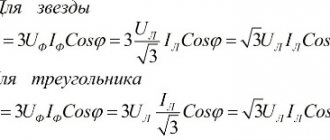Watts to amps or vice versa
Ampere is a unit of current, and watt is a unit of power (thermal, mechanical or electrical). Due to the fact that the operation of electrical appliances is closely related to both concepts and quantities, they are expressed in certain ratios to each other. However, this does not mean that you can directly convert watts to amperes or vice versa. There is no unambiguous, direct coefficient by which one could multiply or divide the existing number. Some amateur electricians do not understand this and are indecisive, so delve into it and figure it out further , gentlemen. In this case, it is customary to express some indicators in terms of others. To understand how this happens, let's look at how power and current relate to each other in various electrical networks.
Errors when calculating V•A
The ratios of volt amperes and watts for certain types of electrical appliances and devices, for example, light bulbs, are identical. But when talking about computers, watts and V•A will be different, but V•A will always be greater than or equal to watts. The gap is related to power factor (PF), which varies among devices. If you do not take it into account, then when selecting equipment elements an error will be made and they will not fit the main device.
If we consider the choice of a UPS for a personal computer, and on the passport data the rating is indicated in voltamper, this will make it difficult to select a rating in W. When there are no exact indicators of P, do the following - the load data indicated on the nameplate is taken equal to 60% of the V•A indicator of the UPS.
You might be interested in why they install RCDs
Online calculator
Additional Information. In order to more accurately determine the data, you can use an online calculator. Some websites provide the user with the required P if they click on the device type, such as TV or desktop. These sites often show graphical charts that make it easy to measure the V•A of various appliances, from refrigerators to computers.
It can be concluded that V•A is an important characteristic for modern electrical devices and equipment. If this indicator is not taken into account when purchasing electrical devices, they will operate in overload mode, which will lead to their premature failure.
How to measure power in volt-amps
Before you convert volt-ampere (V•A) into amplifiers, you need to understand what these measurements are. The current-voltage characteristic is an apparent measure of power, while the ampere is a measure of current.
Volt-ampere characteristics
So to convert between them you need to use the formula:
Power = Voltage × Current Using the P formula as a starting point and modifying it, you can convert power to V•A: I (A) = power (V•A) : voltage (V) For example, you need to calculate amplifiers for a single-phase electrical circuit with P = 1800 V•A at 120 volts. I (A) = 1800 V•A : 120 volts I (A) = 15 A
Thus, a circuit with 1800 VA apparent power at 120 volts has an I rating of 15 amps.
Converting VA to current for a three-phase electrical circuit is slightly different. For the calculation, a modified three-phase formula is used.
I (A) = Power (V•A) : (√3 × Voltage (V))
For a three-phase electrical circuit, I in amperes is equal to the power in volt-amps divided by the square root of three.
Reactive power in VAR
For example, you need to find amplifiers for a three-phase electrical circuit with P = 33,255 V at a voltage of 480 V.
I (A) = 33,255 V•A : (√3 × 480 V) I (A) = 33,255 V•A : 831.38 VI (A) = 40 A It can be seen that a circuit with an apparent power of 33,255 V •A at 480 V will have a nominal I = 40 A.
You may be interested in this Features of power measurement
Instructions for converting amperes to watts (kilowatts)
At first glance, converting amperes to watts seems like a simple task, but you start studying the subject and realize that not everything is so simple. But once you start doing this, you will realize that everything again becomes simple and understandable.
To carry out this simple operation it is necessary (this is, of course, ideally, so to speak according to the textbook) the presence of:
- tester;
- electrical reference book;
- current clamps;
- calculator.
Procedure (it is worth remembering that the mechanism for alternating and direct current is different, in our case we are talking about an electrician in a house where alternating current is used):
- Find out the operating network voltage using a tester.
- On an alternating current network, measure the current using a current clamp (there are also current clamps for direct current).
- For networks with single-phase alternating voltage, you need to multiply the U value by the current strength and power factor. The result of the product is the power consumption of the device in watts.
- With three-phase alternating voltage. It is necessary to multiply the power factor by the product of the current and voltage of each phase. The sum of the obtained values will be equal to the power of the electrical installation. When the load is distributed symmetrically across phases, the active power is calculated by multiplying the phase voltage and current by triple the power factor.
Based on the current flowing through the wiring, it is necessary to select the cable taking into account the cross-section. Wires that are too thin will heat up when overloaded, which can, at best, lead to their failure, and at worst, a fire. Copper wires can withstand a significantly greater load than aluminum wires, but this is not a reason to put the maximum load on them.
Please pay due attention to safety precautions. Electrical work may not be very difficult, but it is extremely responsible and potentially dangerous. So once again carefully read the highlighted text above, and after that, welcome to reviews and comments.
How many watts are in an ampere, how to convert amperes to watts and kilowatts
Not every housewife will immediately figure out how to convert amps into watts or kilowatts, or vice versa - watts and kilowatts into amperes.
Why might this be needed? For example, the following numbers are indicated on the socket or plug: “220V 6A” - a marking that reflects the maximum permissible power of the connected load.
What does it mean? What is the maximum power of a network device that can be plugged into such an outlet or used with this plug?
To get the power value, just multiply these two numbers: 220 * 6 = 1320 watts - the maximum power for a given plug or socket. For example, an iron with steam can only be used at two, and an oil heater can only be used at half power.
What is current strength:
Converting watts to amperes
Or the case when power in watts needs to be converted into amperes. This is the problem faced, for example, by a person who decides to choose a circuit breaker for a water heater.
On the water heater it is written, for example, “2500 W” - this is the rated power at a network of 220 volts. Therefore, to get the maximum amps of the water heater, we divide the rated power by the rated voltage, and we get: 2500/220 = 11.36 amps.
So, you can choose a 16 amp machine. A 10-amp circuit breaker will clearly not be enough, and a 16-amp circuit breaker will work as soon as the current exceeds the safe value. Thus, to get amperes, you need to divide the watts by the supply volts - divide the power by the voltage I = P/U (volts in a household network 220-230).
How many amperes are in a kilowatt and how many kilowatts are in an ampere
Since there are 1000 watts in one kilowatt, then for a mains voltage of 220 volts we can assume that there are 4.54 amperes in one kilowatt, because I = P/U = 1000/220 = 4.54 amperes.
The opposite statement is also true for the network: in one ampere there are 0.22 kW, because P = I*U = 1*220 = 220 W = 0.22 kW.
For approximate calculations, it can be taken into account that with a single-phase load, the rated current I ≈ 4.5P, where P is the power consumption in kilowatts. For example, with P = 5 kW, I = 4.5 x 5 = 22.5 A.
What to do if the network is three-phase
To find the total power, multiply the line voltage, current, and multiply by √3. We have: P = 380*0.83*1.732 = 546 watts. To find amperes, it is enough to divide the power of the device in a three-phase network by the value of the line voltage and by the root of 3, that is, use the formula: I = P/(√3*U).
- Conclusion
- Knowing that the power in a single-phase network is equal to P = I*U, and the voltage in the network is 220 volts, it will not be difficult for anyone to calculate the appropriate power for a particular current value.
- Knowing the inverse formula that the current is equal to I = P/U, and the voltage in the network is 220 volts, everyone can easily find amperes for their device, knowing its rated power when operating from the network.
Calculations are carried out similarly for a three-phase network, only a coefficient of 1.732 is added (the root of three is √3). Well, a convenient rule for network single-phase devices: “there are 4.54 amperes in one kilowatt, and 220 watts or 0.22 kW in one ampere” - this is a direct consequence of the above formulas for a network voltage of 220 volts.