Let's start the calculations
Since you cannot plug an LED strip into a standard outlet, to connect it, as we have already found out, you should use a power supply with a specific power.
The size of this parameter can be calculated mathematically. But to do this you need to know how it is done. Today, LED strips are produced with voltages of 12 and 24 volts. To calculate the power, you need to know the type of tape used (for example, SMD 5050 RGB tape) and how many LEDs are placed on one meter of its length. For this type of tape, 30 LEDs are placed on one meter. To find out this value for other models, you need to use the following table.
Table. Number of LED strips per meter
The power calculation itself consists of the following steps:
- First, we find out how much power one meter of lighting fixture will consume. This parameter is already given in the table;
- Next you need to calculate how much power the whole tape will consume. To do this, you simply need to multiply the total length of the backlight by the power of one meter. For example, in our case, it is necessary to multiply 10 meters (we will take this length for ease of calculation) by 7.2 watts. The result is 72 watts.
In fact, this is the whole calculation. You just need to perform the last action, which, if done incorrectly, can nullify all your mathematical calculations. The required power for the power supply to connect an LED strip to it should include a reserve that will protect the device from possible overloads. Typically, the reserve is at least 20% of the total power of the lighting installation, i.e. in our case from 72 watts. Some recommend taking as much as 30% to be sure.
Note! These 23 or 30% of the reserve, for ease of calculation, can be represented as a safety factor. For 20% it will be 1.20, for 25% - 1.25, and for 30% - 1.30
If we take a margin of 30%, then the final figure will no longer be 72 watts, but 93.4 watts. It is this power (rounding of the value is allowed) that you should buy a power supply of the type that you like best in terms of its technical characteristics or operating features. Remember that correctly calculated converter power is the key to long-term and high-quality operation of the backlight connected to it. Therefore, mathematical calculations in this situation must be approached very responsibly if you want to go to the store or market for a new power supply as little as possible.
Types of diode strips and what their power depends on
LED strips differ in the number of semiconductor LED crystals, which are placed on 1 linear meter. Standard strips are produced with the number of diodes: 30, 60, 120 and 240 per 1 linear meter. The more diodes, the greater the power of the diode strip. It is best to calculate the power consumed by the entire tape based on the energy consumed per 1 meter of its length. Below is a table with the corresponding values:
Table 1. Power of SMD 3528 diode strip in terms of 1 linear meter.
| Total diodes per linear meter | Diode strip power per 1 meter |
| 30 | 2.4 W |
| 60 | 4.8 W |
| 120 | 9.6 W |
| 240 | 19.2 W |
As can be seen from the table, the power of the tape is small, but the conductors of the electrical circuit also have a small cross-section, smaller than that of traditional wiring. If you add another section of tape to the existing section, then even more current will flow through the very thin wires. It’s easy to imagine the consequences: first overheating, then melting of the insulation and fire.
In addition, it is important to choose the right power supply with the required power, adding 25% to it as a reserve. Therefore, you should always determine the energy consumption of the tape based on its actual length, measured with an accuracy of 5 cm.
There is a very simple way to determine what voltage a diode strip is designed for, regardless of the total power. Pay attention to how many emitting crystals are located on a 5-centimeter section of its length (between two cut lines):
- if 3, then it is designed for a voltage of 12 volts;
- if 6 or more, then the electrical circuit is designed for 24 volts;
- but there are also heavy-duty options, where up to 60 crystals can be located in a 5-centimeter area - in this case, the tape is designed for 220 volts.
In all cases, the current consumed is exclusively constant. Thus, in the first two cases, the power supply provides a decrease in the supplied voltage, as well as rectification of the current. And in the latter case - only straightening.
Main selection criteria
When choosing a power supply for SL, you need to pay attention to the following main characteristics:
- Voltage conversion method.
- Cooling principle.
- Execution.
- Output voltage.
- Power.
- Additional functionality.
Conversion method
As I said above, the power supply can be transformer or switching. If you need a power supply of relatively low power, then it is better to give preference to a switching design. Buying a serious UPS will pay off only with a power of hundreds of watts - UPSs of such power are expensive and often have cooling fans that create noise and collect dust.
Cooling
Cooling can be passive or active. In the first case, the device components are cooled naturally; in the second, a fan is used for this purpose. If the power of the power supply is small, then it is better to refuse a device with forced cooling: the fan is noisy and, together with the air, sucks in a lot of dust that settles on the unit’s components. Such sources require regular maintenance and, most importantly, are poorly protected from moisture.
Such a unit not only makes noise, but also acts as a kind of vacuum cleaner.
Execution
The degree of protection from the environment depends on the design. If the power supply will operate outdoors or in a damp/dusty room, you will have to choose a dust and moisture-proof, or even better, sealed design. No holes, cracks and, of course, no fans. For difficult mechanical conditions (vibration, shaking, shock, etc.), a device in a solid metal case is ideal. For a typical living space, you can choose a unit with an open casing with many ventilation holes - it will cool better.
Output voltage
Everything is simple here. SLs are available in 2 voltages - 12 or 24 V. Read on the packaging box or even on the tape itself what supply voltage it is designed for. Then select a power supply that has the required parameters.
This SL is designed for 12 V, which means a power supply is needed for the same voltage
Power
The power supply power must be at least 15-20% higher than the power consumed by the tape(s). Everything seems simple, but there is one nuance. It is rare, but it happens that the power supply is not written on the power supply, but only the maximum permissible current is indicated. How to convert it into power? Elementary. Multiply the operating voltage (12 or 24 V) of the unit by its maximum permissible current in amperes, and you get the power in watts.
This power supply (photo above) indicates a power of 20 W, a current of 1.67 A and a voltage of 12 V. Let’s check for interest: 12 * 1.67 = 20.04 W. Everything fits together.
Additional functions
In addition to its main job, the power supply can also perform some additional functions. There are, for example, devices with built-in dimmers (brightness controls), timers, effects machines, and even wireless remote controls. This is up to your discretion, but keep in mind that any additional function affects the cost of the design.
Do you need a powerful power supply for LED strip?
How to calculate the power supply for an LED strip
First of all, it is necessary to determine the power consumed by the tapes. To do this, the power of one meter of tape indicated on it is multiplied by the total length. If LED strips of different types are connected from the same power supply, then this operation is repeated for each type separately, after which the resulting values are added. In addition, it is necessary to take 25-30% of the reserve power for greater reliability and durability of the block for the LED strip.
Let's say you want to install work area table lighting in your kitchen. To do this, you need 2.5 m of SMD5050 tape with a density of 60 diodes per meter. The power of such a tape is 14.4 W meter. Multiply 14.4W by 2.5m. We get the power consumption of the tape 36W. To obtain a power reserve of 30%, 36W is multiplied by 130% or 1.30, depending on the calculator used. We get a minimum power supply of 46.8W. We select the closest value from those available for sale - 60W. If you need to connect tapes of different types, then the task becomes more complicated. Let's assume that in the kitchen not only the work area is illuminated, but also the floor. This means that in addition to 2.5 m of SMD5050 tape with a density of 60 diodes per meter and a power of 36 W, we connect 4 m of SMD3528 tape with a density of 60 diodes. We calculate the power of SMD3528 tape in the same way as SMD5050. We get 19.2W. We add the resulting values 36W and 19.2W. We get 55.2W. Considering the 30% power reserve, a power supply of at least 71.76 W is needed. The nearest higher standard value is 72W. We buy it.
Having determined the required power, you can decide which and how many power supplies are needed. A unit with insufficient power will quickly fail, and a unit that is too powerful will be more expensive than necessary.
A dimmer is used to control brightness. Its power must match the power of the power supply.
Having determined the required power, you can decide which and how many power supplies are needed for LED strips. A diode strip unit with insufficient power will quickly fail, and a unit with excess power will be more expensive than necessary.
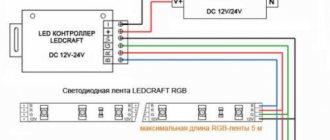
Connecting RGB strip
The RGB strip is connected via an RGB controller. Its power is selected in the same way as for a regular tape. If it is impossible to power all the segments from one controller due to the high power of the tape or the distance between them, then an RGB amplifier is used. Each amplifier is powered through a separate power supply, or, if possible, several amplifiers can be connected to one power supply. This is described in more detail in the article “Connecting an LED strip“.
Degree of protection
The second, no less important selection criterion is the degree of protection and type of housing. Today, you can find on sale a power supply for LED strip with a degree of protection of IP20, which can be selected only for dry rooms, and IP67, the use of which is permissible even in places with high humidity.
It is recommended to choose an unprotected device (pictured number 1) for interior lighting, for example, hidden ceiling lighting in the kitchen. The advantage of such a power supply is that it can be hidden in a cornice and is compact in size.
The sealed aluminum case (second in the photo) is larger and can also weigh more than 1 kg, so it is quite problematic to hide it in a room. This type of housing is best chosen for installation in rooms with high humidity. Quite often, a block in an aluminum casing is used in outdoor advertising to illuminate signs.
The open type of design (3) is rarely used, especially for connecting LED strips. This is due to the fact that it needs to be additionally protected from dust and, moreover, the dimensions of the device are the largest. The only advantage of this version is low cost.
Key issues when designing lighting
Both craftsmen and professionals installing lighting systems containing conventional or more complex RGB strips have to look for answers to typical questions about selecting and calculating the power of a power supply for an LED strip.
This article is intended to help answer these listed questions and reveal some of the nuances of lighting systems using LED strip.
For greatest safety, any electrical system is based on a transformer. The electrical circuits that are powered by it are galvanically isolated from the electrical network. Knowing the power of the LED strip, choose a transformer. To determine its rated power, the power consumption of the LED strip is multiplied by a factor of 1.43. In this way, optimal operation of the entire lighting system is ensured.
The answer to the question of how much an LED strip consumes must be sought in the laws describing electrical circuits, formulas and corresponding calculations. Ohm's, Kirchhoff's and Joule-Lenz's laws make it possible to obtain the desired result. But that is not all. To correctly calculate the power of an LED strip, you also need to know:
- what model the LEDs in the selected product belong to;
- 12 volts, 24 volts or higher voltage is required to power it;
- what is the power consumption of one LED;
- what is the total length of the light emitters in the lighting system, 5 meters or more.
Types of power supplies for LED strip
There are three main types in total. They can be found in any store; they differ only in the installation method. For example, one can only be installed in a dry room, the other can be installed even in the bathroom.
Sealed power supply for LED strip in a plastic case
They are considered the most popular, although many people do not even use their functionality to its fullest. The maximum power of such a unit is 75 watts. This power is enough for an average LED strip. This block can be used.
Power supply in aluminum case
Its power is 100 watts, and it can power two LED strips at once. It has quite a lot of weight (more than a kilogram) and serious dimensions.
Can be installed outdoors, this unit is reliable, not afraid of moisture, protected from frost, sun, rain and minor mechanical damage.
The power is 100 watts, it has the largest dimensions, so it cannot be installed as lighting for walls or ceilings, because it cannot be hidden anywhere. It is used to illuminate large areas and only indoors, for example, it can be hidden in an ordinary closet. It is afraid of moisture and mechanical stress, but has a low cost. Interesting article
In the modern world, LED strips are used to illuminate a wide variety of objects both indoors and outdoors. That's why this product is so popular. But in order for it to fully perform the functions assigned to it, you need to take the choice of device very seriously.
It is generally accepted that among all the characteristics that an LED strip has, power is one of the primary indicators. It and a number of other features determine the scope of application of the lighting device.
Therefore, when choosing the presented products, you need to know what parameters you need to pay attention to first.
How to choose a power supply for an LED strip - calculation method
Independent calculation of the required indicators is carried out according to the formula: N=L*U*K, where N is the calculated power, U is the consumed power of the tape, calculated per 1 meter, L is the length of the LED backlight with diodes, K is the safety factor (20%).
The calculation takes into account the safety factor. Part of the energy is spent on losses in the wires during operation of the tape. If you do not take this coefficient into account, the power supply will operate at maximum power, which will lead to heating of the element. In the worst case, a short circuit will occur and the backlight will malfunction.
To make the right choice of indicators, it is recommended to use a calculator for calculating the power supply for an LED strip. A transformer with correctly selected power will ensure stable operation of LED lighting in the room, reducing the likelihood of diodes overheating. We invite you to use our online calculator to calculate the power supply for the LED strip.
Overview of types and principle of operation
Such devices operate according to a similar scheme: the 220V mains voltage is converted to a lower voltage - 12V. This feature is realized by means of a transformer, which reduces the voltage to the level of 12V. This is the simplest power supply that allows you to connect low-power lighting devices. To install more powerful lamps, power elements designed for 24V, 36V, 48V are used. In addition to the step-down transformer, the design of the unit includes a rectifier, stabilizer and filters (RC or LC).
There are two types of such devices, which differ in the cooling method:
- with passive heat transfer;
- with active cooling system.
In the first case, the power supply can be made in a closed or perforated case, and the heating intensity of the case is reduced through natural cooling.
The second option includes a fan in the design. Such a unit has very significant disadvantages: the need to regularly clean the device, since the fan pumps in quite a lot of dust, and, in addition, during operation, an obsessive noise is heard, which does not always suit the owner of the room. There are different versions of the power supply unit for the LED strip, different in size. If you plan to install decorative low-power lighting, you can use a compact version.
In addition, the market offers models of devices that differ in the material from which the body is made: plastic, aluminum. The main difference is the set of functions:
- providing power to the light source;
- devices with built-in dimmer;
- possibility of remote control;
- Full-featured devices: with dimmer and remote control function.
The power range of such equipment can vary from 4 to 2,000W. If you plan to install the lighting in a room with a high level of humidity, use a special type of power supply - a moisture-proof one.
Calculation for a transformer
In order for the device to work correctly and not create problems later, you need to calculate the power of the purchased transformer before you begin installing the LED strip ceiling lighting. This is not difficult to do.
As an example, you can consider a product labeled 3528 and a placement density of 60 pieces per meter. The amount of energy consumed is 4.78 watts per meter. The power of the converter must be no less than what the chips consume.
If the total length of the segment is, for example, 5 meters, then together they will consume 24 watts of energy. This means that the converter must produce at least 24 watts. But these are not the only parameters that need to be taken into account. A 20% energy reserve is required. This means that we need a converter that will provide 24+20% of energy. The final value is 28.8 W, so it must be more powerful than this figure.
You have to choose a converter that will best meet the specified requirements for output watts of energy and voltage.
Calculation of LED strip per power supply
As we have already discussed, driver power for LED lighting must be taken with reserve. Therefore, the maximum length of tape allowed for connection is calculated using the formula:
Length (m) = Unit power / (1.3 * Nsmd/m * Psmd)
Ncmd/m – number of smd matrices per linear meter
Pcmd – rated power of one matrix
1,3 – safety correction factor
Calculation of a transformer for LED strip
We calculate the power of the power supply using the same principle:
Unit power = Length (m) * 1.3 * Nsmd/m * Psmd
Connecting a transformer to an LED strip
Self-installation of an LED strip light indoors sometimes involves connecting a dedicated electrical line, which will prevent overload and, as a consequence, failure of the diodes as a result of voltage surges.
The connection diagram for a 12V LED strip and a 24V device is as simple as possible, so there are no significant differences.
Transformer connection diagram
However, it is very important to first provide for a number of certain features:
at the first stage, it is important to determine the total length of the lighting line, and only after that begin cutting strips of the correct length; the tape is cut in areas marked by the manufacturer, which will prevent the electrical circuit from breaking and the device from malfunctioning; Before connecting the diode illuminator, you must read the manual given by the manufacturer, and also be sure to take into account the polarity.
The connection of the power supply, which reduces the mains voltage from 220V to 12V, is carried out using a standard two-wire wire. Inside the LED transformer, a two-core wire is fixed using terminals, and the other end of the wire is soldered to the lighting strip itself on a contact pad.
It is important to remember that connecting the power supply for a 12-volt LED illuminator must take into account the polarity, so the “plus” is attached to the “plus”, and the “minus” - only to the “minus”. Before performing the installation, it is recommended to independently solder all the wires that fit the lighting strip, which is due to the lack of the proper level of quality of connections during factory production
Before performing the installation, it is recommended to independently solder all the wires that fit the lighting strip, which is due to the lack of the proper level of quality of connections during factory production.
Power supply for LED strip
The LED strip is powered by voltage.
Special power supplies are made for the LED strip; they are available in different voltages - 5, 12, 24 or 36 volts (but 48 volts are also possible). The block is a converter for changing alternating voltage to direct voltage in a 220 V network. The output voltage level corresponds to the needs of a specific LED strip. How to calculate power for a power supply
The voltage that is generated at the output of the LED strip power supply is the most important parameter of this type of product. Exceeding the permissible power will cause the LED lamp to burn out, and if the declared power is lower than necessary, the strip will not work. The next most important characteristic of a power supply is its power, or the ability to produce a voltage that should be enough to operate all those elements that are included in the LED strip.
In cases where it is necessary to draw up a lighting project, or create decorative lighting, it is important to first calculate the power of the power supply. The calculation is also required to ensure that the LED strips have the required brightness level and to avoid overloading the power supply.
How to connect several LED strips to one block at the same time
The power of LED strips is usually indicated per linear meter. In the case when several LED strips that are connected simultaneously to one power supply have the same or similar characteristics, then the power per linear meter is simply multiplied by the number of strips. After this, a margin of approximately 20% is added to the result obtained for unforeseen cases, and the finished result is rounded.
We can say that the calculated power for the power supply should be higher than the actual power consumption. This is necessary so that the power supply does not fail prematurely and there is no actual overload.
A high-quality range of products - LED strips, profiles, components - is presented in our online store ledluks.ru. With us you will find exactly what suits you best.
Driver circuits and their operating principles
To carry out a successful repair, you must have a clear understanding of how the lamp works. One of the main components of any LED lamp is the driver. There are many driver circuits for 220 V LED lamps, but they can be divided into 3 types:
- With current stabilization.
- With voltage stabilization.
- No stabilization.
Only devices of the first type are, in essence, drivers. They limit the current through the LEDs. The second type is better called a power supply for LED strip. It’s difficult to name the third one at all, but its repair, as I indicated above, is the simplest. Let's look at the circuits of lamps on drivers of each type.
Driver with current stabilization
The lamp driver, the diagram of which you see below, is assembled on an integrated current stabilizer SM2082D. Despite its apparent simplicity, it is complete and of high quality, and its repair is simple.
The mains voltage is supplied through fuse F to the diode bridge VD1-VD4, and then, already rectified, to the smoothing capacitor C1. The constant voltage thus obtained is supplied to the LEDs of the lamp HL1-HL14, connected in series, and pin 2 of the DA1 chip.
From the very first output of this microcircuit, the LEDs receive a current-stabilized voltage. The amount of current depends on the value of resistor R2. Resistor R1 is quite large, a shunt capacitor, and does not participate in the operation of the circuit. It is needed to quickly discharge the capacitor when you unscrew the light bulb. Otherwise, if you grab the base, you risk getting a serious electric shock, since C1 will remain charged to a voltage of 300 V.
Driver with voltage regulation
This circuit, in principle, is also quite high quality, but you need to connect it to the LEDs a little differently. As I said above, such a driver would be more correctly called a power supply, since it stabilizes not the current, but the voltage.
Here, the mains voltage is first supplied to the ballast capacitor C1, which reduces it to approximately 20 V, and then to the diode bridge VD1-VD4. Next, the rectified voltage is smoothed by capacitor C2 and supplied to an integrated voltage stabilizer. It is smoothed again (C3) and, through the current-limiting resistor R2, powers a chain of LEDs connected in series. Thus, even if the mains voltage fluctuates, the current through the LEDs will remain constant.
Driver without stabilization
The driver assembled according to this circuit is a miracle of Chinese circuit design. However, if the voltage in the network is normal and does not fluctuate much, it works. The device is assembled according to the simplest circuit and does not stabilize either current or voltage. It simply lowers it (voltage) to approximately the desired value and straightens it.
In this diagram you see the already familiar damping (ballast) capacitor, shunted by a resistor for safety. Next, the voltage is supplied to the rectifier bridge, smoothed out by a capacitor of an offensively small capacity - only 10 μF - and through a current-limiting resistor it is supplied to the LED chain.
What can be said about such a “driver”? Since it does not stabilize anything, the voltage on the LEDs and, accordingly, the current through them directly depend on the input voltage. If it is too high, the lamp will burn out quickly. If it “jumps”, the light will also blink.
This solution is usually used in budget lamps from Chinese manufacturers. It is, of course, difficult to call it successful, but it occurs quite often and can work for quite a long time at normal network voltage. In addition, such circuits are easy to repair.
Features of LED strips
LED strip is a strip of flexible material with insulating properties, which is equipped with two conductive copper foil bars, LEDs and resistors.
Flexible strip with installed LEDs creates a bright light source up to 5 meters long
Structurally, the LED strip consists of many sections consisting of three diodes and a resistor, which are connected by a common circuit. The device is powered by supplying a stabilized DC voltage of 12 or 24 V to conductive busbars installed in parallel on the tape. Thanks to this connection scheme, exactly the voltage that was supplied to the input, for example, 12 V, is supplied to each section of the tape.
The LED strip consists of sections of three diodes, each of which is connected to the power source in parallel
Breaking the tape into sections is very convenient, since this allows you to cut off the amount of material that is needed for a specific purpose. However, in order not to interfere with functionality, you should adhere to the integrity of the section, cutting off, for example, 3, 6, 9, etc. LEDs.
LED strip can be cut into fragments with the number of LEDs divisible by three
When the wires are correctly connected to the power buses, voltage will begin to flow to the section or cut section of the tape, which will cause current to flow through the LEDs. Due to the peculiarities of their design, under the influence of current, LEDs will begin to emit a luminous flux (glow). It is worth noting that the level of glow directly depends on the magnitude of the current. If the current is too low, the diode will emit a dim glow or not glow at all, and if the current is too high, it will quickly deteriorate and burn out. In general, the average current for diodes used in LED strips is between 15 and 20 milliamps (mA).
Power supply for LED strip 12V
12V LED strips cannot be powered directly from AC power. To connect them to a 220 V network, you will need a special power supply, which is most often called a driver or LED driver. The driver reduces the AC voltage from a 220 V network to the 12 V DC voltage required by a standard LED strip.
Power supplies for LED strips are divided according to sealing or IP protection into three types, sealed, non-sealed and semi-sealed. The degree of protection of the power supply for the LED strip is selected depending on its location.
Sealed power supplies for LED strips with a degree of protection of IP67 and higher are protected from moisture and dust, and can be used in places where they may be exposed to water. This could be bathrooms or even the street. Unprotected power supplies for LED strips usually have an open or well-ventilated housing. They are installed only indoors and away from possible moisture. The degree of protection of such drivers is IP20 and IP33.
When choosing a power supply, you must pay attention to its power. The power is selected depending on the power of the connected LED strip. As a rule, LED strips indicate the power of one meter. To find out how much power an LED driver will need, you need to multiply the power of one meter of strip by the total number of meters of LED strip and add another 20% to 30% of the reserve. To ensure a stable output voltage with the required output current, the LED power supply should not work at the limit, so it is always taken with a power reserve. This way it will overheat less and work longer.
LED Size
Power directly depends on the size and number of its individual elements. They allow you to create the required glow intensity. First of all, it is necessary to consider the issue of diode sizes. Product labeling allows you to understand what type of illuminator is on sale.
First, this designation indicates the type of product (RGB or SMD). Further marking contains 4 digits. This is the size of the diodes. If, for example, the marking says SMD3528, this means that its lighting elements have a length and width of 3.5 x 2.8 mm.
There are also larger diodes - 5050 or 5630. The brightness of the SMD3528 is 5 lumens. This is a specific measure of the glow of the tape. Power and 5630 will be more. The luminous flux emitted by these diodes will be 15 and 18 lumens, respectively. Thanks to these qualities, an LED strip can replace a conventional energy-saving light bulb in terms of lighting brightness.
How to choose a transformer for lamps
Content:
A transformer is a device that is designed to convert alternating current of one voltage into alternating current of another voltage. These devices are divided into current transformers, which are powered by a current source, and voltage transformers, which are powered by a voltage source.
They, in turn, are divided into so-called step-down current or voltage transformers and reduce the current or voltage values to specified limits. Step-down voltage transformers, as a rule, have found their application when connecting electric lamps. A huge selection of lamps with halogen lamps involves the use of step-down transformers. Lamps require a voltage of 12 V, and from the socket we are offered 220, so the use of transformers is necessary so that the lamp does not fail. Transformers can be electronic, they are used for halogen and LED lamps, and electromagnetic ones are necessary for track systems. The use of a step-down transformer extends the service life of the lighting source, and the surface in which it is mounted does not overheat, thereby ensuring a high level of safety. Electronic transformers are compact in size, which allows installation in narrow spaces. A huge selection of step-down transformers can become a problem for an inexperienced consumer in this matter. After all, an error in choice can cause a decrease in the brightness of the lighting and deterioration in the operation of the device. When choosing an electronic transformer for halogen lamps, keep these parameters in mind. 1. The efficiency of the device should tend to unity. 2. Temperature thresholds. The wider the temperature range in which the transformer can operate, the better. However, when used indoors, this parameter is not of great importance. 3. Operating voltage range. 4. Power. 5. Moisture and dust resistance class. Application of step-down transformers Step-down transformers can find their application in rooms with high humidity - bathrooms, basements, cellars. Due to its compactness and low weight, the transformer can be installed on a suspended ceiling, a furniture shelf, or attached to a chandelier box. As a rule, the reliability of a transformer depends on the manufacturer and, accordingly, the price of the product. High-quality transformers are protected against short circuits, overheating, and have a soft-start device for lamps. In order to correctly select the power of the transformer you need, you need to add the power of the lamps connected to it (in w) with a 10% margin. For example, if we have 5 20w light bulbs, then the ideal option for you would be a transformer with a power of 110-115 w
Please note that exceeding the rated load of the transformer and loading more than 90% is strictly prohibited. Divide the lamps into groups and install a transformer for each of them
How to choose a transformer for LED strip
General questions about choosing a power supply
To correctly select a power supply unit (PSU) for an LED backlight system, you need to know the parameters of the connected LED strip and the parameters of the proposed power supplies.
The first parameter of the tape that influences the choice of power supply is the supply voltage of the tape. Most often it is 12 or 24 volts. Whatever voltage the tape is designed for, the power supply is selected for the same voltage.
The second parameter of the tape that we need to calculate the power supply is the power consumption per 1 meter of tape. This parameter is necessarily given by a conscientious manufacturer in the characteristics of the tape and is usually indicated on the packaging of the tape. The power of LED strips available in our range varies from 4.2 to 31 W/m. Typically, the higher the power consumption of the tape, the brighter it shines. True, such an indicator as efficiency introduces ambiguity here, but it does not affect the given calculation of the power supply, so we will not take it into account now.
The next indicator is the length of the tape connected to the power supply. Everything is simple here. Length is length. Measured in meters.
We've sorted out the tape, now let's look at the power supplies. The main characteristics of the power supply are the output voltage, the maximum permissible current that the power supply can supply to the load for a long time, and the output power of the power supply.
With the output voltage everything is simple. The tape is 12 volt, and a power supply is needed for 12 volts, a tape for 24 volts - we take a power supply for 24 volts.
The next parameter - the maximum current supplied by the power supply - is a very important parameter, but is rarely used in standard calculations for systems with LED strip. Although, knowing it, you can always determine the output power of the power supply. You just need to multiply the output voltage in volts by the maximum current in amperes and we get the power in watts. For example, a power supply with an output voltage of 12 volts and a maximum current of 5 amps has a power output of 60 watts.
And the output power of the power supply is exactly the parameter that is needed for our calculations.
For clarity, let's look at calculating the required power supply using an example.
UPS options
LED strip power supply options
According to their design and performance characteristics, power supplies for LEDs are divided into the following types:
- a compact power supply that looks like a phone charger;
- a small-sized module placed in a rectangular oblong body;
- electronic ballast in a completely sealed box;
- a similar circuit housed in a standard size non-hermetic housing.
The units have low power (30-36 watts), but are quite cheap. The modules have a high power rating (up to 75 watts). Like the first samples, they are designed to work with decorative lighting, but unlike them they have a higher cost.
Electronic ballasts in a completely sealed housing are designed for use in harsh climatic conditions. They are used to illuminate billboards and similar outdoor products. Their non-hermetic analogues, placed in a standard-sized housing, are widely used in everyday life and in work offices. Among modern manufacturers of transformer power supplies, Russian and IPS, as well as foreign “Helvar” and “Mean Well” (Taiwan), are especially popular.
Power supply power calculation
In some cases, calculating the power supply for an LED strip is simply not required. For example, if you need to connect 1 meter of LED strip on SMD LEDs 3528 powered by 12 volts. There is nothing to calculate - any power source with a stable output voltage of 12 V will do. If we are talking about a more powerful load, then you will have to tinker a little with the numbers.
The power of the power supply is selected based on the maximum length and power consumption of one meter of LED strip. To simplify the task of calculating power, we suggest using the reference data in the table below.
So how to calculate the power supply for an LED strip? You can make the calculation yourself using the formula Ptot. = Potr. × L × 30%. In this formula, Potr. – power consumption of 1 meter of LED strip, L – total length of the segment, 30% – power reserve.
Calculation example. Let's say you need to calculate the power of a power supply for a three-meter section of an SMD 3528 LED strip with a density of 60 LED chips per meter. A 1 meter long segment consumes 4.8 W, therefore 3 meters will consume 14.4 W. If you purchase a power supply close to the rated power, it will work at the limit and will not last long. Therefore, the obtained result should be further increased by at least 30%. In our case, the result is 18.7 W, which corresponds to the nearest standard value of 20 Watt.
Precautions when using high-power LEDs
The greater the power of the LED, the more carefully you need to approach the installation and operation of the product. By following a few rules, you will protect yourself from trouble.
Firstly, the tape should not be damaged. Secondly, consider the electrical polarity when connecting the products. Third, beware of unbalanced voltage drops, which can damage the LEDs. Fourthly, connect the pieces of tape only in parallel. Connecting high-power LEDs in series can cause them to burn out.
Start shopping
Section: Plain
Return to list
Principle of operation
The current flowing through the electrode into the lighting installation must be limited in some way, otherwise, as soon as the lamp lights up, its value will increase to an excessively high value. This regulation is carried out using electromagnetic conductors mounted in the core of the device; they provide strict control of the strength of the electric current within fairly narrow limits.
Magnetic shunts dissipate some of the electromagnetic energy that is produced by the primary coil and then spreads along the metal core of the transformer. As the current consumed by the secondary winding increases, most of the primary electromagnetic flux is diverted through the magnetic shunt. As a result, in those areas of the core frame where the secondary coils are located, the intensity of the magnetic current is much weaker.
Some current converters may have more than one secondary winding and more than one secondary shunt. If the converter is equipped with two secondary windings, then the midpoint connection between them can be grounded on the device body. Depending on the exact configuration of shunts and secondary windings, neon lamp transformers may be balanced or unbalanced.
Power
The first thing you need to decide is how powerful the power source should be. There are units from 20 to 400 W. To select the correct characteristics, you must first determine the power of the LED strip, and then add another 20% margin to this value.
You can find out the LED consumption from the table:
Unfortunately, it does not indicate how much 5630 LEDs, which are also quite often used by the population, consume. Typically, a 5630 LED strip consumes about 18 watts per meter (60 LEDs per meter).
For example, let's look at how to choose the power of the power supply for a lighting source with 5050 LEDs (60 pieces per meter). According to the table, this model consumes 15 W/m. For a 5-meter segment, the power will be 75 W (15 * 5) and + 20%, we get 90 W. It is better to choose a 100 W power supply, which will be quite enough to power the backlight.
Calculation of the power supply for LED strip
When installing LED lighting, a number of pressing questions usually arise: what is the current consumption of the LED strip, how to calculate the power supply for LEDs, how to calculate the drivers for an unknown strip if the power consumption is not indicated on it? For correct calculation, we use the following table with the nominal parameters of popular matrices.
Table of popular SMD LEDs, characteristics
Calculation of LED strip power parameters
The tape differs in the number of SMD matrices per linear meter. There are options on sale for 30, 60, 120 matrices per linear meter. Depending on the LED matrices used, the rated power of the electricity source for the LED strip will differ.
| SMD matrix type | Number of LEDs per linear meter | Power consumed by 1m/5m tape, W | Required current strength, A at 1m/5m |
| 3528 | 30 | 3,3/16,5 | 0,27/1,35 |
| 60 | 6,6/33 | 0,55/2,7 | |
| 120 | 13,2/66 | 1,1/5,5 | |
| 5050 | 30 | 9/45 | 0,75/3,75 |
| 60 | 18/90 | 1,5/7,5 | |
| 120 | 36/180 | 3/15 | |
| 5630 | 30 | 15/75 | 1,25/6,25 |
| 60 | 30/150 | 2,5/12,5 | |
| 120 | 60/300 | 5/25 |
Which PSU should you choose?
Having visited the first online store you come across for the retail sale of network drivers for LEDs, you can find dozens of various options for transformers for LED strips with a very fair range of costs, which directly depends on the rated power, housing materials, and waterproofing.
The natural desire of every person is to minimize their financial costs. But savings must be expedient and justified. Let's compare several options:
| BP | OEM DC12 12W 1A | OEM DC12 36W 2A | OEM DC12 120W 10A | OEM DC12 360W 30A |
| Appearance | ||||
| Power, W | 12 | 36 | 120 | 360 |
| Current strength, A | 1 | 2 | 10 | 30 |
| Cooling type | Passive | Passive | Passive | Active |
| Housing material | Plastic | Plastic | Metal | Metal |
| Price, USD | 1,8 | 5,2 | 10,5 | 21 |
| Price for 1 W, USD | 0,15 | 0,14 | 0,08 | 0,058 |
As you can see, the stronger the power supply, the cheaper its actual cost per watt. At first glance, purchasing a single sufficiently powerful power supply looks most tempting. Calculation of transformer power for LED strip is done with a margin of about 30%.
Do not forget that absolutely any device has the rather unpleasant property of unexpectedly breaking down at the most inopportune moment. If such force majeure occurs, you will formally be left without coverage. It is most rational, in the case of installing lighting in a room, to power the areas from two to three independent sources.
Calculating the power of the power supply for the LED strip
For the sake of example, let's take a guest room of 18 square meters (3 x 6 meters). The perimeter of the room will be 18 meters. We will need an LED lighting source with a total brightness of 350 lumens/mp (we calculate the brightness based on the recommended lighting levels), for example, let's take smd 3528 60led with a nominal brightness of 360 lm/mp. The total power of this tape for the entire perimeter of the room will be:
6.6 W/m * 18 = 118 W.
From different manufacturers, the brightness of the media may vary significantly; accordingly, the strip in your situation may require a slightly different one; it is advisable to calculate the power of the LED strip according to the passport data from the manufacturer. With a reserve of strength, we will need a device rated at 150 W.
When using several current sources, we divide the entire length of the tape into three sections, taking into account that the standard coil is five meters long. We get two segments of five meters, 33 W and one section of eight meters, 53 W. Power supplies will be required for 40 and 70 W, respectively.
Types of LED strips
Types of LED strips Based on installation methods, this type of lighting is divided into two types - DIP and SMD. In the first case, LED bulbs are placed directly into the tape housing, with two outputs from them on each side. In the latter case, resistors and LEDs are soldered to a strip on the surface.
Visually, DIP tape is a sequence of small cylinders, while SMD has a flat appearance.
Also, when choosing an LED strip, the color of the bulbs plays a big role. It not only creates a mood and affects a person’s emotional state, but also determines performance. LED strips are divided into the following types by color:
- Monochrome ribbons. They are made from LED bulbs of the same type. They can come in different colors, such as yellow, red, green, blue and white. If desired, you can find non-standard colors - orange or pink. There are also tapes with ultraviolet and infrared radiation.
- Multi-color strips are equipped with three LED crystals in one chip, causing the strip to emit different colors.