Systems and types
Industrial lighting systems take into account both natural and artificial views. Natural lighting is created by direct or diffuse sunlight entering the room through windows.
Artificial light may include incandescent lamps, gas-discharge lamps or diode lamps and others. There is also combined lighting, in which the lack of daylight is partially compensated by artificial lighting.
Combined lighting in production
High-quality lighting is the key to successful negotiations and productive planning meetings
The topic of artificial lighting is discussed in as much detail as possible in the article.
According to their functions, artificial lighting is divided into:
- working;
- duty;
- emergency;
- security;
- signal;
- bactericidal;
- erythematous.
A worker used for work in production.
An attendant who remains on duty outside of working hours.
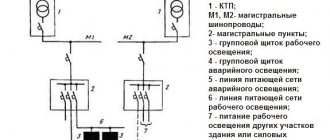
Emergency, which turns on in case of emergency, instead of the main one. There is safety lighting designed to maintain the normal level of the work process at the minimum acceptable level, if, after turning off the main one, there is a danger to human life (for example, in an operating room), an important technological process (in laboratories), etc.
LED emergency lighting lamps with a battery are also available, which is necessary for the safe evacuation of people from an emergency building. It is installed on evacuation stairs and passages.
Security - necessary to create a well-lit area at night to prevent an intruder from undetected entry into the facility.
Signal - used to signal the danger of intrusion into a designated area. Example: aircraft warning lights on tall buildings.
Bactericidal - ultraviolet irradiation turned on to disinfect the territory.
Erythemal - this refers to light produced by UV lamps, which in small doses has a positive effect on the human body. It is used in industrial premises where there is a constant lack of daylight.
By type of artificial lighting there are:
- General. It is light distributed throughout the entire production area. General uniformity is modeled so that the light is evenly distributed throughout the entire space (track lighting for example). The general localized one is built taking into account individual areas that require brighter lighting.
- Local. Used to create a narrow light field in a small work area.
- Combined. It combines local and general lighting.
Classification of industrial lighting
Organizing proper lighting - basic rules and recommendations
In order for organized lighting to be correct and appropriate, and for the interior design to look beautiful, the following important rules should be taken into account:
- First of all, the area of the space is taken into account. To calculate illumination, you need to apply a special formula.
- For the main light, a powerful lamp should be used, which will not only provide effective lighting, but will also have a positive effect on a person’s emotional state. For example, light in “cold” tones is good for work, so it is rational to use it for an office. Lighting fixtures with a “warm” glow will help you relax, which means they are appropriate to use in the bathroom or bedroom.
view album in new windowIn the photo: Bedroom interior in a classic style apartment
- The color of the glow is called color temperature, information about which is indicated on the product packaging. For residential premises in the house, preference should be given to light bulbs with an indicator of 3000 K.
- If lighting is created in the kitchen, then you should definitely pay attention to the illumination of the work surface. LED lighting is ideal for this.
view album in new windowIn the photo: Kitchen interior in an Art Deco style apartment
- To create more intimate and comfortable lighting in the bedroom, it is best to use wall sconces. They are not only ideal for creating additional lighting, but also stylishly complement the interior.
- To organize a more original decor, today lighting devices are offered that smoothly change the brightness of the emitted light or its color.
Taking into account all these features and recommendations, problems with organizing high-quality lighting will not arise.
Peculiarities
The following requirements apply to lighting of work areas:
- The level and quality must be determined by the nature of the work performed in production.
- Constancy over time, i.e. no fluctuations in the level of illumination.
- Should include various spectrums, including fluorescent lamps.
- In accordance with all safety criteria.
- Ease of operation and functionality.
In basements and semi-basements where the sun's rays do not penetrate, lamps with erythema irradiation can be used. This will help avoid health problems for employees and reduced production efficiency.
Additional psychological comfort for employees will be provided by the ability to independently change the lighting characteristics.
Lighting in the office also requires a special approach, since the efficiency and health of employees depend on it
The assembly shop must be lit in accordance with all RF SNiP standards
The most common type of lighting fixtures for offices is the Armstrong lamp.
Norms
In Russia, SNiP 23-05-95 is most often used to determine lighting standards, and in addition to it, regional standards and industry regulations. In Europe they focus on EN12464-1.
Indicators of lighting systems that are taken into account when modeling industrial lighting:
- Illumination. The amount of light falling on the selected unit of the working plane, measured in Lux.
- Colorful temperature. Expressed in K (Kelvins), the proportion between red and blue colors in the visible spectrum of radiation. High values correspond to a cool blue glow.
- Color rendering index. The indicator is measured in Ra index; the closer it is to 100, the more the radiation source is able to convey the true color of objects.
- Flicker frequency is the frequency of changes in light intensity. Measured in Hz (Hertz).
- The glare indicator is the ability of a light source to dazzle, that is, with its strength and brightness to cause a feeling of discomfort in the person working with it.
- Illumination uniformity is an indicator that determines how similar the characteristics of the light flux are in different zones of space.
- Power factor - shows how efficiently a light source uses the consumed electricity to perform useful work. Some of the energy does not turn into visible light, but is lost in the form of heat, which, if the lighting installation is not properly modeled, can lead to overheating of the system.
We also recommend that you read about electronic ballasts for fluorescent lamps.
Be sure to consider the power factor when designing lighting installations in production. This will save electricity and avoid premature failure of the lighting installation.
Warehouse lighting in accordance with all standards and requirements with LED lamps
For the illumination indicator
Lighting requirements depend on the type of visual work performed, criteria for workers and additional characteristics of the room (contrast between object and background, presence of natural light). The higher the accuracy of the visual task being performed, the greater the illumination level required.
In rooms where employees are engaged in high-precision work, the illumination level can reach 5000 Lux, while 200 Lux is enough to monitor the production process.
For color temperature
The impact of color temperature on worker productivity is high. In addition, color temperature indicators are related to color rendering and color discrimination.
For work in which color and shade differentiation is critical, lighting systems with high color temperatures (up to 6000 K) are required. For rooms where ordinary work is carried out that is not related to color discrimination, lamps with a temperature of 2400 K can be installed, focusing more on the feeling of comfort of the people in them.
Cool colors improve employee concentration, but also cause mild stress by increasing cortisol levels (Tommy Gouven Report, 2009). Warm colors, on the contrary, promote a feeling of comfort and relaxation, but can negatively affect productivity.
For Color Rendering Index (CRI)
The more important it is to convey the natural color of objects, the higher the CRI value should be.
In production, as a rule, 50 or 60 CRI is sufficient. LED lamps have a high color rendering index, while fluorescent lamps have a relatively low index.
For flicker frequency
Flickering light creates additional visual strain. When the intensity of the light flux changes, the human eye must have time to adapt to the new conditions. If a worker is engaged in high-precision visual work, visible flicker of light (which is produced by fluorescent lamps) is undesirable.
The use of office fluorescent lamps is also undesirable in rooms where there are a lot of moving mechanisms (machines, machines), since there is a high risk of a stroboscopic effect, when objects seem frozen or moving in the opposite direction.
Flickering up to 300 Hz is perceived by the human brain and can cause a feeling of discomfort, fatigue, and visual strain.
LED lamps for office premises and production workshops are the best option, as they do not produce flickering that is hazardous to health, so their use is highly desirable in production.
For blindness indicators
This value may be higher in areas where the contrast of the subject with the background is not so great, and lower if employees are engaged in high-precision visual work.
Lighting distribution
The higher the visual stress of employees, the more uniform the lighting should be. This is due to the fact that changes in lighting force the human eye to accommodate, which, with increased visual load, has an adverse effect on well-being.
Exact parameter values in numbers
According to SanPin, lighting standards in the workplace must comply with the following:
- if high accuracy is required during visual work, and the minimum size of the recognition object is 0.3-0.5 mm, you will need: artificial lighting standards: with combined light - 2000-400 lux, with general type light - 500-200;
- for natural: with the top or combined option - 5%, with the side option - 2%;
- normalized indicators for combined lighting: with overhead or combined lighting - 3%, with side lighting - 1.2%;
- for the artificial type: with the combined version - 750-300 lux, with the general type - 300-150;
- lighting standards for artificial type: for the combined version - 300-200 lux, for the general type - 200-100;
These are recommended values that lead to optimal KEO, which must be observed when organizing room lighting. It is worth taking into account the characteristics of a particular room, its specifics for correct illumination of the workplace. Depending on them or on the recommendations of industry regulations that regulate issues of this parameter, it may be necessary to carry out additional work that will provide other indicators.
Optimal type of light bulbs, shape and size of housing
There are some of the most popular types of light bulbs:
- incandescent;
- halogen;
- luminescent;
- sodium;
- LED
LED lamps are the optimal solution for both small and large industries and offices
Incandescent lamps are least suitable for use in production. Despite their cheapness, they consume a large amount of electricity, provide dim lighting, are environmentally unsafe and break down very quickly.
Incandescent lamps alone will not be enough for production workshop equipment. They can be used in local lighting systems.
Halogen lamps have a slightly longer service life and are more energy efficient, but they should not be used as the main light source in production either.
Fluorescent lamps are inexpensive and provide sufficient illumination. However, they have a long series of negative characteristics, which include unsafe for the environment and human health, visible flicker, and low color rendering.
They should not be used as the main source of lighting in workshops where there are a lot of rotating mechanisms, since the flickering of this type of lamp contributes to the creation of a stroboscopic effect.
LEDs have a relatively high cost, but consume significantly less energy compared to other lighting sources, and the useful work they do is greater.
They are safe for the environment and the health of workers, have a wide range of color temperatures and luminous flux values, which allows them to be used for almost any task.
The negative side of LED industrial lighting is that for long service they require high-quality voltage stabilization systems.
Sodium lamps have an efficiency 4 times greater than LED lamps, while their cost is lower. It is difficult to use them in indoor production (with the exception of warehouses), since the lamps produce exclusively yellow light and have a low color rendering index.
The distribution of light depends on the shape and size of the lamp body, as well as the type of light bulb.
For general lighting systems in production workshops, it is recommended to choose large rectangular lamps that are suspended or directly attached to the ceiling. This way you can ensure a more uniform distribution of light flux throughout the production area.
For local lighting, small lamps of any shape can be used, the main thing is that they create sufficient visual and psychological comfort for production workers.
Lighting design - what is it and how to approach the issue correctly?
In professional design projects, the arrangement of various lighting fixtures, their required quantity, external design, brightness and type of glow must be indicated. The appearance of the entire interior will depend on all this.
To properly organize lighting in a house or apartment, it is worth deciding what elements its design consists of:
- General view lighting acts as a background light. In the process of organizing it, you need to take into account that the light is comfortable. The choice of brightness and “temperature” of the glow will depend on the type of room. If we are talking about an office and a nursery, then for these rooms you should choose more intense light, and for the bathroom and bedroom - dimmed.
view album in new windowIn the photo: Children's interior after renovation in an apartment in the style of bourgeois minimalism
- Lighting architecture is designed to emphasize the chosen style of room decoration, provide high-quality lighting for work surfaces, niches, and other details, and also create the effect of “floating ceilings.” Certain styles cannot do without such lighting. So, for example, high-tech implies highlighting individual elements with light.
view album in new windowIn the photo: Kitchen interior in an eclectic style apartment
- Interior lighting design. In this case, lighting fixtures are considered as part of the overall decor, which emphasizes its unique features. A wide range of such products makes it possible to create the most unique and creative apartment designs.
view album in new window
In the photo: Bedroom interior after renovation in an Art Deco style apartment
Each of the described lighting elements must be thought out carefully so that the total result is a beautiful and comfortable interior.