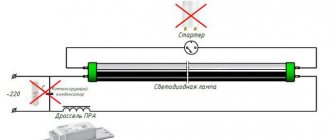
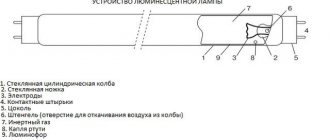
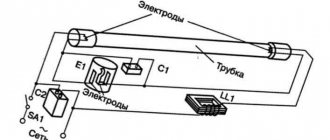
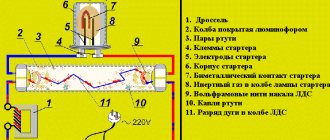
How much electricity does a lamp type LVO 4*18 consume?
We want to install a LVO 4*18 lamp.
Electricians, how much electricity does this lamp consume? The lamps themselves consume 4x18=72 W. How much does a ballast cost? If it is electronic, then its consumption can be ignored. If it is electromagnetic, then we look for the value of the cosine phi on its body. At cosine values of 1, the current is 0.31A at 0.8-0.39A at 0.6-0.53A. What does this mean: If there are a lot of lamps, this must be taken into account, since with a cosine of 0.6 the current increases approximately 2 times.
LVO 4x18 lamp, the marking means that this is a raster lamp (that is, a ceiling lamp built into suspended ceilings, in which fluorescent lamps are shaped like tubes
Each lamp is 18W.
We multiply 18 by 4 and get 72 W, which is exactly how much electricity your lamp consumes.
In general, the answer lies in the marking itself.
72W, we are talking about consumption per hour, knowing this figure you can calculate daily consumption, but you need to take into account the duration of operation of the lamp.
This lamp is designed to work with an alternating current network of 220 Volts.
The letters "LVO" mean:
“L” fluorescent lamp in the lamp.
“B” recessed lamp (see above).
“O” lamp for public buildings (that is, the purpose of the lamp).
It turns out that all the characteristics of the lamps are in their markings, including the power and type of lamps and even where it is best to use them.
A very, very bad idea, firstly, such lamps and lamps for them are already morally and technically outdated, and mercury gas-discharge lamps will soon be removed and banned from production!
Therefore, it would be better to pay attention to LED lamps and lighting lamps, which consume significantly less energy and are more efficient and safe!
But let’s return to your LVO 4 by 18, here he is handsome in the picture, a relic of the past!
We see that it contains 4 mercury lamps with a power of 18 watts each, then we get 72 watts of electricity consumption per hour, plus an insignificant 5-15 watts of inductor and electronics and we get about 80 watts of electricity consumption per hour of operation.
With these 80 watts you can illuminate 8 10 watt LED lamps, which will give you three times more light!
Source
2.9. U-shaped fluorescent lamps
Table 2.9.1. U-shaped fluorescent lamps with a diameter of 7 mm of normal design
| Type | Power, W | Base | Color rendition | Luminous flux, lm | Length l, mm | Tube diameter, mm |
| L 20/25 U | 20 | 2G13 | 2A | 950 | 310 | 38 |
| L 40/25 U | 40 | 2G13 | 2A | 2400 | 607 | 38 |
| L 40/30 U | 40 | 2G13 | 3 | 2700 | 607 | 38 |
| L 65/20 U | 65 | 2G13 | 2A | 3900 | 765 | 38 |
| L 65/30 U | 65 | 2G13 | 3 | 4500 | 765 | 38 |
Table 2.9.2. Short U-shaped fluorescent lamps, 570 mm
| Type | Power, W | Base | Color rendition | Luminous flux, lm | Length l, mm | Tube diameter, mm |
| L 40/21-840 UK | 40 | 2G13 | 1B | 2800 | 570 | 38 |
| L 40/31-830 UK | 40 | 2G13 | 1B | 2800 | 570 | 38 |
| L 65/21-840 UK | 65 | 2G13 | 1B | 4300 | 570 | 38 |
| L 40/25 UK | 40 | 2G13 | 2A | 2300 | 570 | 38 |
| L 65/25 UK | 65 | 2G13 | 2A | 3400 | 570 | 38 |
Rice. 18. U-shaped fluorescent lamps
Consumption calculations
Below we have calculated the consumption of all 3 types of light bulbs: fluorescent, incandescent and LED.
LED light bulbs
Such a light bulb is almost 10 times more profitable than an incandescent lamp and 2-4 times more profitable than an energy-saving one. At the end of the article you will understand this yourself!
When purchasing, they write on the package how many watts the light bulb is (shown by a red rectangle and arrow). Let's look at and calculate the lamp consumption as in the photo - 10 watts.
For example, you have 3 such light bulbs in your house, each consuming 10 W per hour: 3 (number of lamps) * 10 (consumption per hour) = 30 Watt or 0.03 kW/hour.
Energy consumption per day (for example they work 4 hours a day): 4 (hours of work) * 0.03 = 0.12 kW/day.
Electricity consumption per month (if they work every day for 4 hours and 30 days): 0.12 * 30 = 3.6 kW/month.
Amount of electricity costs: 3.6 kW * 3.5 rubles (for example, the tariff for 1 kW/hour, there are different tariffs in each region, district, city and village) = 12.6 rubles. , this is how much you will have to pay for the electricity spent by these 3 lamps.
Do not forget that in this example we calculated the consumption for 3 light bulbs; if you have one light bulb, then the consumption will be 3 times less!
Energy saving light bulbs
These lamps are 2-4 times more profitable than incandescent lamps, but they are also 2-4 times inferior to LED lamps.
conclusions
The payment amounts for 3 light bulbs working 4 hours a day and 30 days are highlighted in red:
- LED (the cost of the paw is from 200 to 800 rubles): 3.6 kW = 12.6 rubles.
- Energy saving (cost from 100 to 400 rubles): 12.96 kW = 46.36 rubles.
- Incandescent (cost from 10 to 100 rubles): 34.2 kW = 119.7 rubles.
It follows from this that the most profitable light bulbs in terms of energy costs are LED ones.
Source
Fluorescent lamps - power consumption?
Gentlemen, electricians, today a friend came into my garage and saw that I had 4 double lamps. he said that the lamps are 40, but the choke takes a lot and that the result is one 100-watt lamp. In principle, I’m not greedy. When it’s hard to see, I turn on the halogen mini spotlight BUT HIS WORDS SOMEHOW HIT THE PSYCHE. It’s true that these lamps take a lot supposedly measured. THANK YOU.
SANDERG wrote: It's true that these lamps take a lot as he supposedly measured. THANK YOU.
You don't have to measure it. Operating current (indicated on the choke) 0.43A.
How much electricity does a light bulb consume?
Good day, dear friends! Today we’ll talk about saving electricity again, in previous articles we calculated how much electricity household appliances (vacuum cleaner, microwave) consume, and today we’ll try to calculate how much electricity light bulbs consume in your home, and whether it’s possible to somehow save on electricity consumption by light bulbs.
So, let’s first figure out what kind of light bulbs we have in our apartment; the following types are most often used in everyday life:
- Incandescent
- Luminescent (energy saving)
- LED
Varieties
Depending on the type of light output, lamps are divided into seven types:
- luminescent (L);
- daylight (D);
- white light (B);
- warm white light (TB);
- cool white light (CB);
- amalgam (A);
- improved color rendering (C).
You may be interested in How to properly connect a fluorescent lamp
Blue energy-saving light bulb
Depending on the use case, the lamps are divided into two types:
- Linear.
- Compact.
Each of these types has its own characteristics.
Linear
Linear fluorescent lamps are used as a local lighting option:
- at workplaces;
- on store shelves;
- furniture lighting;
- wardrobe.
Connected lamp
Linear type equipment can be used as lighting for administrative, public premises and commercial areas.
The advantages of using such lamps are as follows:
- Improved color rendering.
- The equipment has a long service life - a maximum of ten to thirteen thousand hours.
- High light intensity - from 55 lm/W.
Note! Linear light sources are available in the form of long, wide or thin devices, depending on the location.
Compact
The technical characteristics of compact fluorescent lamps allow the use of this light source with significant savings thanks to energy-saving technologies. They reduce energy costs by up to 80% compared to simple incandescent light bulbs of similar brightness.
Multi-colored lamp
Compact fluorescent lamps can become a complete replacement for standard incandescent lamps. Their scope of application is quite wide:
- indoor lighting (offices; cabinets; warehouse, industrial type halls; residential premises; retail premises, areas);
- lighting outside premises (pedestrian areas, shopping areas).
The use of compact energy-saving lamps can reduce energy consumption by 80%.
Incandescent lamps
Let's calculate how much electricity is consumed by ordinary light bulbs of different wattages, the most popular ones in everyday life.
Power consumption: Power 60W - energy consumption will be 60 W or 0.06 kilowatts in 1 hour Power 95W - consumes electricity 95 W 0.095 kilowatts in 1 hour Power 100W - will consume 100 or 0.1 kilowatts of electricity in 1 hour.
Let's calculate how much we will pay for the use of light if, for example, we have 3 acres (hall, kitchen, bedroom) and 3 for 60 W (hallway, toilet, bathroom).
How much electricity do we spend?
Let's take for example 3 at 100W burn for 5 hours in the evening and 1 hour in the morning, resulting in 6 hours a day, we get 3 pieces per hour winding 300 W in 6 hours 1800W or 1.8 kW. 3 more at 60W, let’s assume that each burns for 1 hour a day, in total we get 3 * 60 W = 180 W or 0.18 kW. Total per day is about 2 kilowatts.
Fluorescent lamps (energy saving)
Then, in order for the house to remain as bright as with conventional light bulbs, you need to install the corresponding light bulbs, that is, instead of 60 watts, we put an energy-saving 12W, instead of a hundred we put an energy-saving 20W, this way we will reduce energy consumption and pay 5 times less.
How much electricity do we spend?
So let's calculate how much electricity our fluorescent lamps will consume, for this we take the same example of 6 light bulbs, 3 as hundreds, i.e. 20 W and 3 as 60, i.e. 12 watts. We get: 3 light bulbs, each for 6 hours a day, each light bulb consumes 20 W per hour, then we get 360 W. + 3 light bulbs for an hour a day at 12 watt/hour = 36W. Total for 1 day: 360 W + 36 W = 396 W = 0.4 kilowatts Total for 1 month: 0.4 * 30 = 12 kilowatts
How much will you have to pay?
The total for the month, the amount to be paid for purely lighting will be as follows: Total in rubles for 1 month: 12 kW * 4 r = 48 rubles.
The benefit is obvious: energy consumption is reduced by 5 times. Is it possible to save even more on electricity consumption by lighting devices?
Let's move on to an even more interesting and economical lighting device.
2.6. Linear fluorescent lamps
2.6.1.
Standard
Fig. 11. Spectral characteristics of standard fluorescent lamps
Table 2.6.1. Standard fluorescent lamps
| Type | Power, W | Base | Color rendition | Luminous flux, lm | Length l, mm | Diameter, mm |
| L 4/25 | 4 | G5 | 2A | 120 | 136 | 16 |
| L 6/25 | 6 | G5 | 2A | 240 | 212 | 16 |
| L 8/25 | 8 | G5 | 2A | 330 | 288 | 16 |
| L 13/25 | 13 | G5 | 2A | 700 | 517 | 16 |
| L 15/25 | 15 | G13 | 2A | 720 | 438 | 26 |
| L 16/25 | 16 | G13 | 2A | 950 | 720 | 26 |
| L 18/20 | 18 | G13 | 2B | 1150 | 590 | 26 |
| L 18/25 | 18 | G13 | 2A | 1100 | 590 | 26 |
| L 18/30 | 18 | G13 | 3 | 1150 | 590 | 26 |
| L 30/25 | 30 | G13 | 2A | 1800 | 895 | 26 |
| L 36/20 | 36 | G13 | 2B | 2850 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/25 | 36 | G13 | 2A | 2600 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/30 | 36 | G13 | 3 | 2850 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/25-1 | 36 | G13 | 2A | 2300 | 970 | 26 |
| L 38/25 | 38 | G13 | 2A | 2300 | 1047 | 26 |
| L 58/20 | 58 | G13 | 2B | 4600 | 1500 | 26 |
| L 58/25 | 58 | G13 | 2A | 4100 | 1500 | 26 |
| L 58/30 | 58 | G13 | 3 | 4600 | 1500 | 26 |
Table 2.6.2. Fluorescent lamps in S version
| Type | Power, W | Base | Color rendition | Luminous flux, lm | Length l, mm | Diameter, mm |
| L 20/25 S | 20 | G13 | 2A | 1050 | 590 | 38 |
| L 20/20 S | 20 | G13 | 2B | 1150 | 590 | 38 |
| L 20/30 S | 20 | G13 | 3 | 1150 | 590 | 38 |
| L 40/25 S | 40 | G13 | 2A | 2500 | 1200 | 38 |
| L 40/20 S | 40 | G13 | 2B | 2800 | 1200 | 38 |
| L 40/30 S | 40 | G13 | 3 | 2800 | 1200 | 38 |
| L 65/25 S | 65 | G13 | 2A | 4000 | 1500 | 38 |
| L 65/20 S | 65 | G13 | 2B | 4400 | 1500 | 38 |
| L 65/30 S | 65 | G13 | 3 | 4400 | 1500 | 38 |
Table 2.6.3. Fluorescent lamps in SA version, with foil for external ignition
| Type | Power, W | Base | Color rendition | Luminous flux, lm | Length l, mm | Diameter, mm |
| L 40/20 SA | 40 | G13 | 2B | 2800 | 1200 | 38 |
| L 65/20 SA | 65 | G13 | 2B | 4400 | 1500 | 38 |
2.6.2. Fluorescent lamps of the LUMILUX DE LUXE series (Color rendering degree 1A)
Rice. 12. Fluorescent lamps S and SA versions
Rice. 13. Spectral characteristics of lamps of the LUMILUX DE LUXE series
| Type | Power, W | Base | Color rendition | Luminous flux, lm | Length l, mm | Diameter, mm |
| L 6/32-930 | 6 | G5 | 1A | 220 | 212 | 16 |
| L 8/12-950 | 8 | G5 | 1A | 300 | 288 | 16 |
| L 8/32-930 | 8 | G5 | 1A | 300 | 288 | 16 |
| L 13/32-930 | 13 | G5 | 1A | 600 | 517 | 16 |
| L 15/12-950 | 15 | G13 | 1A | 650 | 438 | 26 |
| L 15/32-930 | 15 | G13 | 1A | 650 | 438 | 26 |
| L 16/32-930 | 16 | G13 | 1A | 850 | 720 | 26 |
| L 18/12-950 | 18 | G13 | 1A | 1000 | 590 | 26 |
| L 18/22-940 | 18 | G13 | 1A | 1000 | 590 | 26 |
| L 18/32-930 | 18 | G13 | 1A | 1000 | 590 | 26 |
| L 30/32-930 | 30 | G13 | 1A | 1600 | 895 | 26 |
| L 36/12-950 | 36 | G13 | 1A | 2350 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/12-950-1 | 36 | G13 | 1A | 2100 | 970 | 26 |
| L 36/22-940 | 36 | G13 | 1A | 2350 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/32-930 | 36 | G13 | 1A | 2350 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 58/12-950 | 58 | G13 | 1A | 3700 | 1500 | 26 |
| L 58/22-940 | 58 | G13 | 1A | 3750 | 1500 | 26 |
| L 58/32-930 | 58 | G13 | 1A | 3750 | 1500 | 26 |
2.6.3. Fluorescent lamps LUMILUX PLUS (Color rendering degree 1B)
Rice. 14. Spectral characteristics of LUMILUX PLUS lamps
| Type | Power, W | Base | Color rendition | Luminous flux, lm | Length l, mm | Diameter, mm |
| L 10/41-827 PLUS | 10 | G13 | 1B | 650 | 470 | 26 |
| L 15/21-840 PLUS | 15 | G13 | 1B | 950 | 438 | 26 |
| L 15/31-830 PLUS | 15 | G13 | 1B | 950 | 438 | 26 |
| L 15/41-827 PLUS | 15 | G13 | 1B | 950 | 438 | 26 |
| L 16/21-840 PLUS | 16 | G13 | 1B | 1250 | 720 | 26 |
| L 16/41-827 PLUS | 16 | G13 | 1B | 1250 | 720 | 26 |
| L 18/11-860 PLUS | 18 | G13 | 1B | 1350 | 590 | 26 |
| L 18/31-830 PLUS | 18 | G13 | 1B | 1350 | 590 | 26 |
| L 18/21-840 PLUS | 18 | G13 | 1B | 1350 | 590 | 26 |
| L 18/41-827 PLUS | 18 | G13 | 1B | 1350 | 590 | 26 |
| L 30/11-860 PLUS | 30 | G13 | 1B | 2250 | 895 | 26 |
| L 30/21-840 PLUS | 30 | G13 | 1B | 2350 | 895 | 26 |
| L 30/31-830 PLUS | 30 | G13 | 1B | 2350 | 895 | 26 |
| L 30/41-827 PLUS | 30 | G13 | 1B | 2350 | 895 | 26 |
| L 36/11-860 PLUS | 36 | G13 | 1B | 3250 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/21-840-1 PLUS | 36 | G13 | 1B | 3000 | 970 | 26 |
| L 36/21-840 PLUS | 36 | G13 | 1B | 3350 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/31-830 PLUS | 36 | G13 | 1B | 3350 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/41-827 PLUS | 36 | G13 | 1B | 3350 | 1200 | 26 |
| L 36/41-827-1 PLUS | 36 | G13 | 1B | 3000 | 970 | 26 |
| L 38/21-840 PLUS | 38 | G13 | 1B | 3000 | 1047 | 26 |
| L 38/31-830 PLUS | 38 | G13 | 1B | 3000 | 1047 | 26 |
| L 58/11-860 PLUS | 58 | G13 | 1B | 5000 | 1500 | 26 |
| L 58/21-840 PLUS | 58 | G13 | 1B | 5200 | 1500 | 26 |
| L 58/31-830 PLUS | 58 | G13 | 1B | 5200 | 1500 | 26 |
| L 58/41-827 PLUS | 58 | G13 | 1B | 5200 | 1500 | 26 |
LED
Lamps of this type are even more economical and consume electricity not 5 times less than conventional light bulbs, but 7 times. That is, if we want to replace 75 watts, then an LED one will be suitable for 10 watts, while the glow will remain the same.
Having expenses for 1 month when using ordinary llamas, we get 240 rubles / 7 = 34 rubles per month, we will pay for lighting fixtures. And per year instead of 2880 we will pay 408 rubles.
Main characteristics
Power
The most important distinguishing characteristic of energy-saving lamps from others is their low power consumption. All the power they receive is converted into light. The power of such light bulbs is 3 – 85 W.
Power table for energy-saving lamps
The table below shows the ratio of an energy-saving lamp and an incandescent lamp: numbers - the average indicates that the same light is supplied by lamps with different wattages (the difference is approximately 5 times). So, for example, a 100-watt incandescent light bulb works the same as a 20-watt energy-saving light bulb
| Incandescent lamp | Energy saving lamp |
| 25 | 5 |
| 40 | 9 |
| 60 | 11 |
| 75 | 15 |
| 100 | 20 |
| 120 | 23 |
Light flow
The efficiency of the lamp is also determined by another important characteristic feature of energy lamps - light movement, with a unit of measurement lm (lumen). It determines how brightly the device shines. Human eyes do not perceive even the most powerful ultraviolet or infrared radiation.
Base type
The base is the most important part and feature of energy-saving lamps. When purchasing it, you should consider the base; it must match the cartridge.
There are various brands of bases on the market: pin and threaded, with sealed contact and non-standard. The table below gives general information about the types of bases.
Light temperature
Qualitative parameters include color temperature (measured using the Kelvin temperature scale (denoted “K”)), which determines the naturalness (whiteness) of the illumination emanating from the lamp.
The following color temperatures are distinguished:
- warm white (less than 3000 K),
- neutral white (from 3000 to 5000 K)
- daytime white (more than 5000 K).
For residential premises it is better to use lamps with warm shades. They relax and calm. Cool tones are better suited for office spaces. The natural and most pleasant color temperature for humans is considered to be from 2800 to 3500 K.
Luminous output
When it comes to saving energy, the main parameter of electrical performance is considered to be luminous efficiency, measured in lm/W. This indicator determines the amount of light produced by the device.
The maximum level of luminous efficiency is 683 lm/W. Previously, the output was 10-15 lm/W, but now it is 100 lm/W.
Light level
The indicator that determines the illumination of a certain surface is called the illumination level (measured in lux (lux)). The standard illumination of a working surface in Russia is 200 lux, in Europe it is 800 lux.
Color rendering index
The color rendering index determines the natural reproduction of the tone of illuminated objects. The color rendition of light bulbs depends on spectral radiation. A lamp with an absolutely correct representation of the color spectrum of objects is assigned the Ra index. A decrease in Ra indicates a deterioration in color rendering properties.
Term of the work
Operational characteristics include lamp operating time, turn-on speed and their number (guaranteed), and design parameters. These characteristic features show the cost of use by which the benefit of purchasing a lamp is determined.