Comparison of the advantages of inverter and conventional household generators
The modern industry in the field of electrical engineering today offers a lot of different generating equipment, which differs not only in price, but also in the principle by which electricity is generated. Therefore, when it comes to buying or renting mobile generator equipment, many may have a question about this, as well as a desire to compare the advantages of different types of equipment, in this case, inverter and conventional generators built according to the classical scheme.
Additional information about generators
But it just so happens that any advantages are accompanied by disadvantages. And the difference between an inverter and a conventional generator is not only in the quality of the generated electricity, but also in price. In addition, there are limitations on power; inverter generators according to this indicator do not exceed 7 kVA.
Therefore, the choice of a backup power supply system must be approached very carefully. Most importantly, it is necessary to determine the requirements for its quality. To power incandescent lamps and hand-held power tools you do not need the best voltage; for these purposes it is quite possible to use conventional gas generators.
But powering a refrigerator, circulation pump of a heating system or gas boiler control controllers requires a high-quality source of electricity. In this case, an inverter generator is the best choice. More information about it can be found here:
The issues of ensuring autonomous power supply are not as simple as it seems at first glance. First of all, this concerns the resulting voltage, which is largely determined by the type of gas generator. In most cases, you can get by with conventional devices, but for particularly critical components you need to use inverter generators. They may be more expensive, but the reliability of some products directly depends on the quality of electricity.
Classic generator
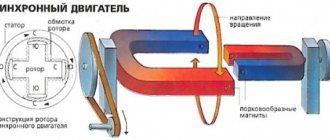
The operating principle of a conventional generator is quite simple. Carbon fuel, using a standard engine designed for a specific type of fuel, drives a shaft that is directly connected to the alternator. The latter is an alternating current electric generator that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy due to the rotor winding and magnets installed in its design.
That is, there are no intermediaries, so it is very important that the rotation of the shaft, and therefore the rotor, occurs at the same speed. Reducing or increasing the rotation speed leads to a decrease in the quality of electric current generation. This is the main disadvantage of a classic generator¸ because over time, rotating components and parts wear out, which mainly leads to a decrease in rotation speed.
- But that's not all. Classic generators have one, so to speak, negative economic aspect. If the unit is not fully loaded (below the nominal value), then the fuel consumption will be high compared to the load indicator. And even more so if the generator will operate in this mode for a long time. In order for you to understand what we are talking about, we will give a simple example.
You purchased a 5 kW generator, and the power consumption of all household appliances and lighting in the house is approximately 3 kW. That is, almost half of the generating set will run idle. But at the same time, it will “eat up” exactly 5 kW of fuel. Therefore, before buying this equipment, you need to accurately calculate the power consumption in the house. And then buy the device itself.
- If a classic type generator is not operating at full load, soot begins to accumulate inside the internal combustion engine. And this will lead to a decrease in operating efficiency, that is, it will again directly affect fuel consumption. Plus, you will have to carry out repairs more often, which is also not a cheap pleasure.
Many consumers, when purchasing a generator set, rarely look at the instructions or data sheet. Namely, in these documents, manufacturers warn that operating the generator below 25 percent load is strictly prohibited. Usually the period during which such a load is allowed is also indicated, because there are many emergency situations in life. This period is indicated in hours per year. That is, exceeding this indicator removes all responsibility of the manufacturer.
Classic gas generator
Attention! The most surprising thing is that a large number of complaints from consumers come precisely for this reason. Therefore, we recommend that you first study the accompanying documents and then purchase or operate the generator.
Despite the fact that generators with classical technologies for generating electricity have so many disadvantages, they also have one rather significant advantage - this is an acceptable price of the equipment in comparison with other varieties. Let's add here the good reliability of the unit and a wide power range. As for reliability and long service life, all this will be possible in reality if the generator is fully loaded and a periodic technical inspection is carried out.
How to choose?
When choosing a power plant, you need to take into account the consumer’s power and its characteristics.
The easiest way is with ohmic consumers; they convert electricity into heat or light. At the time of start-up, their consumption does not exceed operational consumption. Therefore, when connecting an incandescent lamp or iron, you need to pay attention to their total power.
With inductive consumers the situation is a little more complicated. Their design includes an electric motor. Therefore, at the moment of start-up, the short-term power consumption of the inductive device increases from two to seven times compared to the operating power.
It all depends on the load of the consumer. Lightly loaded motors are installed in power tools, for example, in jigsaws and hammer drills. Pumps, compressors, washing machines and refrigerators are called loaded devices because their motors do not idle. Therefore, at the moment of switching on, the jump in power consumption is quite significant.
The total power of consumers should be 15-20% less than the rated power of the generator. Don't forget about inductive loads. Then the power plant will serve you properly and for a long time, and there will be no interruptions in the power supply.
Flaws
Much has been written about the advantages of inverter technology, but not two words can be found about the disadvantages.
In order not to choose a pig in a poke and not regret the purchase, we suggest that you also consider the disadvantages:
- Price;
- Complexity of design;
- Low power;
- Inadmissibility of overloads.
Price for inverters
In contrast to conventional generators, inverters are much more expensive. The high cost is due to the complex design.
For comparison, let's take a regular gasoline generator Hyundai HHY 2500F and an inverter model HY 2000Si;
The price of an inverter generator is almost twice as expensive as its “classic” counterpart.
Design complexity
The complexity of inverter designs increases the likelihood of failures. In addition, the devices use batteries of limited capacity that cannot be replaced.
Hence the need to buy an inverter with a battery of the required capacity for your consumers. When using too powerful devices, the battery will not have time to charge and you will have to turn off the load while waiting for the battery to charge again.
Power
Currently, due to the complex design, it is simply not profitable to produce inverters larger than 7000 watts. This is one of the main disadvantages. But, as production technology improves, prices will fall, and the maximum output power of such devices will only increase.
If you need more than 7000 watts and one of the consumers simply needs high-quality electricity, you can always choose a small inverter to power only a few consumers and a powerful conventional generator to power all other devices.
How to prepare the inverter for operation
- To begin, install the inverter on a flat and horizontal surface.
- Fill in the oil and check the level with a dipstick. The oil level must be checked every time before starting the engine. The electronics will simply automatically turn off the generator motor if the oil level is below the minimum.
- Pour gasoline into the inverter. There is no need to experiment with gasoline. Only fill with 92.
- Checking the air filter. It must be checked every time before starting the equipment. Clean or replace if necessary.
- Before starting the inverter, securely ground the unit.
What kind of oil should I use?
The crankcase of an inverter generator equipped with a four-stroke engine must be filled with appropriate oil. A fuel-oil mixture in proportions of 100:50 is poured into the gas tank of a two-stroke engine. That is, for 100 ml of oil, you need 50 ml of gasoline. But in any case, you should only use the oil recommended by the inverter manufacturer.
Preparing for launch.
- Turn the fuel cap valve to the ON position.
- Engine switch to ON position.
- If the unit is not warmed up, move the choke to the START position.
- Launch. Pull the starter handle until resistance appears. Then pull sharply. After which, smoothly return it to its original position. Do not throw the handle under any circumstances, otherwise the starter will engage with the drive shaft.
- After the device has warmed up, move the air damper to the OPERATION position.
In order to select an inverted generator, carefully study the information provided.
Comparison of conventional and inverter generators
An inverter generator differs from a conventional generator in the principle of converting electric current and the ability to regulate the engine speed depending on the load. Based on owner reviews, one can highlight the negative and positive aspects of various types of generators.
pros
The advantages of inverter models include:
- Low fuel consumption because the microprocessor control system adjusts engine speed depending on the load.
- Small size and weight. On average, an inverter generator is 50% lighter than a conventional one.
- Reduced noise level due to speed control and noise insulation screen.
- The mechanism of the device is protected from moisture and dust by a sealed housing.
- Producing electricity with stable parameters (with an almost ideal sinusoid). Because of this, generators are used to power voltage-sensitive equipment.
- When using a gas generator, the price of 1 kW/hour of electricity is lower than that generated in installations using liquid fuel.
The positive side of classic generators is the ability to create high-power installations (up to hundreds or thousands of kW). When using the device at full capacity and regular maintenance, the installation resource is not inferior to inverter models.
Inverter generator or conventional generator - which one is better to choose for your home and why?
Many devices are very demanding on the quality of the supply voltage, mainly on the stability of its nominal value. This primarily applies to imported models, which either work incorrectly with our networks or are completely disabled because the protection is triggered. There are many examples - heating boilers, PCs, television receivers, circulation pumps and other household appliances.
Consequently, this aspect must be taken into account when deciding on the choice of an autonomous power source. Let's figure out which generator is better for the home - inverter or conventional.
In the private sector, for a number of reasons, gasoline-powered generators are more common. In terms of their design, such mini-power plants are practically no different from their conventional counterparts.
The only difference is in the electronics, or more precisely, in the principle of obtaining voltage at the output of the installation. Actually, this is the criterion for assessing which generator is better.
Features of inverter generator models
In generators of this type the current (
voltage) is not supplied directly to the output terminals. It is first rectified, that is, transformed into a constant one, which charges the battery built into the circuit. Next - to the inverter, the output of which is stable 220/50. The picture explains everything clearly.
Comparison of the distinctive properties of generators
Regular models
- Large selection of power units.
- Reliability of generators. This is understandable - the simpler the design of any installation, the fewer problems there are with it.
- Lower price compared to inverter analogues. For example, the cost of a regular 1.2 kW model ranges from 14,260 – 16,180 rubles (depending on the manufacturer and series).
- Instability of the generated voltage with some (over time) decrease in its nominal value. The main reason is the gradual wear of parts, which is reflected in the speed of rotation of the rotor. It is decreasing. Therefore, when operating a conventional generator, you have to periodically increase the speed, and this means additional fuel consumption.
- Such models require optimal load. By the way, rarely does anyone pay attention to this point when choosing a generator in a conventional, traditional design. First of all, due to ignorance of the specifics of his work. If you carefully read the instructions from the manufacturer (and almost no one does this, either at the point of sale or at home), it will become clear that all its parameters correspond to certain operating conditions. Namely, the minimum load is 25%. This is the limit. Only a few hours are allowed throughout the year, nothing more. If it is systematically less, then the service life of the unit (repair-free) is reduced. But fuel consumption will be more than calculated.
The accumulation of combustion products (soot) inside the engine also leads to increased consumption, that is, the problem of premature maintenance and repair comes up again.
It turns out that an incorrectly selected load on a conventional generator is fraught with a whole “package” of problems. Consequently, saving on its cost, the owner in the future loses on fuel and spare parts. And part of my free time too. How justified this is is for you, the reader, to judge. Especially when you consider that the generator is purchased for systematic (or even constant) use for many years.
What to choose?
Having understood the parameters of different types of units and determined the difference between them, you can say with certainty which gas generator will be the best. Purchasing environmentally friendly, low-noise, compact and reliable inverter gas generators is the right decision, since they are clearly better than conventional analogues in many respects. Their small size and provision of a stable supply of electrical energy deserve very high praise. The cost of the inverter unit is quite high, but rest assured, it is worth the money and will quickly pay for itself.
Another thing that speaks in favor of inverter units is that they are purchased not only as backup equipment (if the power goes out), but also as a stationary power plant where there is no electricity. They are used to connect sensitive electronics without a stabilizer.
If high accuracy of voltage and frequency, as well as mobility, weight, low noise level, and efficiency are important, then purchasing an inverter generator will be an excellent choice.
The advantages and characteristics given and mentioned in this article make it possible to talk about very high performance qualities and properties of inverter units. Their use in everyday life, at industrial enterprises, in offices, educational and medical institutions is more than justified, since they guarantee stable operation of industrial installations, multimedia and computer equipment, security alarm systems, instruments and other equipment that require power supply. Having installed such a unit once, you don’t have to worry about unexpected shutdowns or power surges. And the long service life of the device will make it possible to save on repairing or replacing the generator.
Watch a video about which generator is better for your home: conventional or inverter.
Operating principle of inverters
You should not purchase an inverter generator whose operating principle is unclear to the user. The same applies to other devices.
The inverter generating set is based on a corresponding block. This unit consists of a microprocessor, rectifier and converters.
- High frequency alternating current is generated;
- The rectifier converts the resulting current into direct current;
- Current accumulation occurs in capacitive filters (batteries)
- Oscillations of electric waves are stabilized;
- Using an inverter, direct energy from capacitive filters is converted into alternating current of the required frequency and voltage. This alternating current is supplied to the end user. In the process, we see an ideal sine wave, confirming the highest quality of the generated electricity.
Such an inverter generator device allows you to obtain a very stable output voltage and connect any sensitive devices. The device operates automatically.
Thanks to constant control over the level of fuel, oil and engine speed, the cost of refueling the mini-power station is halved. The built-in air cooling system protects electric generators from overheating.
When the load drops below the minimum, the unit automatically switches to economy mode. Thus, the wear of the electric generator is reduced and the service life is increased.
Classic generator option
The motor-generator circuit works: a gasoline internal combustion engine rotates a rotor with magnets inside the stator winding. On the stator winding, with the help of the emerging EMF, an alternating current is induced, which is removed for the payload. In most cases, a direct connection is made between the motor shaft and the rotor shaft, which ensures the same rotation speed. Changes in the speed of revolutions lead to instability of the current and voltage at the output.
Classic generator design
Unstable rotation speed of the internal combustion engine shaft can be caused by various reasons:
- poor quality fuel;
- wear of individual engine elements;
- inaccurate shaft alignment and other factors.
All of the above reasons make the power supply unstable, the current and voltage parameters at the output have surges. This negatively affects the operation of household appliances, the equipment breaks down, and its service life is reduced.
From the point of view of assessment, economic indicators of fuel consumption, optimal operating mode, calculations are made taking into account the full load. At a minimum load, operation for a long time will be economically unprofitable, high fuel consumption with low electricity consumption.
A classic example of this option is when in a country house all electrical equipment is designed for a maximum electricity consumption of 7 kW. When purchasing a conventional gas generator, you need to proceed from the maximum possible power consumption. During the cold season, work will take place in optimal mode, taking into account that the main electrical appliances are connected:
- lighting;
- heating (electric heated floors);
- boiler for heating water and others.
About autonomous generators
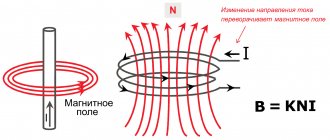
Obtaining electricity in the field or in the event of an accident on a power line is most easily accomplished using an autonomous device. Structurally, it looks quite simple - it is an internal combustion engine connected to a generator. The engine can be any - gasoline, diesel, gas, 2- or 4-stroke, and designed for different power.
It rotates the rotor of the electric generator, and an alternating voltage appears at the output of the latter, the magnitude and parameters of which (voltage and frequency) are determined by the characteristics of the engine and generator. The number of turns in the windings and their number on the generator do not change during operation. Thus, it turns out that the operation of the internal combustion engine affects the quality of the electricity received.
This is expressed in the fact that a change in the speed of the engine crankshaft leads to a change in the output voltage of the generator. There is also an inverse relationship - an increase in load. For example, the starting current that occurs when a new consumer is connected affects the operation of the internal combustion engine and, accordingly, the characteristics of the generated energy.
A conventional generator works in the manner described. The quality of the electricity received is usually suitable for powering many devices. An incandescent lamp will light even with such a floating voltage; it will also have little effect on electronic devices that use a switching power supply. However, certain requirements are imposed on the parameters of the 220 V 50 Hz electrical network. And many devices are designed for them. And violation of the characteristics of electricity leads to failure or premature failure of expensive products.
Design and operating principle
As already mentioned, both types of power plants have a similar design, which includes two main elements:
- Internal combustion engine;
- Alternator.
Next, we will consider the fundamental differences in the operation of generators, since they provide different quality of electrical energy and affect the efficiency and weight of the mini-power plant.
The electrical voltage of the AC mains must satisfy the following conditions:
- Voltage level stability – 220V;
- Frequency stability – 50Hz.
Failure to comply with voltage parameters may cause damage or inoperability of connected devices. This is especially true for voltage level stability. A deviation in the network frequency can lead to disruption of the normal functioning of devices that have AC motors in their design: circulation pumps for heating systems, compressors for refrigeration equipment.
Regular generator
In the classic version of the power plant, a gasoline or diesel engine rotates the rotor of an alternator. The alternating current voltage is removed from the stator windings and then goes to the distribution panel of the power plant for distribution to consumers.
An increase in current consumption by the load causes a braking force on the generator rotor, thus reducing the rotation speed. As a result, the amplitude value of the voltage and its frequency decrease. Reducing the load causes the opposite effect. The most dangerous phenomenon is that with a sharp decrease in power consumption, voltage surges that reach dangerous values are possible.
Stabilization of rotation speed in classical devices is carried out in two directions. The rotation speed of the internal combustion engine is directly controlled by a centrifugal governor, which regulates the fuel supply depending on the crankshaft speed. For finer adjustment, an additional stabilizing winding loaded onto a capacitor is provided in the generator stator. As the frequency of the alternating voltage increases, the resistance of the capacitor decreases. Consequently, the load on the additional winding increases. An increase in the current of the additional winding causes the appearance of a braking magnetic field, which reduces the rotor speed. When the speed decreases, the process occurs in the reverse order. The braking field of the stabilizing winding decreases, the stator speed increases.
From these considerations, the conclusion follows that the main disadvantage of classical generators is that, regardless of the load size, the rotation speed of the crankshaft of an internal combustion engine must be constant. That is, maximum efficiency is achieved only at maximum load. With minimal power from connected consumers, the engine will run in idle mode, wasting fuel.
Note! Long-term operation of the generator in low power consumption mode and at maximum mode is not recommended, since both an underloaded and overloaded gasoline internal combustion engine can quickly fail.
Manufacturers do not recommend the use of conventional generators when operating with a load that is less than 25% of the rated load.
Inverter generator
An inverter generator uses the same principle of generating electricity. The difference is that the output voltage of the generator does not go directly to the consumer. First of all, the voltage is converted to DC using a rectifier, smoothed by a filter capacitor, and then supplied to the inverter for conversion to AC. The inverter includes powerful transistor switches controlled by a microcontroller circuit.
A different approach to power supply.
However, this does not suit most consumers at all. For example, a refrigerator, like circulation pumps in a heating system, gas boiler control controllers, require standard quality electricity for their operation. This is what is provided by so-called inverter generators .
They allow you to avoid the troubles noted above. And this happens thanks to an inverter - a special device that converts a current of one frequency and voltage into a current with other characteristics. This is implemented as follows: the alternating voltage from a conventional generator is converted into direct voltage, and then an alternating voltage of 220 V 50 Hz of high quality is obtained from it. The described principle is shown in the figure:
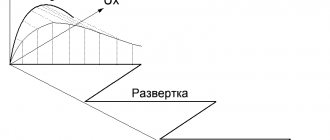
A little clarification needs to be made here. For conventional generators, a voltage of 220 V 50 Hz is generated at the output at 3600 rpm of the internal combustion engine crankshaft. In inverter systems, 300 V is generated. This allows you to obtain a standard sine wave from it, independent of the operation of the internal combustion engine.
A change in the crankshaft speed or network load can lead to a decrease in the DC voltage at the generator output, say from 300 V to 250 V. But in any case, this is enough to obtain 220 V. And from a DC voltage you can generate an alternating voltage of any frequency. The above graphs will confirm this, allowing you to compare the sinusoids at the output of generators of different types under different conditions.
An additional advantage of an inverter generator is its efficiency. Providing the required characteristics of the output voltage is possible at lower engine speeds; accordingly, the consumption of gasoline and oil, as well as the level of noise generated, is reduced by up to 20%.
General characteristics of generators
Let's analyze the advantages and disadvantages of each sample.
Ordinary
In essence, this is a small electrical station in the house: fuel burns, the motor turns the generator, the energy of mechanical movement and interaction of the system is transformed into electrical energy.
Advantages:
- a wide selection of units of varying power: from “tiny” units of 1 kW to solid units of 8-10 kW or “giants” of 20-40-100 kW, which are intended for industrial use;
- ease of use and relative reliability, subject to the conditions of use;
- low cost compared to inverter installations.
There are also many disadvantages.
- The unit must operate at constant load. Operating a generator with a load of less than 25% leads to premature failure.
- High fuel consumption with insufficient load.
- Noise when the motor is running. The operating unit should be located away from housing or in a sound-absorbing box.
For household lighting and individual appliances, minor voltage fluctuations are not particularly critical. However, for certain expensive systems (smart home systems, control units for gas boilers, forced circulation pumps or refrigerators), any change in the quality of electrical energy can lead to equipment failure or premature failure.
Inverter
Most often, inverter electric generators are used for irregular use in the event of an unexpected power outage. They are practiced in houses outside the city or for household needs at a permanent place of residence, in offices where high-frequency equipment operates. Such an installation can be purchased once and for a very long period. The reliability of the device is ensured by a combination of functional properties.
- The alternating current generated by the generator is transformed into direct current, and the resulting wave oscillations become stable. This makes it possible to obtain high quality electricity at the output.
- The principle of operation of the generator is the possibility of a rapid start, which is activated by a special ignition system.
- The generator is controlled by an auto-regulation system, which monitors the engine speed, characterized by the load parameters. This principle makes it possible to practically use fuel (consumption can be reduced by almost 40%).
However, it has many advantages:
- has a wide power range (2-8 kW) with economical consumption of liquid fuel;
- economical because it is able to correctly balance the engine speed based on the actual load and thereby saving fuel consumption;
- lightweight and compact (compared to other models);
- makes almost no noise during operation, since its design includes specialized mufflers and a double soundproof casing;
- produces high-quality electrical energy, while emitting almost no harmful compounds into the surrounding atmosphere;
- extremely reliable and durable: all its elements and connections are adapted to external loads and are resistant to negative environmental factors.
Possessing excellent electrical characteristics and high efficiency, the inverter generator has disadvantages that must be taken into account when purchasing:
- high price: a high-quality inverter has a price 2-3 times more than that of a conventional modification;
- the power of the unit is limited: the permissible maximum power of the majority of common modifications will be no more than 5 kW (you can find models with 7 kW, but they are not yet very common, and their price exceeds reasonable limits);
- the complexity of repair work in case of failure;
- It is problematic to replace the battery if it loses its functionality.