Electricity prices are rising every year, so manufacturers are relying on cost-effective lighting elements. They cost customers more than incandescent light bulbs, but quickly pay for themselves due to their energy-saving properties. A halogen lamp is one of the saving options. It does not consume much energy, is durable and can withstand minor power surges.
Halogen lamps are actively used for video and photography, offset printing, and less often as infrared heating elements. In any area, halogen lamps can replace analogues due to their quality, durability and luminous efficiency.
What is a halogen lamp
A halogen lamp looks like a regular lamp in appearance. It consists of a flask with a tungsten spiral inside. A buffer gas containing bromine, fluorine, iodine and chlorine vapors is pumped into the flask. The vapors suppress the evaporation of tungsten from the coil when heated, preventing the flask from darkening. They also increase the service life several times compared to LN.
Fig. 1 – halogen lamp.
As the chemicals in the flask evaporate, the tungsten particles return to the coil, increasing the heating temperature. This gives the intensity of the glow and high color rendering rates. The glass of the bulb can be frosted or transparent, giving a muted or brighter light. Today, lamps of different wattages are produced, including low-voltage lamps for 12 V and 24 V. High-voltage lamps operate directly from a single-phase network.
Types of halogen lamps for home
The range of halogen lamps is very wide: from low-voltage lamps to large floodlights that can illuminate a stadium. Home light bulbs are available in three varieties:
- With external flask. Standard halogen chandelier bulbs. External protection prevents the scattering of fragments and the spread of gas after breaking.
- With reflector. Designed to create a source of directional light. Used in car headlights and flashlights.
- Capsule. Miniature light bulbs that are used in luminaires not protected by glass.
Linear
The device provides bright illumination of a large area without leaving dark corners, and additional UV protection makes the light bulb safe. It is recommended to install in large warehouse areas:
- Model name: J 500W Camelion 2937;
- price: 64 RUR;
- characteristics: linear capsule, power 500 W, voltage 220 V, base type R7s, luminous flux 9000 lm;
- pros: bright, clean white light, quartz bulb reduces the amount of ultraviolet radiation;
- cons: rare type of base.
An excellent example of an uninterrupted source of external lighting for streets, building facades, roads, and private sector areas. Remember that models of this power are a fire hazard if installed incorrectly:
- Model name: HALOLINE 64740 1000W J189 Osram;
- price: 540 rub;
- characteristics: tubular linear capsule, power 1000 W, voltage 220 V, base R7s, luminous flux 22000 lm;
- advantages: long radiation propagation range;
- cons: high color temperature 3000 K.
With outer box
The second capsule, installed in front of the main one, guarantees safety if the light bulb burns out. The protective flask will prevent the gas from spreading and debris from scattering around the room:
- Model name: Uniel E27 42 W;
- price: 70 rub;
- characteristics: spherical protective capsule, power 42 W, voltage 220 V, luminous flux 670 lm, base E27;
- pros: matte capsule;
- Cons: gets very hot outside.
The model exceeds standard incandescent lamps in efficiency by 30-40% with a total increase in radiation level. Save on energy costs by using halogen from Electrostand:
- model name: Electrostand E14 42W;
- price: 35 rub;
- characteristics: pear-shaped capsule, 42 W, 220 V, luminous flux 630 Lm, E14 base;
- advantages: low temperature;
- cons: not found.
- How to remove a double chin in a week with exercises, video
- Kiwi salad - recipes with photos. How to prepare delicious fruit or chicken snacks
- Registered letter DTI - what is it?
Capsule
Small dimensions combined with a high level of light emission make the model an ideal choice of lighting fixture for jewelry stands. Install several of these side by side and you will be able to see the smallest flaws on the product:
- model name: JC 20W Camelion g4 12V 1955;
- price: 35 rub;
- characteristics: low-voltage capsule, 12 V, 20 W, luminous flux 320 Lm, G4 diode base;
- pros: powerful lighting;
- cons: not found.
The device is manufactured as a point light source for suspended and suspended ceilings. Install small built-in lamps at a distance of 80-100 cm - and the room will always be well lit:
- model name: SVETOZAR SV-44762-M;
- price: 30 rub;
- characteristics: power 20 W, voltage 12 V, luminous flux 266 lm, warm white, yellow;
- pros: small size;
- cons: service life 2000 hours.
With reflector
A light bulb that emits a narrow beam of light of high brightness is ideal for the role of a lighting element for a headlight or flashlight. Low power consumption will prevent you from being left without light at the wrong time:
- Model name: COSMOS MR16 35W GU5.3 12V FMWc LKsmMR1612V35W;
- price: 50 rub;
- characteristics: power 35 W, voltage 12 V, bulb MR16, service life 2000 hours;
- pros: excellent lighting power 525 lm;
- cons: not found.
Blocks of such illuminators are installed in spotlights. It would also be a good idea to mount these lamps in the ceiling to create a network of powerful spotlights:
- model name: SVETOZAR SV-44733;
- price: 60 rub;
- characteristics: 35 W, 12 V, light power 652 lm, soffit capsule, GU5.3 base;
- pros: good focusing of the light beam;
- cons: overheats.
Low voltage
The powerful stream of light that such a small device generates puts the model at the top of the list of the best flashlight lighting elements. Install one of these - and no darkness is scary:
- model name: Navigator 94 204 MR16 50W 12V 2000h;
- price: 70 rub;
- characteristics: 50 W, 12 V, warm white light (3300 K), GU5.3 base;
- pros: high brightness;
- cons: energy consumption, thread wear resistance.
COSMOS lamps with increased lighting brightness are often installed on external store signs, under glass display cases of stands. The 750 lux light source is guaranteed to attract attention:
- model name: COSMOS JC 50W G6.35 12V LKsmJC12V50W;
- price: 35 rub;
- characteristics: 50 W, 12 V, JC bulb, G6.35 base;
- pros: light power 750 lm;
- Cons: fragile contacts.
Varieties
In order for the halogen to last as long as possible, it is important to choose it taking into account the parameters and purposes. First of all, light bulbs are classified according to their power source:
- incandescent lamps 220 V;
- low voltage lamps with 12 V drivers.
The low voltage device can only be connected to dedicated power supplies through a step-down transformer. It converts the mains voltage to 12 V. According to configuration and purpose, halogen lamps are divided into:
- devices with an external bulb;
- capsule;
- with a special reflector;
- linear.
Video on the topic: before purchasing, familiarize yourself with the types of light bulbs
Linear
This type of halogen lamps appeared first and is still produced. The design consists of an elongated bulb and two pin holders at the edges. Due to their high power, such models are unpopular in everyday life.
Fig. 2 – linear lamp.
With external bulb
The product looks like a standard incandescent lamp. The flask is protected from darkening in case of overheating. Models are available with two types of base - E27 and E14. Therefore, in everyday life, light bulbs are used as energy-saving ones, instead of light bulbs.
Fig. 3 – light bulb with an external bulb.
With special reflector
These halogen lamps are popularly called “directional lamps”. The body in the form of a hemisphere is covered from the inside with reflective material, which directs the light flux. In the center there is an incandescent coil. The case can be equipped with glass, but not necessarily.
Fig. 4 – lamp with reflector.
Interference or aluminum reflectors are installed here for heat removal. The most reliable are IRC models, which do not heat up due to the reflection of infrared radiation back onto the filament coil. The resource of such a lamp is higher, and the energy consumption indicators are lower. Devices with a reflector are produced for high-voltage and low-voltage lamps.
Fig.5 – IRC lamp.
Capsule
The body of such a lamp is a capsule, inside of which there is a spiral with metal leads outside for connection to the socket. Devices are divided by base type: G5, 3, 4 or 9. Light bulbs are often purchased for interior illumination, in spotlights built into furniture or plasterboard structures. In rare cases, they are installed in chandeliers and other household lighting devices.
Fig.6 – capsule light bulb.
Lighting fixtures with reflector
Such lamps are also called directional devices. Their standard sizes are distinguished:
- MR 16;
- MR 8;
- MR 11.
The most popular and widespread are models marked MR 16; they are equipped with flasks with a diameter of 50 mm. If we talk about light bulbs with reflectors, they differ in different radiation angles. Structurally, they are represented by small flasks in which reflectors, also called reflectors, are installed. The purpose of such parts is to redistribute the emitted light flux into the space around the lighting fixture. There are different types of designated reflectors.
But the most popular of them are aluminum devices. They are able to direct the heat generated in large quantities forward. If this option is not acceptable, it is recommended to use halogen light bulbs equipped with infrared reflectors (a translucent functional coating is applied). They have the ability to remove the generated heat back.
You may be interested in this Features of an incandescent light bulb
The latest IRC type halogens are extremely economical. The design is designed in such a way that the flask, thanks to the existing coating, does not transmit the infrared radiation emitted by the filament coil, but returns it back. In this way, the temperature indicators of the heating element increase, and heat loss and electricity use are reduced. Compared to standard halogen devices, the service life is increased.
It is worth mentioning halogen light bulbs, equipped with or without protective glass, models with glass caps or colored thickened glass. Products that do not have any protection are intended for use only in closed-type lamps, which will help them look more presentable. The undeniable advantage of most GLNs is that they do not transmit ultraviolet radiation.
Operating principle of a halogen lamp
When current passes through a tungsten filament, it heats up to a high temperature. The thread begins to glow. However, tungsten atoms, when heated, gradually evaporate and accumulate in less hot areas inside the flask. This process reduces the longevity of the light bulb.
Fig. 7 – device of a halogen lamp.
When heated, iodine vapor interacts with evaporating tungsten atoms, which prevents them from spreading throughout the flask. This is a reversible process. When heated, near the filament, the vapors break down into their constituent substances.
Thus, tungsten atoms are returned to the filament, increasing operating temperature and extending service life. The elements are more compact than LNs of similar power.
Halogen lamps are different from incandescent lamps
Halogen lamps are comparable in structure and principle of operation to incandescent lamps. But they contain minor additions of halogens (bromine, chlorine, fluorine, iodine) or their compounds in the filler gas. With the help of these additives, it is possible, in a certain temperature range, to almost completely eliminate the darkening of the bulb (caused by the evaporation of tungsten atoms) and the resulting decrease in luminous flux.
Halogen lamps, like incandescent lamps, emit heat. The spiral, made of heat-resistant tungsten, is located in a flask filled with an inert gas. When electric current passes through the coil, it heats up, generating heat and light energy. Heating leads to the evaporation of tungsten particles, which settle as a black precipitate inside the flask. As gas pressure increases, this process slows down. The dimensions and low strength of the bulb of a traditional incandescent lamp do not allow the gas pressure to be increased further. The higher the temperature of the coil, the more light is emitted. At the same time, the process of evaporation of tungsten is accelerated, which reduces the service life of the incandescent lamp. In halogen lamps, most of these negative phenomena are eliminated.
In addition, the bulb of a halogen lamp is made of refractory quartz glass, which is more resistant to high temperatures and chemical influences. Quartz glass is a heat-resistant material, and its small dimensions guarantee strength sufficient to create higher gas pressure. Therefore, the size of the bulb in halogen incandescent lamps can be greatly reduced, as a result of which, on the one hand, the pressure in the filler gas can be increased, and on the other hand, it becomes possible to use the expensive inert gases krypton and xenon as filler gases.
All this makes it possible to increase the temperature of the coil, resulting in a 2-fold increase in luminous efficiency (13-25 lm/W) and the service life of a halogen lamp (2-4 times higher than that of incandescent lamps).
Halogen lamps with a coating that reflects the infrared component. Infrared radiation coated lamp bulbs are characterized by a significant increase in luminous efficiency.
This is due to the following physical process:
Part of the energy that is converted into invisible infrared radiation in conventional halogen incandescent lamps (more than 60% of the radiation efficiency) is partially converted back into light in coated lamps. This becomes possible thanks to the structure of the coating, which transmits only visible light, and infrared radiation, if possible, returns completely to the spiral, where it is partially absorbed. This causes an increase in the temperature of the coil, as a result of which the power supply can be reduced. Light output increases.
Features of operation
In order for the lamp to last as long as possible, manufacturers advise not to touch the bulb with your hands, even if they are clean. The fat that remains after touching can cause the lamp to burn out. It is better to wear gloves when replacing. If the temperature inside the flask drops below 250°C, interaction with tungsten will not occur.
Fig. 8 – features of halogen lamps.
As a result, the device will work like an ordinary incandescent lamp. It is also not recommended to install a dimmer. Because of this, the light bulb stops working correctly, since the decrease in brightness is directly related to the temperature of the buffer gas. If a dimmer has been installed, it should be turned on at full power as often as possible. This is necessary for heating to the required temperature and interaction of halogens with tungsten.
This way the filament coil can repair itself. It is important to ensure network voltage stability to extend service life. If voltage surges occur, it is better to install a stabilizing protection unit. For suspended ceilings, lamps without an external bulb are not used; a heated element can melt building materials.
Advantages and disadvantages
A significant disadvantage of halogen lamps is low-frequency noise when used in an AC network in conjunction with a dimmer.
The emission spectrum of a halogen lamp, like an incandescent lamp, is close to that of the sun.
Compactness
The addition of halogens prevents tungsten from depositing on the glass, provided the glass temperature is above 250°C. Due to the absence of blackening of the bulb, halogen lamps can be made very compact. The small volume of the flask allows, on the one hand, to use a higher operating pressure (which again leads to a decrease in the rate of evaporation of the filament) and, on the other hand, without a significant increase in cost, to fill the flask with heavy inert gases, which leads to a reduction in energy losses due to thermal conductivity. All this increases the service life of halogen lamps and increases their efficiency (efficiency).
Color rendition
Halogen lamps have good color rendering (99-100), since their continuous spectrum is close to the spectrum of an absolutely black body with a temperature of 2800-3000. Their light emphasizes warm tones, but to a lesser extent than the light of conventional incandescent lamps.
How to check a halogen lamp
To check a halogen lamp you need a multimeter. Set the mode to measure the minimum resistance. Further:
- Place the light bulb next to the multimeter without touching the bulb with your bare hands.
- Take the probes and apply them to the terminals.
- Take the readings and write them down if necessary.
Fig. 9 – multimeter.
The resistance will be different for a 220-volt automotive and household light bulb. Indicators should be in the range from 0.5 to 1 Ohm. Excess indicates a malfunction.
Features of installation and operation of halogen lamps
The quartz flask heats up to high temperatures during operation. Therefore, it is very sensitive to fatty contaminants, which, when turned on, quickly begin to evaporate, cooling the surface of the glass underneath. Uneven heating causes internal stresses to arise, which can lead to instant destruction of the flask - it crumbles into many fragments.
Therefore, during installation you should adhere to certain rules:
- the flasks should not be touched even with clean hands;
- in case of accidental touching, thoroughly wipe the area with a cloth that does not leave fibers on the surface being treated and with a non-streaking degreaser;
- You can handle glass only with clean fabric gloves or through a napkin;
- For fire and injury safety, exclude the possibility of contact of the operating lamp with surrounding objects and accidental touching of it.
You can significantly extend the life of a halogen lamp by connecting it through a protection unit or using a dimmer instead of a regular switch. With constant operation at low brightness, a precipitate of tungsten-halogen compound may accumulate in the bulb. To evaporate it and start the coil regeneration process, you sometimes need to turn on the lamp at full power for 10-15 minutes.
Connection diagram.
Lamps powered by 220 V are connected directly to the network. Several lamps are connected parallel to each other.
Electrical diagram for connecting the GL to a 220 V network.
The service life of halogen lamps depends on the uniformity of the supplied voltage. To smooth out surges in the power supply, it is recommended to connect the lamps through a special protection unit. It functions as a stabilizer.
Electrical circuit with stabilizer.
For luminaires operating on direct current, a step-down transformer is required. For multiple halogen lamps, the connection must also be parallel.
Electrical diagram for connecting a GL operating on direct current.
Remember safety when working with electricity!
Self-connection
Installing a halogen lamp with your own hands is not difficult. The work should be done with gloves or hold the transparent part of the device with a napkin or piece of cloth. The outer bulb is less sensitive, but it is still better to use gloves.
Lamps with reflectors are mounted to a stand with a mounting ring. Tendrils or springs are used as a fastening element (the specific method of fixation depends on the model). The fastener provides mechanical fastening of the device in the mounting ring.
A dedicated wire is connected to the light bulb. Daisy chain connection is allowed. However, this method is undesirable, as it leads to loss of power.
Pulse cables are used because they provide compactness. The phase conductor from the box is connected to the switch, and the wire from the switch is connected to the transformer. The zero is directed from the junction box to the transformer. The device is screwed into the base in the same way as a regular incandescent lamp.
Installation in suspended ceiling
The work is performed in this order:
- Before assembling the ceiling structure, the surface is marked. At the same time, marks are made of the places where the lamps will be installed.
- Next, using a crown, drill a round hole in the box.
- Wires are pulled through the hole.
- The conductor is connected to the lighting fixture using spring clips.
- Once the cable is secured, the suspended ceiling can be installed. The lamps are installed after finishing the finishing touches in the room.
Advice! If during the installation process you accidentally touch the lamp with your bare hand, you must wipe the lamp with a dry napkin or lint-free cloth.
Installation in a suspended ceiling
Installing lamps in a suspended ceiling is done a little differently. The body of the lighting fixture is not fixed to the canvas (it simply won’t support it), but to the reinforcement on the concrete base.
Installation procedure:
- Mount the frame for the suspended ceiling.
- Wiring is being done.
- Fixing reinforcement is installed to the concrete base at marked locations. The mount is a compact plastic box or ring on durable legs.
- Attach a fixing ring to the reinforcement.
- Stretch the ceiling covering.
- Feel for the location of the fastening ring. The thermal insulation ring of the retainer is brought to the ring (directly through the fabric). Make a hole in the canvas.
- Pull the wiring out and connect to the lighting device.
- Secure the lamp with clamps to the fittings.
The process of installing lamps in a suspended ceiling is simple, but requires skill and accuracy. Therefore, in the absence of experience, it is better to entrust such work to specialists.
Safety precautions
Before installing or replacing a halogen lamp, review safety precautions. It will help avoid mechanical failure and overheating of the device. Follow the disposal rules, because... There is a buffer gas inside the light bulb.
Why shouldn't you touch the halogen lamp with your hands?
On a budget halogen lamp, fingers can leave greasy stains. The temperature on them can exceed the permissible limit. But in expensive models, a double bulb protects the lamp from melting and burning out.
Fig. 10 – consequences of installation without gloves.
If the integrity of the device is compromised, this will lead to immediate failure or reduced service life.
Proper disposal
Damaged or broken light bulbs should be disposed of properly. Halogen lamps should not be thrown away with household waste because of the harmful volatile vapors in the bulb. They do not pose a serious danger, however, experts advise collecting damaged products in a separate container and handing them over to special collection points. Their location can be found on the Internet.
How to properly replace a light bulb on a car
Capsule devices
These models are also called finger models due to their compact, small sizes. The channel bodies in them can be located in longitudinal and transverse positions. The scope of application is open lamps without protective glass . It could be:
- decorative lighting;
- lighting built into furniture;
- ceiling niches.
You may be interested in: Types of LED lighting lamps and their characteristics
Capsule halogen lamps are often used to complement general lighting fixtures. The most common bases for the described devices: G 5.3, GY6.35, G4. For mains voltage, the most optimal model is G9.
These types of halogen lamps are not an exhaustive list. Manufacturers regularly introduce improved lighting devices that are widely used by the population.
Advantages and disadvantages of halogen lamps
Halogen lamps are actively purchased for homes instead of incandescent light bulbs and for commercial purposes. You can learn from store consultants about the advantages and disadvantages of halogen elements. Information is also available on thematic forums. This will help you make a choice.
It is recommended to buy a halogen lamp only if its use is justified. Among the advantages of halogen light bulbs are the following:
- light output ranging from 15 to 20 lm/W. For incandescent lamps this is 7-17 lm/W. The value affects the economy and efficiency of lighting;
- Dimensions are more miniature than those of LN. Therefore, they can be installed in a suspended ceiling with spotlights or furniture. Here, “halogen” lamps also beat other energy-saving analogues, which are not installed in all types of lampshades;
- operating time from 2000 to 4000 hours. This is 3-4 times higher than that of LN. When used correctly, soft starters can extend their service life to up to 11,000 hours.
Fig. 11 – characteristics.
Studying the reviews, you can see that buyers most often highlight the following disadvantages:
- installation difficulties . Not every halogen can be turned on immediately after installation in the lamp. For low-voltage lamps, a step-down transformer is installed in the circuit. In addition, to extend the service life, you can additionally install a dimmer;
- The flask is too sensitive to contamination . When installing, it is important not to touch the glass with your fingers, using a napkin or gloves. Sometimes dark spots may form at the spots;
- heating to high temperature . If there is a risk that a child or adult may accidentally touch a burning lamp, special protection must be installed. You can use transparent plastic. Also make sure that the light bulb does not heat other surfaces.
Recommendations for use will help eliminate these shortcomings. Despite the great popularity of other energy-saving lamps, for example, LEDs, halogen lamps are in demand due to the ease of installation in different types of lampshades.
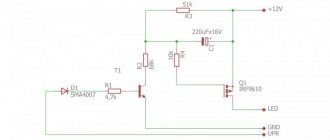
How and which driver to choose for g4 12v LED lamps
Navigator power supply
A driver, also known as a power supply/power supply/step-down transformer, is required to convert 220 V household voltage to 12 V.
There are two types of drivers:
- delivering direct current (suitable for LED operation);
- producing constant voltage (suitable for LED strips and low-voltage light bulbs).
You can read more about drivers in the article “What is a driver and why do LEDs need it?”
For 12 V LED lamps you need a second type: a constant voltage unit.
To select a driver, you need to know two parameters: the total output power of the light sources in the chandelier (just add up all the powers and multiply by a safety factor of 1.2) and the output voltage of the power source. In our case, this is 12 V. Knowing these two parameters, you can select a power supply.
As additional selection parameters, it is recommended to pay attention to the protection class of the power supply. The higher the IP, the better.
Most often, LED manufacturers also produce drivers. It is best to choose a device from a well-known and reliable manufacturer.
- Related Posts
- TOP 10 LED lamps of 2021
- How to determine LED polarity
- Which lamp to choose for plants - the best options