Strengthening concrete structures is a common practice in construction, which helps to significantly extend the life of components and buildings as a whole. We will talk about methods of such amplification and consider their features, as well as methods for implementing basic technologies.
Reinforcing reinforced concrete columns with steel frames increases their load-bearing capacity.
Work to strengthen reinforced concrete structures
General information
Reinforced reinforced concrete lintels and columns increase the strength and load-bearing capacity of construction projects.
Measures to strengthen reinforced concrete structures are aimed at increasing their load-bearing capacity and service life, and also make it possible to restore and restore various reinforced concrete products after prolonged wear or loss of technical qualities for any reason (read also the article “Minimum hardening temperature of concrete - features of concreting in winter time").
These works include a whole range of measures and actions that are aimed at achieving various results.
| Increasing the cross-section of beams, columns, trusses, crossbars, chords and other reinforced concrete elements | Achieved through layer-by-layer concreting using a reinforced frame, spraying concrete at high speed from special guns, injecting mortar into formwork and other means |
| Strengthening nodes and load-bearing elements by adding new parts | It is carried out by redistributing loads and reducing the impact on the reinforced element by including additional beams, lintels, consoles, ribs, crossbars, etc. in the structure. |
| Unloading and redistributing forces to other elements of the building | This is done by including additional consoles or changing the interaction of old units and their parts, as well as by replacing heavy elements with lighter ones, replacing heavy equipment, thermal insulation and other building systems |
| Improving the technical characteristics of reinforced concrete products by adding external metal and reinforced concrete reinforcing structures | Achieved by constructing frames, compression jackets and clips, including additional reinforcement, channels, belts, steel strips and sheets, anchors, prestressing elements and concrete layers |
| Construction of underground concrete piles and various stops, jibs, soles | Here, diamond drilling of holes in concrete and further in the ground is used, which are then reinforced and filled with mortar to create drilled injection piles and additional supports in order to increase the stability of the underground parts of load-bearing structures |
Important! As we can see, we are talking about serious construction procedures that require an appropriate approach and fairly high qualifications of designers and work performers.
Also, the package of work may include additional procedures, such as eliminating defects and cracks by injection, gluing, and other measures to restore the integrity and solidity of products and their parts.
Reinforcing cages and meshes are used most often.
Measures to strengthen the load-bearing structures of buildings are considered work of increased complexity and are considered more responsible than construction from scratch. This is due to the fact that in the case of restoration, we cannot accurately calculate all processes, because the initial data is insufficient and inaccurate.
Moreover, the work is related to old buildings, and we do not know the condition of internal and hidden components, reinforcement, actual load distribution and other important parameters. In addition, such work is dangerous and requires strict adherence to safety regulations and many safety measures.
Particular attention is paid to work safety.
It is also necessary to note the special construction conditions in which it is necessary to work in cramped spaces, without stopping the activity of the facility or enterprise where the work is being carried out, with limited access to special equipment and other inevitable restrictions. This imposes certain difficulties and requires special training for builders.
Finally, work is most often limited in time and does not tolerate delays or changes in deadlines and schedules. This also complicates the process and requires serious labor organization, proven techniques and experienced installers.
Often you have to deal with emergency and dilapidated structures, as shown in the photo.
Considering all the listed difficulties and problems, it is not surprising that such activities are controlled by government services and require high responsibility of contractors, designers, labor protection specialists and other participants in the process. Projects go through several stages of approval and must be drawn up as competently and correctly as possible.
Important! Serious work on strengthening load-bearing reinforced concrete products should be carried out after preliminary research and calculations, taking into account all, including the economic aspects of the upcoming activities. Of course, doing this yourself is unrealistic.
The processes require the participation of expensive special equipment.
It is also important to pay attention to the fact that most modern reinforcement technologies require the participation of special construction and lifting equipment, the price of which exceeds the budget of any independent craftsman. Therefore, it should be understood that work of this level is carried out by serious accredited construction organizations.
Important! It is impossible to predict with high accuracy the nature of the processes and the associated difficulties, therefore the work is carried out under the constant supervision of the design organization and independent specialists. Situations often arise when you need to quickly make responsible decisions and eliminate unforeseen difficulties.
Indications for use
The most common reason for the need for reinforcement is an emergency condition or destruction of the structure.
A set of measures to improve the condition and technical characteristics of concrete structures is carried out only if there are sufficient grounds or necessity for their use. “Just in case” such measures are not carried out (see also the article “Expanded polystyrene concrete - everything you need to know about this material”).
Opening and damage to reinforcement is one of the main reasons for the deterioration of the characteristics of reinforced concrete products.
Let's look at the reasons that may become the basis for deciding to carry out the described procedures:
- Aging of structures and their loss of design strength due to material fatigue, corrosion, chemical changes and other natural causes, which could not be avoided due to certain circumstances;
- Changes in the number of storeys of buildings and the associated increase in loads on the foundation, columns, floors and other elements of the structure, which can lead to destruction and other undesirable or dangerous consequences;
- Redevelopment of buildings with changes in the configuration of load-bearing walls, columns, beams, consoles, trusses and other structural elements involved in the transfer and redistribution of loads in the building and its components;
- Ground movements that lead to changes in the operating conditions of foundations, increased external pressure on their walls, disruption of the established balance of forces in systems of underground supports and load-bearing structures;
- Changing the purpose of buildings or re-equipping workshops, which leads to the emergence of new types of wear, including vibration loads, significant point forces, thermal or chemical effects, etc.;
- Violation of the integrity or destruction of individual parts, components, systems and structures as a whole due to accidents, earthquakes, natural disasters of various types, man-made disasters or military actions;
- Elimination of mistakes made when designing or performing work on the construction of load-bearing structural elements.
Wear and tear of materials leads to the need for reconstruction.
Important! Only the main situations in which a decision can be made to carry out work to strengthen reinforced concrete structures are listed here. Such a decision can be made for other indications and depends on the specific problem and the arsenal of means to solve it.
In order to make a verdict on the feasibility and necessity of carrying out certain activities, an examination is mandatory. This survey should determine the actual characteristics of the materials of the parts or assemblies to be strengthened, their strength limits and expected or existing loads.
The survey is carried out by experienced engineers using sophisticated equipment.
Based on the survey, calculations are made and working drawings of structural reinforcement units are developed, taking into account design and actual loads, loading patterns, the effect of using reinforcement technologies and their contribution to increasing the overall reliability of the building. Costs and economic benefits are also calculated taking into account the shutdown of enterprises during repairs and reconstruction.
Calculating the reinforcement of reinforced concrete columns, floors, walls, foundations and other building systems is a complex and responsible job that only experienced, high-level specialists can do. Most often, this task is performed by entire departments or design organizations.
Strengthening methods
Strengthening foundations with monolithic reinforced concrete frames allows you to extend the life of buildings and structures.
There are many ways to strengthen reinforced concrete structures; we will consider only the main ones.
In certain situations, the following methods are used to improve the structural qualities of parts, components and load distribution systems in buildings:
- Performing repair plaster to restore the integrity of the part and the continuity of its surface, as well as to protect the reinforcement from corrosion and eliminate various surface defects;
- Injecting concrete mortar into cracks, cavities, voids and other defects to repair and restore the integrity of the body of the part;
- Shotcrete of reinforced concrete concrete using special guns that apply concrete to the surface at high speed, which allows it to compact and gain significant strength . Used separately and in conjunction with other methods of amplification;
- Strengthening reinforced concrete beams, columns, walls and ceilings by constructing special cages and jackets that use external reinforcement and concreting by injecting mortar into the formwork, shotcrete and layer-by-layer concreting with vibration;
- Strengthening the foundation with reinforced concrete frames, belts, anchor ties and other metal and reinforced concrete structures;
- Strengthening beams, crossbars, racks, columns, supports and piles with composite materials such as carbon fiber, Kevlar, carbon fiber and other similar materials;
- Changing the nature of the mating parts from moving to rigid;
- Adding unloading parts: jibs, spacers, consoles and others;
- Unloading structures by introducing new units and elements, changing single-span floors to multi-span ones, adding new supports and columns, using ties and prestressed reinforcement, steel belts and jackets.
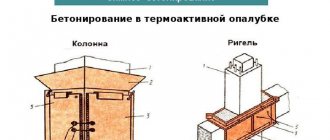
This is how the column is shotcreted to make a reinforced concrete jacket.
Obviously, the methods and related work are so varied that a specific description of them all would fill several volumes. However, there are also general instructions, or rather a set of recommendations that are valid for almost all events.
Strengthening the foundation with a cage of reinforcement and concrete.
They come down to the general rules for preparing surfaces and installing steel reinforcement and include notching the surface of concrete, jointing and cleaning the reinforcement from corrosion (this involves cutting reinforced concrete with diamond wheels or processing with hammer drills), and connecting the external frame to the internal reinforcement or concrete body. Be sure to clean and moisten the surface using water cannons and other devices.
Strengthening a concrete truss with a composite plate.
The rules may also describe tying the outer frame rods together, preheating the plates to create tension, and other generally applicable procedures.
Important! It should be remembered that there are no universal instructions or a general set of rules, since they are prescribed separately for each specific type of work.
General information
Any methods of strengthening reinforced concrete structures require responsible and important construction operations, the implementation of which requires certain design skills, knowledge to make calculations, etc. In order to strengthen and reconstruct elements, a variety of methods and actions can be used.
Operations related to the strengthening of reinforced concrete structures are among the processes of increased complexity compared to conventional installation work. After all, when restoring slabs or floors, foundations or trusses, the master does not have the opportunity to understand and see the original position of the structure, there are no exact technical specifications, etc. This is especially important to take into account when it comes to old buildings, the lack of information regarding the position of internal elements, fittings, actual pressure distribution, etc.
Due to the high level of risks, such operations are carried out strictly according to instructions, in compliance with safety precautions, and a large number of safety measures. Specific installation conditions are taken into account, with limited access to tools, limited space, and the inability to stop work.
To reduce the level of danger and increase the speed of work, everything is done according to a pre-drawn schedule, with a clear definition of methods and technology planning.
The work is supervised by special government services and qualified specialists. Projects require approval from various authorities and proper execution.
The main methods of strengthening reinforced concrete structures:
- Creation of unloading structures with consistent changes in the static work scheme. Extension of sections in the format of clips, concrete strips, shirts. The betonka is made on 1 side, the shirt on 3, the clip on 4.
The creation of unloading structures involves their inclusion in joint work with the structure being strengthened directly during installation; production does not have to be stopped, which in many cases is the most important factor.
The second method involves stopping the process, partially unloading structures for subsequent loading, as well as incorporating various types of extended elements into the work. The method is quite labor-intensive, involves wet concreting processes, requires additional time (when the concrete gains strength), but is universal.
Strengthening reinforced concrete structures by repairing the protective layer of concrete includes the following methods: replacement/restoration of the protective layer (partial/solid), sealing individual sinkholes and gouges. When a complete replacement is performed, the thickness of the protective layer is increased (the minimum value is 3 centimeters for working reinforcement and 2 centimeters for non-working fittings and clamps).
The protective layer is replaced in cases where the properties of the monolith are reduced, the reinforcement is covered with corrosion, and peeling of the protective layer is observed. Then the old layer is completely removed, the reinforcement is cleaned of rust, and a new protective layer of concrete is laid.
Reinforced concrete jackets are made in case of serious damage to the surface concrete layer to protect the structure from further deformation. To repair significant damage, use manual plaster with a trowel: lay it, then after an hour moisten it with water, carefully sprinkle it with dry cement, smooth it with a trowel, or metal/wooden trowels.
Currently reading: Ten basic questions and answers about concrete
The depth of the gouged out zones should not decrease towards the edge of the recess, it should be at least 1 centimeter everywhere, and the transition of the gouge to the whole protective layer is made as a step at an angle of 90 degrees.
If the volume of work is significant, it is important to use shotcrete, when concrete is applied under strong pressure and creates a durable and dense protective layer. When the monolith is being prepared for concreting, single cracks more than 1 millimeter wide are cut into rectangles and caulked with concrete. Where the spalls are large and the reinforcement is visible, use a reinforcing mesh with squares of 2.5-10 centimeters and a wire cross-section of 0.5-6 millimeters, attaching them to the main reinforcement.
To increase adhesion between new/old concrete, add a layer of K-153 glue (epoxy-thiokol). The concrete is laid until the adhesive is no longer sticky.
Ways to eliminate cracks:
- Creation of protective films/coatings - if the opening of cracks is no more than 0.2 millimeters. Coatings of this type are created by painting concrete with synthetic varnishes and polymer-cement paints. Sealing cracks - they are filled with elastic waterproof materials; the method is suitable for cracks larger than 0.3 millimeters. The access of moisture to the crack and reinforcement is closed, mastic and syringes are used. Surface sealing - creates a sealing lining that covers the defect and strengthens the section with a crack, suitable for cracks from 0.2 millimeters. The structure becomes monolithic; the method is implemented by injecting with an epoxy compound or cement solution. The process of performing the work: creating holes, installing nipples for supplying glue, sealing the crack with a fiberglass sticker, injecting the lower and subsequent nipples. Strength sealing - the crack cavity is made monolithic using glue, suitable for cracks from 0.3 millimeters, protects against chemical and atmospheric corrosion.
The most common method of strengthening structures is to increase the cross-section through one-sided extension or the creation of all-round clips. Such methods of reinforcement make it possible to significantly increase the load-bearing capacity of damaged/intact elements.
If a one-sided increase in the cross-section of reinforced concrete structures is implemented, additional reinforcement is welded (by electric welding, double flank seams) to the old one using vertical and inclined clamps, short pieces, and bends.
If there is local damage in the form of single/concentrated cracks at a minimum length, the structure is strengthened as follows: local four-sided cages are made of reinforced concrete (reinforced with clamps, bent/longitudinal reinforcement), metal cages are made of prestressed vertical clamps.
When oblique/vertical cracks are observed, longitudinal distribution angles are installed under the clamps, which should cover the entire damaged part of the beam. All clamps are concreted or covered with shotcrete.
In cases where it is necessary to strengthen the columns, the cages are reinforced with longitudinal rods and clamps or spiral reinforcement. The cage can be concreted in formwork or covered with shotcrete. The wall thickness is at least 10 centimeters for conventional concreting and 5 centimeters for shotcrete. It is better to chip off the corners of a column that is being strengthened.
At the bottom/top of the column at a length corresponding to the largest dimension of the transverse diameter of the column, the pitch of the clamps is reduced by 2 times. If there are local defects, a reinforcing ring is made within the boundaries of the deformed zone with a bypass of 50 centimeters in both directions, but not less than the cross-sectional value.
Strengthening reinforced concrete structures by building up elements:
On the reinforcement side, chop off the protective layer at the welding points, clean the longitudinal bars of the reinforcement to half the diameter. Rinse the surface of the concrete with a stream of water running under pressure; if this is not possible, make notches with a chisel, treat with a brush, blow with air to remove dust, and then rinse with water. Apply plastic concrete to a damp surface (a solution in a ratio of 1:2, in a layer 1-2 millimeters thick). Concreting with new concrete.
All exposed reinforcement bars are thoroughly cleaned with metal brushes, sandblasting or another method to remove rust, dirt, and scale. If the damage to the rods is serious, the damaged film is removed with a hammer or chisel, cleaned with a steel brush, and new reinforcement is welded. Before concreting, the rods are painted with a 1:2 cement mixture in a layer of 2 millimeters.
The formwork is installed in such a way that it can be gradually increased in accordance with the height of the reinforced columns and beams. When formwork is created, the necessary holes and gaps are provided in it, special trays for pouring concrete, and seals. Sprayed shotcrete or poured conventional concrete is then provided with optimal care.