Wood, brick, stone, concrete, etc. can be used to build walls in private buildings. At the same time, technologies in this construction segment are constantly updated, new materials and methods of constructing buildings appear.
One of these relatively new technologies is the laying of ceramic blocks.
Types of building ceramics
Building ceramics are made by firing clay concentrate containing various improving additives.
Due to their strength, durability and remarkable decorative qualities, ceramic elements have found the widest application in various fields of construction.
The availability and low cost of industrial raw materials made it possible to establish the production of this material in almost all regions of the country.
Dense material does not absorb moisture as well as porous material
Ceramic building materials are divided into several types according to their technical properties and purpose. According to their density they are:
- dense;
- porous.
Dense ceramic products have a low moisture absorption rate, amounting to about 5% of their own weight. Porous materials have many interconnected cavities inside, so they can absorb a very large amount of moisture - up to 20% of their own weight. Accordingly, dense materials are more durable and weather resistant.
But at the same time, porous products have better thermal insulation properties, which allows significant savings on additional insulation.
According to their purpose, ceramic building materials are:
- Roofing. These include various types of tiles.
- Floor coverings - tiles, porcelain tiles, etc.
- Special purpose - fire-resistant lining, pipes for laying communications (sewerage, electrical and fiber-optic cables), thermal insulation protection (expanded clay).
- Facing – tiles for decorative wall finishing, facing bricks.
- Wall materials – intended for the construction of load-bearing structures, primarily the walls of buildings. These include ceramic bricks and wall blocks.
Let's consider the last type of building ceramics in more detail.
Technical characteristics of wall materials
Large blocks can be laid in one layer.
According to their purpose and laying technology, wall blocks and ceramic bricks are completely identical to materials such as building bricks, cinder blocks, foam concrete blocks, etc.
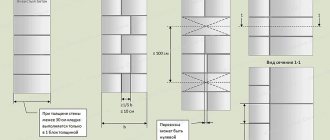
The masonry technology in this case is determined by the size and shape of the ceramic material. Small elements, close in size to ordinary bricks, allow the construction of walls using the standard brickwork method. In this case, they are laid in several layers and tied to each other in all directions.
Large-sized elements, called wall blocks, make it possible to lay them in one layer. This technology is similar to laying slag and foam blocks.
Air-filled voids – thermal insulation chambers
Ceramic blocks differ from bricks not only in their size, but also in their production technology. In addition to clay, they add a certain amount of organic impurities, most often sawdust. This makes it possible to reduce their thermal conductivity.
The presence of air-filled voids inside the blocks also improves the thermal insulation qualities. Thus, a wall made of ceramic blocks 51 cm thick has a thermal conductivity coefficient of 3.3 m x K/W, which is significantly less than that of a wall made of solid building bricks or monolithic concrete.
The compressive strength of ceramic blocks ranges from 75 to 100 kg/sq.cm; for ceramic hollow bricks and small-sized blocks this figure is even higher – up to 100-150 kg/sq.cm. cm. This allows the construction of load-bearing walls of one- and two-story buildings from them.
The table shows the technical characteristics of various types of ceramic blocks.
Ceramic blocks are supplied to the construction market in several standard sizes.
Depending on the dimensions, they can be used to lay walls in one layer with a thickness of 25 to 51 cm, that is, the thickness of the resulting load-bearing structure is similar to that obtained when laying using building bricks (standard size 24 by 12 cm).
Narrow ceramic blocks are used, as a rule, for laying walls in two or more layers. In addition, special additional elements are available for sale, which are non-standard blocks, usually of shortened length - “halves” and “quarters”.
Advantages of ceramic blocks
The light weight of ceramic blocks allows you to reduce the load on the foundation of the cottage being built.
Here only SIP panels and porous concrete products can compete with them. Only for frame structures and walls made of foam concrete blocks can the foundation be made less massive. To cut the material, you will need to use a power saw, which often complicates the masonry process. At the same time, the mason must not only be able to handle such a tool, but also correctly lay the stone itself. It has grooved sides. If the tongue-and-groove joint is made inaccurately, the brick wall will end up with cold bridges.
Cutting ceramic blocks
On the one hand, the large dimensions of porous ceramic stone make it possible to speed up the construction process, and on the other hand, they require additional skills from workers. In this regard, it is much easier to work with aerated concrete. The shape and dimensions of aerated concrete blocks allow a mason to lay walls from them even without experience. Yes, and you can cut them with a regular hacksaw.
Due to the slot structure, the porous ceramic block is quite fragile. This often manifests itself during transportation and loading and unloading operations. If the block is dropped, it can simply crack into two parts.
Advantages and disadvantages of ceramic blocks
Walls made of ceramic blocks will not require additional insulation.
Statistics show that in Western European countries, from a third to a half of all low-rise buildings are built using building ceramics. In our country, this figure is still less than 10%, but tends to grow steadily. This is facilitated by a number of positive qualities:
- The high thermal insulation qualities of the material make it possible to build walls from it without the use of additional insulation. Thus, a wall with a thickness of 44–51 cm corresponds in its heat-saving properties to SNiP standards for such regions as the Baltic States, the Volga region, the Central Black Earth Region, not to mention the more southern regions. This aspect makes construction from ceramic porous materials more financially profitable.
- Simplicity and speed of installation. Due to the large dimensions of the blocks, building a wall from them will take much less time than laying standard bricks. In addition to saving time, this also provides significant savings in masonry mortar.
- Durability of use. The service life of the wall guaranteed by the manufacturer is about 50 years, which is not inferior to similar indicators for concrete or sand-lime brick. It should be borne in mind that in reality this period can be much more than half a century.
- Low weight. Due to the presence of internal voids, ceramic blocks have a much lower density than solid brick or concrete. This makes it possible to use lightweight foundation options in construction - columnar and pile, which again leads to significant savings in building material and time.
- Excellent sound insulation. Due to their porosity, the blocks not only have excellent thermal insulation properties, but also good noise absorption.
- Fire resistance. Since clay is a completely non-flammable material, a wall made of ceramic blocks can withstand the spread of fire.
- Unlike wooden building materials, ceramics do not shrink, so interior decoration can begin immediately after construction is completed.
- Vapor permeability. Ceramic blocks do not interfere with the free exchange of gases between the interior of the building and the outside world. As a result, a comfortable microclimate is created in the premises and the formation of fungus and mold on the internal surfaces of the walls is prevented. For more information about construction using ceramic blocks, watch this video:
Ceramic blocks are fragile, so they must be handled with care during loading and transportation.
Like all other building materials, ceramic blocks also have their drawbacks, which must be taken into account when designing a building and carrying out construction work.
Due to their structure with internal voids, ceramic blocks are not resistant to shock loads, so care must be taken when transporting and constructing them. In addition, the presence of pores determines their high hygroscopicity.
To avoid excessive moisture in the blocks and their subsequent destruction when moisture freezes, moisture should not be allowed to penetrate into the internal cavities during construction.
List of advantages of ceramic blocks – pros and cons
Today, ceramic blocks are one of the most reliable masonry building materials. They are durable, environmentally friendly, and quite economical in price if you calculate the total cost of construction. A house built from ceramic blocks can (according to the manufacturers, of course, in practice no one has yet been able to experience such a period due to the short life of this technology) stand for at least 150 years.
What is their strength
Many people question the fact that a block with a microporous structure cannot be durable. Nothing like this. Ceramic blocks can be used to create a wall of any height that is possible in ordinary, generally accepted construction. Large-format ceramic blocks (38 centimeters in length) have a strength level of M-100. Small-sized and often M-150.
If a simple (not facing) brick can withstand from 15 to 35 cycles of thawing and freezing without signs of deformation of the base and destruction, then the ceramic block is almost always grade F50 and can easily cope with 50 cycles of freezing/thawing (F - from the English “frost resistance” - resistance frost, literally. F-50 – the ability of a ceramic block to withstand 50 cycles of alternating freezing and thawing without beginning to deteriorate).
Fire resistance
Since ceramic blocks undergo a high-temperature firing stage during their production, they are non-combustible building materials. A house made of them can withstand fire for 4-5 hours or more.
Ceramic blocks have excellent, if not excellent, soundproofing characteristics, which they owe to the porous properties of clay as their main component.
The environmental characteristics of ceramic blocks are also at a very high level, almost unattainable for many conventional building materials. There is a good, constant temperature regime and a constant level of humidity favorable for human habitation. The walls made of them “breathe”, creating a natural microclimate in the house.
Technology of laying walls from ceramic blocks
Walls made from ceramic blocks are laid using a special technology that is different from brickwork.
Preparation of masonry mortar
To mix the mortar, it is not sand that is used, but perlite or expanded clay.
When laying a wall of ceramic blocks in one layer, you cannot use the usual masonry mortar used for bricks.
The fact is that the hardened solution has very high thermal conductivity, creating “cold bridges” - areas in the wall through which cold penetrates into the building. Thus, all the thermal insulation properties of ceramic blocks are negated.
The technology for preparing mortar for ceramics is generally similar to preparing conventional mortar. The binding element in it is cement grade M-300 or M-400, but instead of construction sand, the solution uses expanded clay, fine perlite or crushed pumice as a filler. You can prepare the masonry composition yourself or buy a ready-made dry mixture at a hardware store. It is diluted by adding water in the proportions indicated on the package.
Laying the first layer of blocks
The first layer of blocks is laid on the foundation base. It must be perfectly level, otherwise it is necessary to pour a layer of leveling screed on top of it.
Before laying the blocks, a waterproofing layer should be laid between them and the foundation.
The first step is to install the corner blocks.
Waterproofing will prevent the penetration of moisture from the concrete into the pores of the ceramic blocks. For its installation, roll waterproofing is usually used - roofing felt and its analogues.
After this, you can proceed directly to laying the blocks. Masonry begins from the corners of the future building. Using a building level, corner blocks are placed on the mortar.
The thickness of the mortar layer should not be too thick or too thin - according to building regulations, it is about 10 - 12 mm.
It is advisable to moisten each block with water, so it absorbs moisture from the solution less intensively. As a result, the mortar sets more evenly without overdrying or other violations of construction technologies.
To level and settle ceramic blocks, you cannot use a mason’s pick due to the fragility of the building material. When working with them, you should use rubber mallets.
For orientation, twine is stretched between the outer blocks.
After installing the corner blocks, we fill the first row.
To do this, a thin twine is stretched between the outer ceramic blocks, serving as a guide for installing the remaining blocks.
When joining the last blocks of a row, they may not match in size.
To obtain an element of the desired size, you should use a grinder with a special cutting disc. You should not try to break off a piece of the required size using a mason's pick - the ceramics will most likely break into many pieces.
You can also purchase special additional elements measuring ¼ or ½ the length of a solid ceramic block. Upon completion of the laying of the first row, the mortar should be allowed to set thoroughly. This usually takes 12 hours, after which you can begin laying subsequent rows.
Further work
The vertical seams of adjacent rows should not coincide.
All subsequent rows also begin to be installed from the corners, adjusting the installation of the outer blocks using a building level. Particular attention should be paid to seams.
They must be even and of the same thickness - the beauty of the masonry largely depends on this. Vertical seams must be carefully filled to avoid through gaps.
Dressing should also be observed: the vertical seams of adjacent rows should not coincide with each other. To achieve a greater decorative effect, the seams are embroidered using a slightly bent metal rod or tube with a diameter of 10 mm. To learn how to properly lay blocks, watch this video:
Every 3 - 4 rows it is necessary to lay a masonry mesh or reinforcement with a diameter of 6 - 8 mm. In a similar way, walls are erected in accordance with the design drawings. Openings for doors and windows, ventilation holes, etc. are installed in the right places.
After the walls are erected, you can immediately begin arranging the roof to protect the walls from precipitation.