Briefly about sand concrete
The composition of sand concrete consists of the following components:
- sand (responsible for the parameters of strength and plasticity of the dry residue);
- Portland cement (affects the rate of hardening, resistance to loads);
- additional components: granite powder and plasticizers. Improves characteristics - strength and density. If necessary, you can adjust the parameters of moisture resistance, frost resistance and hardening speed.
Carrying out calculations
Construction mixtures are packaged in sealed bags, weight varies from 25 to 50 kg. Therefore, when drawing up cost estimates, you should decide how many bags of sand concrete are needed per 1 cubic meter of finished mortar. If we talk about the volume of one unit of popular mixtures per cubic meter. m, then it looks like this:
- 25 kg: 0.01-0.019;
- 40 kg: 0.017-0.03;
- 50 kg: 0.021-0.038.
The specified data will help you find the consumption of CPS per 1 m3 of finished solution
Using ready-made formulas, we calculate the number of packages using the following algorithm:
- find the total number of cubic meters of the finished solution;
- we calculate the content of sand concrete in the resulting volume;
- cubes of sand concrete must be converted into kg, and accordingly into bags.
The working solution is prepared by mixing a variety of components. Let's consider the consumption of the working solution of the mixture and water for popular brands. So, for M100 you will need 550-570 kg per cubic meter, M150 - 570-590, M200 - 590-620, M300: 620-660, M400: 660-710.
In addition to the density of the CPS, it is important to take into account the mass fraction of cement and the sand fraction. After all, the higher they are, the greater the weight of 1 cubic meter of solution. Regarding consumption, the parameters of the planned monolith must be taken into account.
Weight of cement mortar in 1 m3
To find out the weight of a solution M100, for example, or M400, just look at the corresponding data in a special table. Although there is no direct relationship between weight and strength, the rule generally works is that heavier mixtures have greater density, and this tends to increase proportionally with the level of strength.
Types of concrete by specific gravity:
- Particularly light (grades from M50 to M75) with a specific weight of up to 500 kg/m3 - the material contains cement and fillers that form a structure that is 85% voids. Typically, such concrete is used for thermal insulation; it is fragile; in order to increase this indicator, plasticizers can be used. Porous structures are poorly resistant to water and frost, so they require mandatory waterproofing. Lightweight (grades from M100 to M200) with a specific gravity of 50-1800 kg/m3 - the mixture is used to create special building blocks with a porous structure. Pores are formed through the use of cellular fillers or the introduction of special foaming substances into the composition. Heavy (grades from M200 to M400) with a specific gravity from 1800 to 2500 kg/m3 - ordinary concrete, which is most popular in construction. Load-bearing structures are erected from it. The weight of the material directly depends on the proportion of sand and coarse filler, as well as the density of the latter. Thus, the weight will be different when using gravel and granite filler in the same volume. Particularly heavy (grade M450 and higher) with a specific gravity from 2500 to 3000 or more kg/m3 - such concrete is prepared with metal fillers. The solution is used to create special-purpose structures to prevent the spread of radioactive radiation through walls.
Currently reading: Reinforced concrete supports SV 95/105/110/164
The relationship between the type of concrete and the type of filler: Lightweight concrete is made using foaming agents (foam concrete), aluminum powder (aerated concrete), tuff, expanded clay, pumice. Lightweight concrete - using slag concrete and similar fillers. Heavy concrete - mineral fillers are used (gravel, quartz sand, crushed stone, etc.). Extra heavy concrete - fillers based on groups of minerals (limonites, magnetites, barites and others). When performing calculations of concrete/reinforced concrete structures, SNiP 2.03.01-81 and GOST 25192-82, which regulate the physical and technical properties of concrete (density among them), are taken as a basis. When calculating the weight of concrete in practice, remember the following nuances: The weight of the solution and the hardened monolith are different, since water evaporates during the hardening of concrete. The density of the material is largely determined by its internal structure and fillers. The final mass of the concrete mixture also depends on the method of its preparation - manual kneading usually involves lower density compared to the mechanical method. Using a deep vibrator to compact the mixture, for example, M100, the specific weight of the material increases, since the density is higher.
The final density is very important to know when designing and creating construction projects.
What does specific gravity depend on?
Specific gravity is an indicator of mass, which is calculated as the ratio of the weight of the material and the volume it occupies (in this case, 1 cubic meter of concrete is taken as a guide, which can weigh differently depending on all of the above factors).
The specific gravity of concrete increases in proportion to the increase in the density of the material (in fact, density is determined in kilograms per cubic meter). Density determines the scope of use of the concrete solution. Thus, the densest mixtures are used to make strong reinforced concrete structures, loaded and critical elements of buildings. Where the loads are not very large, less dense mixtures are used.
The specific gravity is influenced by the grain composition of the filler and the water content. To increase density, plasticizers can be used - special additives that regulate the properties of the mixture by reducing the need for concrete in water while maintaining its mobility (which is very important for comfort in work).
Despite the fact that there is no direct relationship between specific gravity and the properties of the material, many important parameters are determined by this criterion. Thus, lightweight porous concrete with a minimum specific gravity is usually fragile and loose, acting as materials for heat/sound insulation, but not as elements of load-bearing structures. Dense and heavy concrete is extremely durable and moisture/frost resistant.
The specific gravity of concrete can range from 300 to 2500 kilograms per cubic meter. Ordinary cement-crushed stone mortar belongs to the group of heavy concretes and exhibits a specific gravity of around 2400 kg/m3. When choosing concrete for repair and construction work, the following factors are taken into account: the low weight of concrete implies greater porosity and better insulating properties, but low strength; large mass gives poor insulation, but high strength and a minimum of air in the structure.
What affects the weight of a cubic meter of concrete solution: Type and characteristics of the filler. Size of filler granules. Method and quality of mixing. Volume of water. Percentage of air in the structure, number of voids. Specific gravity is not usually used as a defining characteristic in construction. Most often, volumetric weight and specific indicators of density, resistance to loads and various impacts are taken into account.
Determining the quantity of materials
There is a table with ready-made coefficients for determining the number of DSP packages in 1 m3 of working solution without filler (except for the large fraction: expanded clay, crushed stone, gravel). Calculations are presented for the M300 brand in a ratio of 3 to 1. To calculate the surface area, you simply need to divide it by the indicated number.
So, for a coating of 1 layer, with a thickness of 1 to 10 cm, the required number of bags will be:
packaging 40 kg:
- 1 cm - 2.6;
- 2 cm - 1.8;
- 3 cm -0.9;
- 4 cm-0.6;
- 5 cm -0.45;
- 6 cm -0.4;
- 7 cm -0.36;
- 8 cm -0.3;
- 9 cm -0.25;
- 10 cm -0.22.
packaging 50 kg:
- 1 cm-3.1;
- 2 cm -2.25;
- 3 cm -1.12;
- 4 cm -0.75;
- 5 cm -0.56;
- 6 cm -0.5;
- 7 cm -0.45;
- 8 cm -0.37;
- 9 cm -0.32;
- 10 cm -0.28.
For example, the calculation for leveling walls S is 45 sq.m, layer 2 cm. Calculation: 45 / 1.8 = 25 units of 40 kg or 45 / 2.25 = 20 units of 50 kg. So for 5 cm screed without filler for 20 sq. you need: 40 kg TsPS - 44 packages, 50 kg - 36 packages.
Weight of a cubic meter of concrete of various brands
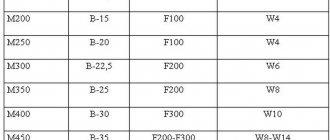
According to GOST, heavy concrete is divided into grades M100-M600. The compositions of the brands differ in the amount of water, sand, filler, binder and Portland cement - usually M400 or M500.
Specific gravity M100-M600
| Brand | 1 cube (kg/m³) |
| M100 | 2494 |
| M150 | 2461 |
| M200 | 2432 |
| M250 | 2348 |
| M300 | 2389 |
| M350 | 2502 |
| M400 | 2376 |
| M500 | 2298 |
As can be seen from the table, concrete of different grades weighs differently, however, so insignificantly that in most cases this difference can be neglected. Developers, when making calculations that use the specific gravity of heavy concrete (any brand), take the average value of 2400 kg/m³ per 1 cubic meter.
Popular
Paint for ceramic tiles
Porous ceramics: advantages of the material and application
Concrete sheet: technical characteristics and application
Classification by weight
The use of concrete mass has become quite widespread: from finishing purposes to the construction of dams. That is why the characteristics of the mixture are displayed by dividing them into classes and brands. This makes it possible to make precise choices for specific purposes. For example, B25 grade of concrete is much stronger than B10 and, naturally, its mass will be greater. There is also a division depending on mass. The table will help you see exactly the weight of concrete in 1m3, but more on that a little later, but for now let’s look at the division by “weight categories”:
| types | stamps | specific gravity, kg |
| especially light | M50 - M75 | up to 500 |
| lungs | M100 - M200 | 500-1800 |
| heavy | M200 – M400 | 1800-2500 |
| especially heavy | M 450 and above | 2500-3000 |
Weight directly depends on the density of all elements and can be in the range of 300-3000 kg.
Thermal insulation (extra light)
This material is made from cement and fillers, which when mixed, produces a structure with about 85% voids. Used for the manufacture of structures with special requirements for thermal conductivity (they are not able to withstand significant load-bearing loads). This category includes mixtures weighing up to 500 kg per cubic meter. In some cases, a plasticizer for concrete is used to increase their strength.
It is worth considering the low resistance of porous structures to frost. When installing them, it is necessary to install waterproofing protection.
Easy
This is how a solution with a mass in the range of 500-1800 kg is classified. It is mainly used to create special building blocks, the structure of which contains pores - they can be formed with the help of foaming agents or due to the use of cellular fillers (expanded clay, for example).
Only ready-mixed concrete can exactly match the specified weight and grade.
Heavy
Heavy concrete is one of the most common in construction. It is ideal for the construction of structural components that perform a load-bearing function. The weight of the cube in this case can be 1800-2500 kg - this figure depends entirely on the percentage of sand and coarse filler, as well as the density of the latter (even when using granite and gravel filler in the same quantity, the final weight of one cubic meter will be different).
Super heavy (extra heavy)
For its manufacture, metal fillers are used, which increases the weight characteristics to a maximum limit of 1 cubic meter - a little more than 3000 kg. Such mixtures are used to prevent the spread of radioactive radiation through walls.
The production of super-heavy mixtures involves the use of materials quite specific to construction, the cost of which will make the construction of a house quite expensive. That is why they are used exclusively in the construction of objects with increased requirements for radiation protection.