Each home has a certain set of tools with which you can solve urgent problems in repairing household appliances, electrical wiring, lighting fixtures and other objects. Among them, special mention should be made of the voltage indicator, which allows you to accurately determine the presence or absence of electricity in a particular area. This device becomes relevant in the event of a sudden loss of light, since it is the voltage indicator that is used during initial measures.
Classification of voltage indicators
Indicators or voltage indicators used in domestic conditions are compact, portable devices. This also includes a multimeter. Their main function is to determine the presence or absence of a potential difference in areas of current-carrying elements and parts. All of them are equipped with light signals - indicators that light up when voltage is detected in the area being tested and are designed for different voltages.
Indicators are divided into voltage measuring devices up to 1000 V and over 1000 volts. Structurally, they are single- or double-pole.
A single-pole voltage indicator only touches one live part. A short circuit to ground occurs directly through the human body when a special pointer contact is closed with a finger. The electric current flowing at this moment is no more than 30 mA and is completely safe for humans.
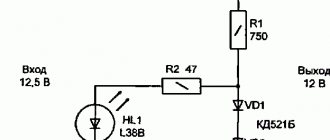
These indicators are made in the form of screwdrivers or pens. All structural elements are placed in a dielectric housing with an inspection hole. First of all, this is the indicator itself and the resistor. At the top there is a metal contact for touching, and at the bottom there is a probe in contact with live parts. With the help of these devices, the following is accomplished: phase and zero are determined, the presence of voltage at the contacts of automatic machines and other safety devices.
Bipolar voltage indicators have significantly more functions. When performing testing actions, the device comes into contact with two points of the site or electrical installation at once. As a result, an electric current begins to flow through the device and an indicator light with a power of no more than 10 W lights up. It consumes a very small amount of current, which does not affect the clarity and stability of the signal at all. A resistor connected in series with the lamp is installed as a current limiter in the circuit.
A two-pole indicator is used in diagnosing direct and alternating current equipment. Devices of this type can perform a wider range of activities compared to conventional indicators.
Terms of use
2.4.20. Before you start working with the pointer, you need to check its serviceability.
The serviceability of indicators that do not have a built-in monitoring device is checked using special devices, which are small-sized sources of increased voltage, or by briefly touching the electrode-tip of the indicator to live parts that are known to be energized.
The serviceability of indicators with a built-in control unit is checked in accordance with the operating manuals.
2.4.21. When checking the absence of voltage, the time of direct contact of the working part of the indicator with the controlled current-carrying part must be at least 5 s (in the absence of a signal).
It should be remembered that although some types of voltage indicators can signal the presence of voltage at a distance from live parts, direct contact with them by the working part of the indicator is mandatory.
2.4.22. In electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V, the voltage indicator should be used with dielectric gloves.
Voltage indicators up to 1000 V Purpose, principle of operation and design
2.4.23. General technical requirements for voltage indicators up to 1000 V are set out in the state standard.
2.4.24. In electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V, two types of indicators are used: double-pole and single-pole.
Bipolar indicators that operate when active current flows are designed for electrical installations of alternating and direct current.
Single-pole indicators operating when capacitive current flows are intended for electrical installations with alternating current only.
The use of two-pole indicators is preferable.
The use of test lamps to check the absence of voltage is not allowed.
2.4.25. Bipolar indicators consist of two housings made of electrical insulating material, containing elements that react to the presence of voltage on the controlled live parts, and elements of light and (or) sound indication. The housings are connected to each other by a flexible wire at least 1 m long. At the points of entry into the housings, the connecting wire must have shock-absorbing bushings or thickened insulation.
Case sizes are not standardized and are determined by ease of use.
Each body of a two-pole indicator must have a rigidly fixed tip electrode, the length of the non-insulated part of which should not exceed 7 mm, except for indicators for overhead lines, in which the length of the non-insulated part of the tip electrodes is determined by technical conditions.
2.4.26. A single-pole indicator has one housing made of electrical insulating material, which houses all elements of the indicator. In addition to the electrode tip that meets the requirements of clause 2.4.25, there must be an electrode on the end or side of the body for contact with the operator’s hand.
The dimensions of the case are not standardized; they are determined by ease of use.
2.4.27. The indication voltage of the indicators should be no more than 50 V.
We advise you to study Electrolytic capacitor
Indication of the presence of voltage can be stepped, supplied in the form of a digital signal, etc.
Light and sound signals may be continuous or intermittent and must be reliably recognizable.
For indicators with a pulse signal, the indication voltage is the voltage at which the interval between pulses does not exceed 1.0 s.
2.4.28. Voltage indicators up to 1000 V can also perform additional functions: checking the integrity of electrical circuits, identifying phase wires, determining polarity in DC circuits, etc. In this case, the pointers should not contain switching elements intended for switching operating modes.
Expanding the functionality of the indicator should not reduce the safety of operations to determine the presence or absence of voltage.
Passive screwdriver - voltage indicator
The only function of such an indicator is to determine the voltage on a section of electrical wiring or equipment contacts. The standard index consists of two working parts. One of them is a flat-head screwdriver that makes direct contact with live parts. The second part is built into the screwdriver handle and creates the necessary resistance.
You can understand how to use the indicator using the example of a regular electrical outlet to which the phase and neutral conductors are connected. To determine the accessory, you need to press the contact located at the top of the handle with your thumb. After this, you need to touch the socket contacts with the working part of the screwdriver one by one. There is voltage on one of them, which will be immediately signaled by the indicator, lighting up orange or red inside the screwdriver. There will be no reaction to touching the neutral wire.
Use of control devices
Before each use, the indicator is inspected for damage to the housing or insulation, after which the functionality of the indicator is checked by touching a phase that is known to be energized. A defective device will cause an error resulting in a short circuit or personal injury. When taking measurements, you must be careful and follow the basic rules:
- the indicator must correspond to the network parameters - it would be useful to verify this by looking at the markings on the device body;
- during the check, take a stable position, excluding unexpected falls and contact with grounded conductors;
- One way to avoid unwanted contact is to keep your free hand in your pocket so you don't accidentally create a closed circuit for electrical charge.
When working with a single-pole indicator, it is prohibited to use dielectric gloves: contact of the plate on the indicator handle with the operator’s finger must be ensured. We must remember that electricity is dangerous - not only beginners, but also experienced installers die from mistakes.
You might be interested in the material from which the artificial ground electrode should be made
Indicator screwdriver with advanced functions
This device is also equipped with a light indication and can be used in contact and non-contact versions. Both methods allow you to determine the presence or absence of normal or low voltage in the area being tested. In addition, the device makes it possible to check the condition of the circuit and its individual elements - fuses, cables and wires.
The index is divided into two main components. One of them is made in the form of a flat screwdriver that is in direct contact with the elements being tested. The second part is used to perform a non-contact voltage test. Both parts, complementing each other, make it possible to determine the integrity of the electrical circuit.
The LED electronic indicator is located in the handle made of transparent dielectric material. If there is a phase, a light signal is given. The batteries are also located here and serve as a power source.
Determination of phase and zero is carried out according to the same scheme as with a conventional indicator screwdriver. That is, the tip of the tool alternately touches the contacts. The presence of a phase wire is confirmed by a lit indicator. Non-contact testing is performed using the upper working part. In this case, the tool must be correctly held in the hand by the middle of the handle and not touch the lower working part. Failure to comply with this rule will lead to a transition to the dialing mode and the signal about the presence of a phase wire will be false.
The upper part of the indicator screwdriver is brought to the insulating coating of the conductor without touching its surface. The presence of a phase will begin to be detected as the pointer approaches the area being tested, and the indicator will give a light signal. The integrity of the conductors is determined by testing. This operation is performed in the complete absence of voltage in the network.
The check itself is performed in the following order:
- Protective gloves must be removed and the upper working part of the device should be pressed with the finger of one hand.
- Use the tip of the indicator to touch the wire core at one end. With your other hand you need to touch the second end of the conductor.
- The activation of the indicator light indicates the integrity of the core being tested. If the probe does not work, then the core has damage, most likely a complete break. This method can be used not only for wires, but also for fuses.
Voltage indicators up to 1000 V
Purpose, principle of operation and design
22. In electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V, two types of indicators are used: double-pole and single-pole.
Bipolar indicators that operate when active current flows are designed for electrical installations of alternating and direct current.
Single-pole indicators operating when capacitive current flows are intended for electrical installations with alternating current only.
The use of two-pole indicators is preferable.
The use of test lamps to check the absence of voltage is not allowed.
23. Two-pole indicators consist of two housings made of electrical insulating material, containing elements that react to the presence of voltage on the controlled live parts, and elements of light and (or) sound indication. The housings are connected to each other by a flexible wire at least 1 m long. At the points of entry into the housings, the connecting wire must have shock-absorbing bushings or thickened insulation.
Case sizes are not standardized and are determined by ease of use.
Each body of a two-pole indicator must have a rigidly fixed tip electrode, the length of the non-insulated part of which should not exceed 7 mm, except for indicators for overhead lines, in which the length of the non-insulated part of the tip electrodes is determined by technical conditions.
We advise you to study the Cable Tester
24. A single-pole indicator has one body made of electrical insulating material, which houses all elements of the indicator. In addition to the electrode tip that meets the requirements of clause 2.4.25, there must be an electrode on the end or side of the housing for contact with the operator’s hand.
The dimensions of the case are not standardized; they are determined by ease of use.
25. The indicator indication voltage should be no more than 50 V.
Light and sound signals may be continuous or intermittent and must be reliably recognizable.
26. Voltage indicators up to 1000 V can also perform additional functions: checking the integrity of electrical circuits, identifying phase wires, determining polarity in DC circuits, etc. In this case, the pointers should not contain switching elements intended for switching operating modes.
Expanding the functionality of the indicator should not reduce the safety of operations to determine the presence or absence of voltage.
Performance tests
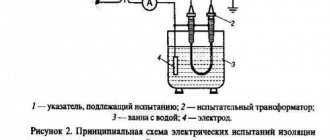
27. Electrical tests of voltage indicators up to 1000 V consist of an insulation test, determination of the indication voltage, checking the operation of the indicator at an increased test voltage, checking the current flowing through the indicator at the highest operating voltage of the indicator.
If necessary, the indication voltage in DC circuits is also checked, as well as the correct polarity indication.
The voltage gradually increases from zero, while the values of the indication voltage and the current flowing through the indicator at the highest operating voltage of the indicator are recorded, after which the indicator is turned on for 1 minute. maintained at an increased test voltage, exceeding the highest operating voltage of the pointer by 10%.
28. When testing indicators (except for insulation testing), the voltage from the test installation is applied between the tip electrodes (for double-pole indicators) or between the tip electrode and the electrode on the end or side of the body (for single-pole indicators).
29. When testing the insulation of two-pole indicators, both housings are wrapped in foil, and the connecting wire is lowered into a vessel with water at a temperature of (25 +/- 15) °C so that the water covers the wire, not reaching the handles of the housings by 8 - 12 mm. One wire from the testing installation is connected to the electrode tips, the second, grounded, is connected to the foil and lowered into water.
For single-pole indicators, the body is wrapped in foil along the entire length to the limiting stop. A gap of at least 10 mm is left between the foil and the contact on the end (side) part of the housing. One wire from the test setup is connected to the tip electrode, the other to the foil.
30. The standards and frequency of operational tests of indicators are given in the table.
Digital indicator with advanced features
Indicators of this type do not have any power sources. Approximately in the middle of the case there is a liquid crystal display in the form of a rectangular window. This screen displays the established digital range of voltage values - 12, 36, 55, 110 and 220 V.
The digital voltage indicator is equipped with two pole buttons. One of them is used for non-contact measurements, the other for contact measurements. The working part is made in the standard version and is a flat-head screwdriver.
Results of digital indicator testing carried out on a disconnected circuit breaker
Based on the results of the performance check, the following was revealed:
- First, the working part came into contact with the zero contact. An insignificant voltage indicator appeared on the screen, although this is only possible when the load is turned on. In this case, the display had to remain clean.
- Upon contact with the phase wire, the tester gave two values. The first, 110 volts, was clearly displayed, but the second, 220 V, was barely visible on the screen, although it is precisely the real indicator.
- The claimed contactless mode did not work, although without pressing the corresponding button, a poorly visible lightning bolt icon appeared on the screen. Thus, the voltage was still determined using a non-contact method that was not reflected in the product data sheet.
Despite the large number of declared functions, in general the pointer proved to be not entirely reliable in operation. The resulting values are displayed only approximately, and the contactless method practically does not work. Perhaps the whole point is the lack of its own power sources that could maintain the operation of the device at the proper level. Disadvantages also include the limited temperature range and the upper limit of the measured voltage, which is 250 V.
General information about indicators
Ammeters, voltmeters and other modular measuring equipment are presented in a wide range by domestic manufacturers and foreign companies. These devices are powered by the mains voltage, which they measure and control.
The most widely used are various types of modern digital indicators that display the received data on a special display. They perfectly withstand vibration, shaking, shock and other mechanical influences. Devices of this type are not affected by temperature fluctuations and pressure changes. Compared to pointer equipment, digital meters can operate in any position, providing accurate data on the measured parameters.
The appearance of single- and three-phase devices is almost the same. All components of the circuit are placed in a durable plastic case, which is marked with all the necessary data. Installation is carried out on a DIN rail - a special metal profile, 35 mm wide. Depending on the layout, 1-3 modules with a standard width of 17.5 to 18 mm can be located on a DIN rail. Control is carried out via a built-in microcontroller.
The temperature range at which the equipment can operate normally is -25C – +60C. More accurate data is indicated in the technical data sheet of the device. The power terminals are located on the front side and are designed to connect conductors with a diameter of 0.5-4.0 mm. The range of measured values depends on the design of the device, and the error is indicated on its body and in the instruction manual.
Indicator with sound signals
This modification of the voltage indicator, in addition to the above functions, is equipped with an audible alarm. Due to this, electrical safety during testing activities is significantly increased.
An audible alarm will only sound in non-contact mode when voltage is detected. At the same time, the green indicator light lights up. When the device operates in contact mode, no sound is produced, but is indicated only by a red indicator. Consequently, the device has two different-colored signal lights.
Selecting and installing meters
When choosing a measuring device, you need to pay attention to the following technical characteristics:
- Minimum and maximum limits of measured values.
- Degree of permissible error in %.
- Temperature range within which normal operation is possible.
- Degree of protection against short circuits and power surges.
- The amount of power consumed by the device itself.
The service life of modern measuring devices is set by manufacturers to be at least 8 years. You should also pay attention to the storage conditions of the device. It is recommended to select modular equipment from one manufacturer; in this case, there will be no compatibility problems.
In electrical panels of apartments or offices, installation of devices is carried out as follows: for a single-phase network, one voltmeter is enough; for a three-phase network, an additional ammeter is required. It is best to install the combination devices required for each phase.
Installation of measuring equipment is carried out in the following order:
- The mains voltage is completely turned off.
- The voltage indicator is mounted on a DIN rail.
- The wires are brought to the terminals in accordance with the connection diagram and secured.
- Power is supplied to the network again.
- Checking the functionality of the device: an indication should appear on the digital display.
After installation, the device will begin to display the mains voltage value in real time. However, such devices do not at all provide protection for household appliances and equipment in cases where performance indicators deviate from the norm. Full protection is possible using single- or three-phase voltage relays and other special devices. They can be installed separately or included in the design of a combined indicator.