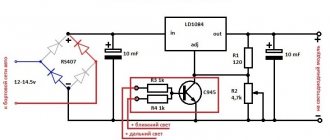
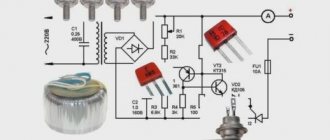
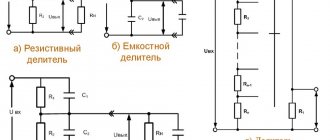
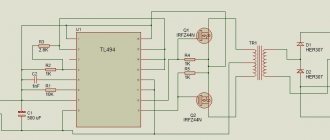
In modern household networks, a huge number of appliances and devices are powered by reduced voltage. As a rule, these are low-current devices that use 12 volts in their power circuit: gas heaters, hand-held power tools, portable and stationary lamps, children's toys and much more.
Due to their widespread use, ordinary people try to organize power for such devices on their own, so in this article we will look at how to get 12 Volts in various ways.
We get 12 Volts from 220
The most affordable power source with a practically unlimited power resource is a household AC voltage of 220 Volts. All that is needed to obtain 12 Volts is to lower, and, if necessary, convert the existing electrical quantity into a constant.
To do this, you can use one of several methods:
- using a transformer for step-down and a diode bridge for further rectification;
- using a quenching capacitor;
- without a transformer - using a resistor or semiconductor device.
Now let's look at each of the methods in more detail.
Method without transformer
If there is no transformer that could lower the network voltage to 12 Volts, you can get by with a regular resistor. The fact is that the voltage drop across a resistor connected in series to a load of 208 Volts will provide 12 Volts on the desired device, provided that the network is 220 Volts.
If the network voltage differs significantly, then the universal formula for calculating the value of the additional resistor will look like this:
R1 = Uc / I - Rн
Where
- R1 – resistance of additional resistor;
- RН – load resistance;
- I – current in the resistor and load circuit (you can take the passport value);
- UC – network voltage.
This method to get 12 Volts cannot be called justified, since the voltage drop across the resistor will lead to power consumption and additional energy costs. Therefore, another option for lowering the voltage level is to use thyristor or triac regulation. An example of such a scheme is shown in the figure below:
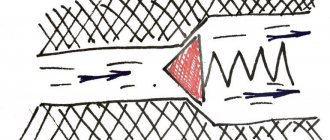
Reducing voltage using a triac
Here is a current-limiting circuit with capacitor C1 and resistors R1 and R2, which determine the time of charging the capacitance and sending a pulse through dinistor VS1 to the control electrode of triac VS2. This is a classic option for controlling the output voltage, which is often used in dimmers.
Using a Quenching Capacitor
In addition to the above methods, to get 12 Volts, you can use a circuit with a quenching capacitor.
Reducing voltage using a quenching capacitor
The figure above shows an example with two quenching capacitors C1 and C2, here both capacitors are designed to reduce the alternating voltage coming from the network. The time it takes to charge the capacitor significantly reduces the duration of the half-cycle supplied to bridge VD1. Next, the electrical quantity is transmitted through the stabilizing resistor R3, capacitors C3 and C6 to the linear converter D1. Then, voltage is supplied from the converter through capacitors C4 and C5 to the powered device.
Circuit with transformer
The most common option for lowering the mains voltage to get 12 volts is to use a transformer. For this, a special electrical machine with appropriate parameters for input and output voltage is used.
Stepping down voltage using a transformer
As you can see, a network voltage of 220 Volts is supplied to the high side of the transformer windings. Next, the reduced voltage is alternately supplied in half waves to the input terminals of the diode bridge VD1 - VD4. From the diode bridge, a constant voltage is supplied to the load through filter capacitor C.
This is the simplest version of the circuit with a step-down transformer, but if constant use is necessary, the device can be supplemented with functional elements - a variable resistor or stabilizer.
>>>> Ideas for life | NOVATE.RU
When all of the above is done, install the brushes. Assembling the drill motor. The functionality of the unit can be checked by connecting a 12 Volt battery. If the design works, we carry out final assembly. Don't forget to connect the drill button. It is important to understand that after such processing, the drill will seriously lose power, but it will still be possible to drill, screw and unscrew.
Source
Sine wave shape
Pure sine and modified sine wave
Some readers ask the question, which sine wave at the output of the 12V 220V inverter is better, rectangular or pure sine wave? Due to the nature of the conversion, the simplest thing is to obtain alternating current with rectangular pulses with a frequency of 50 Hz. Of course, this is not a natural sine wave like in a home network. Modern PWM controllers can make a shape that is almost natural, but consisting of short pulses, the so-called pure sine wave. Not every electrical appliance can operate correctly on a square sine. Electric motors, refrigerators, and microwave ovens refuse to work properly.
We advise you to study the Simple laboratory power supply on lm317
Indicators for additional control
A pure sine wave in a 12-220V auto-inverter is preferable; all electrical appliances are designed for it, but these are much more expensive. The modified sine wave causes the circuits to operate abnormally. The heating of radio-electronic parts increases, the chokes begin to make noise. Similar results can be obtained if you dim an LED lamp that does not support brightness adjustment. At 160V, the LED lamp begins to flicker and crackle loudly.
Modifications for alarm systems
Low power inverters are used for alarm systems. The overload parameter of the converters is no more than 30 A. If we consider a 12 to 220 by 500 W inverter, then the efficiency of the devices, as a rule, does not exceed 70%. Many modifications are sold with impulse protection systems. The average voltage indicator is 10 V. Connecting devices of this type is very simple.
The threshold frequency of the converters does not exceed 50 Hz. If we consider a 12 V 220 by 600 W inverter, then it is sold with a linear sensor. First of all, the device allows you to solve problems with network congestion. The inverter also helps cope with interference. The overcharge protection system is not installed in all modifications. The output voltage parameter of the models is 220 V. At the same time, the limiting frequency of the converter fluctuates around 30 Hz.
We advise you to study Splan - a program for drawing electrical and electronic circuitsAdvantages of Porto
The specified inverter 12-220 5 kW is produced with a protective housing. You can find it in cars of various brands. The case in this case is made of aluminum, so it does not weigh much. The protection system is used with one filter. The output voltage of the converter is 220 V
It is also important to note that the minimum permissible temperature of the inverter is about -20 degrees. The threshold frequency of the converter is at 55 Hz
We advise you to study the Charger for lithium batteries
The device does not have an overload protection system. The input voltage of the modification is 12 V. The efficiency of the device is low. The model is well suited for heating systems.
Main characteristics of converters
The system, consisting of an inverter and batteries, is uninterruptible. When there is a power outage, the devices will receive energy through the converter.
All devices of this type have the following characteristics:
- Rated power (watts).
- Output waveform.
- Operating efficiency (%).
- Type of cooling – active (air or water), passive (radiator).
- Current consumption (amps).
- Type of short circuit protection (mechanical, electronic).
- Minimum and nominal permissible levels of alternating voltage at the output of the converter and direct voltage at its input.
When purchasing, you should pay attention to only two main values:
- inverter power;
- output signal shape.
The choice of converter device must be made taking into account the connected load. A number of devices at the moment of startup consume power many times higher than the nominal value. These include some models of pumps, air conditioners, and refrigerators. This feature should be taken into account when purchasing a device.
To determine this parameter, you need to add up the power of all electrical appliances that will be used. Then buy a PN that is 20% more powerful than the amount received.
It is better to choose expensive devices. All parameters are strictly maintained in them. For budget models, the signal shape is far from a sinusoid, and the numerical value of the power indicated on the case or in the passport may be overestimated.
When purchasing, you need to pay attention to the power.