Most building materials are based on natural components that have the necessary properties and are found in sufficient quantities for industrial production. Quartz sand is one of the most common natural minerals and is used in all areas of construction activities.
What ensures the chemical properties of the material?
The main component of quartz sand is silicon dioxide (quartz). Its formula is SiO2. It may also contain organic impurities, clay, oxides of iron and a number of other metals. The quartz content in the original mineral is usually at least 93-95%.
The principle of operation of building mixtures used to produce building blocks and slabs is based on the chemical interaction of the components. The inorganic chains formed as a result provide the required parameters of the material.
Silicon dioxide is an acidic oxide, so it reacts with calcium and aluminum compounds found in limestone and clay. The interaction can occur both during drying of the wet mixture and during thermal baking.
Secondary quartz: features of raw materials and extraction method
It is also formed as a result of the decay of granite, but its difference from the primary one is that it undergoes a process of transfer from the original deposit of quartz sand. This usually occurs under the influence of water, when the liquid erodes the primary quartz.
Water flows separate sand from kaolin, saturate it with moisture without interfering with contact with air. In the place where the material is transferred, it accumulates. Typically, such areas mean lake and river bottoms or quartz deposits in the ground.
Mining Features
Secondary quartz can be mined in several ways. The first involves quarrying: quartz sand is removed from the quarry using an excavator. The second is to process the river or lake bottom with a dredge. In this case, a pump collects water with the quartz present in it, after which this mixture is supplied to the accumulation sites.
Types of quartz sand and its extraction
There are natural and artificial varieties of sand, differing in the method of extraction.
Natural natural
This type of sand is ubiquitous in nature and is found at the bottom of water basins and in the soil. The sizes of most of its grains range from 0.2 to 1 mm.
There are several ways to extract quartz sand:
- Quarrying is the main method. If mining is carried out above sea level, the resulting sand is called mountain sand. Varieties of soil sand are extracted during mining in the plains. The appearance of quarry sand is distinguished by its pointed shapes and often rough surface, which makes it a valuable building material. The extracted sand can be subjected to additional processing - sifting, washing and drying. The stricter the requirements for sand properties in any industry, the more careful preparation is required. In the construction of small structures, sand is usually not subjected to any impact and is supplied directly from the place of its extraction;
- development of water basins - sand is washed out by a dredger and is characterized by high purity provided by natural washing. Mining is carried out in river beds, lakes, and marine areas. Sea sand is somewhat less valuable due to its higher content of mineral impurities. River sand has a smooth shape - under microscope magnification, the sand grains resemble sea pebbles. The use of smooth (rounded) sand is common in self-leveling mixtures - the grains of sand do not cling to each other.
This is what natural quartz sand looks like in the photo
Artificial sand
Despite its name, the mineral is of natural origin, but is initially found in the form of large crystals. To transform quartz crystals into sand, mechanical action (explosion) is used, after which the fragments are crushed.
Primary quartz: features of raw materials and extraction method
It is represented by kaolin in combination with quartz sand, which were not separated and transferred. In other words, primary quartz is represented by granite in a decomposed state, which has been in the primary place of formation for many years: neither air nor water can affect its state. Essentially, this is a material in a “preserved” state, completely unaffected by any mechanical or physical influences. In this form it is under a thick layer of mixture consisting of primary clay and quartz, under the direct favorable influence of climatic conditions. For this reason, quartz sand crystals are not polished or ground and are protected from the penetration of chemicals.
Kaolin
Mining Features
The development of a quartz sand deposit consists of extracting it from the deposit site, as well as subsequent transportation to the processing site. In production, quartz sand is separated from clay: it is dissolved, after which the quartz is dehydrated. Next, the isolated quartz is subjected to additional washing. As a result, the raw material is freed from residual clay deposits. After this, the material is calcined, distributed into fractions and packaged.
Methods for classifying quartz sand
The starting point in the classification system is the properties of the material and how it is prepared. The following areas of classification of quartz sand are distinguished:
By size (fractional composition)
The numerical expression is the average particle size or range of particle sizes (fraction):
- pulverized quartz – represents a fraction of less than 0.1 mm (sifted into a sieve with a pore diameter of 0.1 mm) and is usually found when crushing quartz crystals;
- fine-grained sand – fraction 0.1-0.25 mm;
- medium sand – fraction 0.25-0.5 mm;
- coarse sand – fraction 0.5-1 (rarely up to 3) mm.
By enrichment
Quartz sand is divided into unenriched and enriched sand:
- unenriched sand is the original mineral that has not been processed to increase the silica content;
- enriched sand contains a several percent increased quartz content, obtained by removing most of the impurities. Thus, white quartz sand is purified from organic compounds, iron oxides and clay impurities by sifting, washing and drying.
Due to the nature of production, the main technical characteristics of the resulting material also differ. This in turn affects the possibilities of further use of quartz sand.
Enrichment technology
High purity of the quartz mixture is a necessary requirement in a number of technological processes. The initial stage of enrichment includes fractionation and washing - with their help, the coarsest impurities are removed.
The next stage is the use of special technologies, such as:
- gravitational enrichment is the main method, the essence of which is to separate the components of the mixture by density. Lighter particles are carried away by the water flow, while heavier ones settle to the bottom of the apparatus. The gravitational effect can be enhanced by centrifugation or the addition of chemical reagents that change the wettability of sand components;
- electric and magnetic separation - is the effect of electric current and magnetic field, leading to the separation of certain impurities. Thus, magnetic action is especially effective in removing iron particles that have magnetic properties.
The parameters of enriched sand fundamentally affect the quality of the work performed. Sand mixtures with the best properties are produced only by certified enterprises using standard technologies.
By color
It can be natural or painted. Natural quartz sand ranges in color from pale yellow to brownish yellow. Artificial coloring is carried out with stable paints based on synthetic binders, allowing you to create original multi-colored ornaments from sand. This sand can be colored or white.
By degree of preparation
Depending on technological requirements, sand can be produced in the following varieties:
- fractionated - represents a specific fraction of sand, the size of which is limited by technical regulations;
- dry – dried to an air-dry state. Together with fractionated sand, it can be used as a working fluid for sandblasting machines;
- calcined sand – completely dehydrated by calcination. Heating significantly above 100 °C ensures desorption of moisture even from the deep pores of quartz. Such sand is used in ready-made building mixtures that are stored for a long time - even a slight moisture content can render the entire mixture unusable;
- rounded quartz sand – has less abrasive properties and is therefore suitable for delicate applications, for example, sandboxes on playgrounds;
- molding quartz sand – used to produce cast quartz products and is characterized by a high degree of enrichment.
Characteristics and properties of quartz sand
Features of quartz sand
The peculiarity of quartz sand, which distinguishes it from other types of sand, is that this material is monomineral, that is, consisting of only one mineral - quartz. This uniformity makes it a valuable industrial raw material. A small proportion of impurities makes it possible to obtain glass with a high degree of transparency from raw materials. Another feature is intergranular porosity. Compared to other materials, quartz sand provides the greatest dirt holding capacity. In addition to this property, there is a low degree of wear of sand grains, and quartz sand already performs well as a filter material.
Chemical properties of quartz sand
The crystalline structure of quartz gives it and the sand obtained from it exceptional characteristics of strength and resistance to alkaline and acidic materials. The very high hardness, refractoriness and chemical composition of quartz sand determine its increased fire resistance and fire safety. The material's properties correspond to a dielectric and is inert to a wide range of chemicals.
Physical properties of quartz sand
Sand has all the properties of quartz:
- bulk density 1300-1500 g/cm3
- abrasion - 0.1
- crushability - 0.3
- hardness (Mohs scale) - 7 (for comparison, the hardness of diamond is 10)
- radioactivity use - class 1
The density of quartz sand is determined by two different approaches. There is bulk density, and there is true density. Bulk is calculated as the ratio of the mass of the material in a loose state to its volume. This value includes the pores in the sand grains and the air spaces between them. That is, this value may vary depending on the moisture content of the material. True density is a constant value and represents the ratio of a substance in an absolutely dense state to its volume. The moisture content of the sand does not matter. To change density, the chemical composition or molecular structure must be changed. Bulk density is less than true. The density of the material is an important characteristic that must be taken into account when calculating storage space, its transportation and movement by lifting and transport equipment.
Abrasion, crushability and hardness of quartz sand are indirect indicators of its strength. To determine the values, grains are tested on a rotating abrasive metal circle, the mass of fractions is compressed mechanically and the grain scratches the standard and, conversely, the grain standard.
Quartz sand fractions:
- dusty - less than 0.1 mm
- fine-grained: 0.1-0.8 mm
- medium-grained: 0.8 - 1.6 mm;
- coarse: 1.6 - 6.0 mm
Silica sand, dusty and fine-grained, is used in various building materials, such as building mixtures, putties, grouts, abrasives, thin plasters and paints.
Medium-grain quartz sand is used for filtering and purifying liquids, for sandblasting, for building mixtures, facade and interior plasters, self-leveling floors, concrete mortars, in landscape design, and for backfilling sports fields.
The material of large fractions is used for the manufacture of paving slabs, concrete blocks, and landscape decoration. It is also used for filtering.
Sand of all fractions is used in the glass, foundry and chemical industries.
Production and extraction of quartz sand
There are a significant number of large deposits of quartz sand on the territory of Russia. The most famous include the Chulkovskoye (Moscow region), Kozlovskoye (Bryansk region), Elshanskoye (Volgograd region), Berezichskoye (Kaluga region) deposits and a number of others.
The differences between quartz construction sand extracted from these places are the initially high quality parameters and higher cost. It is important to understand that the properties of sand from a nearby quarry will be quite sufficient for the construction of small country houses, so you should not overpay. If the goal is to build a large mansion, then skimping on the quality of sand can negatively affect the longevity of the house.
This is how quartz sand is extracted on a special production line:
Extraction and production of quartz sand
Extraction of quartz fractional sand is carried out by open-pit mining or by dredging from natural deposits in the floodplains of rivers and lakes.
A small amount of impurities and a large amount of quartz - this is what distinguishes the developments in which quartz sand is mined from the quarries in which ordinary construction sand is mined. The extracted raw material undergoes a number of technological processes: washing to remove mud deposits and cleaning from impurities using a chemical method. This process is called beneficiation, it serves to obtain sand of the required quality. As a result, the content of quartz rock increases, and the purest material is obtained, which, after drying in special installations, passes through a series of sieves and is distributed into fractions. The resulting product is called fractional quartz sand.
The extraction process with a dredge goes like this: a mixture of sand and water from the bottom of the reservoir is pumped and transferred through a special pipeline to the storage site. The water is gradually separated from the extracted soil and goes through the drains back into the reservoir. The resulting material is sent to the enterprise for further enrichment and separation into fractions.
Artificial quartz sand is obtained from vein quartz rock, which is first sent to a crushing complex. There the raw materials are crushed into grains. Then follow procedures similar to those when working with quarry sand: the material is washed, dried and separated into fractions by a technical sieve.
How are sand characteristics standardized?
The main regulatory document is GOST 2138-91; there are also other regulatory documents (GOST 22551 77, GOST 51641 2000, 8736 93). They reflect the requirements for the main quality parameters and properties, namely:
- content of clay component. There are 5 groups with established amounts of clay from 0.2 to 2.0%;
- silicon dioxide content – from 99% to 93%, corresponding to groups from K1 to K5;
- uniformity coefficient, reflecting the variation in particle sizes relative to the average (in %). The higher the value, the more homogeneous the sand mixture. There are five groups in total (from O1 to O5), differing in their homogeneity coefficient (from 80 to 50%);
- factional composition. This parameter reflects the average particle size of quartz sand: up to 0.14 mm; 0.14-0.18 mm, 0.19-0.23 mm, 0.24-0.28 mm, more than 0.28 mm;
- humidity. Dry sands contain no more than 0.5% moisture, wet sands - no more than 4.0%, wet sands - no more than 6.0%;
- the content of metal oxides, the surface area of grains, their shape, gas permeability, as well as weight loss upon ignition are also standardized in the sand composition.
High-quality sand must have a certificate of compliance with the specified standards.
Quartz sand: the most important information
Quartz is a common mineral found in the earth's crust. In its pure form, the mineral is colorless or white. However, even minor admixtures of other minerals guarantee a certain color. Quartz is not only white, but also red and black, because everything is determined by additional components. Quartz sand is often found in nature and is valued in construction.
You need to understand that quartz sand is mined in a regular quarry, but it requires the presence of a high level of quartz and a small amount of impurities. In rich deposits that have already shown their best side, the percentage of pure quartz contained in the sand can even reach 99% .
It is mandatory to carry out a long procedure of washing the extracted sand, because it must get rid of contaminants and impurities, while simultaneously obtaining most of the quartz rock. After washing with mandatory drying, it is supposed to be sifted through a technical sieve for further breakdown into small-sized fractions.
When using quartz sand, you need to pay special attention to its fraction. The most commonly used are fine-grained sands , the size of which is about 0.1 millimeters.
Fine grain quartz sand
Possibility of using fine-grained quartz sand:
- Glass industry.
- Production of window and technical glass.
- Production of fiberglass for electronic systems.
- Making faience.
- Production of porcelain and ceramics.
- Paint and varnish production.
- Production of putties and glue.
- Creation of fire-resistant materials needed in construction activities.
The next variety is quartz sand of medium fractions . In this case, the particle size is 0.3 - 1 millimeters. In most cases, such sand is used to fill filtered units. Increased dirt holding capacity allows quartz sand to act as a filter element to remove large impurities and bacteria. This aspect makes it possible to successfully use sand for water purification in domestic and drinking water supplies, and for the creation of filters for the purification of petroleum products in a liquid state. Quartz sand is also popular for construction and finishing activities.
Quartz sand of medium fractions
The popularity of coarse-grained quartz sand is increasing every year. Popularity is expressed in the volume of sales, which is increasing on an ongoing basis. Coarse quartz sand can act as a coating for soft roofing, an element in the construction of epoxy, self-leveling polymer and polyurethane floor coverings used in industrial premises.
Coarse quartz sand
The effectiveness of using quartz sand has been proven by many years of successful practice. The material is of high quality, harmless and cheap, as a result of which it successfully demonstrates its best characteristics during its use.
You need to understand that the cost of quartz sand varies, because it depends on the following parameters:
- The uniqueness of the deposit.
- Color range of quartz sand.
- Features of production.
- Transport distance.
- Fraction (prices increase if a large fraction is expected).
Thus, it is initially impossible to count on the exact cost of a building material and you need to be prepared for potential variations.
Performance properties of quartz sand
Material parameters that affect the quality of work and determine the scope of application include:
- bulk density is about 1300-1500 kg/m3;
- true density is in the range of 2600-2700 kg/m3. The true density value is used when calculating the volume of cement or concrete mortar obtained by mixing the components;
- The thermal conductivity of quartz sand is about 0.30 W/(m?°C). The shape and size of sand granules have a significant impact on the heat-insulating properties - the denser their arrangement and the smaller the gaps, the higher the thermal conductivity coefficient;
- melting point - the maximum working temperature of quartz sand is estimated at 1050 °C, which is quite sufficient for any construction work. When casting quartz products, temperatures of 1700 °C and higher are used.
- ordinary quartz sand in a loose state has a volumetric weight of 1,500 kg/m3, and a bulk density of 1,600 kg/m3.
Composition and chemical and physical properties of quartz sand
The composition of quartz sand is regulated by GOST 21-38, TU. According to this GOST, the composition must contain at least 95% silicon oxide, the presence of clay no more than 1%, iron no more than 1%.
Humidity should not exceed 10%. The color of sand depends on the impurities in it, so the presence of titanium in the composition gives the sand a pink color, iron gives it a brown color, pure quartz has a milky tint or no color. Yellow is usually burnt sand.
However, there are other requirements.
For example, if sand is intended for the silicate industry, it can be divided into three classes. Class A must have at least 70% silicon oxide, B - at least 60%, C - at least 50%. Sand for the glass industry is divided according to levels of translucency.
Quartz sand is a very hard, refractory and fireproof material, resistant to acids and alkalis, is not afraid of temperature changes, and is also a dielectric.
These properties allow it to be used in various industries. Moreover, the use of quartz sand in a particular area depends on its specific characteristics. The quartz sand that we offer has undergone heat treatment, which is required to eliminate moisture and improve the quality of the sand.
Advantages and disadvantages of the material - overall assessment
Quartz sand is an almost irreplaceable component in many areas of application, and technologies involving it have been developed to perfection. The material gets a “5” for practicality.
The appearance of sand is familiar from childhood, and sand playgrounds are often associated with the beach and relaxation - we also give a solid “5” for appearance.
Despite the massive use of sand, its fine dust can lead to chronic illnesses among builders. The material gets a “4” for environmental friendliness.
The cost of sand is comparable to the cost of other building materials. Without having any special price advantages, quartz sand deserves a “4” rating.
The approximate cost of various fractions of quartz sand is given in the table:
| Name | Cost, rub |
| Quartz sand VS-050-1 | 3000 |
| Quartz sand fr.0.1-0.63 | 3200 |
| Quartz sand fr.0.5-0.8 | 3750 |
| Quartz sand fr.0.5-1.0 | 3750 |
| Quartz sand fr.0.8-1.4 | 3950 |
| Quartz sand fr.0.8-2.0 | 3950 |
| Quartz sand fr.1.2-3.0 | 3950 |
Along with clay and limestone, quartz sand is one of the most important and necessary components for production and everyday life. The variety of material properties provides a wide range of applications. The presence of sand quarries near the construction site significantly reduces the cost of building a house.
Application of quartz sand
- In construction work, quartz sand is used as a basis for preparing concrete and plaster mixtures. It is used as a decorative material when covering surfaces or arranging landscapes and recreation areas.
- In production, quartz sand is an indispensable component in the manufacture of porcelain, earthenware, glass, enamel, and paints and varnishes.
- The physical and mechanical properties of the material make it an indispensable element of water filtration systems.
- In industry, sand rock is used for casting rolled metal, steel smelting and refractory products.
- During the installation and installation of electrical networks, the mineral serves as an arc extinguishing element.
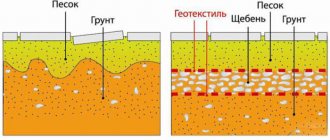
- Among other things, sand is widely used in the construction of road surfaces, helicopter and sports fields.