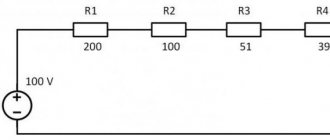
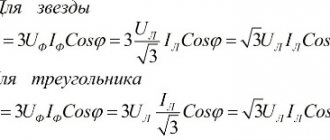I want to say right away that there is no fuss about power here, and only the necessary information. In order to better understand what power, mechanical power, electrical power is, I strongly recommend reading everything from the category Physical foundations of mechanics
power is a scalar physical quantity, generally equal to the rate of change, transformation, transmission or consumption of system energy. In a narrower sense, power is equal to the ratio of the work performed in a certain period of time to this period of time.
The quantity characterizing the speed of work is called power. Power is numerically equal to the ratio to the period of time during which it is performed.
or in general
,
Substituting the value we get
| (4.5) |
Units
The International System of Units (SI) unit of power is the watt (W), equal to one joule per second (J/s). In theoretical physics and astrophysics, the erg per second (erg/s) is often used as a unit for power.
Another common, but now outdated, unit of power measurement is horsepower.
In its recommendations, the International Organization of Legal Metrology (OIML) lists horsepower as a unit of measurement “which should be withdrawn from use as soon as possible where it is currently used and which should not be introduced if it is not in use.” Relationships between power units
| Units | W | kW | MW | kgf m/s | erg/s | l. s. (met.) | l. s. (eng.) |
| 1 watt | 1 | 10−3 | 10−6 | 0,102 | 107 | 1,36⋅10−3 | 1,34⋅10−3 |
| 1 kilowatt | 103 | 1 | 10−3 | 102 | 1010 | 1,36 | 1,34 |
| 1 megawatt | 106 | 103 | 1 | 102⋅103 | 1013 | 1,36⋅103 | 1,34⋅103 |
| 1 kilogram-force meter per second | 9,81 | 9,81⋅10−3 | 9,81⋅10−6 | 1 | 9,81⋅107 | 1,33⋅10−2 | 1,31⋅10−2 |
| 1 erg per second | 10−7 | 10−10 | 10−13 | 1,02⋅10−8 | 1 | 1,36⋅10−10 | 1,34⋅10−10 |
| 1 horsepower (metric) | 735,5 | 735,5⋅10−3 | 735,5⋅10−6 | 75 | 7,355⋅109 | 1 | 0,9863 |
| 1 horsepower (English) | 745,7 | 745,7⋅10−3 | 745,7⋅10−6 | 76,04 | 7,457⋅109 | 1,014 | 1 |
System units
Let's give a definition: in physics, power is understood as a quantity that characterizes the performance (speed of energy transfer or conversion) of mechanisms and devices. It is connected with another concept - work.
In mechanics, power is found using the formula:
$P = frac {dA}{dt} = F cdot v cdot cos alpha$, from which it follows that power is understood as work, measured in Joules, divided by the time of its execution in seconds.
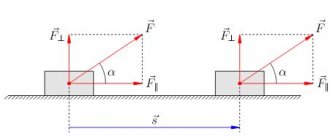
Rice. 1. Work on moving cargo.
Or:
$P = frac {dW}{dt}$, i.e. as the rate of change of energy of the system.
In electrodynamics, power has its own formula:
$P = U cdot I$
Thus, the unit of power is Joules divided by second (Volts times Amps), or Watts. The last name was given in honor of the engineer James Watt, who created the steam engine. Watt is the SI unit of power.
In industry and on devices, larger units are often used - kilowatts, megawatts, etc. They are obtained by adding standard decimal prefixes. Accordingly, 1 kW = 1000 W, 1 MW = 1,000,000 W.
Rice. 2. Power on an electrical appliance.
In the CGS system (centimeter, gram, second), which has become widespread in electrodynamics, power is usually measured in ergs per second. $ 1 : erg = 10^{-7} : J $, then $ 1 : Watt = 10^7 : frac {erg}{s} $
In the MKGSS system (meter, kilogram-force, second), power is measured in kilogram-force multiplied by meter and divided by s. $1 : kgf = 10 : N$, and then $1 : Watt = 0.1 : frac {kgf cdot m}{s}$
electric power
Electrical power is a physical quantity that characterizes the speed of transmission or transformation of electrical energy.
Instantaneous electrical power of a section of an electrical circuit:
where is the instantaneous current through a section of the circuit;
- instantaneous stress in this area.
When studying AC networks, in addition to instantaneous power corresponding to the general physical definition, the following concepts are also introduced:
- active power equal to the average value of instantaneous power over the period, instantaneous active power:
- reactive power, which corresponds to energy circulating without dissipation from source to consumer and back, instantaneous reactive power:
at
at
- total power, calculated as the product of the effective values of current and voltage without taking into account phase shift. instantaneous full power:
where is the current amplitude;
— voltage amplitude;
- the angle between the initial voltage angle and the initial current angle -
— angular velocity;
- time.
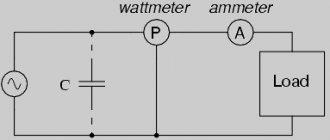
Instruments for measuring electrical power and radiation power[edit | edit code]
Analog dial wattmeter
- Wattmeters (including varmeters) are measuring instruments designed to determine the power of electric current or electromagnetic radiation.
Based on their purpose and frequency range, wattmeters can be divided into three categories - low-frequency (and direct current), radio frequency and optical.
Radio wattmeters are divided into two types according to their intended purpose: transmitted power, connected to the break of the transmission line, and absorbed power, connected to the end of the line as a matched load. Depending on the method of functional transformation of measurement information and its output to the operator, wattmeters can be analog (displaying and recording) and digital.
What is the total power?
The theory of complex numbers will allow you to thoroughly understand the concepts of total, active, and reactive powers. Accordingly, the coefficient can be easily determined. This theory represents a whole triangle of active, reactive and total powers.
Calculation of active performance of a three-phase circuit
Active Performance
The unit of measurement for the active power of a three-phase electrical circuit is the watt (Russian designation: W, kilowatt - kW; international: watt -W, kilowatt - kW).
You may be interested in: Features of tantalum capacitors
Important! The average instantaneous performance, which is denoted by the letter T, is active power.
Where non-sinusoidal current predominates, the equality of the electrical capacitance corresponds to the average powers of the individual elements. An active quantity is, first of all, the rate of irreversible conversion of electrical energy into other types of energy. These include thermal and electromagnetic. As a rule, active performance is expressed in terms of current, voltage and the active component of the circuit resistance r or its conductance g.
Defining any electrical circuit (sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal current), the active output of the entire circuit will be equal to the sum of the active powers of the individual elements. It is important to note that for three-phase circuits, electrical performance is defined as the sum of the performance of the individual phases. With the total capacity S, the active one is related to the ratio of the total and active output.
Unfortunately, the consumer of electricity has to pay not for active (useful) power, but for full power. The difference in power at the input and output of the uninterruptible power supply system was 58 kVA! It is necessary to take into account that the tariff for electricity consumption with low cosj (Pf) is significantly higher. Thus, the use of an uninterruptible power supply system made it possible not only to protect equipment from voltage failures and sags, but also to obtain significant energy savings.
Considering long lines (analysis of electromagnetic processes in a transmission line, the length of which is comparable to the length of the electromagnetic wave), a complete analogue of active power is the transmitted capacity, which is defined as the difference between the incident and reflected capacity.
Determination of a reactive quantity using an example
Reactive capacity
The question often arises about what reactive power is - a quantity that characterizes the load that is created in electrical systems by fluctuations in the energy of the electromagnetic field in a circuit where sinusoidal alternating current predominates.
Reactive capacitance represents energy that is transferred from the source to the reactive elements of the device. These include: inductance, capacitor, motor windings. After which this capacitance, together with the elements, moves to the source during one oscillation period.
It is important to emphasize that the sin φ indicator for a φ value from 0 to plus 90° is a positive value. This value, which is denoted as sin φ for φ from 0 to minus 90°, is a negative value. Taking into account the formula by which reactive performance is determined, it is possible to obtain both a positive value (for a load with an active-inductive nature) and a negative value (for a load with an active-capacitive nature). All this is characterized by the fact that reactive recoil does not occur when electric current is supplied.
Some electrical systems have positive reactive capacitance. It is already said here that there is a load of an active-inductive nature. When negative performance is determined, a load with an active-capacitive nature is produced here. This factor is characterized by the fact that many power-consuming devices, which are connected using a transformer, are active-inductive.
You might be interested in this: Features of watt and volt
Electric power stations are equipped with synchronous generators. They can consume and produce reactive capacity. In addition, the magnitude of the electric excitation current that enters the generator rotor windings is determined. Thanks to the distinctive features of a synchronous electric machine, you can freely adjust the given network voltage level. To reduce loads, as well as increase the performance coefficient of electrical systems, specialists compensate for reactive capacitance.
Note! If you use modern electrical measuring transducers on microprocessor technology, then an accurate assessment of the energy indicator from the inductive and load capacitance to the alternating voltage source is made.
Determination of full performance
Full capacity
In order to determine which systems have full performance, it is necessary to study the features of this value. Total power is a physical quantity equal to the product of the operating elements of the periodic electric current I in the circuit and the voltage U at its terminals. To determine the ratio of total output with active and reactive capacitances, you need to decipher the values that are calculated using the formula. For example, the performance ratio, where P is active, Q is the reactive capacity (if the load is inductive, Q"0, and if the load is capacitive, it is designated Q"0).
Important! The full capacity describes the load imposed on the elements of the supply network (wires, distribution boards, transformers, power lines). After all, all this load depends on the energy consumed, and not on the energy consumed by the user. Based on these results, the total power of a transformer or switchboard is measured in volt-amperes rather than in watts.
What unit is capacity measured by?
see also
- Power density
- Active power
- Reactive power
- Luminosity
- Energy
- Explosive power
- Sound power
- Amplifier
I wrote an article about power especially for you. If you would like to contribute to the development of theory and practice, you can write a comment or article by sending it to my email in the contacts section. By doing this you will help other readers, because this is what you want to do? I hope that now you understand what power, mechanical power, electrical power are and what all this is needed for, and if you don’t understand, or if you have any comments, then don’t hesitate to write or ask in the comments, I will be happy to answer. In order to gain a deeper understanding, I strongly recommend studying all the information from the category Physical foundations of mechanics
How to calculate correctly
Active power, how to make the correct calculation?
The power of the electric current affects how quickly the device can complete the job. For example, an expensive heater with twice the power will heat a room faster than two cheap ones with half the power. It turns out that it is more profitable to buy a unit with more power in order to heat a cold room faster. But, at the same time, such a unit will consume significantly more energy than its cheaper counterpart.
The power consumption of all appliances in the house is also taken into account when selecting wiring for installation in the house. If you do not take this into account and subsequently connect too many devices to the network, this will cause network overload. The wiring will not be able to withstand the power of the electric current of all devices, which will lead to melting of the insulation, short circuit and self-ignition of the wiring. As a result, a fire may start, which can lead to irreparable consequences.
You might be interested Features of insulating tape
Single-phase sinusoidal current in electrical circuits is calculated by the formula P = U x I x cos φ, where υ and Ι. Their designation is encrypted as follows: the root mean square value of voltage and current, and φ is the phase angle between them.
For non-sinusoidal current circuits, the electrical capacitance is equal to the square root of the sum of the squares of the active and reactive performance. Active performance is characterized by the speed of the irreversible process of converting electrical energy into other types of energy. This capacitance can be calculated through the current, voltage and active component of the circuit resistance r or its conductivity g using the formula P = I(2) xr = U(2) x g.
Reactive Power
It should be noted that:
- The resistor consumes active power and releases it in the form of heat and light.
- inductance consumes reactive power and releases it in the form of a magnetic field.
- The capacitor consumes reactive power and releases it in the form of an electric field.
In any electrical circuit of both sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal current, the active capacity of the entire circuit is equal to the sum of the active powers of the individual parts of the circuit; for three-phase circuits, the electrical capacity is defined as the sum of the throughput of the individual phases. With the total performance S, the active one is related by the relation P = S x cos φ.
In the theory of long lines (the analysis of electromagnetic processes in a transmission line, the length of which is comparable to the length of the electromagnetic wave), the complete analogue of active power is transmitted power, which is defined as the difference between the incident power and the reflected performance.
How to find reactive apparent power through active power? This performance, which characterizes the loads created in electrical devices by fluctuations in the energy of the electromagnetic field in a sinusoidal alternating current circuit, is equal to the product of the rms values of voltage U and current I, multiplied by the sine of the phase angle φ between them: Q = U x I x sin φ (if the current lags behind the voltage, the phase shift is considered positive, if it is ahead, it is negative).
Reactive quantity designation
Mechanical power
If a force acts on a moving body, then this force does work. Power in this case is equal to the scalar product of the force vector and the velocity vector with which the body moves:
where F
- force,
v
- speed, \alpha - angle between the vector of speed and force.
A special case of power during rotational motion:
M
- moment of force, \mathbf \omega - angular velocity, \pi - number,
n
- rotation frequency (rpm, rpm).
Submultiples and multiples
If the power is too large or, conversely, small, then using the usual watt as a unit of measurement will be inconvenient. In this case, multiples and submultiples will come to the rescue. If we talk about only one light bulb and for short periods of time, then the power will not be very large. For example, in an hour such a lighting device can generate about 100 joules of energy.
But when you need to determine the power of not one, but several such light bulbs (tens, hundreds, thousands), and not in one hour, but, for example, in a month or a year, then the number will turn out to be cumbersome. It is advisable to use not watts, but their multiple designations - kilowatts (kW), megawatts (MW), gigawatts (GW).
You might be interested in this Classification of overhead and underground power lines and their purpose
The meaning of multiples is easily determined by the prefixes, which are used in the same way as with most other units. The prefix “kilo” indicates 1000 units, “mega” indicates a million, and “giga” indicates a billion.
Most often in practice kilowatts are used. In one such multiple unit there are a thousand watts. The same applies to submultiples, which are used in cases where it is necessary to indicate low power, which is tens, hundreds, thousands and millions of times less than 1 W. For example:
- a tenth of a vata is a decivat;
- hundredth part - centiwatt;
- thousandth - milliwatt.
Some medical devices use microwatts as a unit of measurement. Each such unit is a million times smaller than a watt.
Relationship between quantities
To better understand the purpose of this unit, you should have an idea of what power is. Many people think it's just power. However, in physics these are completely different quantities that have almost nothing to do with each other. To put it as briefly as possible, ignoring some minor nuances, power is the rate at which an object consumes energy.
You might be interested in: Electrician safety precautions when working with electricity
For example, a light bulb in a lighting fixture may glow brightly or dimly. It all depends on the speed at which it consumes electrical energy. If it burns brightly, it means energy is being consumed quickly. When the light coming from a lamp is dim, it consumes energy at a low rate. Even simpler, you can say this:
- if the lamp glows brightly, it means its power is high;
- if its light is dim, it means it has little power.
The same applies to any other devices powered by electricity. But when they talk about power, they don’t always mean electrical appliances or some other objects related to electricity.
For example, if you take a moving car, it has a certain force. The faster the energy generated by the fuel in the gas tank is consumed, the more powerful the car. True, motorists measure the power of their “iron horses” in other units called horsepower. However, this does not mean that traditional watts are not applicable for this case. One unit can easily be converted to another, knowing that one horsepower is approximately 735 watts. There are three types of power:
- Electric. This is what they mean when they talk about light bulbs or other electrical appliances.
- Mechanical. The “horsepower” of a car falls into this category.
- Thermal. How much thermal power a particular object has can be judged by its temperature.
Power is the rate at which energy is consumed. Trying to understand what 1 watt is equal to, what energy and for how long an object must be used so that it can be said that its power is equal to one watt, physicists derived such a quantity as power based on other simple quantities - time and energy. They took their basic units of measurement and agreed that if a physical body receives or produces 1 joule of energy in 1 second, then it has a power of 1 watt.
You may be interested in How to give first aid in case of electric shock
This simple definition is based on the formula: N=A/t. The designation of the signs here is as follows:
- N is the designation for power;
- A in physics traditionally denotes work, which is measured in the same units as energy;
- t is a symbol for time.
If it is necessary to determine the mechanical value, then another formula based on other values can be used for this purpose: N=FV. Simply put, you need to multiply force by speed.
How to measure power of different types
Measurement of different power types occurs according to formulas derived from the end of the last century and the century before last. Each variety has its own exact algebraic rule. So, you can measure the mechanical one using the first formula, and the electrical one using the second. As for the hydraulic one, it can be calculated using the third algebraic rule.
Measuring using formulas
Mechanical
Mechanical power is the scalar form of the product of the force vector and the speed vector at which some object is moving. Based on the formula for calculating this indicator, in order to find it, you need to know the indicator of the force vector with the speed vector, and the last of them is equal to the magnitude of the force multiplied by the magnitude of the velocity and the vector angle of the velocity with the force.
Regarding the calculation of a body that performs rotational movements, it can be noted that you need to have an idea of the indicator of the moment of force with angular velocity.
You might be interested in the principle of operation of a thyristor, purpose and connection diagram
Additional Information! If this data is unknown in the problem, you can multiply the double number Pi by the rotation speed per minute at the moment of force, and then divide the obtained information by 60. In this way, calculations are made in mechanics if you need to understand what force an engine or other power unit has.
Electric
Electrical power is a quantity that shows the speed or transformation at which electrical energy moves. To study the instantaneous electrical power characteristic in a certain section of the circuit, it is necessary to know the value of the current and voltage of the instantaneous current and multiply these values.
To understand how much the active, total, reactive or instantaneous reactive power indicator is, you need to know the exact numbers of current amplitude, voltage amplitude, angle of current with voltage, as well as angular velocity and time, since all existing physical formulas are reduced to these parameters. The formulas also use the sine, cosine of the angle and the value 1/2.
Electric power concept
Hydraulic
The hydraulic power indicator in a hydraulic machine or hydraulic cylinder is the product of the machine pressure drop and the liquid flow rate. Typically this is the basic formulation taken from the only existing formula for the calculation.
Note! More algebraic and engineering rules can be found in the applied science of the movement of liquids and gases, namely hydraulics.
Direct and alternating current
As for direct and alternating current power, they are most often classified as the electrical variety. There is no specific concept for the two varieties, but they can be calculated based on existing algebraic settings. Thus, direct current power is the product of current and constant voltage, or twice the current and electrical resistance, which, in turn, is calculated by dividing twice the voltage by the usual resistance.
As for alternating current, this is the product of the current strength with the voltage and the cosine of the phase shift. In this case, only the active and reactive varieties can be easily counted. You can find out the full power value through the vector dependence of these indicators and area.
To measure these indicators, you can use both the above instruments and a phase meter. This device is used to calculate the reactive variety according to the state standard.
You might be interested in Soldering hair dryer
Concept of variable current power
In general, power is a quantity whose main purpose is to show the strength of a particular device and, in many cases, the speed of activity interacting with it. It can be mechanical, electrical, hydraulic and for direct current and alternating current. Measured according to the international system in watts and kilowatts. The instruments for calculating it are a voltmeter and a wattmeter. The basic formulas for independent calculations are listed above.
Formulas for measurement
Power is a quantity that is directly related to other indicators. Thus, it is directly related to time, force, speed, force vector and speed, force and speed modulus, torque and rotation frequency. Often, in formulas when calculating the electrical power type, the number Pi, the resistance indicator, instantaneous current with voltage in a specific section of the electrical network, active, total and reactive power are also used. A direct participant in the calculation is the amplitude with angular velocity and the initial current strength with voltage.
You may be interested in this Features of the electricity transmission network
In the calculations of the hydraulic power type, pressure and fluid flow take part. Often the number of engine revolutions for a specific period of time is taken into account.
Additional Information! To calculate thrust, efficiency with other operating parameters of the device, temperature, friction force and conductive resistance with reactive loads are studied.
Basic formulas for measurement