The choice of protective circuit breakers is made not only during the installation of a new electrical network, but also when upgrading the electrical panel, as well as when additional powerful devices are included in the circuit, increasing the load to a level that old emergency shutdown devices cannot cope with. And in this article we will talk about how to correctly select a machine based on power, what should be taken into account during this process and what are its features.
Failure to understand the importance of this task can lead to very serious problems. After all, users often do not bother themselves when choosing a circuit breaker based on power, and take the first device they come across in the store, using one of two principles - “cheaper” or “more powerful”. This approach, associated with the inability or unwillingness to calculate the total power of devices connected to the electrical network and select a circuit breaker in accordance with it, often becomes the reason for the failure of expensive equipment due to a short circuit or even a fire.
What are circuit breakers for and how do they work?
Modern AVs have two degrees of protection: thermal and electromagnetic. This allows you to protect the line from damage as a result of prolonged excess of the flowing current of the rated value, as well as a short circuit.
The main element of the thermal release is a plate made of two metals, which is called bimetallic. If it is exposed to a current of increased power for a sufficiently long time, it becomes flexible and, acting on the disconnecting element, causes the circuit breaker to operate.
The presence of an electromagnetic release determines the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker when the circuit is exposed to short-circuit overcurrents, which it cannot withstand.
An electromagnetic type release is a solenoid with a core, which, when a high power current passes through it, instantly moves towards the disconnecting element, turning off the protective device and de-energizing the network.
This makes it possible to protect the wire and devices from an electron flow, the value of which is much higher than that calculated for a cable of a particular cross-section.
Thermal release (TR)
This part of the circuit breaker protects the circuit from overload. Current passes through the bimetallic strip, heating it. Thermal protection is inertial, and can briefly pass currents exceeding the operation threshold (In). If the current exceeds the rated current for a long time, the plate heats up so much that it deforms and turns off the AV. After the bimetallic plate has cooled (and the cause of the overload has been eliminated), the machine is turned on manually. In a 25A machine, the number 25 indicates the TP response threshold.
What is the danger of a cable mismatch with the network load?
Selecting the correct power circuit breaker is a very important task. An incorrectly selected device will not protect the line from a sudden increase in current.
But it is equally important to choose the correct cross-section of the electrical cable. Otherwise, if the total power exceeds the rated value that the conductor can withstand, this will lead to a significant increase in the temperature of the latter. As a result, the insulating layer will begin to melt, which can lead to a fire.
To more clearly imagine the consequences of a mismatch between the wiring cross-section and the total power of the devices connected to the network, let’s consider this example.
New owners, having bought an apartment in an old house, install several modern household appliances in it, giving a total load on the circuit equal to 5 kW. The current equivalent in this case will be about 23 A. In accordance with this, a 25 A circuit breaker is included in the circuit. It would seem that the choice of the circuit breaker in terms of power was made correctly, and the network is ready for operation. But some time after turning on the appliances, smoke appears in the house with a characteristic smell of burnt insulation, and after a while a flame appears. The circuit breaker will not disconnect the network from the power supply - after all, the current rating does not exceed the permissible one.
If the owner is not nearby at this moment, the melted insulation will cause a short circuit after some time, which will finally trigger the machine, but the flames from the wiring may already spread throughout the house.
The reason is that although the power calculation of the machine was done correctly, the wiring cable with a cross-section of 1.5 mm² was designed for 19 A and could not withstand the existing load.
So that you do not have to take out a calculator and independently calculate the cross-section of electrical wiring using formulas, we present a standard table in which it is easy to find the desired value.
Selection of machine according to cable cross-section table
We briefly mentioned that choosing a circuit breaker based on power is only half the battle. The table of machine power printed above must be combined with the cable cross-section table. If the wiring does not correspond to the rating of the AB, as well as the total power passing through it, it will overheat, and then the insulation may melt and even fire.
This often happens in old houses, when residents thoughtlessly connect powerful modern equipment to the network. The total load on the circuit seems to correspond to the selected current equivalent of the circuit breaker, there are no questions here. However, despite the correct choice of power protection and the readiness of the network for operation, the smell of burnt wiring appears in the house, and smoke and fire are quite likely.
One of the main mistakes is to calculate the rating and power of the machine correctly, but not take into account the wiring characteristics. The network will not be cut off until the rating is exceeded, and thin heated wires will gradually melt the insulation. The result may be a short circuit, as a result of which the machine will work, but the situation becomes critical if fire has spread through the house.
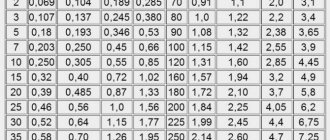
Therefore, we offer you a new table on how to choose a circuit breaker, taking into account the current, power and cross-section of the conductor in mm.
| Electrical wiring cross-section, mm | Voltage 220V | Voltage 380V | ||
| current, A | power, kWt | current, A | power, kWt | |
| 120 | 300 | 66,0 | 260 | 171,6 |
| 95 | 260 | 57,2 | 220 | 145,2 |
| 70 | 215 | 47,3 | 180 | 118,8 |
| 50 | 175 | 38,5 | 145 | 95,7 |
| 35 | 135 | 29,7 | 115 | 75,9 |
| 25 | 115 | 25,3 | 90 | 59,4 |
| 16 | 85 | 18,7 | 75 | 49,5 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,4 | 50 | 33,0 |
| 6 | 46 | 10,1 | 40 | 26,4 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,3 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 2,5 | 27 | 5,9 | 25 | 16,5 |
| 1,5 | 19 | 4,1 | 16 | 10,5 |
Let’s summarize how to choose a machine as correctly as possible. It doesn’t matter how many electrical appliances you connect, only their total power is important. It is also extremely important to know the wiring cross-section. If you have a non-uniform cable cross-section in a line, your task is to protect the weakest section (this means the section with the minimum cross-section).
Thus, when you ask the question of how much load a 16 amp circuit breaker can withstand, or how many amps a 15 kW machine corresponds to, the answer will not be complete without understanding the condition of your wiring. There is a good chance that it will need to be replaced if you live in an older home and your energy consumption needs have increased.
The cross-section of the current-carrying cable must withstand the total power of simultaneously connected electrical appliances.
Weak link protection
So, we are convinced that the calculation of the circuit breaker should be made based not only on the total power of the devices included in the circuit (regardless of their number), but also on the cross-section of the wires. If this indicator is not the same along the electrical line, then we select the section with the smallest cross-section and calculate the machine based on this value.
The PUE requirements state that the selected circuit breaker must provide protection for the weakest section of the electrical circuit, or have a current rating that will correspond to a similar parameter for the installations connected to the network. This also means that the connection must be made using wires with a cross-section that can withstand the total power of the connected devices.
How to select the wire cross-section and rating of the circuit breaker - in the following video:
If a careless owner ignores this rule, then in the event of an emergency that arises due to insufficient protection of the weakest section of the wiring, he should not blame the selected device and scold the manufacturer - only he himself will be to blame for the current situation.
How to calculate the rating of a circuit breaker?
Let's assume that we took into account all of the above and selected a new cable that meets modern requirements and has the required cross-section. Now the electrical wiring is guaranteed to withstand the load from switched on household appliances, even if there are quite a lot of them. Now we proceed directly to the selection of a circuit breaker based on current rating. Let's remember the school physics course and determine the calculated load current by substituting the corresponding values into the formula: I=P/U.
Here I is the value of the rated current, P is the total power of the installations included in the circuit (taking into account all consumers of electricity, including light bulbs), and U is the network voltage.
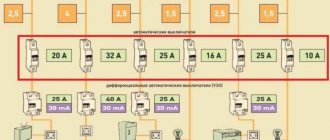
To simplify the selection of a circuit breaker and save you from the need to use a calculator, we present a table that shows the ratings of the circuit breakers that are included in single-phase and three-phase networks and the corresponding total load power.
This table will make it easy to determine how many kilowatts of load correspond to which rated current of the protective device. As we can see, a 25 Ampere circuit breaker in a network with a single-phase connection and a voltage of 220 V corresponds to a power of 5.5 kW, for a 32 Ampere circuit breaker in a similar network - 7.0 kW (this value is highlighted in red in the table). At the same time, for an electrical network with a three-phase delta connection and a rated voltage of 380 V, a 10 Amp circuit breaker corresponds to a total load power of 11.4 kW.
Visually about the selection of circuit breakers in the video:
How to calculate the power of a machine
In order to provide the most effective and accurate overload protection, the formula is used to calculate the machine’s power for a 220V network:
in which the rated current is expressed by I, the sum of the powers of all powered consumers including lighting devices is P, and the voltage of the electrical network is U. Thus, the value of the rated current will increase with an increase in the total power of consumers.
And for a 380V network, the power calculation of the machine is made according to the formula:
in which the cosφ value is added, meaning the power factor (the exact value can be found in Table 6.12 of the SP 31-110-2003 standard “Design and installation of electrical installations of residential and public buildings”). To simplify calculations in everyday conditions, cosine phi is taken equal to one. In general, this coefficient depends on the type of electrical receiver, for example:
- for lighting networks with fluorescent lamps, the power factor is 0.92;
- for lighting networks with incandescent lamps - one;
- for gas-light advertising installations - from 0.35 to 0.4;
- for computers without technological air conditioning - 0.65;
- for refrigerators and air conditioners with an electric motor up to 1 kW, cosφ is equal to 0.65, and with a motor of 1 - 4 kW, the power factor increases to 0.75.
Let's try to calculate the machine's power using an example. Let's say you are trying to protect a group of three kitchen outlets from short circuits. In one, a refrigerator with a power of 400 W is constantly turned on, in others, a microwave or kettle (1000 W) or a blender (300 W) is periodically connected. Let's calculate the total power if you want to simultaneously connect the most powerful devices: 400 + 1000 + 1000 = 2400 W. The current strength for a 220V network is as follows:
2400/220 = 10.9A
And we recommend choosing a machine based on power in favor of the closest 10A rating. A natural concern may arise: will it “knock out” when applying more voltage to such a nominal value? In fact, if you apply a load of 15 amps to a 10-amp protective device, the operation will occur in eight minutes, and if you apply 11 amps, then it will take as long as twenty minutes. During this time, the kettle will turn off and the load will again become acceptable - much earlier than the release switches on.
How to choose a circuit breaker in the case of a three-phase input, which is relevant for private houses and some new buildings? You can either use the power factor formula or refer to the table.