Types of operating current systems
The following operational current systems at substations are distinguished:
1) direct operating current - a rechargeable battery (AB) with chargers (CHD) is used as a power source;
2) alternating operating current - measuring current transformers, voltage transformers, auxiliary transformers, pre-charged capacitors are used as power sources;
3) rectified operational current - sources - power supplies and rectifier power devices, pre-charged capacitors;
4) mixed operating current system – a combination of the above systems is used.
Operating current sources
Operational current is the current that supplies remote control circuits, operational circuits of relay protection, automation, telemechanics and various types of alarm systems.
Operating current sources are divided into dependent and independent. Division by function depending on the operating mode and state of the primary circuits of the installation:
– independent – batteries 110, 220, 24 and 48 V; diesel generators, turbojet units,
– dependent – asynchronous motors, current generators, current transformers, voltage transformers, auxiliary transformers (TSN).
The power supply of operational circuits and especially those of its elements on which the disconnection of damaged areas depends must be particularly reliable. Therefore, the main requirement that operative current sources must meet is that during a short circuit and during emergency conditions in the network, the operative current voltage and its power are of sufficient magnitude both for the operation of auxiliary protection and automation relays, and for the reliable shutdown of the corresponding switch.
The following operative current systems are used at substations: direct and alternating current, rectified operative current, mixed operative current system [8].
Constant operating current.
SK type rechargeable batteries with a voltage of 110 - 220 V without an element switch, operating in constant recharge mode, are used as a source of direct current. At small substations, batteries with a voltage of 24 - 48 V are used, from which the operational circuits of all connections are centrally supplied. To increase reliability, the DC network is sectioned into several sections that are independently powered from the battery busbars.
The most responsible consumers are protection circuits, automation and trip coils of switch drives, which are powered by control circuit breakers (
, then the circuits of switching coils, powered from separate buses ( ) due to the large currents consumed by the switching coils of oil switches, then a section of alarm circuits), visual and audible. Other consumers (emergency lighting, engines, etc.) are supplied via separate lines.
Rechargeable batteries provide power to operational circuits at any time with the required level of voltage and power, regardless of the state of the main circuit and are therefore the most reliable power source. At the same time, this is an expensive source; charging units, special premises, and qualified personnel are required. Due to the centralization of power, complex, long, expensive DC circuits are created.
Alternating operating current.
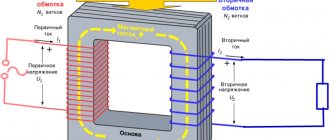
AC current or voltage is used to power operating circuits with alternating current. In accordance with this source of alternating operating current, current transformers, voltage transformers, and auxiliary transformers (TSN) serve. They are cheap, do not require special premises and have individuality, eliminating the need for a developed chain. The negative is the lack of versatility; they can only be used for certain types of short circuits.
Current transformers are the most reliable source of power for operational circuits for short circuit protection. During short circuits, the current and voltage at the terminals of the current transformer increase, therefore, at the moment the protection is triggered, the active power of the current transformer increases, which ensures reliable power supply to the protection circuits. However, in case of damage and operating modes that are not accompanied by an increase in current on the protected element (ground fault in circuits with an isolated neutral, operation of gas protection, etc.), they cannot be used as sources of operational current.
Voltage transformers, TSN are used as sources of operational current for signaling single-phase short circuits to ground in networks with an isolated neutral, for overload protection, i.e. when the voltage is not zero. TSN, if powered not from the substation buses, but from the supply line, can provide any protection against short circuits on the substation buses. If a capacitor is charged through TSN, then any short circuit protection can be provided if the closing contact of the KA current relay discharges the capacitor to the trip coil of the circuit breaker drive. By selecting the parameters of the circuit, it is possible to provide any value of the shutdown current and duration of action.
Universal power supplies for operational current circuits are BPT and BPN (current and voltage circuits). The main thing is to ensure the voltage and power of the control circuit of the switches, therefore, for switches with an electromagnetic drive, it is necessary to pay attention to the values of the switching currents of the drive electromagnets or use switches with a spring or pneumatic drive, varying the powers of different sources.
In order to ensure switching operations are carried out in the absence of voltage on the buses, transformers supplying the protection circuits are connected to the lines supplying the substations, or mechanical drives are installed on the switches, operating due to the energy of a raised load or a compressed spring, i.e. Each source has its own area of application. The main requirement is for the power of the source; it must be greater than the power consumed by the operational circuits. The greatest difficulties in this regard arise when using voltage and current transformers, but since turning on and off the circuit breaker is a short-term operation, it is possible to significantly overload the instrument transformers without damaging them.
Rectified operative current
is a system for powering operational circuits with alternating current, in which alternating current is converted into direct current (rectified) using power supplies and rectifying power devices. Pre-charged capacitors can be used as additional pulsed power sources. For rectified alternating current the following are used:
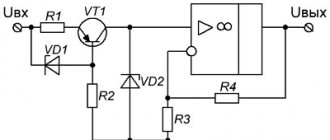
· stabilized power supplies of the BPNS-2 type, together with current relays BPT-1002 for powering protection, automation, and control circuits;
· power supplies BPN-1002 instead of BPNS-2 - for powering protection, automation, and control circuits, when the possibility of their use is confirmed by calculation and stabilization of the operating voltage is not required;
· PM power rectifier devices on UKP and UKPK with inductive storage for powering switching electromagnetic drives of oil switches. The inductive storage ensures that the switch is turned on in the event of a short circuit with dependent power supply to the switching circuits.
Mixed operating current system.
To power operational circuits, different operational current systems are used (direct and rectified, alternating and rectified). A mixed system of direct and rectified operating current is used to reduce the battery capacity through the use of power rectifier devices to power the electromagnets for turning on oil switches. A mixed system of alternating and rectified operating current is used:
· for substations with alternating operating current when installing switches with an electromagnetic drive at the power inputs, to power the switching electromagnets of which power rectifier devices are installed;
· for 35-220 kV substations without circuit breakers on the high voltage side, when reliable operation of protection from power supplies during three-phase short circuits on the medium or low voltage side is not ensured.
The considered power options are simple and sufficiently reliable.
Source
Purpose
Direct operating current is used at distribution points (DP) 6(10) kV, as well as at all substations 35 kV and above at newly installed facilities [1].
Alternating operating current is used at distribution points (DP) 6(10) kV, at existing substations 35/6(10) kV, and substation 35-220 kV without circuit breakers on the high voltage side.
Rectified operational current is used at existing 35/6(10) kV substations, and 35-220 kV substation without circuit breakers on the high voltage side.
Thus, the most promising at the moment is the operational direct current system, despite the fact that its use requires the installation of rechargeable batteries (AB), which increases the cost of the structure and necessitates the organization of a direct current network.
Substation operating current sources
Operating current is used to power control, automation, alarm and protection circuits. There are three main types of operating current: alternating, direct and rectified. Sources of alternating operating current are current and voltage measuring transformers, as well as auxiliary transformers (TSN). Rechargeable batteries serve as sources of constant operating current. As sources of rectified operational current, rectifier units and special power supplies are used, which receive alternating current from current and voltage measuring transformers and TSN. In addition, pre-charged capacitors are used as sources of operating current. Operating current sources must be constantly ready for action in any operating mode of the electrical installation, including emergency. Direct operating current is usually used at power plants, traction substations, large transformer substations with a primary voltage of 110 kV and higher. Alternating current is used in transformer substations with voltages of 35 kV and below, in small substations of 110 kV without circuit breakers on the high voltage side, having circuit breakers with spring drives on the medium and low voltage side. Rectified current is used at substations with a voltage of 35 kV and below with switches equipped with electromagnetic drives, as well as at substations with a voltage of 110-220 kV with the number of switches on the higher voltage side of no more than two with an electromagnetic drive, or no more than three with spring or pneumatic drives. In some cases, power supply circuits for operational circuits are used using various current sources. So, for example, when the power of the battery is low, the control and protection circuits are powered from it, and the switching electromagnets are supplied from rectifier devices. The most reliable sources of alternating operational current for the operation of protections are current transformers, which ensure their smooth operation during overloads and short circuits. Voltage transformers cannot be used to power operational shutdown circuits, since in the event of close three-phase short circuits, the voltage on the busbars of the electrical installation may drop so much that the tripping coil of the circuit breaker drive will not operate. For this reason, voltage transformers are used to power those protections that operate in conditions that are not associated with a significant decrease in bus voltage. Devices and circuits that do not require special stability of the supplied voltage and allow temporary interruptions in the power supply (for example, electric motors of spring drives) receive power from the TSN. Rectified current sources can be divided into three main groups: sources for charging and recharging batteries; operational current sources for powering control, protection, automation and alarm circuits; power supplies for turning on electromagnets of switch drives. Sources of rectified current should also include capacitors pre-charged from rectifiers. Power supplies in use can be divided into four groups: current (BPT); voltage (BPN); chargers (UZ); combined, combining power supplies and chargers. In Fig. 1, a shows a schematic diagram of the power supply of operational circuits from the BPT and BPN units. The BPT unit consists of an intermediate transformer TLy rectifier bridge K5, auxiliary elements - inductor L and capacitor C, which ensure stabilization of the output voltage. The BPT receives power from a current transformer. Transformer TL
Composition of SOPT
In general, an operational direct current system consists of the following components:
- Rechargeable batteries (AB) are the main element of SOPT with a voltage of 110 or 220 V, consisting of batteries - chemical energy sources that allow multiple charges and discharges.
- Charger (charger).
- DC switchgear (DCB) is a complete low-voltage cabinet-style switchgear designed for connecting power sources (AB and charger) and distributing DC electricity among groups of electrical receivers.
- Operating current distribution cabinets (OCC) - are designed for distributing electricity along the power supply circuits of final power receivers, placing switching and protective disconnecting devices. SHROT must have power inputs from different sections of the same switchboard.
An operational direct current system can have a centralized or decentralized structure. In a decentralized COPT, two or more galvanically isolated sets of direct current sources are used to provide power to individual groups of electrical receivers; in a centralized one, one is used.
Scope of application of SOPT
At substations of 35 kV and above, as a rule, a centralized (general substation) operational direct current system should be used. When locating relay protection and automation systems for substation connections in separate distribution switchboards close to the primary equipment, it is necessary to consider the feasibility of using a decentralized COPT system, consisting of galvanically unconnected batteries located in control centers and distribution switchboard buildings.
At substations with a voltage of 220 kV and higher, substation 110 kV with 3 or more switches, as a rule, two batteries are used in the HV switchgear. At a substation with a voltage of 35 kV and other substations with a voltage of 110 kV - one battery.