Where does consumer food come from?
Sources of electrical energy receive voltage after converting the force of wind, kinetic movement, water flow, the result of a nuclear reaction, heat from the combustion of gas, fuel or coal. Thermal power plants and hydroelectric power plants are widespread. The number of nuclear power plants is gradually being reduced as they are not entirely safe for people living nearby.
A chemical reaction can be used; we observe these phenomena in the batteries of cars and household appliances. Phone batteries work on the same principle. Wind turbines are used in places with constant wind, where electrical energy sources contain a conventional high-power generator in their design.
Sometimes one station is not enough to power an entire city, and sources of electrical energy are combined. Thus, solar panels are installed on the roofs of houses in warm countries, which power individual rooms. Gradually, environmentally friendly sources will replace stations that pollute the atmosphere.
Operating principle
Each marking of current sources determines the principle of its operation. In a standard situation, energy is generated through the interaction of component parts, namely:
- Mechanical type. As a result of the interaction of mechanism parts, friction occurs. Due to this phenomenon, static electricity arises and is converted into current.
- Mechanical structures work by producing sequentially moving charged particles. The phenomenon occurs due to the interaction of a chemical element with an electrolyte. Charged particles leave the structure of the metal crystal lattice, becoming part of the conducting liquid.
- Solar batteries (light sources) work by knocking out charged particles from a dielectric (silicon) base under the influence of a light flux. This creates constant tension.
- Thermal. As a rule, these are 2 metal bases connected in series. One part heats up, while the other remains cooled. When the temperature regime changes, a temperature difference occurs, resulting in the movement of charged particles.
You may be interested in Reactive and active resistance
Important! Any change in the structure of a substance can lead to irreversible consequences that will manifest themselves during the operation of the device.
In cars
The battery in transport is not the only source of electrical energy. The car's circuits are designed in such a way that when driving, the process of converting kinetic energy into electrical energy begins. This occurs thanks to a generator in which the rotation of coils within a magnetic field generates an electromotive force (EMF).
A current begins to flow in the network, charging the battery, the duration of which depends on its capacity. Charging begins immediately after the engine starts. That is, energy is generated by burning fuel. Recent developments in the automotive industry have made it possible to use the EMF of an electrical energy source for vehicle movement.
In electric vehicles, powerful chemical batteries produce current in a closed circuit and serve as a power source. Here the reverse process is observed: EMF is generated in the coils of the drive system, which causes the wheels to spin. The currents in the secondary circuit are huge, proportional to the acceleration speed and weight of the car.
Types of sources
There are several types of devices for generating current, each of which has its own main indicators, characteristics and features, listed in the following table:
| Source type | Current source characteristics |
| Mechanical | A special device (generator) ensures the transformation of mechanical energy into electrical energy. Currently, a large amount of current is produced using mechanical sources. |
| Thermal | The operation of the units is based on the principle of converting thermal energy into electrical energy. This transformation occurs due to the temperature difference between the semiconductors in contact with each other. Currently, current sources have been developed in which thermal energy is generated due to the decay of radioactive elements. |
| Chemical | Chemical options can be divided into 3 groups - galvanic, batteries and thermal. · A galvanic cell works through the interaction of 2 different metals placed in an electrolyte. · Batteries are devices that can be charged and discharged several times. There are several types of batteries with different types of cells included in their composition. · Chemical-thermal ones are used only for short-term work. They are mainly used in the field of rocketry. |
| Light | At the end of the 20th century, solar panels became quite popular, which “collect” light particles, which are subsequently converted into electrical energy. This occurs due to the output of voltage and due to the effect on light particles. |
You may be interested in this How to calculate the resistance of a conductor
Important! Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are determined by the principle of use, as well as the initial indicators of the generated energy.
Mechanical sources
Mechanical units are the simplest in terms of their use and arrangement. The characteristics of such generators are very easy to understand. Special devices generate energy, which is subsequently converted into electricity. Such devices are used in thermal power plants and hydroelectric power plants.
Mechanical
Heat sources
Thermal source options provide a unique operating principle. Energy is generated through the formation of a thermocouple, which... This means that a calculated temperature difference is provided at the ends of the conductors, the elements interact with each other, creating an electric field.
Thermal
Note ! Radioactive thermocouples are used in the space industry. The effectiveness of such use is possible due to the long service life and efficient power output.
As a result of this movement of charged particles from the hot part of the conductor to the cold part, an electric current arises. Moreover, the greater the temperature difference, the higher the effective energy indicator. In practice, thermocouples are often included in measuring instruments.
Light sources
Lighting devices for generating electricity are considered the most environmentally friendly, efficient and relatively cheap. A special panel of semiconductors absorbs light particles, which during such interaction produce a certain voltage.
Light
At the same time, light panels have a low efficiency rate of 15%. Panels of this type have found wide application - from household appliances to innovative developments in the space industry.
Important! Light sources began to be used instead of lithium batteries due to the high cost of the latter. Despite the fact that many industrial facilities require significant re-equipment to switch to light sources, the final savings occur already in the initial stages of operation.
Chemical sources
This group includes 3 main devices that differ in structure and operating principle:
- A voltaic cell is an option for generating electricity that can be used once. That is, after complete discharge, re-accumulation of charge on the internal substance is impossible. Such devices include salt, lithium or alkaline batteries.
- Batteries are divided into several types: lead-acid, lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium.
- Thermal elements - used in the space and innovation industries to produce short-term current with high performance. The practical application of the units is based on the need for backup power sources.
You might be interested in How a capacitor is charged
Important! Chemical-thermal devices require initial heating to 500–600 °C to activate the solid electrolyte.
Chemical
Each industry uses its own version with specific parameters. In domestic conditions, batteries are mainly used; in production - batteries.
The principle of operation of a coil with a magnet
The current flowing through the coil causes an alternating magnetic flux to appear. This, in turn, exerts a buoyant force on the magnets, which causes the frame with two oppositely polar magnets to rotate. Thus, sources of electrical energy serve as a hub for vehicle movement.
The reverse process, when the frame with a magnet rotates inside the windings, due to kinetic energy, allows the alternating magnetic flux to be converted into the EMF of the coils. Further in the circuit, voltage stabilizers are installed to ensure the required performance of the supply network. According to this principle, electricity is generated in hydroelectric power plants and thermal power plants.
EMF in a circuit also appears in an ordinary closed circuit. It exists as long as a potential difference is applied to the conductor. Electromotive force is needed to describe the characteristics of an energy source. The physical definition of the term is as follows: EMF in a closed circuit is proportional to the work of external forces that move a single positive charge through the entire body of the conductor.
Formula E = I*R - resistance takes into account the total resistance, which is the sum of the internal resistance of the power source and the results of adding the resistance of the fed section of the circuit.
Fossil fuels
Currently, three types of fossil fuels are used: coal, oil and natural gas. They account for about 90% of the world's energy. Coal. World reserves of all types of coal are estimated at 13,800 billion tons, and additional potential resources at 6,650 billion tons. The geographical distribution is as follows: approximately 43% of the world’s coals are located in Russia, 29% in North America, 14.5% in Asian countries, mainly in China, and 5.5% in Europe. The rest of the world accounts for 8%.
Although coal is not the leading fuel worldwide, it is still dominant in some countries, and it is possible that future difficulties in the supply of oil and gas will lead to increased use of coal. There are many difficulties when using coal. It contains from 0.2% to 7% sulfur, present mainly in the form of pyrite FeS2, ferrous sulfate FeSO4⋅7H2O, gypsum CaSO4⋅2H2O and some organic compounds.
When coal burns, it releases oxidized sulfur, which is released into the atmosphere causing acid rain and smog. Another problem is coal mining itself. Underground mining methods are difficult and even dangerous. Open-pit mining is more efficient and less dangerous, but it causes disruption of the surface layer over a large area. In the modern world, oil and natural hydrocarbon gases are mainly used as energy sources.
Restrictions on the installation of substations
Any conductor through which current flows produces an electric field. The energy source is an emitter of electromagnetic waves. Around powerful installations, in substations or near generating sets, human health is affected. Therefore, measures have been taken to limit the construction of objects near residential buildings.
At the legislative level, fixed distances to electrical objects are established, beyond which a living organism is safe. The construction of powerful substations near houses and on people's routes is prohibited. Powerful installations must have fences and closed entrances.
High-voltage lines are mounted high above buildings and carried outside the settlements. To eliminate the influence of electromagnetic waves in residential areas, energy sources are covered with grounded metal screens. In the simplest case, a wire mesh is used.
Concepts and types
Renewable energy comes from natural sources, the resource of which is practically inexhaustible. They are able to constantly recover and replenish naturally. The peculiarity of using renewable energy is that it is obtained from natural processes and transferred to the consumer for use.
There are renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
Both types are part of the planet's natural resources. Non-renewable energy sources are represented by fossil organic reserves of various types of fuel: gas, oil, coal, peat. The rate of consumption of these resources is much faster than the rate of restoration of their volumes, so the reserves of this type of energy resources are either running out or will run out in the not too distant future. Nuclear power stands apart, but its use carries many risks for people’s lives and activities. The use of oil and coal leads to air pollution and disruption of the natural ecosystem.
Thermal power plant
The energy of these sources is obtained through targeted human actions and leads to additional heating of the environment. Recent studies show that the average temperature of the earth's biosphere is steadily increasing. This causes negative changes in the Earth's climate.
Renewable energy sources are natural sources of energy that exist in the biosphere of our planet and are constantly replenished by the energy of the sun and natural processes. They are not the result of direct human activity, which distinguishes them from non-renewable sources.
The use of renewable energy sources does not add additional energy load and does not lead to an increase in temperature on Earth. They are environmentally waste-free and do not pollute the environment.
The main advantage of renewable energy sources is inexhaustibility and environmental friendliness.
Let's look at what renewable energy sources are. According to the definition given by the UN, renewable energy sources include:
- Sun;
- wind;
- sea and ocean tides and waves;
- underground hot springs,
- hydropower resources of large and small rivers.
- biomass products.
Traditional and non-traditional renewable sources
There are two types of renewable energy sources: traditional and non-traditional.
Let us list which renewable energy sources are considered traditional. These are sources that have long been known and actively used by humanity:
- hydroelectric power stations;
- traditional methods of burning biomass products (wood, peat) to produce thermal energy;
- geothermal springs.
Now let’s list which renewable energy sources are considered non-traditional. This group includes resources that have come into use relatively recently:
- solar stations of electric and thermal energy;
- wind generators;
- power plants operating on the energy of sea waves, currents, tides and the ocean and other new renewable energy generators.
Units
Each quantity of energy source and circuit is described by quantitative values. This simplifies the design task and load calculation for a specific power supply. Units of measurement are interconnected by physical laws.
The following units are set for power supply values:
- Resistance: R - Ohm.
- EMF: E - volt.
- Reactive and impedance: X and Z - Ohm.
- Current: I - ampere.
- Voltage: U - volt.
- Power: P - Watt.
What is a power plant
Any power plant is an entire energy complex, which includes various installations, apparatus and equipment necessary for obtaining, converting and transporting electricity. All these components are located in special buildings and structures located compactly on a common territory. Regardless of the type, they are part of the Unified Energy System, created with the aim of efficiently using the power of the power plant, ensuring uninterrupted power supply to consumers.
The operating principle of power plants and their related facilities is based on the rotation of the generator shaft, which is the main element of the system. Its main functions are as follows:
- Ensuring stable long-term operation in parallel with other energy systems, supplying energy to its own autonomous loads.
- The ability to instantly respond to the presence or absence of a load corresponding to its rating.
- Starts the engine that powers the entire station.
- Together with special devices it performs a protection function.
The distinctive features of each generator are its shape and size, as well as the energy source used to rotate the shaft. In addition to the generator, the power plant consists of turbines and boilers, transformers and switchgear, switching equipment, automation and relay protection.
Currently, the direction in the field of compact installations has been developed. They make it possible to provide energy not only to individual objects, but also to entire villages located at a considerable distance from stationary power lines. These are mainly polar stations and mining enterprises. Now let’s look at what types of installations are used in the Russian energy sector.
Construction of serial and parallel power circuits
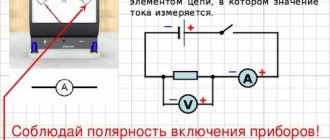
Circuit calculations become more complicated if several types of electrical energy sources are connected. The internal resistance of each branch and the direction of the current through the conductors are taken into account. To measure the EMF of each source separately, you will need to open the circuit and measure the potential directly at the terminals of the supply battery with a device - a voltmeter.
When the circuit is closed, the device will show a voltage drop that is smaller. Multiple sources are often required to obtain the necessary power. Depending on the task, several types of connections can be used:
- Consistent. The EMF of the circuit of each source is added up. So, when using two batteries with a nominal value of 2 volts, 4 V is obtained as a result of connecting.
- Parallel. This type is used to increase the source capacity; accordingly, a longer battery life is observed. The EMF of the circuit with such a connection does not change with equal battery ratings. It is important to maintain the polarity of the connection.
- Combined connections are rarely used, but they do occur in practice. The resulting EMF is calculated for each individual closed section. The polarity and direction of the branch current are taken into account.
SECONDARY POWER SOURCES
Secondary sources are connected to the primary ones and convert the received electricity into an output voltage with the required parameters of frequency, ripple, etc.
Main functions of secondary sources:
- ensuring the transmission of the required power with minimal losses;
- transformation of the voltage form (alternating voltage into direct voltage, changing the frequency, forming pulses;
- transforming the voltage value (increasing or decreasing its value, forming several values for different circuits);
- voltage stabilization (its output values must be within a given range);
- protection (so that voltage exceeding permissible values due to a malfunction does not damage the equipment or the power supply itself);
- galvanic separation of circuits.
There are two main types of secondary power sources (SPS) - transformer and pulsed.
Transformer power supply.
Transformer or linear IVP is a classic power supply. The output voltage is adjusted continuously, that is, linearly.
Its design sequentially includes:
- transformer (adjusts the voltage in one direction or another to the required value);
- rectifier (converts alternating voltage to direct voltage);
- filter (smoothes out ripples (oscillations) in the rectified voltage).
The circuit may also include short circuit protection, a high-frequency noise filter, a stabilizer, etc.
Advantages of transformer IVP:
- simplicity of design;
- galvanic isolation from the network;
- reliability in operation.
Flaws:
- large dimensions and weight, which are directly proportional to its power;
- relatively low efficiency.
In household appliances, low-power linear power supplies are used to power control boards of washing machines, microwave ovens, and heating boilers.
Pulse IVP.
The switching power supply is designed fundamentally differently and has a more complex design.
He contains:
- rectifier (the input voltage is first rectified - converted from AC to DC);
- pulse-width modulation block - PWM (converts DC voltage into pulses of a certain frequency and duty cycle);
- frequency filter (in blocks without galvanic isolation);
- transformer (in units with galvanic isolation from the network).
In pulsed secondary voltage sources, stabilization is realized through feedback, which makes it possible to maintain the output voltage at a given level regardless of changes in input parameters.
For example, in units with galvanic isolation, depending on the magnitude of the output signal, the duty cycle (the ratio of the pulse repetition rate to their duration) at the output of the PWM controller changes.
Advantages of switching power supplies:
- light weight and small size;
- high efficiency (up to 98%);
- wide range of permissible input voltage;
- built-in protection against short circuit and other force majeure;
- low price;
- The reliability is comparable to transformer power supplies.
Flaws:
- are sources of high-frequency interference that cannot be completely eliminated;
- have a limitation on the minimum load power: they do not turn on if it is lower than the required one.
Pulse sources are mobile phone chargers, power supplies for computers, office equipment, and consumer electronics.
Mains ohms
The internal resistance of the electrical energy source is taken into account to determine the resulting emf. In general, electromotive force is calculated using the formula E = I*R + I*r. Here R is the consumer resistance, and r is the internal resistance. The voltage drop is calculated using the following relationship: U = E - Ir.
The current flowing in the circuit is calculated according to Ohm's law of the complete circuit: I = E/(R + r). Internal resistance can influence the current strength. To prevent this from happening, the source is selected for the load according to the following rule: the internal resistance of the source must be much less than the total total resistance of the consumers. Then it is not necessary to take its value into account due to the small error.
Thermal power plants
Thermal power plants operate by converting the thermal energy of fuels such as oil, coal, natural gas into mechanical and then electrical energy.
The disadvantages of thermal power plants include the use of non-renewable resources. The disadvantage will also be the impact on the environment, since the chemical composition of the fuel includes carbon, which has a detrimental effect on the atmosphere, creating the so-called “greenhouse effect”. The release of heat into the hydrosphere with water will also be negative. Thermal power plants are fire-explosion and chemically hazardous objects.
How to measure Ohms of the mains supply?
Since sources and receivers of electrical energy must be matched, the question immediately arises: how to measure the internal resistance of the source? After all, an ohmmeter cannot be used to connect to contacts with the potentials present on them. To resolve the issue, an indirect method of taking indicators is used - the values of additional quantities will be required: current and voltage. The calculation is made using the formula r = U/I, where U is the voltage drop across the internal resistance, and I is the current in the circuit under load.
Voltage drop is measured directly at the power supply terminals. A resistor of a known value R is connected to the circuit. Before taking measurements, you should record the source emf with a voltmeter when the circuit is open - E. Next, connect the load and record the readings - U load. and current I.
The required voltage drop across the internal resistance is U = E − U load. As a result, we calculate the required value r = (E − U load)/I.