Getting to know the phenomenon
Let us connect in series with a current source a lamp and an electrolytic bath with distilled water, into which carbon electrodes are lowered. Chemically pure water almost does not conduct current.
If you dissolve salt in water (for example, CuSO4, CuCl2), the light bulb will light up, and copper will be released from the solution at the cathode.
What substances conduct electric current?
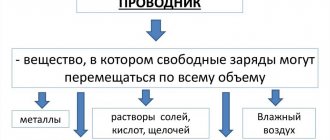
It is known from physics that electric current is the directed movement of electrically charged particles. Different substances conduct electricity in different ways. Based on their ability to transmit electrical charges, substances are divided into CONDUCTORS and NONCONDUCTORS of electricity.
Conductors are bodies through which electric charges can pass from a charged body to an uncharged one; conductors contain a lot of free charged particles. Good conductors of electricity are metals, soil, water with salts, acids or alkalis dissolved in it, graphite and some types of organic substances. The human body also conducts electricity. This can be demonstrated by experiment with an electroscope. We charge the electroscope using an ebonite or glass rod, the arrow will deflect. Then we touch the charged electroscope with our hand. The arrow will immediately return to its original position - to zero. The charge from the electroscope goes into our body. In this experiment with a small charge, this is not dangerous, but it does noticeably “click” your fingers. And large charges and currents are dangerous to life and health.
The best conductors of electricity among metals are silver, copper, and aluminum. Even in ordinary tap water there are so many different salts dissolved that it is a very good conductor, and this should not be forgotten when working with electrical equipment in conditions of high humidity, otherwise you can get a very noticeable electric shock, this is dangerous.
Passing through a living organism, an electric current produces different effects: thermal - burns of certain areas of the body, heating of blood vessels, blood, nerves; electrolytic (or chemical) - decomposition of blood and other organic liquids; biological - irritation and excitation of living tissues of the body, which is accompanied by involuntary convulsive contractions of muscles, including the muscles of the heart and lungs. As a result of all this, various disturbances in the body can occur, up to a complete stop of the heart and lungs.
Nonconductors are those bodies through which electric charges cannot pass from a charged body to an uncharged one, since there are very few free charged particles in dielectrics. Non-conductors of electricity, or dielectrics, are ebonite, amber, porcelain, rubber, various plastics, silk, nylon, oils, air (gases), glass, plexiglass, dry wood and paper. Bodies made of dielectrics are called INSULATORS (from the Italian word ISOLARO - to isolate).
Conductors serve to transmit electrical energy (electric current) over a distance; it is from them that high-voltage electrical cables and household electrical wiring are mainly made. Insulators are used to separate, insulate conductors and ensure the safety of people when working with electrical appliances. To transmit electricity, it is necessary to assemble a closed electrical circuit, which includes a source of electrical energy, conductors through which electric current flows from this source to consumers of electrical energy, and the consumers themselves.
When conducting experiments on electricity, both conductors and dielectrics are always used. For example, using two electroscopes, we charged one of them with a negative charge obtained on an ebonite stick when it was rubbed against wool. At the same time, the electroscope needle deviated, indicating the presence of a charge on it. If you then take a metal rod on an insulating plastic handle and connect a charged electroscope to an uncharged one, then through the current-conducting rod the charges will partially transfer to the second electroscope, but the electroscope will not discharge, as if touched with a bare hand, since the handle does not conduct current to a person's hand. That is why the handles of various tools, such as screwdrivers, pliers, and wire cutters, are made of non-conductive materials.
Basic measures to protect against electric shock:
• ensuring that live parts under voltage are not accessible to accidental contact,
• protective grounding, protective shutdown of electrical appliances;
• use as low voltages as possible, especially in wet areas;
• use of double insulation.
Knowledge and compliance with safety rules when working with electric current and various electrical appliances is mandatory for both adults and children. To make it easier for elementary school students to remember these rules, you can use various memorable posters and poems. I selected examples from various sources, came up with some myself and presented them as electrical safety tips in Appendix 1 to my work. Appendix 2 provides first aid measures for electric shock.
EXPERIMENTAL CHECKING THE ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY OF VARIOUS SUBSTANCES
The electrical conductivity of substances can be tested using a special device, but we used a regular electrical circuit. The main element of any electrical circuit is a source of electric current. Without it, the electrical circuit will not work. When you plug in the power cord of a TV, an electric iron, kettles and other electrical appliances that consume electrical energy, you are essentially connecting to a power plant that produces this electricity.
In order to test the electrical conductivity of solid substances, I assembled an electrical circuit, which included: a current source, a key to close and open the circuit, a lamp to check whether there is current or not, and contacts to connect the substance to the circuit.
When contacts are placed into a substance, it becomes clear whether the substance conducts current. If the substance conducts an electric current, the circuit is completed and the light bulb lights up. If the substance is not electrically conductive, the circuit remains open and the light bulb does not light.
Experiment 1. Study of solids.
Table 1 lists the ten solids we tested for electrical conductivity. As a result of the inspection, it turned out that
brass + org. glass -
wood - rubber - that aluminum, steel, brass, copper conduct electric current, but wood, plastic, glass, plexiglass, magnet and rubber do not conduct electric current.
Experiment 2. Study of liquid substances.
In order to test the electrical conductivity of liquid substances, we changed the electrical circuit (Fig. 5). In addition to the current source and the key, an ammeter was added to the circuit instead of a lamp and an electrolytic glass instead of contacts.
table salt solution +
copper sulfate solution +
sea salt solution +
We placed different liquids into an electrolytic beaker. If the ammeter's needle deviates when the circuit is closed, it means that the liquid conducts electric current.
As a result of our experiment, it turned out that a solution of table salt, copper sulfate and sea salt conducts electric current, but pure water and sugar syrup do not.
Experiments have confirmed that some substances conduct current well, these are various metals and salt solutions. Other solid and liquid substances are dielectrics, i.e. non-conductors, these are plastics or rubber, from which the insulation of electrical wires and the housing of electrical devices is made, and many other substances.
My work is quite important for me and other schoolchildren, because in order to work safely with electrical appliances at home and at school, you need to know what to do in some life situations. For example, a person was electrocuted by a broken wire. Under no circumstances should you touch this wire or the person with your bare hands. You need to move the wire away using some kind of non-conductive object, such as a dry wooden stick.
To teach elementary school students the rules of electrical safety, you can use the tips I have prepared.
Dielectric research
Substances that do not conduct electricity are called dielectrics or non-conductors of electric current. The molecules of such a body are neutral; they have the same number of positive and negative charges. But, despite this, the particles of the body still have electrical properties. In general, bound atoms can be considered as a dipole with a moment: P = q * l, where q is the total charge of all particles in the dielectric, l is the distance between the centers of the particles.
When the dipoles rotate, the bonds are deformed and induced moments are created. If no external field is applied to the nonconductor, then due to random motion they are randomly oriented. Therefore their sum is zero. If a dielectric is introduced into an electromagnetic field, polarization will occur. In any elementary volume there will be a dipole moment different from zero.
There are several types of polarization, here are the main ones:
- Orientation. The applied field tends to rotate the dipoles along its direction. This is prevented by thermal movement. As a result, a preferential orientation occurs in the direction of the electromagnetic induction lines. It depends on the value of electromotive force and temperature.
- Electronic. Another name for it is deformation. With this type, induced dipoles occur. Thermal fluctuations do not affect polarization. This type is characteristic of polycrystalline ceramics, perovskite CaTiO3.
- Ionic. Can exist only in dense dielectrics, the structure of which is determined by the crystal lattice. In this case, positive and negative ions are separated, following the example of conductors. Moreover, the first ones shift along the direction of the electric field.
Thus, any material can essentially conduct electric current. But in dielectrics its strength is so small that it is neglected. Moreover, for its appearance you need to apply a great voltage.
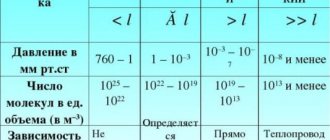
The electrical properties of a dielectric material are characterized by the dielectric constant of the medium. Its physical meaning is to show how many times the electrostatic field inside a nonconductor is less than in a vacuum: E = E0 / Eв. For example, for polyethylene E = 2.3; glass - 10; water - 81; air - 1.00057. Interestingly, the dielectric constant can have dispersion.
Faraday's law of electrolysis
The mass of the substance released on the electrode during the time Dt during the passage of an electric current is proportional to the current strength and time:
k is the electrochemical equivalent of substance ().
The resistance of the electrolyte decreases with increasing temperature because the number of ions increases due to electrolytic dissociation.
Faraday's law allows us to determine the charge of an electron:
The conclusion about the existence of an elementary electric charge in nature was made by Helmholtz in 1881.
Experience with an electroscope
The simplest device for detecting electric charge is an electroscope. The device got its name from the Greek word skopeo - to observe. The first device was created by physicist William Gilbert in 1600. Its operating principle is based on the ability of unlike charges to attract, and like charges to repel. The simplest electroscope consists of a metal rod with a ball that conducts electricity at the end. On the reverse side, two petals made of thin paper are attached through a bracket. The rod is installed in a transparent vessel.
To conduct the experiment you will need to do the following:
These experiments show that any material has an electrical charge. But despite this, the dielectric is an insulator, that is, it does not pass electric current through its structure. At the same time, if it begins to pass, then in this case they talk about a breakdown. The parameter depends on the voltage value and the thickness of the electrical insulating material.
There is a type of electroscope - an electrometer. Instead of petals, it uses an arrow and a graduated scale. Therefore, with its help you can not only detect the charge, but also determine its quantitative value.
Formulas for calculating current in a capacitor
The capacitance of a capacitor connected to an alternating current circuit is calculated by the formula: C = q / U, where:
- C - capacity;
- q is the charge of one of the plates;
- U is the voltage inside.
Capacitance Capacitors come in different shapes, so they are calculated using several formulas:
- flat - C = E × E0 × S / d;
- cylindrical - C=2 π × E × E0 × l / ln(R2 / R1);
- spherical - C = 4 π × E × E0 × R1 × R2 / R2 - R.
Note! The resistance in a variable circuit that a resistor connected to an electrical circuit can provide cannot be calculated, since it is considered infinitely large. However, in this case, this can be done using the formula: Xc = 1 / 2πvC = 1 / wC.
You may be interested in Installing an RCD in an apartment
The capacitor voltage in an AC circuit is calculated using the following formula: Wp = qd E / 2.
The voltage is calculated using a certain formula
To calculate the voltage across a capacitor in an AC circuit, you need to use current formulas.
Applications of Electrolysis
Refining (cleaning) of metals
The process takes place in an electrolytic bath. The anode is the metal to be purified, the cathode is a thin plate of pure metal, and the electrolyte is a solution of a salt of a given metal, for example, when refining copper, a solution of copper sulfate.
Under certain conditions, pure copper is released at the cathode, and impurities precipitate or go into solution.
Electrometallurgy
Some metals, such as aluminum, are produced by electrolysis from molten ore. An iron box with a coal hearth serves as an electrolytic bath and at the same time a cathode, and carbon rods serve as an anode. The temperature of the ore (about 9000 C) is maintained by the current flowing through it. The molten aluminum drops to the bottom of the box, where it is released through an opening into a mold for casting.
Galvanostegy
An electrolytic method of coating metal products with a layer of noble metals that cannot be oxidized.
Electrotype
Used to reproduce the shape of relief objects (medals, coins, exact copies of artistic products).
Source
Electric current and its main characteristics. Electrical conductivity of substances
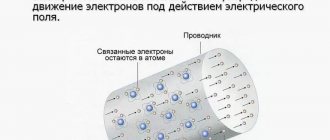
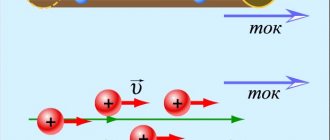
Free electrons are in a state of random motion (Fig. 1.8.a). If you introduce an electrical conductor into an electric field, then free electrons, under the influence of field forces, will begin to move towards the positive pole, creating an electric current. Therefore, electric current I in metal conductors
called
the ordered (directed) movement of charged particles (electrons)
(Fig. 1.8.b).
Figure 1.8. Diagram of the occurrence of electric current in metal conductors:
a) random movement of electrons; b) ordered movement of electrons
The electric field travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second, and the electric current travels at the same speed, although the electrons move at a speed of several mm or cm per second.
The unit of current is ampere A : this is the current at which 1 coulomb of electricity passes through the cross-section of the conductor every second.
When free electrons move in a conductor, they collide with ions and atoms of the substance from which the conductor is made, and transfer to them part of their energy, which is released in the form of heat, heating the conductor.
Electrons, colliding with conductor particles, overcome this resistance to movement, i.e. conductors have electrical resistance.
Resistance of a conductor to the passage of electric current
is called
electrical resistance R. Units of measurement are Ohms . a resistance of 1 ohm , through which a current of 1 A with a potential difference at its ends (voltage) equal to 1 V.
If the resistance is low, the conductor is slightly heated by the current. If the resistance is high, the conductor may become hot.
The wires conducting electric current to the electric stove hardly heat up, because... their resistance is low. The spiral of the tile, which has high resistance, becomes red-hot. The filament of the electric lamp heats up even more.
The property of a substance to conduct electric current under the influence of an electric field
called
conductivity G. Electrical conductivity is the reciprocal of resistance. The unit of measurement is Siemens (cm). G=1/R (cm).
The electrical conductivity of substances depends on the concentration of free electrically charged particles. The greater the concentration of these particles, the greater the electrical conductivity of a given substance.
All substances, depending on electrical conductivity, are conventionally divided into conductors, semiconductors and dielectrics .
Conductors have very high electrical conductivity. There are two types of conductors that differ in the physical nature of the flow of electric current.
· These are metals
– the current in them is due to the movement of free electrons (electronic conductivity) and;
What have we learned?
The division into conductors and non-conductors of electricity is carried out depending on the number of free electrical charges in the substance. Conductors are substances in which there are many free electrical charges, typical representatives are metals. Nonconductors (dielectrics, insulators) are substances in which there are few or no free electrical charges; typical representatives are glass and plastic. In addition, there are semiconductors that occupy an intermediate position, such as silicon.