There are different methods for compacting a concrete mixture, and all of them are aimed at improving the quality of the concrete solution, removing air bubbles from the thickness of the poured monolith, which increases strength and resistance to mechanical stress, reliability and durability. If concrete is not compacted, cavities with air may remain inside the structure of the material, which negatively affects operation and load-bearing capacity.
Compaction of the concrete mixture can be done by several methods - manual, mechanical, using special devices and tools. Vibrators come in different types and methods of influence, suggesting a certain frequency and type of vibration. The compaction mode must be selected in accordance with the characteristics and characteristics of the concrete mixture.
Criteria for choosing compaction mode:
- Oscillation frequency is the number of oscillatory cycles that occur in one unit of time.
- Vibration amplitude – shows the maximum distance of the vibration point from the center of vibration.
- Process time.
How to correctly determine the vibration mode of a concrete mixture
In order to correctly choose the appropriate method for compacting a concrete mixture, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the solution itself, the conditions for its pouring and other nuances.
Selecting vibration mode for concrete compaction:
- A mixture with a large filler – low-frequency vibrations with large amplitude.
- Concrete with fine filler - it is better to vibrate with a small amplitude but a high frequency.
- Solutions with fillers of different sizes - it is advisable to use multi-frequency mechanisms: mechanisms that vibrate with a changing frequency are most effective in this case.
Modern vibrators can provide vibration frequencies in the range from 2800 to 20,000 cycles per minute, the vibration amplitude can be 0.1-3 millimeters.
Compaction methods
Various methods and devices are used to compact concrete mortar. On the modern market you can find vibrators of different designs, with one or another method of influence. The simplest option is manual bayoneting, which is performed with a metal rod or any other suitable tool. The option is simple, cheap, but also the least effective, therefore it is suitable only for home use and pouring non-critical structures and structures without serious loads.
Mechanisms for vibrating concrete:
- Internal (aka deep) vibrators - the working part of the mechanism is in the mixture, and the vibrations are transmitted through the body.
- External vibrators - they are attached to the formwork structure.
- Surface mechanisms are installed on the surface of the solution, and vibrations go through the working platform.
- Vibrating platforms are stationary forming equipment, which is usually used only in factory conditions for the production of reinforced concrete products.
According to the type of power supply, vibrators can be electromagnetic, electromechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic, or powered by an internal combustion engine. If power tools are not available or their use is considered unprofitable, the concrete is compacted manually.
The most effective option for laying concrete mortar with maximum compaction is layer-by-layer pouring of the mixture with deep-type vibration. Each subsequent layer is laid with a maximum thickness of 10 centimeters (but preferably 3-5 centimeters), the mobility of the mixture is 6-8 centimeters. To ensure a homogeneous structure, concrete in such cases is supplied precisely, at certain intervals, optimal for vibrating.
Manual seal
If the work is done with your own hands at home and the use of equipment is unjustified, you can compact the concrete solution manually. This option is suitable for working out small volumes of mixture. Plastic concrete is compacted using the bayonet method: a long pin or piece of reinforcement (in extreme cases, a pipe) is immersed in the solution, performing pushing movements with a small amplitude, and when they reach the bottom, they begin to swing the pin from one side to the other. Next, the instrument is carefully and slowly removed, making horizontal and vertical oscillatory movements.
Any mixture must be bayoneted to the very bottom. If the work is carried out with hard concrete, then it is advisable to make a tamper from a piece of timber or log weighing 15-30 kilograms. To make the work more convenient, a handle is nailed to the tool, and the lower end of the tamper is covered with a piece of metal (to protect the wood from absorbing moisture and crumbling).
For high-quality vibration of small concrete parts, lighter tampers are used, which resemble a mop in shape with a platform made of metal or a wooden block mounted below.
Deep vibrators: characteristics and scope of application
This type of vibrators is relevant for working with reinforced and non-reinforced structures - they are used in the process of creating foundations, pouring floors and beams. An electromechanical deep vibrator works on the following principle: it transmits high-frequency vibrations of the tip to the solution through a flexible shaft using an electric motor.
Another name for the tip is a mace. It is immersed in the concrete mixture, provoking high-frequency waves that reduce the friction of the material particles and increase its plasticity. The viscosity of the mixture decreases, the concrete flows freely in the free volume, thus filling the most inaccessible places. During the process, air bubbles are squeezed out and come to the surface.
Compaction of large masses requires the use of powerful vibrators moved by cranes. Such vibrators can be combined into packages if necessary. At construction sites without access to electricity, vibrators are used that operate on the basis of drives with internal combustion engines.
Surface vibrators: design features
Surface-type vibrators are used for processing concrete reinforced with single reinforcement or unreinforced - usually floors, ceilings, vaults, airfield and highway surfaces with a thickness of no more than 25 centimeters. When concreting structures with double reinforcement, the thickness should not be more than 12 centimeters.
Tools of this type include a working platform with an electric motor mounted on it. There are two unbalances on its shaft, which rotate and initiate oscillations. Vibrations are transmitted to the concrete solution through the working platform.
The vibrator is powered by a step-down transformer, which eliminates the risk of electric shock to workers. The type of surface vibrators also includes vibrating slats - a device for compacting and leveling mixtures that are poured when arranging the base and floors. The vibrator includes two parallel profile parts connected to each other by rigid transverse links.
To eliminate the risk of deformation of the slats, tension devices with an unlimited warranty are provided inside the profile. The tension of the profiles is adjusted using screws located at the ends of the rail. The vibrating slats are rotated by electric or gasoline vibrating units of a removable type.
External vibrators: types and their characteristics
To compact the concrete mixture, which is placed into thin elements of various types of monolithic structures, is used in the production of parts of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures, and also to speed up the unloading of viscous materials from bunkers and dump trucks, vibrators are used, which require installation on formwork, a bunker or any other structure with an external sides.
The most popular are electromechanical vibrators of this type with directional and circular vibrations; pneumatic tools are also often used.
Main types of external vibrators:
- A tool with circular vibrations includes a vibrator motor, and unbalances are located on its shaft. By moving the unbalances along the shaft, the amount of torque is adjusted.
- Vibrators with directional oscillations (also known as pendulum vibrators) are devices equipped with a pendulum stand and retractable weights. The vibration axis and the support plate are combined with the vibrator. The amplitude of swing of the mechanism body around the axis is limited by the shock absorber.
- Pneumatic vibrators are equipped with a pneumatic motor, which is located in a housing with brackets (intended for fastening to structures), a starting device, and a hose for air supply. There are models created specifically for the manufacture of pipe products.
Due to their energy safety, pneumatic vibrators can be used even in explosive environments and where other types of tools might pose a hazard.
Compaction with deep vibrators
Compaction with deep vibrators. Deep vibrators are designed for compacting concrete mixtures when placing them in concrete or reinforced concrete structures with varying degrees of saturation with reinforcement. With the help of deep vibrators, it is possible to compact well plastic and low-moving concrete mixtures with a cone draft of at least 0.5-1 cm.
The effectiveness of the impact of deep vibrators on a concrete mixture is determined by the ratio of the frequency and amplitude of vibrations, as well as the size of the active surface of its body. The compacted volume of concrete in a vertical position of the I-86A vibrator has the shape of a body of rotation with expansion downwards to a height of 10-15 cm with a mobility of the concrete mixture of 4 cm. The radius of action of deep vibrators depends on the magnitude of the statistical moment of unbalance, the frequency and amplitude of vibrations. There is an optimal value for the vibration frequency, which can be explained by the faster attenuation of high-frequency rotations in the concrete mixture.
As the hardness of the mixture increases, the radius of action of the vibrator decreases. At the same time, the optimal oscillation frequency also decreases, and the amplitude increases. With an increase in the active (in contact with the concrete mixture) surface of the vibrator, the power dissipated by the vibrator in the concrete mixture and the efficiency of its operation increase.
Deep vibrators with a flexible shaft are designed for compacting concrete mixtures with a cone slump of 3-5 cm when placing them in structures with varying degrees of reinforcement or in elements of a small cross-section. Vibrators of this type are also effective when concreting thin-walled structures with low reinforcement saturation. The distance between the reinforcement bars must be at least 1.5 times the diameter of the vibrating tip. Vibrators IV-75, IV-66, IV-17 are recommended for compacting concrete mixtures in densely reinforced structures, and vibrators IV-27, IV-67, IV-47 - in small reinforced structures.
To start a vibrating tip with external running of the runner (IV-17, IV-27, IV-67, IV-75), you need to lightly hit the lower part of the body on the ground or wooden formwork 1-2 times. All other types of vibrators start without shocks or blows to the body. The vibrator is immersed in the concrete mixture along the entire length of the working part. When vibrating, it is necessary to insert the vibrating tip into the underlying layer of concrete by 5-15 cm to ensure reliable connection between the individual layers. The distance between the immersion points of the vibrating tip should not exceed 1.5 times its radius of action.
The vibration time at one point should be 15–30 seconds, depending on the parameters of the vibrator, the mobility of the concrete mixture, and the degree of reinforcement. The vibrating tip should be removed from the concrete mixture slowly with the engine running so that shells do not form in it.
Do not press the vibrator against the reinforcement or formwork, as in this case the electric motor will be overloaded and the vibrator may fail. It is necessary to avoid tension or kinks in the flexible shaft, hose or cable of the vibrator. The bending radius of the flexible shaft must be at least 300-350 mm.
The operating time of the vibrator at idle should not exceed 5-10 seconds—this is enough time to move it from place to place.
Deep vibrators with a built-in electric motor are used to compact concrete mixtures with a cone slump of 1-5 cm. When operating from a single frequency converter, vibrators of this type are switched on one by one with a delay that ensures full start-up of the electric motor.
Operating the vibrator in air or with the working part not completely immersed in the concrete mixture leads to rapid wear of the electric motor windings. During operation, do not turn off the vibrator immersed in the concrete mixture, clamp it between reinforcing bars, or press it against the formwork.
Manual pneumatic internal vibrators have the same field of application as vibrators with a built-in electric motor. The rules for working with electromechanical vibrators equally apply to pneumatic ones.
For normal operation of internal pneumatic vibrators, you should use a hose with an internal diameter of at least 16 mm and a length of no more than 8-10 cm. When working in winter conditions, it is necessary to ensure that the compressed air is thoroughly cleaned of moisture to avoid freezing of condensate and the formation of ice plugs.
Types of vibration platforms
Any vibrating platform includes two frames. A container with concrete mortar is mounted on the upper movable one. The lower one is motionless and is attached to the base. The upper frame, together with the vibration mechanism located on it, is supported on a stationary frame using shock absorbers - springs, springs, rubber gaskets.
Typically, the vibration mechanism is made in the form of shafts with unbalances, which begin to rotate due to the operation of an electric motor. The upper frame (which is movable) must be sufficiently rigid, otherwise uneven amplitude of vibrations may occur. Where the vibrations are weak, the compaction of the solution will be insufficient.
Quality indicator for laying concrete mixture
To ensure sufficient compaction of the concrete mixture, certain rules must be followed. Even with the correct choice of high-quality vibration equipment, the main goal (namely removing air bubbles from the solution, increasing strength and density) may not be achieved due to certain factors.
Recommendations for uniform compaction of the concrete mixture:
- When installing wooden formwork, you need to very carefully fix all the parts, eliminating the possibility of cracks appearing (through which the solution can be squeezed out). The formwork must be smooth and sanded, otherwise it will leave dents on the product and may contribute to the formation of voids inside.
- Formwork parts made of plywood or wood must be well fastened so that the boards do not move.
- When performing vibration compaction, you need to periodically change the position of the vibrating screed to avoid the formation of cavities in a non-uniform solution.
- You should not vibrate for too long, as you can achieve the opposite effect and worsen the characteristics of concrete, causing delamination or uneven distribution of the filler.
The quality of compacted concrete is determined by one main indicator, which is the compaction coefficient. This value is equal to the ratio of the actual weight of the concrete solution (volume) to the theoretical weight, which is calculated taking into account the absence of air in the mixture. The compaction coefficient depends on the following parameters: the shape and nature of the surface of the fillers, the percentage of water content in the mixture.
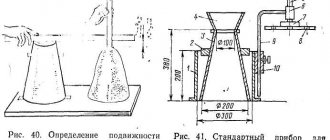
Well-placed concrete exhibits a compaction coefficient ranging from 0.98 to 1.0. You can determine it at home using a special device. It consists of two bunkers in the form of a cylindrical vessel and an inverted cone.
Correct and optimal compaction of the concrete mixture is an important task when creating any objects and products, since the properties and technical characteristics of the hardened stone depend on this measure.
The purpose of compacting the concrete mixture
One of the most important properties of the solution is that it must evenly fill the form/formwork in order to qualitatively combine all components and form a solid monolith. Fluidity is increased with the help of various chemical additives, but you still cannot do without forced action. It solves several problems at once:
- uniform distribution of filler and cement particles;
- reducing the porosity of hardened concrete;
- increasing the strength of the structure.
During work, they use both improvised means and mechanical tools.