Electrician Basics
Time to talk about electrical terminology. Knowing it will be useful to you when you read further publications and other literature on electrical engineering.
Circuit diagram of the circuit breaker.
A circuit breaker (AB) is a type of fuse that trips if the current in the circuit exceeds the set value.
AD is a differential automatic machine. A hybrid device that combines an RCD and an overcurrent protection mechanism.
Ampere is a unit of current.
Anode is the positive terminal of the battery.
A battery is two or more cells connected in series or parallel to provide the required voltage and current.
Watt is a unit of electrical power.
Connection diagram of wires with a cap.
External conductor is a wire that connects the current source to the consumer.
Volt is a unit of electrical voltage.
Potential equalization is the elimination of potential differences between conducting objects.
ASU (input distribution device) is a device through which electricity is introduced into the house via overhead and cable lines.
Visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength from 380 to 780 nm.
Internal resistance is the resistance to current flow through an element, measured in Ohms.
Energy output is the capacity consumption multiplied by the average voltage during the discharge time of the batteries, expressed in Watt-hours.
Putting in is the placement and fastening of a mechanism or device.
A wet room is a dry, unheated room in which vapors are released only temporarily in small quantities, and the relative humidity is in the range of 60-75%.
Hertz is a unit of alternating current frequency.
Corrugation is a flexible PVC pipe. Corrugated plastic pipe is used as an additional insulator for electrical wiring.
Solidly grounded neutral - the neutral of a transformer or generator, connected to a grounding device directly or through low resistance.
Sleeves are aluminum or copper tubes, the inner surface of which can be lubricated with quartz-vasilin paste.
Types of socket boxes.
Group network - a network that powers lamps and sockets.
Gas discharge lamp - a lamp in which the glow is created directly or indirectly from an electrical discharge in a gas, metal vapor or a mixture of gas and steam.
Bare wire - a wire that does not have protective or insulating coatings over the current-carrying cores.
Dismantling electrical wiring - removing old wires that connected the panel, lamps, sockets.
Removal of sockets and switches - removal of old sockets and switches.
Dismantling the power cable - removing the old liner.
Removing the telephone/TV cable - removing the old cable.
Dismantling of lamps - removal of old lamps.
Allowed - this decision is applied as an exception, as forced.
Capacity is the amount of electrical energy that a battery releases under certain discharge conditions, expressed in ampere-hours or coulombs.
Core - a copper or aluminum thread in a wire or cable through which current passes.
A harness is a bundle of wires laid and interconnected, with lugs for connection to elements of a circuit or product.
Socket diagram with grounding.
Grounding conductor is a wire that discharges electric current.
Protective conductor (PE) is a wire connecting exposed conductive parts of electrical appliances with other conductive parts and/or with a grounding electrode.
A bell is a signaling device that is triggered when a button is pressed.
Charge is electrical energy transferred to an element to be converted into stored chemical energy.
Replacement of circuit breakers - replacement of a device designed to protect against overload and short circuit.
A short circuit to the frame is an accidental connection of energized parts of an electrical installation with their structural parts that are not normally energized.
Ground fault is an accidental connection of live parts of an electrical installation with structural parts that are not insulated from the ground or directly to the ground.
Grounding device – a combination of ground electrode and grounding conductors.
Grounding is an intentional electrical connection of a part of an electrical installation to a grounding device.
Grounding is a deliberate connection of parts of an electrical installation that are not normally energized with a solidly grounded neutral of a generator or transformer in three-phase current networks.
An insulator is an electrical device for isolating parts of electrical equipment that are under different electrical potentials and preventing an open short circuit to the ground or housing.
An isolated neutral is a neutral that is not connected to a grounding device or connected through devices that compensate for the capacitive current in the network.
Induction lamp circuit.
An induction lamp is a lamp that operates on the principle of a high-pressure mercury lamp, but does not have an electrode.
Infrared radiation is optical radiation with a wavelength longer than visible radiation.
Insulation is a material that prevents the spread of electric current.
Cathode is the negative terminal of the battery.
Ceramic burner – metal halide lamps equipped with a ceramic burner.
Efficiency – efficiency factor.
Compulsory charging is a method that uses direct current to bring the battery to a fully charged state and maintain it in this state.
Kilowatt hour is a unit of electrical current consumption. Electricity meters measure.
Diagram of the contact clamp device: 1– screw; 2 – spring washer; 3 – washer or contact clamp base; 4 – current-carrying core; 5 – stop that limits the spreading of the aluminum conductor.
Contact clamp – a clamp with two screws for connecting wires.
The bell button is a contact mechanism.
Terminal group – a terminal for connecting wires.
Contact is the main working element of the device.
Cable – several insulated wires in a protective sealed sheath.
Color rendering coefficient is the ratio of the colors of objects when illuminated by a given light source to the colors of the same objects illuminated by a light source taken as a standard, under strictly defined conditions.
KZ – short circuit.
KUP – potential equalization terminal.
A contactor is a device designed for frequent remote switching of an electrical circuit during normal operation.
As a rule, this requirement is predominant, and deviation from it must be justified.
CFL – compact fluorescent lamp.
Luminescence is radiation that does not require heating of bodies and can occur in gaseous, liquid and solid bodies under the influence of electron impacts.
Phosphors are solid or liquid substances capable of emitting light under the influence of various types of pathogens.
Diagram of a fluorescent lamp.
Fluorescent lamps are low pressure gas discharge lamps.
A lamp is an electrical device designed to emit light.
Metal halide lamps are high-pressure mercury lamps that use additives from metal iodides, including rare earth ones, as well as complex compounds of cesium and tin halide.
Monochromatic light is one-color light, light of one specific wavelength. In practice, it contains a narrow portion of the spectrum.
Installation of the electrical box - attaching the electrical box to the wall.
Voltage is the potential difference between two points, for example, between the phase and neutral wires.
Rated voltage – 220-240 V for AC mains.
Neutral wire (N) is a wire used to return current.
Hanging chandeliers, sconces, lamps - hanging and connecting chandeliers, sconces, lamps.
A surface-mounted electrical outlet is a socket/switch installed on the wall surface.
Cut-off voltage is the minimum voltage at which the battery is capable of delivering useful energy under certain discharge conditions.
Open circuit voltage is the voltage at the external terminals of the battery in the absence of current draw.
No more – the values of the quantities are the greatest.
Not less – the values of the quantities are the smallest.
Bathroom lighting diagram.
Normal rooms are dry rooms, if there are no conditions (especially damp, hot, dusty).
Ohm is a unit of electrical resistance.
Lighting is the application of light in a specific setting, near objects or in their surroundings, to make them visible.
Illumination is a value that reflects the ratio of the incident luminous flux to the illuminated area. The unit of measurement is lux.
Reflection is the property of materials to return light falling on them.
A particularly damp room is a room where the relative humidity is close to 100%.
Conductor is a component of electrical wiring that serves to transmit current.
Alternating current is an electric current that periodically changes its magnitude and direction.
Direct current is an electrical current that always flows in one direction.
Electricity consumers are all electrical appliances that operate by consuming electricity.
Switchboard bulkhead - replacement of circuit breakers with reconnection of wires.
A socket is a device for installing and securing an electric lamp in a lamp.
A fuse is an electrical switching element designed to disconnect the protected circuit by melting the protective element.
Wire connection diagram in the distribution box.
Buckles are devices for fastening cables and wires to bases when laid open.
Wire – a conductor of electric current, consisting of one or more conductive wires.
Carrying - lighting provided by portable lamps connected to a voltage of 220-240 V in normal rooms and 12 V in high-risk rooms.
Wire (PEN) – wire with a protective function.
Energy density is the ratio of the energy of an element to its mass or volume, expressed in watt hours per unit mass or volume.
Ballasts (ballasts) are a device that operates in an electrical circuit with gas-discharge lamps and serves mainly to stabilize the current during discharge.
Soldering is the joining of wires using a soldering iron and special solders.
Distribution panel - location for installing fuses, remote switches, etc.
Discharge is the consumption of electrical energy from an element into an external circuit.
Detachable contact connections are devices consisting of a plug and socket.
Dismountable contact connections are devices that can be disassembled without destroying the parts being connected.
Junction box is a box in which wires are connected.
Current strength is the amount of electricity flowing through a wire over a certain period of time.
High current – current voltage up to 1000 V.
Circuit diagram of the circuit breaker line.
A low current fuse is a small fuse used in electrical appliances.
Low current – current voltage up to 50 V.
An electrical wiring diagram is a diagram that shows the position of all electrical devices and wires.
Power line – a line of wires for connecting power outlets (electric stove, water heater, etc.).
The lamp is a lampshade with a socket and a light bulb.
Drilling through holes in walls - drilling through holes in walls.
Power wire is a wire through which electricity is supplied.
Network cable for a computer - a computer network line.
Luminous efficiency - luminous efficiency shows the efficiency with which the received electrical power is converted into light. It is measured in lumens/W and is the main indicator of lamp efficiency.
Luminous flux is the entire radiation power of a light source, estimated by the light sensation of the human eye. Measured in lumens.
Luminous intensity is the intensity of light emitted in a certain direction. Measured in candelas.
A starter is a device used to ignite gas-discharge lamps by heating the electrode.
A dry room is a room in which the relative air humidity does not exceed 60%.
A damp room is a room in which the air humidity exceeds 75% for a long time.
The resistance of the grounding device is the sum of the resistances of the grounding conductor (relative to the ground) and the grounding conductors.
Spreading resistance is the resistance that the ground electrode provides in the area of current spreading.
Options for twisting wires.
An LED is a semiconductor device with an electron-hole p-n junction or a metal-semiconductor contact, which generates optical (visible) radiation when an electric current passes through it.
A meter is an electricity metering device.
Twisting is a device for connecting individual monolithic conductors of small cross-section.
Leakage current is the current that occurs when the wiring is damaged.
PVC pipe is a rigid plastic pipe. Used as an additional insulator for electrical wiring.
Telephone line – cable for telephone communication.
Television crab is a device for branching a television cable into several separate lines.
Ground fault current is the current passing through the ground at the fault location.
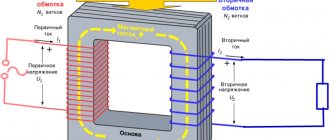
Transformer is a device that converts alternating voltage of one level to voltage of another level.
Residual current device (RCD) is a device for protection against electric shock.
The overcurrent protection device is a fuse or a circuit breaker.
Ultraviolet radiation is optical radiation with a wavelength shorter than visible radiation.
An ignition device is an electrical device that provides the conditions necessary to initiate a discharge.
Installation of an electrical outlet - installation of a socket/switch.
Installation of an internal electrical point - grouting the socket box.
Socket layout diagram.
Installing the socket - installing the socket mechanism.
Installing a terminal group - connecting wires using a terminal.
Phase wire is the main current-carrying wire.
A cycle is one sequence of charging and discharging an element.
Color temperature is a measure of the objective impression of the color of a given light source.
Color sensation is the general subjective sensation that a person experiences when looking at a light source.
Frequency is the number of vibrations per second. The frequency of alternating current in a conventional electrical network is 50 Hz.
Grooving – cutting grooves in walls and ceilings for laying wires.
Busbar is a complete device for laying an electrical network. Consists of separate sections connected by welding and bolting.
An electrical circuit is a closed section of electrical wiring.
Screening grille is a part of a lamp made of transparent or opaque elements in such a way as to cover the lamp from direct observation at a certain angle.
Electrolyte is a material that conducts charge carriers in a cell.
An electrode is a conductive material capable of producing current carriers when reacting with an electrolyte.
An electrical panel is a set of electrical devices installed in one box and designed to distribute electricity along lines and protect them from overloads, short circuits and ground leakage currents.
Electrical wiring - wires connecting the panel board, lamps, sockets, stationary electrical appliances.
An electrical box is a plastic cable channel for laying wires in it. Used when installing external electrical wiring.
Electrical point - socket/switch.
Electrical contact is the contact of elements that ensures the continuity of the electrical circuit.
The electrical installation bracket is a plastic round or flat strip bent in the shape of an arc or the letter P (depending on the cross-section of the cable).
Of course, these are not all the terms that exist in electrical engineering. Only the most frequently encountered ones are presented here.
Main types of conductors
Unlike dielectrics, conductors contain free carriers of uncompensated charges, which, under the influence of a force, usually an electrical potential difference, move and create an electric current. The current-voltage characteristic (the dependence of current on voltage) is the most important characteristic of a conductor. For metal conductors and electrolytes, it has the simplest form: the current strength is directly proportional to the voltage (Ohm's law).
Table of electric current in various environments.
- Metals - here the current carriers are conduction electrons, which are usually considered as an electron gas that clearly exhibits the quantum properties of a degenerate gas.
- Plasma is an ionized gas. Electric charge is transferred by ions (positive and negative) and free electrons, which are formed under the influence of radiation (ultraviolet, x-ray and others) and (or) heating.
- Electrolytes are “liquid or solid substances and systems in which ions are present in any noticeable concentration, causing the passage of electric current.” Ions are formed through the process of electrolytic dissociation. When heated, the resistance of electrolytes decreases due to an increase in the number of molecules decomposed into ions. As a result of the passage of current through the electrolyte, ions approach the electrodes and are neutralized, settling on them. Faraday's laws of electrolysis determine the mass of a substance released on the electrodes.
It will be interesting➡ What is a Peltier element and how to make it yourself?
There is also an electric current of electrons in a vacuum, which is used in electron beam devices.
Transmission of current through wires