The well-being and comfort of modern society depends entirely on high-tech gadgets. People can no longer imagine life without “smart” devices. Microelectronics have consumed our lives at home and at work. The equipment operates solely on electricity. Such devices have a number of advantages, as well as disadvantages - sensitivity to electrical changes. voltage.
If in the company's office this problem can be eliminated by a staff of qualified employees, then at home you often have to rely solely on your own strength. When buying new equipment for your home, you need to take into account the technical characteristics of the device. The manufacturer indicates such information for buyers on a nameplate located on the back wall of the gadget.
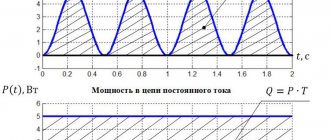
The power formula is the product of current and voltage. If you know this parameter, then the user gets a clear idea of how much electricity the device will consume and whether it will cause problems with power supply.
What is power in electricity: simply about the complex
Mechanical power as a physical quantity is equal to the ratio of work performed to a certain period of time. Since the concept of work is determined by the amount of energy expended, it is also possible to represent power as the rate of energy conversion.
Having analyzed the components of mechanical power, let’s consider what electrical power is made up of. Voltage is the work done to move one coulomb of electric charge, and current is the number of coulombs passing in one second. The product of voltage and current shows the total amount of work done in one second.
Electric current power
Having analyzed the resulting formula, we can conclude that the power indicator depends equally on current and voltage. That is, the same value can be obtained at low voltage and high current, or at high voltage and low current.
Taking advantage of the dependence of power on voltage and current, engineers have learned to transmit electricity over long distances by converting energy at step-down and step-up transformer substations.
Science divides electrical power into:
- active. It involves the conversion of power into thermal, mechanical and other types of energy. The indicator is expressed in Watts and calculated using the formula U*I;
- reactive. This value characterizes the electrical loads created in devices by fluctuations in the energy of the electromagnetic field. The indicator is expressed as reactive volt-amperes and is the product of voltage by force and shear angle.
To make it easier to understand the meaning of active and reactive power, let us turn to heating equipment, where electrical energy is converted into thermal energy.
What formula is used to calculate
Calculation of current strength by power and voltage in a DC network
To calculate the force I (current), the value U (voltage) must be divided by the value of resistance.
Current calculation by power and voltage:
I = U ÷ R
Measured in amperes.
For such a case, electrical P (active power) can be calculated as the product of the electrical force I by the value U.
Formula for calculating power by current and voltage:
P = U × I
All components in these two formulas are characteristic of direct electric current and are called active.
Based on these two formulas, we can also derive two more formulas by which we can recognize P:
P = I2 × R
P = U2 ÷ R
Single-phase loads
In single-phase alternating current networks, it is necessary to calculate separately for P and Q loads, then they must be added using vector calculus.
S = P + Q
In scalar form it will look like this:
S = √P2 + Q2
As a result, the calculation of P, Q, S looks like a right triangle. The two legs of this triangle represent the P and Q components, and the hypotenuse is their algebraic sum.
S is measured in volt-amperes (VA), Q is measured in volt-ampere-reactive (VAr), P is measured in watts (W).
Knowing the sizes of the legs for triangles, you can calculate the power factor (cos φ). How to do this is shown in the triangle image.
Calculation in a three-phase network
Alternating I (current) differs from constant in all respects, especially the presence of several phases. Calculation of P in a three-phase load is necessary to correctly determine the characteristics of the connected load. Three-phase networks are widely used due to ease of use and low material costs.
Three-phase circuits can be connected in two ways - star and delta. In all diagrams, the phases are designated by the symbols A, B, C. The neutral wire is designated by the symbol N.
When connected by a star, two types of U (voltage) are distinguished - phase and linear. Phase U is defined as the U between phase and neutral. Linear U is defined as U between two phases.
These two U are related by the relation:
UЛ = UФ × √3
Linear and phase electric currents when connected by a star are equal to each other: IЛ = IФ
Calculation form S for star connection:
S = SA + SB + SC = 3 × U × I
Active P:
P = 3 × Uph × Iph × cos φ
Reactive Q:
Q = √3 × Uph × Iph × sin φ
.
When connected by a triangle, phase and linear U are equal to each other: UЛ = UФ
Linear I when connected by a triangle is determined by the formula:
IL = IФ × √3
Formulas for the power of electric current when connected by a triangle:
- S = 3 × Sph = √3 × Uph × Iph;
- P = √3 × Uph × Iph × cosφ;
- Q = √3 × Uph × Iph × sinφ.
Average P in active load
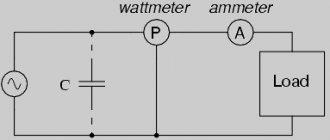
In electrical networks, P is measured using a special device - a wattmeter. Connection diagrams depend on the method of connecting the load.
With a symmetrical load, P is measured in one phase, and the result obtained is multiplied by three. In the case of an unbalanced load, three instruments will be required for measurement.
The P parameters of the electrical network or installation are important data for the electrical appliance. Data on P consumption of the active type are transmitted for a certain period of time, that is, the average consumed P for the calculated period of time is transmitted.
How to calculate electrical power at home
Theoretical electrical engineering considers indicators as instantaneous values that are recorded in a certain time period. If the instantaneous power of a constant network remains unchanged at any point in the chain and in all time intervals, then for a variable this indicator will always be different.
From here we get the formulas for calculating power (P):
- U*I;
- I2*R;
- U*I*cos(phi).
There are now online calculators on the Internet that will do the calculations and give you the result. The user only needs to substitute the values of the characteristics that are on the device nameplate.
How to measure electrical power at home
It is always necessary to know the power characteristics of household equipment. This is required to calculate the wiring cross-section, take into account electricity consumption or electrify the house. Before installation work begins, such information can only be obtained by adding up the power indicators of each individual device, adding a 10% margin.
A meter will help determine the consumed load at home. The device shows how many kilowatts were spent in one hour of equipment operation. And in order to ensure that the readings are correct, the apartment owner can check the accuracy of the device using electronic measuring instruments. This includes an ammeter, voltmeter or multimeter.
There are also wattmeters and varmeters that display measurement results in watts.
Wattmeter
While taking readings, leave only active loads such as light bulbs and heaters on. Next, measure the current voltage. At the end, check the meter readings with the resulting calculation results.
How to find out voltage by knowing current strength
To calculate the voltage, use the formulas:
U=P/I – direct current;
U=P/(I*cos(phi)) - single-phase network;
U=P/(1.73*I*cos(phi)) - three-phase network.
From the expression it can be seen that voltage is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to current.
How to calculate power knowing current and voltage
The power characteristics of electrical installations are calculated using the formula:
P=U*I – direct current;
P=U*I*cos(phi) – alternating current of a single-phase network.
P=1.73*U*I*cos(phi) - three-phase network.
The article provides simplified formulas for calculating the active power of the electrical network, which give approximate results.
To obtain accurate results, it is also necessary to take into account reactance and ordinary resistance, as well as losses.
Features of determining network power
In general, the electrical network is designed so that its operation does not require special knowledge. It is enough to follow some rules, the main one of which is to prevent overload.
You might be interested in this: 220 V socket power
Important! Failure to comply with the rules for using the electrical network can lead to failure and even fire.
It is important to note that the technical characteristics of the outlet and the household appliance differ from each other:
- In sockets, the maximum permissible alternating current is measured in Amperes: in the old housing stock of Russia it is 6 A, in Europe - 10 or 16 A;
- The power of connected devices is measured in Watts.
Information on an electrical appliance can be marked in different ways.
How to calculate the power of electricity? To calculate, you will need a formula:
P = U*I, where:
P - power,
U - voltage in Volts,
I is the current strength in Amperes.
The voltage of a working outlet is 220-230 Volts; the current can be measured with a multimeter.
To determine the current strength in the outlet, you should use a multimeter
Interesting info on the topic
A three-phase power supply circuit is used in production. The total voltage of such a network is 380 V. Also, such wiring is installed in multi-story buildings, and then distributed to apartments. But there is one nuance that affects the final voltage in the network - connecting the voltage core results in 220 V. Three-phase, unlike single-phase, does not cause distortions when connecting power equipment, since the load is distributed in the panel. But to connect a three-phase network to a private house, special permission is required, so a scheme with two cores, one of which is zero, is widespread.
Current power
Having understood the concept of mechanical power, let's move on to considering electrical power (power of electric current). As you should know, U is the work done when moving one coulomb, and the current I is the number of coulombs passing in 1 second. Therefore, the product of current and voltage shows the total work done in 1 second, that is, electrical power or electric current power.
Active electrical power (this is power that is irrevocably converted into other types of energy - thermal, light, mechanical, etc.) has its own unit of measurement - W (Watt). It is equal to 1 volt times 1 ampere. In everyday life and in production, it is more convenient to measure power in kW (kilowatts, 1 kW = 1000 W). Power plants already use larger units - mW (megawatts, 1 mW = 1000 kW = 1,000,000 W).
It will be interesting➡ What is resonance, what are its benefits and dangers
Reactive electrical power is a quantity that characterizes this type of electrical load that is created in devices (electrical equipment) by energy fluctuations (inductive and capacitive) of the electromagnetic field. For conventional alternating current, it is equal to the product of the operating current I and the voltage drop U by the sine of the phase angle between them: Q = U*I*sin(angle). Reactive power has its own unit of measurement called VAR (volt-ampere reactive). Denoted by the letter "Q".
In simple language, active and reactive electrical power can be expressed using an example as follows: we have an electrical device that has heating elements and an electric motor. Heating elements are usually made of high resistance material. When an electric current passes through the heating element's spiral, the electrical energy is completely converted into heat. This example is typical of active electrical power.
The electric motor of this device has a copper winding inside. It represents inductance. And as we know, inductance has the effect of self-induction, and this contributes to the partial return of electricity back to the network. This energy has some offset in current and voltage values, which causes a negative impact on the electrical grid (further overloading it).
Current power calculation formulas
Capacitance (capacitors) also has similar abilities. It is capable of accumulating charge and releasing it back. The difference between capacitance and inductance lies in the opposite displacement of the values of current and voltage relative to each other. This energy of capacitance and inductance (phase-shifted relative to the value of the supply network) will, in fact, be reactive electrical power.
We will talk in more detail about the properties of reactive power in the corresponding article, and at the end of this topic I would like to say about the mutual influence of inductance and capacitance. Since both inductance and capacitance have the ability to phase shift, but each of them does this with the opposite effect, this property is used to compensate for reactive power (increasing the efficiency of power supply). This is where I will conclude the topic, electrical power, electric current power.