The strip foundation occupies the main place among all supporting structures for buildings and structures.
It is able to work effectively on the most difficult soils and has an optimal set of performance qualities.
Monolithic tape structures do not lose their performance qualities for up to 150 years, which exceeds the service life of the walls of a house.
Such high possibilities arose due to the high rigidity and strength of the tape, which is ensured by the joint work of concrete and metal reinforcement.
Each of them performs its own function, together providing reliability and high load-bearing capacity of the strip base.
Reinforcement scheme
The location of the reinforcement in the strip foundation in cross section is a rectangle. And there is a simple explanation for this: this scheme works best.
Reinforcement of a strip foundation with a strip height of no more than 60-70 cm
There are two main forces acting on the strip foundation: heaving forces press from below during frost, and the load from the house from above. The middle of the tape is almost not loaded. To compensate for the action of these two forces, two belts of working reinforcement are usually made: above and below. For shallow and medium deep foundations (up to 100 cm deep) this is enough. For deep belts, 3 belts are already required: too high a height requires reinforcement.
For most strip foundations, the reinforcement looks like this
To ensure that the working fittings are in the right place, they are secured in a certain way. And they do this using thinner steel rods. They do not participate in the work, they only hold the working reinforcement in a certain position - they create a structure, which is why this type of reinforcement is called structural.
To speed up work when knitting a reinforcing belt, clamps are used
As can be seen in the strip foundation reinforcement diagram, the longitudinal reinforcement bars (working) are tied with horizontal and vertical supports. They are often made in the form of a closed loop - a clamp. It’s easier and faster to work with them, and the design is more reliable.
What fittings are needed
For strip foundations, two types of rods are used. For longitudinal ones that bear the main load, class AII or AIII is required. Moreover, the profile is necessarily ribbed: it adheres better to concrete and transfers load normally. For structural lintels, cheaper reinforcement is used: smooth first class AI, 6-8 mm thick.
Recently, fiberglass reinforcement has appeared on the market. According to manufacturers, it has better strength characteristics and is more durable. But many designers do not recommend using it in the foundations of residential buildings. According to the standards, it must be reinforced concrete. The characteristics of this material have long been known and calculated; special reinforcement profiles have been developed that ensure that metal and concrete are combined into a single monolithic structure.
Reinforcement classes and their diameters
How concrete will behave when paired with fiberglass, how firmly such reinforcement will adhere to concrete, how successfully this pair will resist loads - all this is unknown and has not been studied. If you want to experiment, please use fiberglass. No - take iron fittings.
Rules for reinforcing strip bases
The method of metal distribution based on long-term practical experience is common in this work:
- if the length of the tape does not exceed 3 m, then it is permissible to use a 10 mm rod in a horizontal position;
- if its dimensions are more than 3 m, you need to choose a rod from 12 to 16 mm;
- all longitudinal reinforcement used in the frame must be strictly the same diameter.
If the thickness of the existing rods is different, then larger ones are installed in the lower tier, and sections with a smaller cross-section are installed in the upper tier. It should be understood that products with d = 10 and d = 16mm differ significantly in weight and, if you purchase it with a maximum safety margin, this can significantly increase the load on the ground and increase the cost of purchasing material.
As for the comparative analysis of rolled products with and without corrugation, the following principle applies here: the greater the depth of the pattern, the stronger the bond between concrete and metal. This is very important to know when pouring voluminous and heavy strip bases, where it is inappropriate to give preference to a smooth profile. The work uses a special fastening wire made of low-carbon steel with a thickness of 0.8 to 1.5 mm, which is pre-cut into equal sections.
Calculation of the amount of reinforcement
First, the perimeter of the future house structure is determined, and the number of longitudinal rows of rods is taken into account. As an example, we can take a building measuring 8 by 12 m, a strip-type foundation 40 cm wide and 100 cm high (the soil on the site is heaving). The total length of the load-bearing wall around the perimeter is 40 m (8+8+12+12).
- When creating a strip-type foundation, two reinforcing mesh must be installed, the lower one of which prevents concrete rupture during soil subsidence, and the upper one - during soil heaving.
- The optimal mesh pitch is 0.2 m. For a strip base, you will need 2 longitudinal rods, which are located in each layer of the reinforcement frame.
The reinforcing mesh is not necessarily assembled on site - it is much easier to use a ready-made oneSource mega-les.ru
- The diameter of the rod is selected depending on the wall material that creates loads on the base. The frame of a wooden house is not heavy compared to a brick one, so rods with a diameter of 12 mm are quite suitable. In total, 96 meters of rods (2*12*2*2) will be required to reinforce the foundation of the two long sides of the building. For the short sides you will have to spend 64 m (2*8*2*2). You should also take into account the joints where the fittings are launched. As a rule, it is enough to add 10-15% to the total footage. The resulting figure is 160*10%=16 meters. In total, the estimated length for the longitudinal elements is 176 meters (96+64+16).
- Transverse connecting elements with a diameter of 10 mm are located at a distance of 50 cm from each other. Their number is 80 pieces - the perimeter of the foundation should be divided by the laying step (40/0.5). The length of the rods is equal to the width of the tape 40 cm. The total length is 32 meters (80 * 0.4).
- Vertical connections are made from a rod with a diameter of 10 mm. The height of the reinforcement is the same as that of the tape - 100 cm. The number of steel rods is determined by the number of intersections: 80 transverse elements are multiplied by 4 longitudinal elements, resulting in 288 pieces. With a length of each segment of 1 m, the total length is 288 meters.
Ready-made reinforcement frame for strip foundationSource hobbymaniya.ru
Summing up all the calculations, it turns out that to create a reinforced frame for a house measuring 8x12 you will need to purchase:
- 176 meters of steel elements class A-III with a diameter of 12 mm.
- 320 meters of class A-I rods with a diameter of 10 mm (32+288).
The weight of the reinforcement for a strip foundation is determined in accordance with GOST 2590. A linear meter of a 12 mm bar weighs 0.888 kg, 6 mm - 0.222 kg. The total mass is: 176*0.888=156.29 kg, 320*0.222=71.04 kg. In total, the fittings weigh 227.33 kg.
The transverse and longitudinal elements are connected using a knitting wire. The knitting method is performed as follows: at the junction, the wire is tightened, and the protruding ends are twisted with pliers, a special hook, or a screwdriver. Specialists use special guns, which significantly speed up the process.
For information on various methods of tying reinforcement, watch the video:
Calculation of the cost of reinforcement for the foundation
Reinforcement and wire are often sold by the kilogram. Therefore, the found amount of rod will need to be converted into mass. In the place where you are going to purchase the rod, you will find out how much a linear meter weighs and how much a ton of products of the size you need costs.
By multiplying the found footage by the weight of one meter, you get the required mass. From there you will find out how much it will cost.
Table with the weight of one meter of reinforcement and one ton of footage
For example , let’s calculate how much reinforcement for a slab foundation will cost (see above). Let the rod be used 14 mm. One meter of it weighs 1.21 kg. In total, 650 m of reinforcement is needed. The mass will be 650 * 1.21 = 786.5 kg. Let's round up to 800 kg. Let one ton cost 25 thousand rubles. The fittings will require 0.8 * 25,000 = 20,000 rubles.
To install the strip foundation we calculated, you will need 84 m of 12 mm rod. Its meter weighs 0.888 kg. The total mass will be 0.888 * 84 = 74.592 kg. Let's assume that you need 80 kg. A ton costs almost the same 25 thousand rubles. That is, a profiled rod will require 0.08 * 25000 = 2 thousand rubles. The cost of smooth reinforcement is also considered. It will cost about 1.5 thousand rubles. In total, reinforcing the strip frame will cost 3.5 thousand rubles. (plus the cost of the wire, it is calculated similarly).
The weight of the reinforcement is indicated accurately, and the cost varies quite a lot depending on the exchange rate, region and volume of purchases. Some metal warehouses sell by linear meters, not by weight, but you need to look at the cost: sometimes they are very overpriced.
Possible errors and how to fix them
A small overlap of reinforcement or its absence in the frame is unacceptable, since the frame may move during the concreting process.
This may damage the finished product. It is better to leave allowances of 200 mm.
Welding elements or tying with unsuitable material, such as rope, is not permitted.
Welding makes the fastening unit fragile, and the rope does not provide sufficient strength to the connection.
Reinforcement of corners without overlaps. Reinforcing lap corners with whip can lead to rapid failure and uneven load transfer between the two parts of the foundation structure. To solve the problem, additional bent elements are included.
Counting the amount of reinforcement
The easiest way to calculate how much metal reinforcement is required for a foundation is to use the example of a base measuring 10x10 m.
Since the reinforcement frame is one of the most expensive elements of the foundation, in order to avoid unnecessary costs, it is necessary to especially carefully calculate the consumption of reinforcement per cube or for the entire foundation. Typically, in order to calculate the required amount of reinforcement, the following formula is used: L=4xP, where:
- “L” is the amount of material that is needed for the longitudinal load-bearing reinforcement bars;
- “P” is the perimeter of the foundation.
In this case, reinforcement with diameters from 10 to 12 mm is used. The rods must be placed in two belts, securely connected to one another.
Each such belt is a reinforcing mesh with a cell diameter of about 20 cm. Provided that the thickness of the frame is about 20 cm, the length of the lintels should be 25 cm.
If you make simple calculations, it turns out to be quite simple to calculate the consumption of reinforcement: for 10 m of a slab you need 51 metal rods, each of which is 10 m long. For a perpendicular mesh you need a similar number of rods. In total, the total consumption of reinforcing bars will be 102 bars for one belt. It will be even easier to count how many rods are needed for the second reinforcing belt: 102x2 - 204.
How to calculate reinforcement for a foundation - example calculations
As an example, let's consider how much reinforcement is needed for a 10x10 foundation formed in the form of a monolithic reinforced concrete strip.
To perform calculations we use the following information:
- base width 60 cm, allows you to lay 3 horizontal rods in each belt;
- 2 reinforcement belts are made, connected by vertical rods at intervals of 1 m.
- for a building 10x10 m and a base depth of 0.8 m, reinforcement with a diameter of 10 mm is used.
Consumption of reinforcement for strip foundation
Calculation algorithm :
- We determine the perimeter of the building’s foundation by adding the length of the walls - (10+10)x2=40 m.
- We calculate the number of horizontal elements in one belt by multiplying the perimeter by the number of rods in one tier - 40x3 = 120 m.
- The total length of the longitudinal bars is determined by multiplying the resulting value by the number of tiers 120x2=240 m.
- We calculate the number of vertical elements installed 10 pairs on each side 10x2x4 = 80 pcs.
- The total length of the vertical rods will be 80x0.8=64 m.
- We determine the length of the jumpers, each measuring 0.6 m, installed on two belts (20 per side) - 10x2x4x0.6 = 48 m.
- Adding the length of the reinforcing bars, we get a total footage of 240+64+48=352 m.
Determining the length of steel wire is easy. The number of connections multiplied by the length of one piece of wire equal to 20–30 cm will give the desired result.
Tools and accessories
To reinforce a strip foundation with our own hands, we will need certain tools and devices. First of all, the reinforcing bars will need to be cut into pieces in accordance with the prepared drawing. To do this, you can use a grinder with a metal cutting disc, or purchase a mini-machine. Thin rods can be cut with powerful professional cutters.
To reinforce the frame in the corners and make □-shaped clamps, you will need a device for bending rods, which you can make yourself or purchase ready-made.
How to properly tie reinforcement for a strip foundation: you need to tie the rods only with a special baked steel binding wire and use a tool convenient for you (an automatic or manual hook for tying reinforcement, a knitting gun, a screwdriver or pliers). All connected joints must be tight to prevent the bars from moving when pouring concrete.
The reinforcement can be laid in prepared formwork. But it is possible to make a metal frame for the foundation in separate fragments (outside the formwork). This operation can be greatly facilitated by a simple device consisting of two sheets of thick plywood. Drawing:
The holes in the blanks correspond to the location of the reinforcement in the foundation. First, we insert the longitudinal rods into the holes of one plywood panel. Then we put the required number of clamps on them. We insert the free ends of the rods into the holes of the second shield. This results in a convenient spatial structure for knitting a fragment of a reinforced frame.
After the reinforcement for the strip foundation has been knitted in separate fragments, it is necessary to lay them in the formwork and firmly fasten them together.
How much reinforcement is needed for a 10x10 slab foundation
To create a platform, a foundation is made in the form of a slab (slab base). Before you start pouring the foundation, you need to pour a layer of sand and crushed stone, cover it with a small layer of mortar and lay out the reinforcement. Typically, rods with a diameter of 12 mm are used for this purpose. The cell size in this case is 20 mm and a two-belt system of laying the reinforcing layer is used.
With a base slab size of 10x10 m, ten rods are required per linear meter. Accordingly, for 10 m - 50 pieces. Let's add here 50 transverse rods and we get the material consumption for one belt - 50 rods. Since two belts are required, we multiply the resulting number of rods by this number and obtain the required volume of material - 100 rods.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=qUEtdKOfE0k How much reinforcement is needed for a 10x10 columnar foundation. To reinforce a columnar foundation, reinforcing bars with a cross-section of 10 to 12 mm will be required. They are installed vertically in increments of 10 to 15 cm. There are 4 rods per post. To calculate the amount of reinforcement, you need to know the total number of all pillars. You can find out this figure from the project documentation.
Calculation for a monolithic base
A monolithic reinforced concrete slab is laid under the entire area of the building.
Laying a monolithic base is justified on soft and moving soils.
Scheme of reinforcement of a monolithic foundation slab.
It provides maximum stability and best resists heaving forces. Whenever there is any movement of the ground, the entire slab is lowered or raised, preventing distortions and cracking of the walls. Because of this, the monolithic base is called floating.
Let us calculate the reinforcement for a slab foundation for a 10x6 m building. The thickness of the slab is determined by calculating the load on the base. In our example, it will be 30 cm. Reinforcement is performed by two belts with a grid pitch of 20 cm. It is easy to calculate what will be needed for each belt:
1000/200 = 50 transverse rods 6 m long,
6000/200 = 30 longitudinal rods 8 m long.
The total length for 2 belts will be:
(50x6+30x8)x2 = 1200 m.
The connection of the belts is made with smooth profile reinforcement. In total we count:
50 x 30 = 1500 knots.
Taking into account the 5 cm indentations from the edges of the slab, the length of the connecting rod is 0.2 m. Thus, for a smooth profile you need:
1500x0.2 = 300 m.
In addition, you will need to take care of purchasing wire for the bundle. The required quantity is determined at the rate of 30 cm per knot. In our case:
3000x0.3 = 900 m.
The tying is done with pieces of wire folded in half.
Rules for installing reinforced frames according to SNiP
The amount of reinforcement required for the structure being laid and the distance between the reinforcing bars directly depend on the size of the foundation.
According to SNiP 52-01-2003, the distance between the rods is calculated based on:
- rod diameter;
- concrete aggregate size;
- concreting directions;
- laying technologies;
- type of concrete compactor.
Technologically correct reinforcement implies that the distance between the longitudinal reinforcement bars should be in the range from 25 to 40 cm. The transverse reinforcement bars should be no more than 30 cm from each other.
You will find all the most important things about strip foundation reinforcement in this publication.
Requirements for concrete
Concrete for a strip foundation must meet certain physical and technical requirements. Among them:
- strength;
- frost resistance;
- waterproof.
Strength is the ability to withstand compressive loads, expressed in kilograms per square centimeter.
Frost resistance is indicated by the letter “F” and a numerical equivalent. The number is the number of cycles of complete freezing and thawing of a prototype concrete sample without changing its characteristics.
Water resistance is indicated by the letter “W” and also by a numerical equivalent. The number, in this case, is the maximum pressure, measured in megaPascals, at which a concrete sample does not allow moisture to pass through.
Concrete grades recommended for the construction of strip foundations:
| Concrete grade | Concrete class | Strength of concrete, kg/cm2 | Frost resistance | Waterproof |
| M-200 | B-15 | 196,5 | F-100 | W-4 |
| M-250 | IN 20 | 261,9 | F-100 | W-4 |
| M-300 | V-22.5 | 294,4 | F-200 | W-6 |
| M-350 | B-25 | 327,4 | F-200 | W-8 |
| M-400 | B-30 | 392,9 | F-300 | W-10 |
The relationship between the type of structure, soil and grade of concrete for a strip foundation:
| Type of structure | Slightly heaving soils | Heaving soils |
| Light wooden or frame houses | M-200 | M-250 |
| Houses made of timber, log cabins | M-250 | M-300 |
| Houses made of arbolite blocks and similar materials | M-300 | M-350 |
| Houses made of brick, stone, reinforced concrete | M-350 | M-400 |
Requirements for fittings
To reinforce the strip foundation, steel or composite reinforcement is used. Its surface is profiled, which leads to the transfer of maximum load from sagging concrete to the reinforcing bars.
For longitudinal reinforcement, metal rods are usually used, the diameter of which ranges from 10 to 16 mm.
For transverse reinforcement, metal rods are used, the diameter of which ranges from 6 to 8 mm.
In accordance with SNiP 52-01-2003, the following types of reinforcement can be used when constructing a strip foundation:
- hot rolled;
- thermomechanically strengthened;
- mechanically hardened in a cold state;
- non-metallic composite.
This article will tell you what kind of reinforcement is used to reinforce a strip foundation.
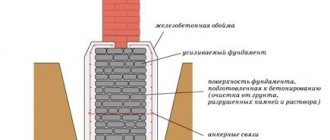
Strip foundation design
Purely structurally, a strip foundation is a strip (hence, in principle, the name), which is constructed under all the walls of the building. This is a continuous structure laid in the ground, for which formwork is erected for it, installed in a previously dug trench.
Strip foundation
Advantages of a strip foundation:
- high load-bearing capacity;
- ease of construction;
- high construction speed.
The design also has its drawbacks:
- the heavy weight of the structure, which can cause uneven shrinkage, so it is very important to first conduct a soil study and determine the level of groundwater;
- after pouring, you will have to wait 28 days for the concrete to gain its original strength, after which the foundation can be loaded.
Calculation procedure
Let's look at how to calculate the reinforcement cage of the tape yourself.
First of all, it is necessary to determine the number of working rods in one row. To do this, you will need to use the requirement of SP 52-101-2003, which limits the maximum distance between adjacent rods to 40 cm.
Considering that the immersion depth of the working reinforcement should not exceed 2-5 cm, we obtain:
- For tapes less than 50 cm thick - 2 working rods.
- For tapes wider than 50 cm - 3 rods.
In cases where it is possible to use both 2 and 3 rods in one row, they usually try to play it safe and take a larger value, since the foundation is a responsible and important section of the building.
The second stage is to determine the diameter of the working rods. To do this, you will need to calculate the cross-sectional area of the working part of the tape by multiplying the width by the height.
The total cross-sectional area of the reinforcement is 0.1% of the cross-section (this is the minimum possible value, it can be increased, but cannot be decreased).
Having received this value, you need to divide it by the number of working rods. Using the table of diameters of reinforcing bars, the most successful option is found, which is accepted for work.
The diameter of the vertical reinforcement is selected based on the height of the tape:
- For heights up to 60 cm - 6 mm.
- From 60 to 80 cm - 8 mm.
The diameter of the transverse rods is usually taken to be 6 mm.
To calculate the number of working rods, you need to multiply their number in the lattice by the total length of the tape, after which the resulting value is divided by the length of the working rod (usually 6 m, but it is better to find out exactly this value from the sellers).
Vertical reinforcement is calculated by multiplying the number of clamps by the length of the unit.
The quantity is obtained by dividing the total length of the tape by the pitch of the clamps (usually 50-70 cm).
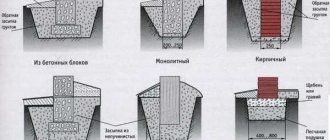
Formwork
To assemble the formwork, panel materials are used (OSB sheets, plywood or boards at least 5 cm thick). It is designed with an indentation upwards of several centimeters from the level of the poured concrete and consists of an outer and inner deck.
This step is not always required. Instead of formwork, it is possible to use polystyrene foam or other insulating material and use reinforced concrete blocks.
Sand-gravel concrete (SGMC)
Construction costing is a stage that will save not only money, but also time!
The calculator's interface is easy to understand, and to perform calculations you only need to specify the parameters of your foundation.
Calculation of the amount of reinforcement for a slab-type foundation
The foundation of a slab structure is used for the construction of residential buildings on heaving soils. To ensure strength characteristics, reinforcing bars with a diameter of 10–12 mm are used. With increased mass of buildings, the diameter of the rods should be increased to 1.4–1.6 cm.
You can calculate the amount of reinforcement for the foundation of a slab structure using the following information:
- a spatial frame made of reinforcement is constructed in two levels;
- the connection of the rods is made in the form of square cells with a side of 15–20 cm;
- The binding is performed with annealed wire at each connection point.
Reinforcement diagram for a monolithic foundation slab
To determine the need for reinforcement, perform the following operations:
- Determine the number of horizontal rods in each tier.
- Calculate the total footage of the reinforcing bars that form the cells.
- Add the total length of the vertical supports connecting the tiers.
Calculation of slab base reinforcement
To form a monolithic slab, two iron belts are installed, which are formed by horizontal meshes, united by a 10-16 mm rod. First you define a pattern, for example, a square with sides 20x20 cm.
Next, calculate how many rods are needed for each tier separately and their total number. The volume of vertical jumpers inserted at the intersections of the metal is added to the resulting amount. Then, according to the number of tie points in the cells, calculate the footage of annealed wire that will be used for fastening.
Corner reinforcement
In the design of a strip foundation, the weakest point is the corners and the junction of the walls. In these places loads from different walls are combined. In order for them to be successfully redistributed, the reinforcement must be properly tied. Simply connect it incorrectly: this method will not ensure load transfer. As a result, after some time, cracks will appear in the strip foundation.
The correct scheme for reinforcing corners: either bends are used - L-shaped clamps, or longitudinal threads are made 60-70 cm longer and bent around the corner
To avoid this situation, when reinforcing corners, special schemes are used: the rod is bent from one side to the other. This “overlap” should be at least 60-70 cm. If the length of the longitudinal rod is not enough to bend, use L-shaped clamps with sides also at least 60-70 cm. Schemes of their location and fastening of the reinforcement are shown in the photo below.
The abutments of piers are reinforced using the same principle. It is also advisable to take the reinforcement with a reserve and bend it. It is also possible to use L-shaped clamps.
Reinforcement diagram for adjacent walls in a strip foundation (to enlarge the picture, right-click on it)
Please note: in both cases, in the corners, the installation step of the transverse jumpers is reduced by half. In these places they already become workers - they participate in the redistribution of the load
Calculation of strip foundation reinforcement with an example
Input data:
- strip foundation length – 20 m;
- width – 40 cm;
- height - 80 cm.
First of all, it is necessary to calculate the amount of longitudinally laid reinforcement.
- The cross-sectional area of the foundation strip is 40x80=3200 cm².
- Total area of longitudinal reinforcing bars: 3200x0.1%=3200x0.001=3.2 cm². Or you can do it this way: 3200/1000=3.2 cm².
Now the resulting value must be divided by the area of one rod, thereby obtaining the amount of required longitudinal reinforcement. There are two ways to obtain the area of one rod. The first is to find on the Internet a table of the ratio of diameter and area of reinforcement. One of these is pictured below.
Table of the ratio of diameter and area of reinforcement
The second is to carry out the calculation yourself using the formula for the area of a circle: S=πD²/4, where
- "π" is the Archimedean number equal to 3.14,
- D – reinforcement diameter.
If the diameter of the longitudinal reinforcement was chosen to be 10 mm (1 cm), then: S= 3.14x1²/4= 0.785 cm². Now the total area of the reinforcing bars (3.2) must be divided by 0.785, resulting in 4.
The next stage of calculating the reinforcement of a strip foundation is determining the total length of the longitudinal rods. It should be noted that in the longitudinal direction the rods are laid relative to each other with an overlap of 5-10 cm. That is, the length of the rods, the standard length of which is 10.7 m, is reduced by the selected size. It turns out that the length of each after connection will be equal 10.6 m or 1160 cm.
Considering the length of the strip foundation - 20 m, you can calculate how many rods are required to lay one longitudinal element: 20:11.6 = 1.72 pieces. And since there are four of them, the total number is: 1.72x4 = 6.89 or, rounded, exactly 7.
Now it is necessary to determine the number and length of the vertical and transverse elements of the reinforcing frame of the strip foundation. Taking into account position number “2” of the requirements for assembling the reinforced frame, we can say exactly what length the transverse and vertical rods will be:
- for transverse ones: 40-10=30, where “10” is two by five distance from the edges of the foundation structure to the frame, “40” is the width of the tape;
- for vertical ones: 80-10=70 cm.
That is, in total, if both elements are made from the same type of reinforcement, then their production will take 1 m of steel material (30 + 70 = 100 cm). Next, you need to calculate the number of rods of this type used in the frame itself. If the distance between them is chosen within 30 cm, then the quantity is determined by dividing the total length of the foundation by the installation step: 2000:30 = 66.66 pieces. Round up to 67.
And since the total length of the two elements is 1 m, their manufacture will take 67 m of reinforcement. This indicator is multiplied by “2”, because in the reinforcing frame there are two pairs of transverse and vertical rods. The first are located at the top and bottom of the structure in a horizontal plane, the second on the sides in a vertical plane. This means that for their manufacture you will need 67x2 = 134 m.
The pitch of laying the vertical bars does not always coincide with the step of the transverse ones, as was discussed in the example above, because the crossbars mainly function as ties between the gratings. And their number can be reduced. For example, lay in increments of 50 cm.
Therefore, the calculation of the required reinforcement will have to be carried out for two elements separately.
Cross members are calculated as follows:
2000:50x30=120 cm or 12 m, where “20” is the length of the foundation strip, “50” is the step of installing the crossbars, “30” is the length of one transverse element.
Vertical rods like this:
2000:30x30=2000 cm or 20 m, where the installation step is 30 cm.
It turns out that the total length of the reinforcement required for the manufacture of vertical and transverse elements is 12 + 20 = 32 m. With a caveat, if reinforcement of the same diameter is used for them. Otherwise, each parameter will need to be taken into account separately.
It is necessary to indicate that the presented calculation of reinforcement for a strip foundation in terms of counting the number of rods is incomplete. Because in the corners of the foundation structure a special connection of frames located on different sides of the strip structure is used. Depending on the tying scheme of the mating corners, the total length of the reinforcement used may change. In the total mass, the addition is insignificant and can be up to 5 m. But it must be taken into account. Therefore, most often the total design length of the reinforcement is increased by 5-10%.
Purpose of the calculator
Easy to use, it allows you to calculate the number of reinforcement bars, the selected material for formwork, and also calculate the volume of m3 of concrete that will be required during construction.
Helpful information:
- Strip length calculator for gates made of corrugated sheets
- Penetrating waterproofing for concrete
- How much does a cube of concrete weigh?
- Brand of concrete for the foundation
- Pipe length calculator for corrugated gates
- Ironing of concrete surface
Purpose of online calculation:
- Save time when preparing cost estimates.
- Predict the volume of work and timing of foundation formation.
- Calculate the parameters, which will allow you to construct a high-strength and reliable frame.
A well-planned foundation design minimizes the risk of its destruction in the future, ensuring the safety of the entire structure.
Soil type, freezing depth, load-bearing capacity and swelling are factors for a thorough study of the area when searching for a construction site.
Another equally important factor is the level where groundwater lies. It is also important to clarify the depth of soil freezing. Laying the foundation taking into account this level is a guarantee of the safety of the building under the influence of natural processes on the soil.
With a high level of groundwater, the long-term prognosis for construction is unfavorable. In regions with a warm climate, dampness and frequent flooding are possible in this case; over time, the concrete will loosen and dissolve. In regions with a sharply continental and predominantly cold climate, an irrationally laid foundation runs the risk of collapsing over several winter seasons due to soil heaving.
DIY printed concrete: easy!
The type of foundation, which is a closed system of reinforced concrete structures located under each of the load-bearing walls, is called strip. This design in the form of a ribbon under the house ensures uniform distribution of the load. The bearing capacity of a foundation of this type makes it possible to erect buildings of different heights on almost all types of soil.
A properly constructed structure remains stable regardless of changes in soil characteristics caused by natural factors. It is a leader in private construction due to its durability, affordable pricing and relatively simple construction technology.
The base is suitable for any walls: timber, foam concrete, aerated concrete, brick.
Depending on the differences in the frame, strip foundations can be monolithic or prefabricated. In the first case it is a continuous concrete strip, in the second case it is a structure made of separate blocks. The prefabricated base lasts for a significantly shorter period.
In terms of depth, it can be shallowly buried or deeply buried.
Foundation reinforcement
In order to qualitatively strengthen the foundation of a future building, it is necessary to reinforce it. To do this, you must first calculate all the necessary material from which the foundation frame will subsequently be assembled. Correct calculations will allow you to use up the metal “to zero”, thereby saving you from the difficulties associated with ordering and delivering the missing material.
Material calculation
This stage involves accurate calculations and the correct sequence of calculations. Often, in order to obtain a particular value, you need to build on previous calculations. Thus, all values are interconnected, and incorrect calculations can lead to undesirable consequences that can be detrimental to the thickness of your wallet. Take the work at this stage extremely seriously, or better yet, count everything twice, then you will have enough metal rods for future use.
To calculate the amount of metal required to reinforce a strip monolithic foundation for a house measuring 8x8 m with two partitions of 8 m and 4 m, proceed as follows, proceeding in stages:
- To calculate the total length of the horizontal elements that perform the load-bearing function of the frame (reinforcement with a cross-section of 10-12 mm), you need to do the following: measure the total perimeter of the foundation, taking into account the internal walls ((8+8)*2=32 m). Don't forget to take into account the partitions: (32+8+4=44 m). Multiply the result by 4: (44*4=176 m). Thus, the required number of load-bearing horizontal elements is 176 m.
- To calculate the number of lintels (reinforcement with a diameter of 8 mm): divide the total length of the foundation by the value of the interval between the tie elements (50 cm). Multiply the resulting value by 4: (44/0.5*4=352 pcs).
- To calculate the number of horizontal and vertical jumpers, it is enough to know the width and height of the frame. Let's say the frame has dimensions of 50*30 cm. Thus, to calculate the horizontal jumpers you need: (352/2*0.5=88 m). For vertical: (352/2*0.3=52.8 m). Therefore, the total number of jumpers is equal to: (88 + 52.8 = 140.8 m, rounded to 141 m).
- To calculate the amount of knitting wire (3 mm wire rod), first count the number of points of future knitting. Since our frame has 352 connection points, 4 ties on each side, we apply the formula: ((352+(4+4)*4)*0.5=192 m of wire rod).
As you can see, making all the necessary calculations is not difficult; the main thing is to make all the measurements correctly and accurately indicate all the values. In addition, always take material with a 10% margin. Since when assembling the frame you will often cut metal, unusable remnants of reinforcement simply cannot be avoided.
We make coasters
The bottom layer of the reinforcing frame is laid on ready-made plastic stands, after which special “tables” are installed on it, which support the next layer of the structure. They are made from a piece of reinforcement, the size of which is calculated based on the thickness of the monolithic slab. Let's say we are dealing with a base 40 cm thick. In this case, the calculations will be as follows:
40 cm (height of the slab) – 8 (two protective layers of 4 cm each) – (4 x 1 cm) (thickness of the rods multiplied by their number) = 28 cm.
A supporting “table” is made by bending it into a U-shape. The bending radius is selected individually. The “tails” of the stand are bent in opposite directions, thereby forming reliable stops that will allow you to lay and fix both layers of the structure.
Consumption of reinforcement per cubic meter of concrete
Separately, the consumption of reinforcement per m 3 of concrete should be considered. The calculation is made according to the current GOST individually in each individual case. This is due to the fact that the characteristics of concrete itself can vary within fairly wide limits depending on the filler and additives.
To reinforce the foundation, steel ribbed reinforcement with a diameter of 8 to 14 mm is most often used. Such a surface allows for maximum adhesion to the concrete layer. On average, a 10 by 10 foundation requires 150-200 kg of reinforcement per cubic meter of concrete (for columns, the consumption ranges from 200 to 250 kg per cubic meter of concrete). Recently, fiberglass reinforcement has been used in the construction process. Its cost is slightly higher than the cost of its metal counterpart. But if you calculate how many such reinforcing rods are needed per m 3, most likely the use of composite reinforcement for the foundation will be much more profitable. As a rule, the cost of composite reinforcement is on average half that of steel. This is due to the fact that the consumption per cube of concrete for the rods is similar, but the weight of the composite is much lower.
In principle, it is not so difficult to calculate the consumption of rods per cube of concrete and not make a mistake. You just need to know how many m 3 of concrete will be used to fill the foundation. If you are afraid of making a mistake in calculating the reinforcement for a cube of concrete, you can always take the help of professionals. They will calculate with maximum accuracy the consumption of materials per m 3 of solution and, if necessary, will lay the foundation itself, as well as its reinforcement.
Calculation of concrete for the foundation
Concrete is the base of any foundation. This is a mixture of cement of the required grade, sand, water and crushed stone prepared in maintained proportions. It is used in absolutely all construction work, from erecting a fence to building skyscrapers.
Classification (marking) of concrete is carried out according to compressive strength (M), mobility (P), water resistance (W) and frost resistance (F).
The grade of concrete is determined by the permissible loads (compressive strength). Characterizes the load per cubic centimeter of surface (expressed in kg/cm²).
Among the variety of concrete grades to choose from (from M50 to M800), M100-M400 grades are most often used in the construction of private houses and outbuildings.
For lightweight buildings, concrete grade 100 is used. Concrete 150 is used for pouring shallow foundations for light buildings such as garages and bathhouses.
When forming retaining structures, a more suitable grade of concrete is M200. M250 is not the most commonly used brand of concrete due to the slight difference in price with M300, although the latter has great advantages. Therefore, M300 is the number one choice for buildings up to three floors high. Concrete M400 is the option of choice for multi-storey buildings.
A solution is prepared based on cement of a selected brand. It is necessary to calculate in advance the consumption of the cement mixture and how much sand and cement is needed in those proportions for pouring the foundation site, which will ensure its long service life without deformation. For example, cement grade M400 in the preparation of concrete M100 requires proportions of 1: 4: 5 (cement, sand and crushed stone, respectively).
Perlite: what is it and insulation characteristics