - this diode is working.
If the reverse connection shows low resistance, and the device beeps (with an audio indication), this diode is broken and needs to be replaced. Thus, we call the remaining three pieces and if a faulty one is found, we simply unsolder it and replace it with a new one.
Checking the diode assembly
The whole trick of the diode assembly is that we do not see the diodes separately. But there is nothing complicated here; a diode bridge circuit comes to our aid. For clarity, we place it close to us and begin checking. We will check as in the first paragraph of the article - one diode at a time. In the diode assembly, each pin is labeled, so finding the diode we need is not difficult.
Diode leads in a monolithic housing:
- Diode 1: minus assembly - anode, one of the variable terminals - cathode;
- Diode 2: minus assembly - anode, one of the variable terminals - cathode;
- Diode 3: variable output - anode, plus assemblies - cathode;
- Diode 4: variable output - anode, plus assemblies - cathode.
Knowing the designation of the terminals, we check each diode in two directions. If any of them has a breakdown or break, then get ready to replace the entire diode assembly. Images for clarity:
Checking diodes 1 and 2 with direct connection:
Checking diodes 1 and 2 when switched back on:
It will be interesting➡ How to test a transformer using a multimeter
Checking diodes 3 and 4 with direct connection:
Checking diodes 3 and 4 when switched back on:
If something is still not clear, perhaps you should watch a video on checking the diode bridge.
Operating principle of generator and diode
A generator is a device used to convert mechanical energy supplied from an engine into electrical energy. If it malfunctions, the following problems occur:
- headlights become dim;
- The battery charge signal lights up continuously;
- an extraneous sound is heard in the area where the generator is located;
- The analog needle of the voltmeter goes into the red zone.
Since the generator is directly connected to the charging circuit, the primary signs of a malfunction of the rectifier will be an overcharge or complete lack of charge of the battery. If such problems appear, the generator requires checking.
The output generator produces a sinusoidal signal, but devices located in the car require constant voltage. To generate a constant signal, a rectifier unit is built into the generator. It consists of six power diodes.
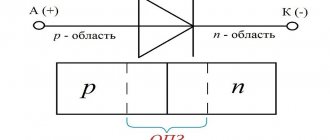
A diode is a semiconductor element with a pair of leads, electrodes. The principle of its operation is based on the ability to pass current in one direction. If the positive polarity of the signal is supplied to the p region of the device, and the negative polarity to the n region, then such a connection is called direct. If the polarity is reversed, then this is reverse connection.
In direct connection, the resistance of the pn junction is negligible and does not affect the passage of electric current, and when connected in reverse, it practically does not allow it to pass.
Principle of operation
The operation of a diode semiconductor bridge that conducts current is simple. The principle of operation is based on the property that a semiconductor diode passes electric current in one direction and does not pass in the other. So, if the charges are connected correctly, current will flow through the device.
The difference between alternating current and direct current is that it can only move in one direction. Moreover, do this in one half-cycle. During the other half of the period, it can make the opposite movement. When several diodes are connected in a circuit, they will begin to move, creating a direct current.
You might be interested in Features of Fuquay eddy currents
It is easy to assemble a diode bridge circuit. Anyone can do this. It includes four diodes, which are connected to each other by a square. Current is supplied to several opposite corners from the generator apparatus. From several other opposite angles the constant is removed. During the first period, several electrodiodes are opened and the alternating voltage wave is rectified. In the second period, several more diodes are opened. Thus, the second wave is transformed. The result is a constant voltage with a pulse frequency several times higher than that with alternating voltage.
Interesting! The presented scheme has its pros and cons. To use rectified current, the pulse component must be smoothed with a filter. Thanks to rectification, it is possible to power the transformer and reduce its volume. Among the disadvantages, note the fact that power is lost due to thermal dissipation, the voltage drops twice and the device breaks down if one diode fails.
How the device works
Features of testing depending on the type of diode
In the production of modern radio-electronic devices, several types of diodes are used:
- regular or protective;
- LEDs;
- Schottky diodes;
- Zener diodes;
- thyristors and triacs;
- infrared;
- photodiodes.
Protection diodes can be found in most modern household appliances. They are common and are the simplest elements of circuits for electric kettles, fans, blenders and other devices that make life easier.
The area of application of LEDs is the well-known lamps. They are divided into devices such as household and street lighting. Schottky diodes are used in assembling computer power supplies, and the main task of zener diodes is to protect devices from voltage surges, in other words, to stabilize them.
Diodes such as thyristors ensure smooth engine starting. They are actively used in the automotive industry. Triacs can pass current in two different directions.
Infrared ones are built into remote control panels and optical control and measuring instruments. Photodiodes convert the light that hits the sensitive board into an electrical signal. They are also used in organizing street lighting systems.
A multimeter is most often used to measure the characteristics of LEDs, conventional semiconductors and Schottky diodes. Testing of all these types is carried out by the tester in accordance with the same principle.
The main reasons for the malfunction of such semiconductors are:
- Exceeding the maximum permissible level of electric current.
- Poor quality parts or manufacturing defects.
- High reverse voltage.
- Violation of the operating instructions for the device.
Diagnostics is performed using a special device designed for this purpose - a multimeter.
What is a generator diode bridge and what functions does it perform?
The rectifier unit (another name for the device) is an integral part of the generator and serves to modify the alternating current produced by the unit into direct current, necessary for charging the battery and powering all electrical appliances of the car.
It is located on the frame of the generator and consists of 4, 6, 9 or more diodes placed on two insulated aluminum or steel horseshoe plates that act as cooling radiators.
The main components of the bridge are semiconductor diodes (most often silicon) that conduct current in the required direction. They are the rectifiers that convert alternating current into direct current. The battery acts as a capacitor, softening the inevitable voltage drops.
Instead of diodes, the circuit can use valves of any type - for example, selenium columns, the principle of operation of the circuit will not change.
How to check without installation
You can check household or automotive equipment on site without having to disassemble the generator and solder off the parts. This is not a difficult task. To do this, you need to unscrew the existing generator wires with a voltage regulator, which play a big role in the process, set the control multimeter tester to ohmmeter mode and connect the lamp to the transport electrical equipment.
You may be interested in this Features of the capacitor
Test diagram without installation
Thanks to this method, you can quickly check the serviceability of the entire bridge or individual diodes without looking at the table of contents of textbooks. Semiconductors can also be tested using a lamp. To do this, the battery is connected to the lamp and a break is made near it. The stripped ends will serve as feeler gauges to make checking easier. Together they attach to the body part and diode terminals in one polarity, and then in the other. In the first case, a working semiconductor will light the light bulb, but in the other case this will not happen. In this case, a quiet squeaking sound will be heard, and a current conversion will occur.
How to check a diode bridge: known methods
Before checking the diode bridge with a multimeter or autotester, familiarize yourself with the principle of operation of the circuit. A modern diode bridge has 3 positive, negative and additional diodes. The working element passes current in one direction. If the current does not pass or passes in both directions, then a break or “breakdown” has occurred.
The diode bridge is tested using a tester (called a multimeter). First you need to disconnect all wires from the generator. The check does not require dismantling the device itself unless you check the integrity of each diode individually.
Next, the diode bridge is analyzed with a multimeter in accordance with the data given in the table:
If the multimeter shows infinite resistance, then the device or group of diodes being tested is working. Otherwise, the check indicates a breakdown.
Checking a car diode bridge with a multimeter is not the only possible diagnostic method. You can also use a test light or check the bridge with a self-assembled analogue.
Using a test lamp, we make calls in the same way as with a multimeter. The unit is fully checked by connecting the “plus” through the lamp to pin 30, the “minus” - to the generator housing. For groups of diodes:
- Positive: “plus” with a test lamp is supplied to pin 30, “minus” - to one of the mounting bolts.
- Negative: “plus” with a light bulb – on the mounting bolt of the electrical component, “minus” – on the generator housing.
- Additional: a light bulb with a “positive” wire is connected to pin 61, a “minus” wire is connected to the mounting bolt.
If the control light comes on when the circuit is closed, then there is a malfunction; If it doesn’t light up, the circuit is working.
If necessary, you can, of course, test all diodes individually, but this will require unsoldering each diode.
Testing the diode bridge with a multimeter
Any part on the board can be desoldered for testing or ringing without desoldering. However, the accuracy of the check in this case is reduced, because perhaps a lack of contact with the board tracks, with visible “normal” soldering, the influence of other circuit elements. This also applies to the diode bridge; you don’t have to desolder it, but it’s better and more convenient to desolder it for testing. A bridge assembled from individual diodes is quite convenient to check on the board.
Almost every modern multimeter has a diode test mode, usually it is combined with an audio continuity test of the circuit.
This mode displays the voltage drop in millivolts between the probes. If the red probe is connected to the anode of the diode and the black probe to the cathode, this connection is called forward or conductive. In this case, the voltage drop across the PN junction of the silicon diode is in the range of 500-750 mV, which you can see in the picture. By the way, it shows a test in resistance measurement mode, this is also possible, but there is also a special diode test mode, the results will be, in principle, similar.
Read also: Do-it-yourself blade for a walk-behind tractor, photo drawings
If you swap the probes - red to the cathode, and black to the anode, the screen will show either one or a value of more than 1000 (about 1500). Such measurements indicate that the diode is working; if the measurements differ in one of the directions, then the diode is faulty. For example, if the continuity test is triggered - the diode is broken, there are high values in both directions (as with reverse switching on) - the diode is broken.
Important! Schottky diodes have a lower voltage drop, about 300 mV.
There is also an express check of the diode bridge with a multimeter. The procedure is as follows:
- We place probes at the input of the diode bridge (
or AC), if the bell is triggered, it is broken.
- We put the red probe on “–”, and the red one on “+” - a value of about 1000 appears on the screen, swap the probes - on the screen 1 or 0L, or another high value - the diode bridge is working. The logic of this test is that the diodes are connected in series in two branches, pay attention to the diagram, and they conduct current. If the positive power supply is applied to – (anode connection point), and the power supply minus is applied to “+” (cathode connection point), this is what happens during dialing. If one of the diodes is broken, current may flow through the other branch and you may make erroneous measurements. But if one of the diodes is broken, the voltage drop across one diode will be displayed on the screen.
The video below clearly shows how to check a diode bridge with a multimeter:
Causes of diode bridge failure and its symptoms
The diode bridge of the generator is structurally designed as a separate module. The forming elements may fail during ongoing operation. This happens for the following reasons:
- moisture entering the electrical circuit when washing a car or engine;
- penetration of dirt and oil into the generator housing with broken seals (occurs when driving at high speed on dirt roads);
- reversing the polarity of the battery contacts while “lighting” another car.
Indirect signs of bridge failure are manifested in the fact that
- the voltage at the generator output does not exceed 13.5 V or the ammeter needle is in the red sector;
- spark power decreases;
- the brightness of the headlights changes noticeably with changes in engine speed;
- the performance of the cooling system fan decreases;
- the starter does not develop the required number of revolutions;
- the normal functioning of the on-board air conditioning is disrupted.
Location of the diode bridge on the board and precautions
Diode bridges are installed in power supplies, both pulse and transformer. It is worth noting that in pulse units, which are now used in all household appliances, the bridge is installed at the 220V input. At its output, the voltage reaches 310V - this is the amplitude voltage of the network. In transformer power supplies they are installed in the secondary winding circuit, usually with a reduced voltage.
If the device does not work and you find a blown fuse, do not rush to turn on the device after replacing it. Firstly, if there are problems on the board, the fuse will burn again. This power supply must be turned on via a light bulb.
To do this, take a socket and screw a 40-100 W incandescent lamp into it and connect it to the phase wire to connect to the network. If you are going to frequently repair power supplies, you can make an extension cord with a socket installed in the gap in the power wire to connect the lamp, this will help save your time.
If there is a short circuit on the board, when connected to the network, a high current will flow through it, a fuse or a track on the board, or a wire will blow, or the machine will trip. But if we insert a light bulb into the gap, the resistance of the spiral of which will limit the current, it will light up at full intensity, maintaining the integrity of all of the above.
If there is no short circuit or the unit is working properly, either a slight glow of the lamp or its complete absence is acceptable.
How to check the diode bridge in a transformer power supply using a light bulb
This method requires the use of a light bulb of up to 100 watts, screwed into a socket. The lamp is connected to the groove of the power phase wire. If there is a short circuit on the board, the fuse will burn out, the wire itself will burn out, or the circuit breakers will burn out when the device is connected. If you check with an incandescent lamp, such troubles can be avoided. In the event of a short circuit, the light bulb inserted into the socket will glow brightly. It doesn't light because the coil resistance limits the current. If the electronic components of the board are working properly, the light will not light up at all or will glow dimly.
Broken diode bridge
Features of diodes
A standard diode is a component of the electrical network and acts as a pn junction semiconductor. Its structure allows current to pass through the circuit in only one direction - from the anode to the cathode (different ends of the part). To do this, you need to apply “+” to the anode and “-” to the cathode. Due to this feature of the product, if you suspect a breakdown, it can be checked with a tester or multimeter.
Various types of diodes.
Today in radio electronics there are several types of diodes: Types of diodes:
- Light-emitting diode. When an electric current passes through such an element, it begins to glow as a result of the transformation of energy into a visible glow;
- protective or regular diode. Such elements in the electrical network act as a suppressor or voltage limiter. One of the varieties of this element is the Schottky diode. It is also called a Schottky barrier diode. Such an element, when connected directly, gives a low voltage drop. In Schottky, instead of a pn junction, a metal-semiconductor junction is used.
Here is a small selection made up of specific diodes and their corresponding Vf values, which were obtained when testing them with a multimeter. All diodes were previously checked for serviceability.
Table of measurements of diode characteristics using a multimeter.
If ordinary parts and LEDs are used in the vast majority of electrical appliances, then Schottky ones are used mainly in high-quality power supplies (for example, for devices such as computers). It is worth noting that testing a conventional diode and a Schottky diode is practically no different, since it is carried out according to the same principle. Therefore, there is no need to worry about this issue, because the operating principle of both Schottky and conventional diodes is identical.
Schottky diode
Being a component of an electronic circuit, such semiconductor elements often fail. The most common reasons for their failure are:
- exceeding the maximum permissible direct current level;
- excess reverse voltage;
- poor quality part;
- violation of the device operating rules established by the manufacturer.
Moreover, regardless of the cause of loss of performance, failure can be directly caused by either a “breakdown” or a short circuit. In any case, if there is an assumption that the electrical network has failed in the semiconductor area, it is necessary to diagnose it using a special device - a multimeter. Only to carry out such manipulations you need to know how to check the diode using it correctly.
What is a multimeter
A multimeter is a universal device that performs a number of functions:
- measures voltage;
- determines resistance;
- checks wires for breaks.
Using this device you can even determine the suitability of the battery.
Checking the LEDs in the lamp.
How to test a diode
After we have figured out the semiconductors of the electrical circuit and the purpose of the device, we can answer the question “how to check the diode for serviceability?” The whole point of checking diodes with a multimeter is their one-way electrical current carrying capacity. If this rule is observed, the electrical circuit element is considered to function correctly and without failures. Conventional diodes and Schottky diodes can be easily tested using this device. To check this semiconductor element with a multimeter, you need to do the following manipulations:
- you need to make sure that your multimeter has a diode test function;
- If such a function is available, we connect the probes of the device to the side of the semiconductor from which the “ringing” will be carried out. If this function is missing, then use the switch to switch the device to 1 kOhm. You should also select the mode for measuring resistance;
- the red wire of the measuring device must be connected to the anode end, and the black wire to the cathode end;
- after this, you need to observe changes in the forward resistance of the semiconductor;
- we draw conclusions about the presence or absence of voltage
The unit can then be switched to check for leaks or high circuits. To do this, you need to change the location of the diode output. In this state, it is also necessary to evaluate the obtained values of the device.
How is the check carried out?
To check a semiconductor using a tester, you need to make sure that the multimeter has a diode test mode. After this, the work algorithm will be as follows:
- the red probe is inserted into the socket marked “VΩmA”;
- black – to the “COM” connector;
- select the mode for measuring resistance;
- the end of the red probe is connected to the anode, and the black one to the cathode;
- readings of changes in direct resistance are taken.
After all the operations performed, we can draw a conclusion about the performance of the semiconductor.
Checking the diode bridge
In a number of situations, it is necessary to check the condition of the diode bridge. It is a system of 4 diodes connected in such a way that the alternating voltage supplied to the two soldered components is converted to direct voltage.
The measurement algorithm is very similar to the classic method for testing a diode. However, there are also some nuances, namely the presence of 4 connection options depending on the pin number. The following combinations are usually called:
Analysis of results
Having received the test result, we can conclude that the semiconductor is serviceable. Signs of diode performance are:
- Coincidence of the forward voltage value displayed on the display when the element is connected to the tester with the indicators for a given type of diode.
- The zero value produced by the multimeter when connected in reverse.
Important! The voltage level of the semiconductor depends, among other things, on the type of diode, which must be taken into account during measurements.
If these parameters are observed, one can judge the working condition of the diode and the presence of a breakdown elsewhere. If one of the indicators does not meet the requirements, the semiconductor is considered non-working and must be replaced.
Checking diodes for serviceability using a tester is not so difficult on your own. A large assortment of multimeters on the market will allow you to choose a completely budget model, which will allow you to assess the performance of the diode in the circuit of any household electrical appliance.
How to test a diode with a multimeter without unsoldering it
Checking the Schottky diode is carried out without unsoldering it from the circuit, since this type of semiconductor is placed in a double case with a common cathode. So the measurement in this case can be done “on the spot”.
Read also: Homemade iron wheels on a walk-behind tractor
The same difficulties can arise when checking an LED. In some cases, it is necessary to evaluate a semiconductor without soldering it. Standard multimeter probes are not suitable for this, so you will have to make a special device that allows you to reach the electrodes in the circuit.
All work will include the following operations:
- On each side of a small foil fragment of PCB it is necessary to apply a small amount of solder on which the wires will be fixed.
- Straighten paper clips or small pieces of steel wire, which will then be soldered to the textolite gasket. Secure the entire structure with electrical tape.
- Prepare a multimeter with transistor testing mode.
- Connect the designed adapter to the tester.
- Place the probes on the legs of the semiconductor located in the circuit.
- To inspect.
Checking with a light bulb
To implement this method, you need a 12-volt low-power light bulb and three wires 1 meter long. Two of them are used to form the indicator cord. To do this, they are first connected to the contacts of the light bulb, which as a result ends up in their gap. The third wire connects one of the battery contacts to the bridge.
To check the circuit, the bridge body is connected to the battery negative with a third wire. Then one end of the indicator cord is connected to the negative terminal of the bridge, and the other end is connected to pin 30 of the bridge. The light coming on is a sign of a breakdown of the bridge, and its absence indicates a break.
To check the negative diodes, the minus voltage of the battery is applied to the bridge body. The plus of the battery is connected with an indicator cord to the fixing screw of the bridge. If the lamp lights up, it indicates a breakdown; its absence indicates a break. Testing positive diodes begins by applying the battery positive to terminal 30, and the negative is connected through the indicator cord to the bridge mounting screw. If the diodes are working properly, the lamp does not light up.
Something else useful for you:
- How to check and replace the alternator belt on a car
- Replacing the alternator belt on a Renault Logan with power steering and air conditioning
- How to quickly and easily check the generator relay regulator
Checking with a multimeter
The multimeter switches to resistance measurement mode (range 1 - 2 kOhm) or continuity with a sound signal. Before starting work, touching the contacts of the probes to each other controls the choice of the desired mode (reading 0 kOhm or sound signal, respectively).
Bridge diodes are divided into two types, conventionally called positive and negative. Positive diodes have a red body, and negative diodes have a black body. All diodes must be checked individually.
During the test, the multimeter probes are touched to the diode outputs and the result is recorded, then the probes are swapped. For a working diode, the resistance should be in the range of 400 - 800 Ohms in one position of the probes and become equal to infinity for a given range in another (the presence of a buzzer in the first case and its absence in the second).
If there is a different combination of test results (small + small or large + large resistance according to the indicator, or sound + sound, no sound + no sound), the diode is considered to be faulty.
How to Accurately Test a Diode Assembly: Detailed Analysis
To check, you will need a multimeter that has a diode test mode.
Training stages:
- We start the test from LEDs 1 and 2. To do this, connect the red probe of the tester to the terminal marked “-”. Above the two center pins is marked AC or. Connect the black probe first to one of these contacts, and then to the other in turn. This is a direct connection in which current flows freely. When turned on directly, the digital multimeter display will show the voltage drop across the pn junction. In foreign tables this value is designated as Vf. For silicon diodes the range is 0.4-0.7 V. For Schottky semiconductors it is lower, approximately 0.3 V. If these values are displayed on the meter, the diode assembly is fine.
- To clarify the test results of diodes 1 and 2, a reverse connection was made. To do this, connect the black probe (negative probe) to the “-” terminal. The red probe is applied alternately to the contacts marked AC or ̴. One should appear on the display, indicating high resistance and no reverse current. If yes, then the effectiveness of LEDs 1 and 2 is confirmed.
- Then diodes 3 and 4 are checked when connected directly. To do this, connect the black probe in series to the positive, and the red probe to the AC contacts. The display should show the voltage drop across the pn junction, which was described in the first paragraph.
- To confirm the result, connect the red probe to the positive and the black probe to the AC terminals. One should appear on the display.
If the diode assembly passes this test, you can be confident that all components are in working order.