A fluorescent lamp or fluorescent lamp (FL, LDS) is an inert gas in a glass bulb that emits visible light.
The principle of operation of the LDS is to saturate the gas with mercury and then pass a discharge through it, resulting in the formation of UV radiation, which is converted into visible light due to the phosphor layer contained in the inner surface of the bulb. This article will discuss LDS, their description and technical characteristics.
Application area
Fluorescent light sources are in great demand in public organizations: schools, hospitals, government agencies.
With further development, the lamps were equipped with electronic ballast, and it became possible to use them in common E14 and E27 standard sockets.
LL is more relevant to use in industrial premises to provide a larger lighting perimeter with minimal energy consumption. They are also used in lighting billboards and facades.
Luminescent devices combine the characteristic features of efficient and economical use of electricity. In everyday life, ceiling and table fluorescent lamps are used for plants, work surface lighting and living rooms.
Where are fluorescent lamps used?
Varieties of forms of fluorescent lamps
Fluorescent lamps are gas-discharge types of light sources. This means that inside the flask, which represents the main massive part of the lamp body, an inert gas is pumped through which a constantly burning electric discharge passes during operation of the device.
The gas represents a medium within which a discharge will occur without any problems when the required voltage is created at the contacts. The burning discharge begins to spread a large amount of ultraviolet radiation in all directions, which passes through the layers of phosphor that cover the inner walls of the bulb.
A phosphor is a class of substances that can convert ultraviolet radiation into the visible part of the light spectrum. The composition of the phosphor varies, depending on the glow that needs to be obtained as a result. Most often, calcium halophosphate with additives is used as a phosphor.
Applications and types of fluorescent lamps
We have already mentioned low pressure lamps. It is logical that there are also options for high blood pressure.
High pressure lamp with screw base E 40
High-pressure lamps do not have the most pleasant spectrum for the human eye to perceive, but they are capable of producing a large luminous flux per unit of consumed watt of power and can operate at subzero temperatures. For this reason, these light sources are still used for street lighting and high-power installations.
Interesting to know! Until recently, high-pressure gas-discharge lamps held the lead in light output (up to 200 Lumens per Watt). Today the record is held by LEDs, which were able to exceed the 300 Lm mark. However, we note that in most cases, records were set using prototypes, and the price of such lamps in comparison with the same fluorescent lamps is simply astronomical. For this reason, gas-discharge lamps have not yet completely left us.
Phillips Low Pressure Fluorescent Lamp
GRLND (low pressure gas discharge lamps) - filled from the inside with amalgam, mercury and argon under a pressure of 400 Pa. They are widely used in various fields - household, public and industrial.
Industrial lighting
- Tubular lamps are most often used in offices, public buildings - such as schools, kindergartens, clinics, etc. They are also used in warehouses, workshops and production facilities.
Fluorescent lamps for office
- In private households, they have also found application in everyday life - lamps for lighting the garage, cellars, basements, and local areas.
Garage Lighting Lamps
- In the mid-eighties of the last century, engineers were able to combine fluorescent lamps with the common compact E14 and E 27 screw-type sockets. Since that time, the era of conquering houses and apartments with energy-saving lighting sources began. In Russia, this boom occurred approximately in 2007-2010, but it did not last long due to the fact that just at this time LEDs began to spread en masse.
Fluorescent lamp with E 27 base
- Gas-discharge lamps have become widespread in the advertising business - this is the well-known neon. These lamps, of course, do not belong to daylight sources, but still.
A variety of shades of light is achieved by changing the composition of the phosphor
- Fluorescent lamps are actively used in crop production, and there is no one to replace them 100% yet. It's all about the emitted spectrum of light, selected specifically for the desired plant.
Greenhouse lighting
- These lamps are also widely used in aquarium farming. They allow you to achieve high gloss with good light dispersion.
Illuminating the aquarium with a fluorescent lamp
More recently, fluorescent lamps were used as backlight for LCD monitors, and such TVs served well and for a long time. Your humble servant still has the LG TV he bought in 2007 and is working normally.
Now LEDs, which have less complex starting equipment and dimensions, completely reign in this area, which has made it possible to make screens very thin.
The relevance of the use of fluorescent lamps
LL has become widespread due to many advantages, namely:
- high luminous efficiency (10 W LDS provides illumination comparable to a 50 W incandescent light bulb);
- large range of shades of emitted light;
- complete diffusion of light.
The guaranteed service life of LDS is from 2 thousand hours versus 1 thousand hours for incandescent lamps.
Disadvantages of fluorescent devices:
- chemical hazard (LDS contains up to 1 g of mercury);
- uneven spectrum that is unpleasant to the human eye;
- gradual destruction of the phosphor layer, leading to a decrease in illumination;
- lamp flickering at twice the mains frequency;
- the presence of a mechanism that regulates the start;
- LL power does not provide a high coefficient.
Work principles
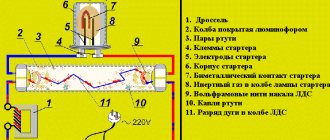
During operation of the LL, an arc-shaped discharge burns between two electrodes located at its edges, which leads to the creation of UV glow inside a flask filled with a gas containing mercury vapor.
Human vision is immune to the UV range of luminescence, therefore the inner walls of the flask are treated with a phosphor composition that has the properties of absorbing ultraviolet radiation with its further conversion into a visible white glow. Calcium-zinc orthophosphates and halophosphates form the basis of the phosphor layer. Also, the phosphor can be saturated with other substances in order to obtain a certain shade of light. Thermionic emission of electrodes from the cathode creates support for the electric arc in the LDS. Further heating of the cathodes by passing current through them or by ion bombardment causes the device to start.
Specifications
The final operation of the LDS—the required lighting—depends on the technical characteristics.
Power
The light output, which affects the illumination area, depends on the LL power indicator. Lamps of various wattages are common in implementation.
Lamps 4–6 W
Suitable for small rooms. Great for agricultural areas, guardhouses or tents. These LDS are unpretentious in terms of electricity consumption, and thanks to transformer converters, these lamps are able to operate on 12 volts, which makes it possible to start the lamp by connecting it to a car battery in conditions of no power supply. Low-power fluorescent devices are also used to illuminate plants or aquariums.
18 W
The most common LL in terms of lamp power. They can be found everywhere: in a room, car garages, offices, pavilions.
36 W
They have also become widespread. They are used in the same rooms as LL 18 W, with the difference in increasing the lighting area.
58 W and 80 W
These high-power LDS are used only in large production workshops, storage facilities and hangars, in underground areas.
Sometimes LLs of such power can be found in open areas in conditions of high light scattering. Such LLs, unlike 18 W and 36 W lamps, are more energy-consuming and their use in everyday life or office lighting is unprofitable. They are also equipped with additional fluorescent lamps, which makes their use even more irrelevant as ceiling fluorescent lamps in small areas.
Colorful temperature
Another main parameter of LDS. The quality of lighting depends on the quality of light and color temperature. These parameters are displayed as a three-digit value on the device bulb.
Value 627
Complies with devices with 60% light quality and 2700K color temperature.
Value 727
Lamps with 70% light quality and similar color temperature.
Value 765
The color temperature is 6500 K, which is what all LDS have without exception. Color quality at 70%.
It is necessary to take into account that 2700 Kelvin is the color temperature of incandescent light bulbs, and a LL with the same color temperature will emit rays perceived by human vision that are yellow. Taking into account the human perception of the color of the glow, luminescent devices of different color temperatures are manufactured.
Many compact-shaped LLs (energy-saving light sources) emit yellow light. A color temperature of 6500 is common to all linear devices and corresponds to white light with a slight blue tint. Narrow-profile luminaires with a color temperature of 1300K are also manufactured, when turned on, a red tint is observed. In some cases, colored LDS are used to obtain a unique shade of glow.
Types of lighting devices, areas of application
The modern world offers the following fluorescent ceiling light sources:
- linear electric model - designed for lighting office buildings, long corridors, and other similar premises;
- ring (or round) - such lamps are used for lighting residential, kitchen premises, apartments and country houses;
- high-pressure lamps - used in high-power lighting installations and for illuminating streets and neighborhoods;
- Low pressure devices are used as ceiling fluorescent lamps in residential premises and in production.
Various types of fluorescent lamps
Fluorescent lamps are widely used in public spaces: medical and school institutions, office organizations. When the first compact fluorescent lamps with E14 and E27 sockets appeared, the latter began to be installed everywhere on the ceilings of domestic premises and residential apartment buildings. Also, these types of devices are used to illuminate large public places, since this reduces the amount of energy consumed and increases the service life of the lamps. It should be noted that in addition to public spaces, luminescent devices have found wide application in individual workplaces, for illuminating home areas, various advertising, and show business.
LED devices are used as directional as well as local lighting, since an LED lamp can only emit light in one direction. They can be divided into the following groups:
- lamps for parks, road avenues, streets and squares, architectural objects. The housing of such lamps is specially protected from environmental influences;
- special ceiling light sources for buildings of industrial services, housing and communal services, office premises. Such lamps are characterized by a particularly durable body, and their diffuser is made of polycarbonate materials, which are much stronger than ordinary glass;
- low power fluorescent lamps for the domestic sector. They are subject to requirements for increased quality of light, appearance, and fire safety. In addition, they are usually made with replaceable lamps.
It should be noted that LED lamps are used for lighting museums, since their spectrum does not have an ultraviolet component, and therefore does not affect works of art.
Industrial lighting
Network connection
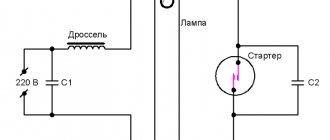
The simplest diagram for connecting fluorescent lamps is based on a starter, a choke (ballast) and a capacitor. The lamps themselves do not provide for their direct connection to an electrical circuit, since when turned off, fluorescent devices have high resistance, which can only be overcome by a high-voltage pulse.
It is also possible to connect two lamps in series, with 2 starters and one inductor, but it must be designed for the total power of the lamps. The diagram of a 2-lamp lamp is shown below. There is no capacitor in the diagram, but it can also be installed at the input of the lamp.
The schematic diagram of the lamp is sometimes applied to the starter housing.
The choke (ballast) is included in the electrical circuit as an additional resistance that protects against short circuits. The starter allows you to charge the inductor at moments of high lamp resistance and at the same time warm up the lamp coils.
It is impossible to start a fluorescent lamp without a throttle. The total energy consumption of all devices connected together with the fluorescent light source to the electrical circuit depends on how the connection diagram is arranged.
Electromagnetic choke (EMPRA)
A constant inductive reactance choke, connected only to a circuit with a LL of a certain power. When switched on, the resistance of the electronic ballast included in the circuit begins to play the role of limiting the current supply to the lamp.
The design of the electronic ballast is simple and cheap to produce, and accordingly, lamps with electromagnetic ballast are also cheaper. Despite its cheapness and simplicity, it has a number of disadvantages:
- startup duration up to 3 seconds (time depends on lamp wear);
- high power consumption by the throttle;
- a gradual increase in frequency in the throttle plates due to wear;
- flickering at twice the mains frequency (100 or 120 Hz) when turned on, which negatively affects vision;
- massiveness and dimensions of luminescent devices (in comparison with analogues of electronic ballasts);
- probable failure of the electrical circuit with the throttle mechanism at temperatures below zero Celsius;
- a short circuit leading to soldering of the inductor electrodes to the device, after which it cannot be removed.
The connection diagram for gas-discharge fluorescent lamps with electronic ballasts provides for the presence of a starter that regulates the ignition of the lamp. However, it additionally consumes electricity.
Electronic throttle
An electronic ballast (EPG) provides the lamps with high-frequency power 25–133 kHz. When the LDS with an electronic throttle is turned on, a person observes a bright flickering for a short time. Using an electronic ballast, two operating principles for turning on lamps are implemented.
Cold start
It starts the device immediately, but causes significant damage to the electrodes. Lamps with such starting options are designed for low frequency on/off during the day.
Hot start
Before turning on the lamp, the electrodes heat up for 1 second, then it works. There is also a thermal indicator that provides the device with protection against overheating.
LLs based on electronic ballasts are more economical, which is why they have gained significant popularity, which cannot be said about analogues of electronic ballasts.
Causes of malfunction
LDS electrodes are represented by a tungsten spiral coated with active alkali metals that provide a charge. Over a period of operation, the active mass falls off from the electrodes and they become unusable.
At the moment the lamp is turned on (starting the discharge and subsequent heating of the electrodes), an additional load occurs on the active mass, which further destroys it. In areas with the greatest loss of active mass, less voltage is supplied, which leads to uneven output, and a person observes the flickering of the lamp during its operation. Also, shedding of the active mass leads to complete malfunction of the lamp, and a dark tint appears at the ends of the tube.
It follows that the service life of the LL also depends on the quality of the active mass and the frequency of switching on the lamp. But even with these limitations, the service life of the LDS is at least much longer (2000 starts versus 1000 for conventional incandescent light bulbs).
Types of execution
Luminescent devices are divided into two types according to the design of the bulb.
Linear lamps
These LLs are represented by low pressure mercury lamps. Most of the light from these lamps is emitted by phosphor. Luminescent devices mounted on the ceiling are the main representative of linear luminaires. The fluorescent ceiling lamp has received huge demand all over the world in premises for various purposes.
Among linear lamps in Russia, LDS with a T8 round tube (D=26 mm) and a G13 base are common. The power of these lamps is related to the size of the tube - standard 18 W LDS have a tube length of 600 mm, and 36 W lamps are already twice as long, 1200 mm. There are also lamps of other powers, but they are less widespread or have a narrow range of applications.
It is worth noting that in the Soviet period, LDS with a T12 flask, the diameter of which was 38 mm, were most widely used. These lamps were more energy-consuming - 20 W short and 38 W long versus 18 W and 36 W, respectively. There were also lamps with a T10 tube (32 mm), but they were not in widespread demand compared to T12.
In Western countries, in recent years, lamps with the latest generation T5 tube with a diameter of 16 mm have become predominant. They are quite thin and have received more extensive use in the interior.
If we touch on technological progress, then just recently Chinese developers created a device with a T4 flask (12.5 mm). This is only a new product that has not yet received widespread use, and it is too early to talk about the prospects of such tubular lamps. LDS with an even smaller tube diameter have not yet been made in practice.
A double-ended straight lamp is a glass tube with glass legs welded at the ends into which electrodes are mounted. The hermetically sealed tube contains argon or neon enriched with mercury, which turns into a gaseous state when the lamp is turned on. The sockets at the ends of the tube are equipped with contacts for connecting the lamp to the circuit.
Linear LDS consume only 15% of the consumption of an incandescent lamp, providing similar illumination. These lamps are often found in production, offices, and transport.
Compact lamps
They are fluorescent lamps with a curved tube.
Compact lamps can have a free (any) bulb shape and are common for private use. Compact fluorescent devices also include so-called energy-saving lamps.
Also common are compact lamps chambered for E14, E27, and E40 standards, which are used in lamps.
Classification of fluorescent lamps
According to the spectral radiation indicator, luminescent type devices are divided into 3 categories:
- standard;
- with improved color rendering;
- with special functional purposes.
Standard devices are equipped with single-layer phosphors, which allow them to emit different tones of white. The devices are optimal for lighting residential premises, administrative and production units.
Fluorescent lamps with improved light transmission are equipped with a phosphor with 3-5 layers. The structure allows high-quality reflection of shades due to increased light output (12% more than standard lamps). The models are suitable for shop windows, showrooms, etc.
Fluorescent lamps for specialized purposes are improved with the help of different compositions in the tube, allowing them to maintain a given spectrum frequency. The devices are used in hospitals, concert halls, etc.
The devices are divided into high and low pressure models.
High-pressure designs are optimal for installation in street lamps and high-power devices.
Low pressure lamps are used in apartments, administrative complexes, and industrial premises.
In appearance, LLs are presented in linear and compact versions.
The linear design of the flask is elongated, used for industrial premises, shopping centers, offices, medical institutions, sports organizations, factory floors, etc. The linear model is represented by different options for tube diameters and base configurations. Devices are identified by codes. A device with a diameter of 1.59 cm is marked on the packaging with a T5 sign, with a size of 2.54 cm - T8, etc.
Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) are a spiral-shaped glass tube and are designed for installation in apartments, offices, etc. CFLs are divided into 2 types, the main difference being the types of bases (standard and with a pin-shaped base).
Traditional base in the form of a thread and a code with a diameter size.
The pin type of the base is marked with the symbol “G”; The numbers indicate the distance between the pins. This lamp is optimal for installation in table lamps and pendant sconces in small rooms.
Fluorescent lamps differ in power (weak and strong). The power of a fluorescent lamp in W can exceed 80 units. Devices with low power are represented by products up to 15 W.
In terms of light distribution, devices can be directional (reflective, slot type) or non-directional.
Based on the type of discharge, devices are divided into arc, glow or glow discharge devices.
The scope of application of lighting devices differs (external, internal, explosion-proof, console).
External devices are suitable for decorating the outside of buildings, for lighting gazebos, decorating a yard, etc. When choosing, it is necessary to take into account the temperature conditions of the region.
Internal suitable for office and residential buildings. The devices are equipped with protection from moisture and dust. The body parts are connected in a hermetically sealed manner. The design of the lamps can be straight, pendant, designed for attachment to the ceiling surface.
Explosion-proof devices are designed for areas with a risk of explosions (warehouses, dye production workshops, etc.).
Console-type devices are mounted using special fasteners and have an individual housing.
Application options
Currently, luminescent devices are widely used both in lighting industrial facilities and in organizing the interior of a room. Lamps with fluorescent and white light lamps are used for many purposes:
- Low pressure fluorescent lamps LB 40, designed to illuminate the entire area of a closed room.
- Fluorescent lamp for aquariums and indoor plants, providing local lighting.
- Phytolamps (floral lamps) are fluorescent lamps for flowers and plants.
- A table and wall fluorescent lamp that provides soft lighting for a cozy atmosphere when reading or relaxing.
Types of fluorescent lamps
Modern models are usually divided according to the principle of operation - LED and gas, and according to the shape of the bulb - tubular and compact.
Linear and compact fluorescent lamps, differing only in the shape of the bulb and base
The most complete separation of fluorescent light sources can be achieved based on the emission characteristics. In fact, fluorescent lamps represent only a small group of a huge number of lighting devices in which the fluorescent glow differs significantly from the range that most people are familiar with.
Fluorescent ultraviolet lamps are unsafe for vision, but are indispensable for disinfecting microflora
These can be gas-discharge tubes for solariums, special lamps for producing pure ultraviolet light and lighting for hydroponic plants and aquariums. They cannot be used as home lighting.
Three types of lighting devices are used to illuminate a residential or office space:
- Daylight lamps;
- White light sources;
- Low-power fluorescent bulbs for ceiling and wall installation.
A lamp is not always needed to obtain illumination close to the usual daylight. In many cases, high contrast and color rendition are required, which is achieved by using lamps of pure white color, a wide spectrum, at the same time high temperature and low intensity.
Marking
The labeling is designed so that the consumer can easily select the required LL when purchasing. The most common designations are:
- LB (white light);
- LD (daylight);
- LCB (cold white light);
- LTB (warm white light);
- LE (natural light);
- LHE (cold natural light).
The visible hue is directly dependent on color temperature. The color temperature of LDS is 6400–6500K, which corresponds to the approximate color of white light.
In addition to the type of lamp, the necessary technical characteristics of the lamp are also indicated: voltage, shape, dimensions, and so on. The marking is applied to the glass flask or LDS body.
Without exception, all LDS contain gases saturated with mercury vapor. In accidents where the lamp breaks, mercury vapor enters the air.
In the future, mercury may end up in the human body and cause harm to health. Therefore, you should handle fluorescent lamps with care.
Fluorescent lamps in the interior: photo
The most budget-friendly design and design are raster ceiling lamps.
Due to their low light output, they usually do not have a decorative light diffuser at all.
In more modern lamp models, the presence of a lampshade or reflector is considered a mandatory attribute.
Shades for fluorescent lamps
For the most popular two-lamp fluorescent lamps, the decorative cap is made of polycarbonate, either transparent or milky white.
Table and wall lamps are additionally equipped with decorative shades and reflectors, without which the lighting efficiency significantly decreases.
Luminaires with fluorescent lamps
T-class lamps with a tubular linear bulb type often become the material for creating ceiling lamps and chandeliers of special designs. In this case, the designs are quite functional and even practical; they can be used for illumination or even as the main source of lighting.
Where can I buy
You can purchase light sources as quickly as possible at your nearest specialty store. The optimal option, in terms of price-quality ratio, remains purchasing from the AliExpress online store. Mandatory long waits for parcels from China are a thing of the past, because now many goods are in intermediate warehouses in destination countries: for example, when ordering, you can select the “Delivery from the Russian Federation” option:
| Goodland E27 LED lamp 220V | 2 pcs/lot LED lamp E14/E27, from 3 to 20 W | LED corn lamp for refrigerator, 2 pcs/lot, 3 W, E14 |
| Bluetooth LED Bulb, E27, E14, GU10, RGB | CHIZAO LED lamp with dynamic flame effect | 10 pieces. LED lamp E14/E27 |