Example
To convert the specified parameters of an electrical device from kW to W, it is necessary to clarify the information from the markings on the product body, or obtain data from the equipment passport developed by the manufacturer and included in the product package.
If it is determined that the power rating of an electric kettle is 2.2 kW, this means that in watts this value will be 2.2 x 1000 = 2200 W.
In some situations, it is necessary to determine the value of the total power characteristics of household consuming devices. This need may arise in the following cases:
- to select a sufficient cable diameter when installing electrical wiring;
- when choosing safety devices that disconnect the network if the parameters exceed permissible values;
- to ensure the correct layout of household equipment in the house and proper wiring.
The calculation is performed by summing the above indicators for each of the devices. After this, the obtained value is compared with that indicated as a control value in the characteristics of the cable or safety devices, and is taken into account when locating the equipment.
For the calculation to be correct, all values must first be converted into common units of measurement from watts to kilowatts or vice versa, using the previously described method.
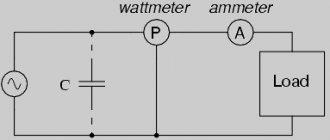
Wattmeter device
The power of household appliances simultaneously connected to the AC network should not exceed the permissible power of the network. Failure to comply with this condition can lead to overheating of the electrical wiring, failure of technical equipment, short circuit and fire in the room.
Power is determined using a special measuring device - a wattmeter. This device helps:
- control the operation of equipment,
- carry out testing of installations,
- keep track of energy consumption.
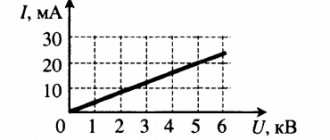
In a DC circuit, power is the product of current in amperes and voltage in volts, so no special equipment is required to determine this value.
In an alternating current circuit, power depends on three indicators: voltage, current and the phase shift between them. Therefore, wattmeters are used to determine power in AC networks.
Wattmeters are either analog or digital. Analog instruments can be recording or indicating. The indicator of the indicating wattmeter consists of a semicircular scale and a rotating arrow. The scale is calibrated according to power values in W. The operation of the device is based on the interaction of two inductors. The first, fixedly fixed, with a thick winding, a small number of turns and low resistance. This coil (1) is connected in series with the load (N). The second inductor is movable, with a large number of turns, made of thin copper conductor and high resistance. In the circuit, the coil (2) is connected in parallel to the load (H) together with an additional resistor (R) to prevent a short circuit between the inductances.
When taking measurements, the coils generate magnetic fields, the interaction of which leads to the formation of torque. The moving coil with the arrow deviates at a certain angle. The angle is equal to the product of current and voltage at the current time.
Wattmeter device diagram
Digital wattmeters determine reactive and active power. In addition, the digital screen of the device displays readings of voltage, current, and energy consumption per unit of time.
We advise you to study the Conditions of ResonanceThe operation of a digital wattmeter is based on a preliminary measurement of voltage and current. To do this, a current sensor is installed at the input of the device in series with the load, and a voltage sensor in parallel. The resulting instantaneous values are transmitted to the microcontroller, where the active and reactive components are calculated. The result is displayed on the display or attached external devices.
How many watts are there in a kilowatt?
Almost every person is familiar with the concept of electrical power. The passport of each electrical device must indicate the power it consumes. Even on an ordinary incandescent lamp, on a glass bulb, there is a mark: 40 W, 60 W, 100 W, etc. If you look at a washing machine or microwave oven, the figures are much higher - from 500 W to 2.5 kW.
The prefix “kilo”, as for other physical quantities, is used to indicate a multiple of a thousand - the numerical value of power, which is measured in kilowatts, must be multiplied by 1000 or the decimal point moved three digits to the right. Thus, we obtain an indicator of electrical power in watts.
Answering the question posed about how many watts are contained in a kilowatt, we can give a definite answer: one kilowatt equals 1000 watts. To consolidate and practically understand the translation process, consider several examples of recording electrical power:
- 0.75 kilowatts=750 W;
- 2.1 kilowatts=2100 W;
- 3.075 kilowatts=3075 watts.
Sometimes situations arise when you need to convert watts to kilowatts. Let us remember the relationship between these values: to translate, you need to move the decimal point three digits to the left or divide the value by 1000.
Examples:
- 2300 W = 2.3 kW;
- 50 W=0.05 kW;
- 249 W = 0.249 kW.
Total power in watts (kilowatts)
To correctly determine the cross-section of the electrical wiring cable and correctly select the rating of the network protective equipment, you need to calculate the total power of energy consumers. This value is obtained by adding the rated power of each consumer.
Important! Before adding up the consumer capacities, you need to convert them into the same unit of measurement: watt or kilowatt. Presumably the following consumers are connected to the network:
Presumably the following consumers are connected to the network:
- 5 lamps 100 W;
- 8 lamps 60 W;
- electric oven 2 kW;
- TV – 100 W;
- refrigerator – 0.3 kW;
- washing machine – 0.6 kW.
The power of lamps and TV is indicated in watts, and the power of ovens, refrigerators and washing machines is indicated in kilowatts. It is necessary to convert kilowatts to watts.
Considering how many watts there are in one kilowatt, we can write that the oven consumes 2 kW. Based on the fact that there are a thousand W in one kW, multiply 2 by 1000, you get 2000 W. The translation for a refrigerator is similar, the result is 300 W. Washing machine – 600 W.
Connection diagram for single-phase receivers
Next, add to 5 lamps 100 W each 8 lamps 60 W, 2000 W oven, 100 W TV, 300 W refrigerator, 600 W washing machine. You get a total figure of 500 W + 480 W + 2000 W + 100 W + 300 W + 600 W =3980 W = 3,980 kW. The result obtained is rounded up to give 4 kW.
Based on the resulting total value, the wire cross-section and automatic protective equipment are calculated.
Watt and kilowatt - what is it?
The watt is a measurement unit of power, as well as heat flux in physics, sound electrical energy flux, direct current power, active and apparent electric current power, radiation flux and ionizing radiation energy flux in the international measuring system. It is worth pointing out that this is a scalar measurement quantity, that is, measured and calculated.
We advise you to study Ohm's Law for alternating current
Description from the reference book
To make it convenient to use watts, the international system has adopted the use of prefixes that determine the decimal multiple of the original indicator. As a rule, kilowatt is used for it. Translated from Greek, the prefix kilo means thousand. The use of a prefix means an increase in the original value by 103 times.
Note! KWh is a non-systemic unit of measurement that shows when energy is produced or consumed and in what quantity. It also shows mechanical work done and heat
Used to measure household electrical energy consumption or measure electrical energy production in the energy sector.
What is being measured
Watt is a measurement unit of power, as well as heat flux, sound electric energy flux, direct current power, active and apparent electric current power, radiation flux and ionizing radiation energy flux in the international measuring system. It is worth pointing out that this is a scalar measuring quantity.
Convert watt to kW
To make it convenient to use watts, the international system has adopted the use of prefixes that determine the decimal multiple of the original indicator. Generally, kilowatt is used for watt. Translated from Greek, the prefix kilo means thousand. The use of a prefix means an increase in the original value by 103 times.
Kilowatt per hour is a non-systemic unit of measurement that shows when energy is produced or consumed and in what quantity. It also shows mechanical work done and heat. Used to measure household electrical energy consumption or to measure electrical energy production in the energy sector.
What is power data needed for? This is necessary to calculate the total instrument power and calculate the required wire cross-section, selecting a suitable machine that could withstand their load.
Note! Kilowatts are used to denote the power of many machines with units that surround a person in terms of everyday life and production. Electric stoves with kitchen appliances, household air conditioners, washing machines and vacuum cleaners are an incomplete list of electrical devices on which it is possible to see how the rated power in kilowatts is indicated. This applies to the internal combustion engine of modern cars. While kilowatts are used, power is often expressed in horsepower.
This is an off-system unit that has been created since the advent of the horse-drawn steam engine. To understand the relationship, you can convert kilowatts to horsepower using the following formula: 1 kilowatt = 1.36 horsepower.
You might be interested in what power is the 16a machine designed for?
Power consumption of lighting devices
Value watt-hour or kilowatt-hour
To take into account the consumption of electrical energy, a special device is installed at the entrance of the power cable into the room - an electric meter. Unlike electrical appliances, which are marked as W (W), the meter has a different abbreviation - kW⋅h (kWh), the full name of which is kilowatt-hour.
Counter
The power indicated on a household appliance is the amount of energy consumed in 1 hour. For example, a 2000 W oven for 2 hours of continuous operation, according to the meter readings, will consume 2000 * 2 = 4000 W = 4 kW.
In this way, the consumption of a household device is calculated over a period of continuous operation. If the consumer works intermittently, for example, a refrigerator, this value will be significantly less. Understanding how many watts household appliances consume in total, you can calculate the average consumption for a designated period of time. To calculate the amount to be paid for this period, the resulting value is multiplied by the cost of one kilowatt.
When calculating the volume of electricity consumed, concepts such as kilowatt-hour, watt-hour are used. This is the actual energy consumption of the device in watts or kW for a certain period of time in hours.
How is current measured?
Units of measurement of the main indicators of the electrical network: ampere, watt (kilowatt), volt. In this case, the current strength is measured in amperes and shows the speed of charge passing through the conductor over a certain period of time.
Instruments for measuring current strength
The current strength of the electrical network is measured by a special device - ammeter . The type of equipment depends on the network voltage (DC or AC). The data obtained is used to determine the maximum load on the wiring, as well as to calculate the rated and actual power of the electrical appliances used.
What is current (Ampere [A])
It is important for the user to calculate the rated current of the electrical network in advance. The choice of cross-section of the wiring cores, as well as the equipment of the safety circuit breaker, depends on this.
What is voltage (Volt [V])
The concept of “voltage” includes the energy required to move an electric charge over a certain distance in a specified period of time. This indicator is measured in volts.
What is power (Watt [W])
The power indicator determines the rate of energy consumption over a certain period of time. Power is measured in watts or kilowatts , but there is also the concept of kilowatt/hour , according to which all consumers are charged for the electricity actually used.
Typically, manufacturers indicate the power consumption of electrical appliances (watts, kilowatts) , it can be seen on the packaging or product data sheet. When connecting powerful equipment, it is also important to calculate a sufficient reserve of sockets or machines, the parameters of which are measured in amperes. To connect safely, it is important to understand the difference between these concepts and be able to quickly convert amps to watts and vice versa. Using the online calculator on our website, you can do this in a matter of seconds.
Where is the power indicated (W and kW)
Manufacturers of electrical consumers indicate the rated power for each product. In this case, the receiver itself is marked, or the data is entered into the technical documentation accompanying it.
For large household consumers, for example, a TV, dishwasher, kitchen hood, the nominal value in W or kW is applied to the rear or front panel and duplicated in the technical documentation.
Markings on the kitchen hood
Marking of incandescent lamps (40 W, 60 W, 100 W, 150 W, 500 W) is applied to the glass bulb and cardboard packaging. The same indicator for an iron, hair dryer, or heater is indicated on their body.
The difference between kilowatt and kilowatt hour
In electrical engineering, a quantity called a kilowatt-hour is determined by electric meters. Due to the similarity of names, kilowatt-hours are sometimes confused with kilowatts. In fact, these are different parameters.
KWh is used to determine the amount of electrical energy produced or consumed per unit of time. For example, a receiver with a flow rate of 1 kWh determines the amount of energy consumed by a 1 kW device over 1 hour.
Unlike a kilowatt-hour, a kilowatt is a unit of power that characterizes the intensity of electricity consumption.
How kW and kW∙h are related can be seen using the example of a TV (200 W). The estimated viewing time of the television program was 1 hour. This could mean that the TV used 200 watts during this period. Multiplying 200 W by 1 hour, we get 200 W * 1 hour = 200 Wh = 0.2 kWh.
We advise you to study Contactors and magnetic starters
At the beginning of the electrification era, electricity was used only for indoor lighting. Those using this service understood that a 100 W light bulb would generate exactly 1 kW in 10 hours. With the beginning of the use of kW⋅h when calculating energy consumption, people began to better understand what they had to pay for. He now has the opportunity to regulate spending by properly selecting lighting equipment.
Ratios watt and kW
Because kilowatts and watts are similar, users are often confused when using them in daily life. This is especially true for household electrical appliances. It is worth considering that they are two different measuring units that refer to different physical quantities. Watts and kilowatts measure power, which is the measurement of the rate of energy, as well as the transmission, conversion, and consumption of electricity.
Those quantities that have the prefix “hours” express the energy that was produced, transmitted, converted, consumed during a certain time. If the instrument power is constant, then the energy produced with the transmitted, converted and consumed energy is equal to the instrument power product for the period of operation of the electrical equipment.
For example, with a 100-watt lamp power and operation for one hour, the consumption and release of light with heat is 100 watts, multiplied by the outgoing energy, the release of light with heat will occur in 2.5 hours. The above will be valid at the moment the electrical energy is generated. Thus, electrical power is measured in megawatts, but the amount of electricity that will be supplied to consumers over time is equal to the power multiplication of the power station indicators by time and is expressed in kilowatts and hours.
Note! It is worth pointing out that today you can use a special online calculator, where you only need to substitute known scalar measuring quantities. The figure will be valid for electrical, thermal, mechanical and electromagnetic energy.
Ratio of watts to kilowatts
Watts to kilowatts
It is believed that 1 watt corresponds to the power required to do work (1 Joule) in 1 second.
The relationship between power (P), voltage (U) and current (I) is presented as a formula:
P = U ∙ I.
Knowing the voltage in the network and the power of the receiver, this formula is used to determine the current strength, select the wire cross-section and the rating of the power line protective equipment.
Electric discharge
Currently, to calculate how many watts per ampere or kV to convert to V, it is not necessary to do the calculations yourself. It is enough to type an online calculator into a search engine, for example, with a question about converting watts to amperes, and the address of the desired site will be given.
For convenience of calculations and notation, scientists introduced derivatives of W:
- Sub-multiple, less than Watts, used in medical equipment (for example, milliwatts, microwatts, nanowatts);
- Multiples greater than W are used in household electrical appliances (kilowatts) and in the energy field (for example, megawatts, gigawatts).
Converting these values from one to another is possible using an online converter.
The power of electrical appliances is expressed in watts and kW. For the convenience of calculations, it becomes necessary to reduce quantities to one number system. For example, watt needs to be converted to kW. How many watts are in a kilowatt? "Kilo" means that the number is a multiple of a thousand. It turns out that there are one thousand watts in one kW. To calculate how many kilowatts there are in a watt, you need to divide this number of watts by 1000.
An example of how to correctly convert W to kW:
- 1600 W = 1.6 kW;
- 40 W = 0.04 kW;
- 0.7 W = 0.0007 kW.
To find out how many kilowatts there will be in W, perform the opposite action - the value in kW is multiplied by 1000:
- 2.4 kW = 2400 W;
- 0.6 kW = 600 W;
- 11.8 kW = 11800 W.
Convert watts to kilowatts
not be difficult for you to convert watts to kilowatts if you remember that 1 kW = 1000 W. That is, you just need to divide the number of watts by 1000. If you need to convert kilowatts to watts, then, on the contrary, you need to multiply the number of kilowatts by 1000. For example, if you need to convert 20 kW to watts, then 20*1000 = 20000 W . Converting W to kW and back, as you can see, is very simple. If you have a decimal fraction, for example, 0.2 kW, then you just need to move the decimal point to the right by three characters: you get 200. When converting kW to W, the decimal point is shifted three characters to the left.
How to correctly convert these units
A watt is equal to a kilogram multiplied by square meters and divided by cubic seconds. The prefix kilo denotes multiplication by 1000. The same principle applies to power indicators, that is, 1 kW contains 1000 W and 1000 volts. This means that 1 unit = 0.001 subunits. That is, if you convert the power, then a 3 kW electrical appliance will be equal to 3000 W.
Conversion formula
In electricity
To simplify measurements in electricity, a subunit is used. You can find out how many watts are in a kilowatt and convert the units by multiplying watts by 103 and dividing by 1000. To carry out the reverse conversion, you need to multiply kW by 103 or multiply known indicators by 1000.
Quantities in electricity
Translation rules
One watt is defined as the power at which one joule of work is done per second. Thus, a watt is a derived measurement unit that is related to other units. A watt is equal to a kilogram multiplied by square meters and divided by cubic seconds.
In terms of other system units of measurement, a watt can be expressed as follows: in terms of a joule divided by seconds and multiplied by watts, and also in terms of a newton multiplied by meters and divided by seconds by watts. So a watt is equal to a volt multiplied by an ampere. In addition to the fact that power can be mechanical, it can also be thermal and electrical.
The prefix kilo denotes multiplication by 1000. The same principle applies in power indicators, that is, there are 1000 watts in 1 kilowatt, just as there are 1000 volts in 1 kilowatt. This means that 1 watt is 0.001 kW in reverse. That is, if you convert the power, then a 3 kW electrical appliance will be equal to 3000 watts.
You might be interested in: Features of differential current
If we calculate the above data, then the total power indicator of household electrical appliances will be equal to 6.385 kilowatts. This figure may be rounded up. Thanks to this amount, it is possible to calculate the wire cross-section and select the required protective automation. This way you can understand the consumption of electrical energy.
Otherwise, it will be almost impossible to find out and convert these electricity indicators. It is interesting that in new models of electricity meter, such information takes place about each connected device in the network.
Unit conversion rules