Definition - Power Required
We determine the required power for the construction period during which the need for electrical power is maximum. [1]
Determination of the required power of the vibrator motor should be made at the final stage of insertion of the jaws into the array of logs. [2]
To determine the required power of the transformer, the net melting time, or melting time with the furnace on, must be entered into the calculation, which is equal to the total melting time minus all downtime related to the melting process. [3]
To determine the required power of pumps, select their number and type, it is necessary to know the flow of water into the pit. The most accurate water flow can be determined by test pumping. [5]
To determine the required electric motor power, it is necessary to know the efficiency of the machine drive. [6]
To determine the required power of a charge furnace, it is necessary, in addition to the heat balance data, to know the time during which the maximum required power should be released. [7]
To determine the required power of a charge furnace, it is necessary, in addition to the heat balance data, to know the time during which the maximum required power should be released. Typically this time tnagr is equal to the heating time of the load; Simultaneously with loading, it is necessary to heat the auxiliary devices, compensate for the heat losses of the furnace, and, if necessary, heat or reheat the cooled lining. [8]
To determine the required engine power of the mixing machine, the corresponding power values are summed up, correction factors are introduced for unaccounted resistance, and losses due to overcoming resistance in the gear elements are taken into account. [9]
To determine the required power of the power plant of a loader with a group drive, it is necessary to identify the mechanisms operating simultaneously. The total power consumed by a group of such mechanisms will determine the required power of the power plant, unless other mechanisms require more power. [10]
When determining the required power of lamps, the lighting characteristics of the lamps used, methods of their placement, suspension height and relative position are taken into account. It is recommended to place luminaires at the tops of the squares to provide the best overall lighting and illumination of work areas. [eleven]
The calculation period for determining the required engine power of the hydraulic drive Yr of cyclic machines is the end of the process of filling the working element with soil and the simultaneous activation of the hydraulic drive to relieve engine overload by deepening the cutting part of the working element. [12]
Reference materials are provided for determining the required power and selecting ventilation equipment and air conditioners. [13]
Calculations usually begin with determining the required drive power, selecting an electric motor, determining the total gear ratio of the mechanism and breaking it down into stages. Then calculations of belt, chain and gear drives, couplings, screw pairs, etc. are given. In this case, it is necessary to justify the choice of materials for the corresponding parts, the type of heat treatment, permissible stresses, design coefficients, etc. It is also necessary to justify the choice of dimensions, which are established not by calculation, but by design considerations or based on recommendations from educational or reference literature. [14]
Design power (definition)
One of the main stages in the design of power supply systems for a facility is the correct determination of the expected (calculated) electrical loads of both individual electric power supply units and load nodes at all levels of the power supply system.
Load design values are loads corresponding to such a constant current load (
), which is equivalent to the actual time-varying load for the greatest thermal impact (without exceeding permissible values) on the element of the power supply system.
There are various methods for determining design electrical loads, which in turn are divided into main ones; and auxiliary.
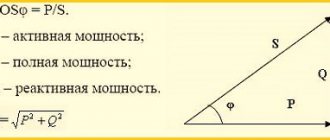
The calculated electrical loads include the calculated values of active power (
), reactive power (
), full power (
) and current (
).
How to correctly calculate power consumption
The amount of electricity consumed by household appliances, lighting, heating, air conditioning and ventilation directly affects the amount of payment for electricity. Any equipment absorbs energy in the amount of the corresponding power of the device. This important characteristic is the basis for calculating electricity consumption. How to calculate the power consumption of electrical appliances and determine the electricity consumption are questions that are answered in this article.
Electricity consumer connection:
Electrical power consumption
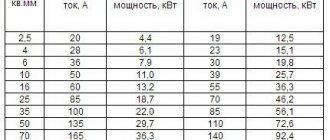
Previously, when publishing material on calculations of power consumption of household electrical appliances, we posted a table indicating the values. In this article we will try to understand other types of power and how they can influence the choice of household appliances. Let's look at the main household electrical appliances found in every home.
First, let's remember the definition of what power is. Power is a physical quantity equal to the rate of change, transmission or consumption of energy receivers. That is, power is equal to the work performed in a certain period of time for the same time period.
When purchasing electrical equipment for our home, we all look in the technical specifications at the electrical energy consumption declared by the manufacturer, which is indicated in power units of watts and kilowatts.
Example of technical characteristics of a BOSCH refrigerator:
In terms of consumption and saving of electrical energy, we are interested in two parameters: consumption class and energy consumption itself.
The energy consumption class of a number of household appliances is understood as a conditional indicator of electrical energy consumption. Why conditional? Because it depends on many external and internal factors. The three most recently accepted classes are considered the most economical - A+++, A++, A+. The more pluses to the “A” value, the more economical the consumer is.
How efficiency is achieved is through the introduction of new technologies in the production of equipment and control automation.
Speaking of energy consumption, since we started talking about refrigerators, we will continue with them.
Refrigerators
The characteristics posted above for the two-chamber BOSCH refrigerator indicate energy consumption of 383 kWh per year. Let's divide the declared consumption by twelve months. We get 31.9 kWh per month! Very good, but this is the minimum consumption value indicated when all the proper conditions are met. To put it in Russian, this is: we bought it, installed it in a warm, ventilated room, turned it on to the minimum cooling/freezing mode, and didn’t open the doors for a month.
Therefore, you should not delude yourself with the declared characteristics, but take into account the normal operating mode of the refrigerator, calculating in this case the normal monthly consumption of 60-70 kW.
The power consumption parameters of the refrigerator consist of the following conditions:
- Power declared by the manufacturer
- Dimensions of the refrigerator,
- Type and design of the heat-insulating seal,
- Availability of No Frost system,
- External equipment temperature,
- The volume of food placed in the refrigerator and freezer compartments is
- Frequency of opening the refrigerator and freezer compartments,
- Cleanliness of external ventilation openings,
- Permeability (drainage) of internal condensate channels.
Origin of the unit of measurement kilowatt/hour
The intensive study of electricity by European scientists began around the 17th century, at which time fundamental discoveries were made that marked the beginning and development of such a science as electrical engineering. Scottish engineer, mechanical inventor (1736–1819) James Watt introduced into use the first unit of power - horsepower.
Portrait of James Watt:
In 1782, the British Association of Engineers assigned the scientist's name to the unit of power meter - Watt. It must be borne in mind that in Russian the English letter “W” has a double reading, like “V” or “Ua”. Therefore, we read the name of the inventor as Watt, and the unit of measurement is Watt. In 1889, the unit of measurement gained worldwide recognition. Only in 1960, “Watt” officially entered the international SI system as a power meter for any type of energy, be it thermal, mechanical or electrical.
The energy consumption consumed over a certain period of time is measured in W/h. To reduce the number of symbols when indicating the power consumption of an electrical appliance, a unit such as kilowatt/hour - kW/h (1000 Wh) was introduced into use.
RMS power (definition)
RMS value of the active power of an individual electric unit for the considered period of time
,
Where
– root mean square value of the active power of the electrical receiver, kW;
– active power consumed by the electric device for the considered period of time
(determined from the load graph by active power), kW; – time interval for which it is determined, min, h.
If there are graphs of reactive power consumption, the root mean square value of reactive power is determined in a similar way.
Root mean square value of reactive power of electric power supply for the considered period of time
,
Where
– root mean square value of the reactive power of the electrical receiver, kVAAr;
– active power consumed by the electric power plant for the considered period of time (determined from the reactive power load graph), kVAr; – time interval for which it is determined, min, h.
In the absence of reactive power consumption schedules, the rms value of reactive power
,
Where
– corresponds to the nominal
EP (
– passport value).
Based on the known root-mean-square values of active and reactive powers, the root-mean-square values of total power and current are determined.
Root mean square value of the total power of the electric generator for the considered period of time
,
Where
– root mean square value of the total power of the electric unit, kVA.
Root mean square value of the electric current for the considered period of time
,
Where
– root-mean-square value of the electric current, A;
– rated voltage of the electrical unit, kV.
One of the natural characteristics of an electric motor is its rated (effective) power ( Pnom
), which for AC and DC machines is the mechanical power on the shaft.
This is the engine power with which it could operate in nominal mode - the mode of efficient operation for a long time (at least several hours). Rated power is measured in W (kW) or horsepower (hp) and is indicated on the electrical panel along with other main characteristics.
, engine power is fully developed. When the engine is loaded to rated power for a relatively short period of time, it can be considered that it is not being used to its full potential. In such a situation, it may be advisable to briefly overload it, the limit of which is determined by the overload power of the engine.
The manufacturer’s electric motor passport always indicates the rated power values Pnom
, voltage
Unom
, power factor
cosϕnom
, rated angular speed of the motor
ωnom
.