Pressure on each axis
Accurate indicators of structural and regulatory loads allow you to correctly calculate foundations. An example of foundation calculation is given for the convenience of novice builders.
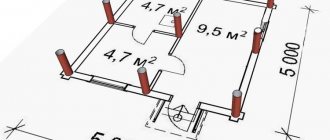
Structural pressure along axis “1” and “3” (outer walls):
From the frame of the wall: 600 x 300 cm = 1800 cm².
This figure is multiplied by the thickness of the vertical ceiling of 20 cm (including external finishing). It turns out: 360 cm³ x 799 kg/m³ = 0.28 t. From the rand beam: 20 x 15 x 600 = 1800 cm³ x 2399 ~ 430 kg. From the base: 20 x 80 x 600 = 960 cm³ x 2099 ~ 2160 kg. From base The total mass of the entire floor is calculated, then 1/4 of it is taken.
Logs with sides 5x15 are placed every 500 mm. Their mass is 200 cm³ x 800 kg/m³ = 1600 kg.
It is necessary to determine the mass of the floor covering and sheathing included in the calculation of the foundations. An example of a foundation calculation indicates a 3 cm thick insulation layer.
The volume is 6 mm x 360 cm² = 2160 cm³. Next, the value is multiplied by 800, the total will be 1700 kg.
The mineral wool insulation is 15 cm thick.
Volume indicators are 15 x 360 = 540 cm³. When multiplied by density 300.01, we get 1620 kg.
Total: 1600.0 + 1700.0 + 1600.0 = 4900.0 kg. We divide everything by 4, we get 1.25 tons.
- From the attic ~ 1200 kg; From the roof: the total mass of one slope (1/2 roof) taking into account the mass of rafter beams, lattice and slate flooring is only 50 kg/m² x 24 = 1200 kg.
The norm of loads for columnar structures (for axis “1” and “3” it is necessary to find 1/4 of the total pressure on the roof) allows for the calculation of a pile foundation. The example of the design in question is ideal for infill construction.
- From the base: (600.0 x 600.0) /4 = 900.0 x 150.0 kg/m² = 1350.0 kg. From the attic: 2 times less than from the base. From snow: (100 kg/ m² x 360 cm²) /2 = 1800 kg.
As a result: the total indicator of structural loads is 9.2 tons, standard pressure is 4.1. Each axle “1” and “3” has a load of about 13.3 tons.
Design pressure along axis “2” (middle longitudinal line):
- From the frame of the wall slabs, rand beams and basement surface, the loads are similar to the values of axis “1” and “3”: 3000 + 500 + 2000 = 5500 kg. From the basement and attic they have double values: 2600 + 2400 = 5000 kg.
Below is the standard load and calculation of the foundation base. Example used as approximate values:
- From the basement: 2800 kg. From the attic: 1400.
As a result: the total design pressure is 10.5 tons, standard loads are 4.2 tons. Axle “2” weighs about 14,700 kg.
We calculate the weight of the house structure.
An example of calculating the weight of a house structure: You want to build a house with a height of 1 floor, 5 m by 8 m, also an internal wall, the height of the floor to the ceiling is 3 meters.
Let's substitute the data and calculate the length of the walls: 5+8=13 meters, add the length of the inner wall: 13+5=18 meters. As a result, we get the length of all the walls, then we calculate the area, multiply the length by the height: S = 18 * 3 = 54 m.
We calculate the area of the basement floor, multiply the length by the width: S=5*8=40 m. The attic floor will have the same area.
We calculate the area of the roof, multiply the length of the sheet by the width, for example, a sheet of roofing has a length of 6 meters, and a width of 2 meters, as a result the area of one sheet will be 12 m, in total we will need 4 sheets on each side. In total, you will get 8 roofing sheets with an area of 12 m. The total area of the roofing will be 8 * 12 = 96 m.
Strip type foundation. Quantity of reinforcement and binding wire.
For a strip foundation you will not need too thick reinforcement (10-12 mm), because this foundation has a high load-bearing capacity. The longitudinal reinforcement bars experience the main load and are laid 10 cm from the concrete surface. Vertical and transverse bars do not experience loads, which is why smooth reinforcement is used for them.
For a house 5 by 8 m and one more internal wall, the entire length of the foundation will be 45 meters. The total consumption of smooth reinforcement for the entire foundation area will be 97.5 meters. We also add the length of the foundation for the internal walls.
The number of binding wires for the entire foundation length of 45 m and a step of 40 cm for one connection will be equal to 30 cm, and the total quantity (45 m / 0.4 m) * 3 (number of levels) = 338, multiplied by the wire size 338 *0.3=102 meters of binding wire.
The procedure for determining the constant load
- The current SNIP determines that the thickness of a monolithic foundation, taking into account the constant load, is calculated depending on the soil:
- When determining how to calculate the thickness when constructing a building on sandy soils, the weight of the slab is not taken into account
- When working on clay substrates, the mass indicator must be divided by 2
- Calculation of the thickness of a slab foundation during construction on floating foundations is taken into account completely
- The coefficients that are used when performing calculations for a house can be taken from the “Guide to the design of frame buildings and tower-type structures.”
- They are presented in the “Loads and Impacts” section. The minimum reliability coefficient corresponds to metal structures and is 1.03. Concrete and reinforced concrete structures, screeds, and insulating layers have a maximum coefficient of 1.3.
Determining the volume of a strip foundation
In general, you can calculate the amount of concrete for pouring a strip base yourself. To do this, you need to know the height, width and length of the tape. If the foundation has the same width and height along its entire length, then you can use a simple geometric formula:
V = S*L.
In this formula, the letter “S” denotes the cross-sectional area of the foundation, which can be calculated by multiplying the width of the foundation by its height. The letter "L" indicates the total length of the concrete strip.
For example, you can consider the following option:
The strip base for a house measuring 10*8 meters has a width of 0.4 meters and a height of 0.8 meters. First, the cross-sectional area of the foundation is determined:
Concrete for pouring strip foundations
S = 0.4*0.8= 0.32 m2.
Next, calculate the total length of the concrete strip, which is equal to the perimeter of the house:
L = (10+8)*2 = 36 meters.
Now you can safely calculate the volume of a strip base with the same cross-section along its entire length:
V = 0.32*36 = 11.52 m3.
Consequently, to pour a strip foundation for a house measuring 10*8, about 12 cubic meters of concrete solution are needed.
If the foundation has different widths in individual sections, then the calculation is carried out separately for each section, then the resulting values are summed up.
It is also important to take into account those parts of the foundation that are located under all load-bearing partitions, calculate their volume and add to the overall result
Determining the required width of the sole (“pillow”) of the strip foundation
The required width of the sole is determined by the ratio of the calculated resistance of the base to the linearly distributed load.
Previously, we determined the linear load acting at the level of the foundation base - 7925 kg/m. Our accepted soil resistance was 2.15 kg/cm2. Let's bring the load into the same units of measurement (meters into centimeters): 7925 kg/m = 79.25 kg/cm.
The width of the base of the strip foundation will be: (79.25 kg/cm) / (2.15 kg/cm2) = 36.86 cm.
The width of the foundation is usually taken as a multiple of 10cm, that is, rounded up to 40cm. The resulting width of the foundation is typical for light houses built on fairly dense loamy soils. However, for structural reasons, in some cases the foundation is made wider. For example, a wall will be faced with façade bricks with 50mm thick insulation. The required thickness of the base part of the wall will be 40 cm of aerated concrete + 12 cm of cladding + 5 cm of insulation = 57 cm. Aerated concrete masonry can be “hung” by 3-5 cm along the inner edge of the wall, which will reduce the thickness of the base part of the wall. The width of the sole must be at least this thickness.
Foundation calculation
Calculations are made according to certain formulas, taking into account the material and features of the house, as well as a number of geodetic factors. The dimensions of the foundation for a house made of brick, cinder block or concrete will be different, since the masses of the materials are different and exert different pressure on the ground.
To calculate the base area, you need to know the total mass of the house. The table shows the specific gravity of building materials
Simple calculation
Without taking into account additional individual features, the installation depth of the foundation can be calculated using the standard formula, where 0.8 meters must be multiplied by the number of expected floors - a total of 1.6 meters.
The thickness of the foundation in the classic version is equal to the estimated thickness of the load-bearing walls plus 15 cm. However, it is worth knowing some parameters that can change this indicator:
- soil looseness;
- sole area;
- total weight of the structure.
Foundation thickness depending on the soil and number of storeys
Accurate calculation
To more accurately calculate its depth, you need to know:
- Type of soil (sandy, clay, sandy loam).
- Soil freezing point. It is necessary to know this so that deep freezing of loose and moisture-filled soil does not destroy the foundation. However, if the building is being built on fairly dry or slightly heaving lands, this indicator does not matter.
- Height of aquifers. In a situation where the aquifer is close, its depth should be minimal for the purpose of waterproofing.
- Living in a house.
The basis is the freezing depth of the soil in your area. To this value you need to add 150 mm if the house is wooden or 350 mm if it is brick.
Let's first calculate the depth of a one-story house. We take the freezing depth in the Moscow region with fine sand soil. It is 1.34 m. The house will be brick, therefore we add another 35 cm and get 1.69 m.
There is a relationship between the depth of the foundation and the temperature in the room. This dependence is expressed in coefficients and is shown in the table. According to it, the higher the temperature in the house, the less deep it needs to be.
Relationship between room temperature and foundation depth
We will have a floor on joists on the ground with a temperature of at least 20. This gives us 1.69*0.6≈1 meter. It is enough to deepen the foundation by 1 meter.
Now for the two-story one. The weight of the house will be almost 2 times greater, so it must be stronger. According to the rule written above, the depth should be 1.6 meters. And this is below the freezing point, which is quite satisfactory.
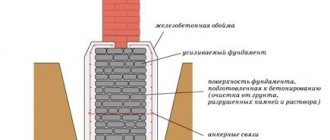
Calculation of the depth and width of the strip foundation
Scheme of laying a foundation in frozen soil.
For the main parameters, it is necessary to know the characteristics of the soil and the dimensions of the structure being built. For a large-sized object, such as a two-story brick house, the foundation is buried below the soil freezing line up to 60 cm. The total depth can reach up to 2-3 m with soft, moving soil. If the structure is light, such as a wooden house or bathhouse, then the foundation can be buried deep only 50 cm. If the soil is homogeneous and strong, then the laying depth will be approximately 45 cm.
When designing a building project, the layout, dimensions and width of all external and internal load-bearing walls, under which the foundation is laid, are taken into account. should be greater than or equal to the width of the walls. It is permissible for the walls to overhang the foundation up to 13 cm, since the reinforced concrete foundation has greater strength compared to wall materials, and therefore can withstand the load of a wider wall, and a narrow foundation requires less material and reinforcement consumption.
Depending on (its lower part), the total width of the supporting structure is calculated by adding the loads pressing on the foundation, which, in turn, exerts pressure on the ground.
The depth of ground freezing in winter in a given region can be found in construction reference books. If there is a possibility of changes in soil heaving and groundwater levels, then it is necessary to order a specialized soil study in order to prevent unreasonable costs that may arise when undesirable soil properties are discovered.
Types of construction of strip foundations depending on the soil.
In any case, a sandy or fine-grained gravel layer 10, 20 cm high is placed under the foundation, so the depth of the trench should be taken into account this layer. Or it can be a mixture of sand and gravel in a ratio of 40:6.
is calculated based on the load of the structure of the walls, floors, roof and the specific gravity of the materials used. To this value is added the weight of what will be present in the house, people (if possible), furniture, equipment, and so on. The size is calculated in such a way that the magnitude of the loads does not exceed the permissible weight on the ground at the construction site. The calculated soil resistance should not be less than the specific pressure of the weight of the building.
If the future structure has a regular square or rectangular shape, then the volume and dimensions are quite easy to calculate. If a complex structure is to be poured, then it is necessary to divide it into main elements, the volumes and dimensions of which are added up.
After determining the height and width, the amount of required material, concrete, reinforcement and formwork material, and its dimensions are calculated.
How deep should the foundation be?
The foundation depth is calculated for each project individually and depends on the following factors:
- Geological properties of the site.
- Relief and freezing depth.
- Estimated weight and area of the future home.
- At what depth are communications laid on the site?
In any case, the foundation must be made below the freezing line and above the groundwater level. In the Moscow region it is 1.35 m for loamy soil and 1.7 m for sandy soil. The foundation of the house must rest on layers of soil that can support the weight of a one-story or two-story house made of foam blocks or timber.
Correct and incorrect options for installing a buried foundation
The building must stand on a strictly horizontal foundation. If the terrain of the site is not ideal, you may have to dig a trench to lay the foundation with sections of varying depths.
If according to the project it is necessary to equip a basement under the building and the type of soil allows this, the depth of the tape must be made such that it forms the walls of the basement.
Another option is to use a shallow strip foundation, which will be discussed below.
Laying depth of shallow strip foundation
A shallow strip foundation is one of the most common types of foundations in the construction of dachas and small one-story houses, including in the Moscow region. This type of foundation requires lower financial costs, they are easier to make than deep-buried ones, since during construction there is no need to dig deep trenches.
Shallow-type strip foundations are prohibited from being made on organic soils such as peat and silty soil.
Such structures are built almost on the surface of the earth, which eliminates the negative impact of seasonal heaving. A reinforced horizontal contour in the form of a tape absorbs the impacts that occur during soil movement.
Schematic diagram of a shallow foundation
It is best to make such foundations on a sand bed made of layer-by-layer compacted sand. The thickness of the pillow is made about 20 cm. Such a base is used for buildings made of glued or ordinary timber, rounded logs, and foam blocks. Often houses are built on them using frame-panel technology. Also excellent for baths, utility rooms and summer kitchens.
The laying depth is:
- 30–50 cm for light non-residential buildings;
- 60–70 cm for a one-story house (wooden or foam blocks) that is light in weight.
SP and SNiP requirements
The design of the foundation is carried out according to SNiP 2.02.01-83. This document regulates all parameters of the foundation, including width. These parameters are calculated based on limit states: bearing capacity and deformations, taking into account the effect of force and unfavorable factors.
Calculation of the foundation based on bearing capacity is carried out in the following cases:
- The foundation will experience significant horizontal loads (there are retaining walls, base struts, and so on).
- The house is built near the slope or on the slope.
- The site has rocky or heaving soil.
The following deformations are taken into account:
- drawdowns;
- subsidence;
- precipitation;
- combination of lifting and settling;
- failures;
- horizontal displacement.
For calculations, SNiP provides tables and formulas, using which you can calculate the optimal width of the foundation. On average, the width of the tape for a standard two-story house is 0.4 m. Calculations are also carried out according to the SP (Code of Rules), based on SNiP and GOST.
Foundation settlement
Another strictly standardized value when calculating a strip foundation is its settlement. It is determined by the elementary summation method, for which data from the geotechnical survey report will again be needed.
Formula for determining the average settlement value according to the scheme of a linearly deformable layer (Appendix G SP 22.13330.2011).
Scheme of application of the linearly deformable layer technique.
Based on the experience of construction and design, it is known that for engineering-geological conditions characterized by the absence of soils with a deformation modulus of less than 10 MPa, weak underlying layers, macroporous IGE, a number of specific soils, that is, under relatively favorable conditions, calculation of settlement does not lead to the need to increase the width of the base foundation after calculating the bearing capacity. The margin for the calculated draft in relation to the maximum permissible is usually obtained several times. For more complex geological conditions, the calculation and design of foundations should be carried out by a qualified specialist after carrying out engineering surveys.
Strip foundation for private construction
The strip foundation is characterized by high stability. Its reliability depends on the depth of immersion in the soil. Suitable mainly for the construction of low buildings, withstands impressive loads.
If the site of the future construction site has heaving soil and the groundwater level is shallow, then a shallow strip foundation will be laid. This foundation is buried almost half a meter into the ground and rises thirty centimeters above the ground.
If the groundwater level is deep, then a buried foundation is laid. If a strip foundation depth of more than 2 meters is required, it is advisable to use other types of foundations.
After drawing up a plan, specifying the type of soil and the depth of groundwater, calculations can be made.
The reliability of a strip foundation depends on the depth of immersion in the soil
Calculation of foundation dimensions: width, length, depth
To calculate a strip foundation, it is necessary to determine the following parameters:
- foundation width;
- foundation length;
- foundation depth, plinth height, total foundation height.
The width of the foundation depends on the width of the walls of the future building (it should be 100 mm greater than the thickness of the load-bearing walls), on the area of the base and the presence of reinforcement in the foundation structure.
The standard foundation thickness is considered to be 400 mm.
The length of the foundation is equal to the sum of the lengths of all the walls of the planned structure.
The most difficult part of the calculations is to calculate the installation depth of the concrete base.
The width of the foundation must exceed the thickness of the walls by 100 mm
Foundation depth; what parameters are taken into account
The depth of the foundation depends on the building itself, climatic conditions, soil and the depth of groundwater. This parameter is also affected by the presence of a basement, heating, number of floors and total weight.
Due to frost heaving of the soil, the foundation must be buried below the soil freezing level by 15-20 cm. To calculate the depth of the foundation in this case, you will need data on the depth of soil freezing at the construction site. This information is freely available.
If the freezing depth exceeds 2 meters, then either choose other options or lay the tape above the freezing level. However, in this case, you will have to insulate the base, foundation and build blind areas. Blind areas around the foundation of a finished house will allow you to retain and drain excess water and will cover and protect the nearby soil from becoming saturated with moisture, which will reduce soil heaving and heat loss from the building. Moreover, the depth of the foundation is usually less than a meter.
The height of the plinth is on average 300 mm. The total height of the foundation is the sum of the depth of the foundation and the height of the base.
The depth of the foundation depends on the mass of the building, soil, climatic conditions and groundwater
To calculate concrete for a strip foundation, the following data will be required: the volume of the strip foundation and the mass of 1 m² of the concrete composition directly used.
The volume of the foundation is calculated based on the length, width, depth and layout of the foundation.
What could be the basis
Initially, you will need to decide on the type of strip foundation and its dimensions: length, width and depth. Next, you need to establish all the data about the house itself, calculate the resulting loads, etc. Upon completion of all the calculations, you will have a clear idea of what type of foundation can be used for a given structure, on a specific type of soil. Also, the article will give an example of calculating a strip foundation for a two-story house.
Today, four main types of foundation are used in private construction. You can calculate them yourself or use an online strip foundation calculator.
- Shallow . This type of foundation is used for small-sized buildings, which can be: a small country house, a garage, a barn, a change house, etc. These buildings must be made of logs or wood, i.e. Do not overload the base. A shallow strip foundation is installed on clay or sandy soils to a depth of about 60 cm. The width of such a foundation rarely exceeds 40 cm.
- Recessed . This type of foundation can withstand more severe loads from the house than the previous type. Based on this, it is used for the construction of massive and large buildings. Before erecting a strip foundation, it is necessary to conduct a thorough analysis of the soil and accurately determine all its properties. The main value in this case is the depth of soil freezing. It must be remembered that the depth of the strip foundation is laid 25 cm more than the freezing level. Its average width is usually 40 cm, but for very large and loaded buildings, it can be increased.
- Monolithic . This type of foundation is intended for the construction of wooden or lightweight brick buildings. This base can be installed on any difficult soils with a high level of groundwater. The design of a monolithic strip foundation is a concrete strip that is poured around the entire perimeter of the house. With increased load, it is recommended to install it under internal load-bearing walls. Before installation, a soil analysis is carried out and the required dimensions are selected.
- Prefabricated . It is used for the construction of buildings of various designs, both single-story and multi-story. The structure of a prefabricated strip foundation is assembled from individual blocks, which are laid in a pre-dug trench. They are fastened together using concrete mortar. Depending on the maximum load that the structure will exert, blocks made of various materials (concrete, rubble concrete, silicate mixture, etc.) can be used to construct the foundation. At the same time, they can be hollow or solid.
What should be done
Most often, in private construction, strip foundations are used. This type allows you to make a basement in your house, but in some cases it may not be economically viable. To make an estimate for the work (or roughly estimate how much investment will be required), you need to calculate the reinforcement for the strip foundation, and also calculate the volume of concrete and its geometric dimensions.
Most often in private construction they lay a strip foundation
The calculation method involves calculating three quantities. The calculation of the strip foundation should result in the following information about the structure:
- depth of the sole;
- base width;
- width over entire height.
Calculation of the foundation for a house made of brick or other materials must begin with determining the depth of the foundation. It depends on the heaving of the soil, groundwater level and climate. If this characteristic is incorrectly calculated, the building may collapse under the influence of frost heaving forces. The tape will be simultaneously exposed to moisture and cold, which will lead to uneven deformations and cracks.
The width of the base must be sufficient to evenly transfer the mass of the building to the ground. The weaker the soil, the wider the base will be needed. Due to the large area, it is possible to distribute the load from the strip foundation for the house onto the base so that each section of it bears no more than the permissible value.
The foundation must be laid below the soil freezing level
The width of the tape over the entire height is usually taken structurally. It should be slightly larger than the outer walls. In this case, the method of manufacturing the tape is taken into account. For a monolithic foundation, a section width of 200-300 mm may be sufficient, while a prefabricated foundation is recommended to be at least 400-600 mm. This indicator also depends on the depth of placement. The larger it is, the stronger the overturning effects will be (more powerful basement walls will be required).
Strip foundation and soils: why is it so important
When choosing the type of foundation, it is important to know exactly two characteristics of the underlying soil: their bearing capacity and heaving. Bearing capacity is highest in rocky soils; they are followed by cartilaginous ones - a mixture of sand and clay with small stones and crushed stone
Sandy soils are prone to subsidence; the properties of sandy-clayey soils (sandy loam and loam) depend on the ratio of clay and sand. The lowest bearing capacity is for soils of organic origin: peat, sapropel, silt
Bearing capacity is highest in rocky soils; they are followed by cartilaginous ones - a mixture of sand and clay with small stones and crushed stone. Sandy soils are prone to subsidence; the properties of sandy-clayey soils (sandy loam and loam) depend on the ratio of clay and sand. The lowest bearing capacity is found in soils of organic origin: peat, sapropel, silt.
Building codes prohibit resting the foundation directly on organic soils with weak bearing capacity.
Soils that are water-saturated and have a variable layer structure are also considered complex. The problem of weak soils is typical, for example, for areas located on the site of drained swamps. Building a house on a shallow strip foundation on such soils is theoretically possible, but requires quite expensive work. So, if the depth of the weak-bearing layer is no more than 1 m, and underneath it there is a more “hardy” one, then during construction the layer of weak soil is removed and a sand substrate or concrete preparation is placed in the trench. Also, poor soil is sometimes compacted mechanically, replaced with a gravel cushion, or reinforced with special meshes. Experts, however, recommend in such situations to abandon the strip foundation in favor of a pile foundation.
The heaving of soil is directly related to its ability to hold water, and frost heaving is an increase in the volume of soil due to the expansion of water when it freezes.
Non-heaving soils: hard clays, low-moisture gravelly, sandy soils with deep groundwater.
Slightly heaving: semi-solid clayey; slightly water-saturated silty and fine sands, coarse soils with a clay and sand content of 10-30%.
Medium-heaving soils: refractory clayey soils, wet silty and fine sands, coarse-grained soils with a clay and sand content of more than 30%.
Highly heaving and excessively heaving: soft plastic clayey, silty and fine sands with strong water saturation.
On highly heaving soils, it is possible to build small (1-2 floors) wooden houses on a shallow strip foundation made of monolithic reinforced concrete. For heavier houses, a complex of works will be required to lower the groundwater level, organize drainage and water disposal.
The higher the groundwater level, the more heaving the soil will be, regardless of its composition. The groundwater level critical for foundation construction varies for different soils and is calculated using the formula: the lower limit of soil freezing (in meters) plus the following number:
- sands – 0.8-1 m
- sandy loam 1 – 1.5 m
- loams 2 – 2.5 m
- clay 2.5 - 3.5 m.
When groundwater levels are below the specified values, they do not affect the degree of soil heaving.
In general, the construction of a strip foundation on highly heaving soils with a high groundwater level is considered inappropriate: in such conditions, a pile-grillage foundation performs best.
When planning construction, it is best not to skimp on a professional soil survey on your site: this will help to avoid big problems in the future. The services of a specialist cost money, but the investment is worth it. Saving a house whose foundation has deformed due to errors in assessing the properties of the underlying soil will cost much more.
Shallow monolithic strip foundation on a sand cushion: stages of construction
Preparing the base of the strip foundation. Before starting work, the bottom of the trench is compacted to avoid soil settlement. The trench is lined with geotextile to protect the filling soil and drainage pipes from silting. Then a sand cushion of coarse or medium sand is laid. The thickness of the layer depends on the characteristics of the soil: on low-heaving soils it can be 30 cm, on heaving ones – 80 or more. There are recommendations according to which the thickness of the cushion on soils with severe heaving can be 3 times greater than the width of the base of the foundation strip. Sand is poured into layers of 20 cm and compacted thoroughly. On soils with weak bearing capacity, a mixture of coarse sand and gravel/crushed stone in a ratio of 40:60 is used to organize the cushion. A layer of waterproofing is laid on the pillow.
Formwork . Most often, it is assembled from shields or boards, and care should be taken that the gaps between them are no more than 2 mm. There is also modern removable formwork in the form of steel metal gratings in a polyethylene casing. The upper edge of the formwork should protrude 5-7 cm above the calculated level of the top of the foundation. A film waterproofing material (for example, polyethylene) is laid inside the formwork, its edges are folded over the edge of the formwork and securely fastened.
Strip foundation formwork
Reinforcement of strip foundation . It should be remembered that between the reinforcement and the edges of the foundation there must be a so-called protective layer of concrete, which can be formed using special plastic clamps for the reinforcement. The thickness of the protective layer is determined according to SP 50-101-2004 “Design and installation of bases and foundations of buildings and structures”; the required number of reinforcement bars and their diameter can be determined using SNiP 52-01-2003 (SP 63.13330.2010).
Concreting . For strip foundations, it is most often recommended to use heavy cement concrete grade M200 (strength class B15). However, on heaving soils or when constructing a foundation for a heavy house with several floors, it is advisable to choose higher grades of concrete (M300, M350 or even M400). In addition to the strength class, concrete characteristics such as frost resistance and water resistance are important. For regions with winter temperatures in the range of -20...-40°C, concrete of frost resistance class F100 is required, for winter temperatures -5...-20°C - F 75, in warm climates (-5°C and above) F50 will be sufficient. The optimal water resistance class is W4 (normal), with high groundwater levels and waterlogged soil - W2.
Concreting should begin after thorough cleaning and degreasing of the formwork and reinforcement, in dry weather or if there is protection from rain. Surfaces must be dry. The concrete mixture is laid layer by layer in one direction, making sure that the thickness of the layers is the same - no more than 125% of the length of the working part of the manual deep vibrator. Breaks during installation are unacceptable. Each subsequent layer is laid after vibration compaction of the previous layer and before the concrete of the already laid layer begins to set (1-2 hours). The top layer should not reach the top edge of the formwork panels by 5-7 cm. It is strictly undesirable to take breaks during the process.
After concreting is completed, the foundation is covered with waterproof material. After about 8 hours, the surface of the concrete begins to be periodically watered with scattered jets of water with low pressure (only at average daily temperatures above +5°C).
Strip foundation stripping. Its timing depends on the ambient temperature and the properties of concrete. In warm weather (average daily temperature above +15°C), the formwork can be removed after about 6 days, in cold weather (+5°C and below) - after 10 days. Experts advise checking with the manufacturer about the rate at which concrete gains grade strength and removing the formwork no earlier than reaching 50-80% of it.
Waterproofing . There is a fairly large range of foundation waterproofing products on the market. These can be coating, weld-on, pasting or roll materials based on polymers or bitumen, special films, cement-based compositions, etc. When choosing, you should focus on your needs and financial capabilities, taking into account that the service life of inexpensive and easy-to-use waterproofing materials often small.
Insulation of a strip foundation is necessary for two reasons: to protect the waterproofing layer and to reduce heat loss, which can be very significant in a cold basement and an uninsulated foundation. It is convenient to insulate the foundation with sheets of expanded polystyrene with a thickness of at least 50 mm (for the middle zone climate). The sheets are simply glued over the waterproofing with solvent-free compounds; above the ground level, additional fastening with dowels is required.
Filling the trench and organizing the blind area. Before filling the trench, drainage pipes are laid at its bottom in a backfill of crushed stone 30 cm thick, wrapped in geotextile to protect against silting. The longitudinal slope of the pipes must be calculated to ensure unhindered water flow. After this, the trench is filled with non-heaving soil (gravel, crushed stone, coarse sand) without large solid inclusions that can damage the foundation. The soil is laid in layers 20 cm thick, each layer is compacted. After final backfilling, the soil should have a drainage slope directed away from the foundation with a height difference of 15 cm.
To protect the foundation, it is recommended to organize a soft blind area with insulation. The width of the blind area is calculated so that it ultimately protrudes 20 cm beyond the edge of the eaves overhang. There are different technologies for arranging an insulated blind area; the choice depends on your personal preferences.
Formation of the foundation.
In order to make a monolithic foundation yourself, you must first dig a foundation pit at least 60 cm deep. Then a “cushion” is poured into it, and waterproofing is laid on top. Only after this the reinforcement is laid in several layers, after which the entire structure is filled with concrete.
Strip foundation, suitable for heaving and clayey soils. It is formed from a continuous ribbon of reinforced concrete along the perimeter of the load-bearing walls of the house. The main principle of such a foundation is that the foundation of the house should not only be well stable and reliable, but also light. There are two types of strip foundations: recessed and slightly damaged.
A buried foundation is made as follows: the foundation is laid to a sufficient depth so that the soil does not freeze. It should be remembered that such a foundation should be wider than the walls of the house themselves, by about 100 mm, on all sides. The base of the building must have a minimum of 40 centimeters. After building the base, the reinforcement is laid in two rows, two layers each. However, this type of foundation has its drawbacks.
Firstly, the entire process of forming the foundation takes too much time and effort. Secondly, you must immediately have a certain amount of money so that there is enough for all the building materials that should be purchased in advance. Thirdly, you cannot build such a foundation yourself; you need assistants or a construction team, and their work must also be paid.
Typically, such a foundation is laid during the construction of multi-story buildings, or 3-story mansions with a basement. If, according to the project, the house has a basement, then such a foundation is better than other types.
A slightly damaged version of the foundation, much simpler than the previous one. And it differs from it in that it is suitable for one-story buildings and is laid at shallow soil depths. This type of foundation is low-cost, and even a beginner in the construction business can lay it. The most important thing here is to maintain all the necessary proportions.
So, to begin with, you can use an ordinary shovel; you need to dig a trench yourself, 60 cm deep. Then pour a “cushion” consisting of sand with crushed stone (gravel) into it. You should fill it in even layers of 15 cm each, preferably several times. Now we make the formwork and fill it all with concrete.
Now we make a frame of reinforcement in the upper part of the base and secure it securely. The width of the base should be 10 cm wider than all the walls in the house. A shallow foundation is ideal for non-heaving, hard layers of earth.
Let's build our own house
MZLF Strip foundation (LF) is a closed loop (strip) of reinforced concrete, erected under all load-bearing walls of the building and transferring the load from the building to the underlying soil.
A strip foundation allows you to build various structures on its foundation: from wooden to block and monolithic houses. At the same time, use a much smaller amount of building materials and carry out less excavation work in comparison with a slab monolithic reinforced concrete foundation (and ultimately, significantly reduces the cost of the entire foundation), which makes the strip foundation the most popular type of foundation in the construction of country houses and dachas. When building a foundation, it is important to correctly carry out all preliminary calculations and determine the parameters of the foundation. One of these parameters is the width of the foundation, which depends on the total load on the foundation and the bearing capacity of the soil. An example of calculating the width of a strip foundation for a two-story house made of aerated concrete. Let's calculate the weight of a two-story house made of aerated concrete measuring 10 * 10 m with a fifth load-bearing wall, the length of the walls is 50 meters, LF 1.2 m * 0.4 m (tape height * tape width) + base 0.5 * 0.4 m will have a weight =1.7m*50*0.4=34m³*2.5t/m³= 85t; The weight of the monolithic floors of the first and second floors is 10 * 10 * 0.2 * 2 = 40 m3 = 100 tons; thickness of aerated concrete walls 0.4 m, weight = 5 m * 0.4 * 50 = 100 m³ * 0.5 t/m³ = 50 tons; Roof area two slopes 7.5 * 11 m * 2 = 165 m², Weight of roof + sheathing + rafters (provided that this is the heaviest sheet roofing material slate 19 kg/m²) = 30 kg/m² 165 * 0.03 = 4.95 t ≈5 t Total: foundation with plinth + walls + floors + roof = 85 + 100 + 50 + 5 = 240 t. 240/50 = 4.8 t/m.p. (154t/50m≈3t/m.p. with wooden floors) If we calculate the weight of the house taking into account operational and snow loads and add the snow load (normative snow load for the 3rd snow region vk.com/wall-72891995_96) 16.5 tons and operational for covering the 1st and 2nd floors is 25 tons each, the weight of the house will be 306.5 tons, the linear load will be 6.13 tons/m.p. (220.5/50 = 4.41 tons per linear meter with wooden floors). W ≥ Yn×F/L×Rh, where W is the width of the base of the strip foundation, cm; L is the length of the tape perimeter, cm; F - design load on the base (total weight of the house, including the foundation, payload, snow cover...) (kg); Yn = 1.2 - reliability coefficient; Rh is the bearing capacity of the foundation soil. The values of the calculated soil resistance in the tables for the entry (R0) are given for a foundation depth of 1.5...2 m. If the foundation depth is less than 1.5 m, then the calculated soil resistance (Rh) is determined by the formula: Rh = 0.005R0 (100 +h/3), where h is the foundation depth, cm If the foundation depth is more than 2 m, then the calculated soil resistance (Rh) is determined by the formula: Rh = R0 + kg(h - 200), where h - foundation depth in cm, g - weight of the soil column located above the foundation depth (kg/cm2); k - soil coefficient (for sand - 0.25; for sandy loam and loam - 0.20; for clay - 0.15). vk.com/postroim_svoi_dom Let us determine the bearing capacity Rh for porous sandy loam at a depth of 120 cm (fluidity index - ΥL = 1, Rο = 2 kg/cm²) Rh = 0.005•1(100 +120/3) = 1.4 kg/cm² W ≥ Yn×F/L×Rh W ≥ 1.2•306500kg/5000cm•1.4kg/cm²= 52.5 cm - with monolithic floors W ≥ 1.2•220500kg/5000cm•1.4kg/cm²= 37 .8 cm for wooden floors. The calculation shows one of the weak foundations with low bearing capacity, when installing a sand cushion with layer-by-layer compaction from large and medium-sized sands under the LF with a thickness ≈ the width of the LF and 10 cm wider than the foundation in each direction, the value is Rh = 2 kg/cm². W ≥ Yn×F/L×Rh W ≥ 1.2•306500kg/5000cm•2kg/cm²= 37 cm - with monolithic floors W ≥ 1.2•220500kg/5000cm•2kg/cm²= 26.5 cm with wooden floors .
#Width#strip#foundation
#Let's #build#our#house
Installation of strip base
The entire technology for installing a strip foundation can be divided into stages:
- Preparation for work.
- Installation of trench system and formwork with spacers.
- Installation and tying of fittings.
- Pouring concrete solution.
- Foundation waterproofing.
- Backfilling of soil.
Preparatory work
At this stage, all calculations are made and the cost of the foundation is calculated. Then markings are made on the site
Using pegs and a cord, you need to mark the future foundation. Calculating the cost of the foundation is important, since without accurate results you can incur unnecessary costs
You need to use a special calculator, of which there are many on the Internet, or arm yourself with a regular one. You need to calculate the cubic capacity of the strip base using the formula: LxWxH, where L is length, W is width, H is height
It is important that the foundation does not have the shape of a trapezoid, but a parallelogram. So to fill a platform with a length of 240, a width of 40 and a height of 60 (240x40x60), you need approximately 6 cubes of concrete
But from personal experience I will say that it is better to add 10% to this figure, since it is difficult to create an absolutely level foundation with your own hands.
Simply put, the cubic capacity is calculated by projecting the shape of the foundation onto a suitable geometric figure. If the design is complex, then it is divided schematically into simpler ones, and their cubic capacity is calculated. These numbers are summed up at the end.
Main works
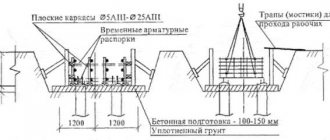
Installation always starts from cycle zero.
If we talk about a shallow foundation, then first a trench is dug along the markings with a depth of 60 cm. Then a cushion of gravel and sand is laid at 25-30 cm. The size of the cushion depends on the future height of the foundation and geodesy. A system of reinforcement with a diameter of 10-16 mm is connected. The connection should be a closed system without breaks with a fastening step of 10-20 cm. After this, formwork with spacers is made from edged boards 40x150-200. After this, future vents are installed using pipes. Concrete is then poured into this structure. Moreover, the height of the formwork must be at least 30 cm. This height will subsequently be the height of the base of the house.
To make concrete, sand, crushed stone and cement M 250 or 400 are used. This can be done independently, or using a special machine that requires access. If it is not available, you will have to additionally order a concrete pump. And these are unnecessary expenses. Each layer of concrete is poured separately and compacted until the planned volume is completely consumed. After the structure has completely dried, the formwork is removed.
How to calculate the cubic capacity of concrete for a foundation?
In most cases, the volume of concrete is calculated by the cubic capacity of the formwork. That is, what is the volume of the internal part of the formwork, so much concrete should be ordered (or prepared).
Moreover, the cubic capacity of the formwork can be determined at the calculation stage, from drawings and from data taken from the finished structure. Moreover, the last option will be a little more accurate than the first.
However, those who like simple solutions can use a special calculator for calculating the cubic capacity of the foundation - a special program that feeds the estimated dimensions of the foundation (length, width, height, wall thickness). As a result, users of the program receive not only an accurate calculation of the volume of solution used, but also recommendations for independently preparing concrete from sand, cement and crushed stone.
As you can see, there are many ways to calculate the cubic capacity of the base and the volume of solution used to fill the foundation. And further in the text we will present the simplest methods of calculations, adapted to specific foundation designs.
Calculation of cubic capacity of a monolithic slab
Such a base is a monolithic, rectangular parallelepiped, the edges of which can be measured using the finished formwork or according to the drawings.
The volume of such formwork is calculated simply - to do this, you need to multiply the area of the base of the foundation and the height of the formwork. In this case, the area of the sole is equal to the product of the width and length of the future grillage.
If we move from wording to numbers, then the cubic capacity of the foundation with grillage dimensions of 10x12 meters and a slab height of 0.4 meters is equal to 48 cubic meters (10m x 12m x 0.4m = 48 m3).
Of course, for accurate calculations, it is necessary to subtract the cubic capacity of the reinforcing mesh from this volume, but such dimensions make such calculations meaningless.
Calculation of the cubic capacity of the strip base
The strip base is the same rectangular parallelepiped, only with a hollow inner part. Moreover, elements to support interior partitions can also be located inside the base.
However, despite the slightly complicated shape, the volume of strip formwork can be calculated without much effort. To do this, you need to subtract from the volume of the rectangular parallelepiped formed by the outer walls of the formwork, the volumes of the same geometric figure formed by the inner walls of the formwork.
After this, the volumes of internal tapes supporting the interior partitions can be added to the result obtained. Moreover, the transverse, internal strips (relative to the front side of the facade) are considered as one parallelepiped, and the longitudinal ones - as two parallelepipeds adjacent to the transverse strip.
And if we move from formulas to numbers, then the volumes of a base of 10x12 meters with a tape width of 0.4 meters, buried 2 meters into the ground and supplemented by one internal tape, 0.5 meters thick, are calculated as follows:
- We determine the volume of the external parallelepiped 10m x 12m x 2m = 240 m3.
- We calculate the volume of the internal parallelepiped (10-0.4-0.4) m x (12-0.4-0.4) m x 2 m = 206.08 m3.
- We calculate the difference in volumes: 240 m3 - 206.08 m3 = 33.92 m3 - this is exactly the volume of the tape under the load-bearing walls of the building.
- The volumes of the internal tape are calculated simply (10-0.4-0.4) m x 0.5 m x 2 m = 9.2 m3.
- The total pour volume is 33.92 m3 + 9.2 m3 = 43.12 m3.
Calculation of cubic capacity of a columnar base
The cubic capacity of a columnar base is defined as the sum of two geometric figures - a wide and low parallelepiped-base and a high and narrow parallelepiped-column.
The specified value is multiplied by the total number of pillars at the base, located along the perimeter of the facade in increments of 2 meters.
In figures, the volume of the columnar foundation for the house is 6x6 meters, with a total number of pillars of 20 pieces (four corner and 16 intermediate), the bases of which have dimensions of 0.5x0.5x0.2 meters, and the pillars are 0.3x0.3x0.8 meters , is calculated as follows:
- The total volume of the base is 20 x 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.2 = 1 m3.
- The total volume of the pillars is 20 x 0.3 x 0.3 x 0.8 = 1.44 m3.
- The total volume of pouring is 1+1.44 = 2.44 m3.
Calculations of a bored foundation with a monolithic grillage
The cubic capacity of this type of base is calculated as the sum of the cubic capacity of the pillars (cylinders) and the grillage slab (rectangular parallelepiped). That is, as in previous cases, we break the complex fill into many simple shapes and, having calculated their volume, we get to the desired result.
Moreover, the volume of the column is calculated as the product of the area of its base and the height from the base to the lower border of the grillage. And the area of the base (circle) is equal to one quarter of the product of twice the diameter and the constant π (3.14)
In numerical terms, the cubic capacity of the foundation on 20 pillars with a diameter of 0.4 meters and a depth of immersion in the ground of 2.5 meters, which support a grillage with dimensions of 10x12x0.3 meters, is calculated as follows:
- The volume of the pillars is 20 x (1/4 x 3.14 x 0.4 x 0.4) x 2.5 = 6.28 m3.
- The volume of the grillage is 10 x 12 x 0.3 = 36 m3.
- The total volume is 36 + 6.28 = 42.28 m3.