There are several options for this design, differing in load-bearing capacity, installation complexity and cost.
Very often, for private buildings for residential and commercial purposes, a prefabricated strip foundation is installed using reinforced concrete blocks.
What does it represent?
This structure is a base made of reinforced concrete, rubble or silicate blocks, laid on a prepared foundation pad and fastened together with cement mortar. Individual sections can be either hollow or solid; the second type is most common.
GOST requirements for the block system
According to the current state standard, any foundation, including prefabricated strip foundation, must meet the following criteria:
The pressure on the soil resulting from the load from the structure should not be greater than the soil resistance force.- The base should not shift or be torn away from the sole due to the tangential impact of the soil during swelling.
- Shrinkage deformation should be within normal limits.
- Mandatory compaction of the sand cushion.
When arranging such structures, specialists are guided by GOST 13580-85, and also take into account the technical conditions for a specific object.
Advantages and disadvantages
A strip foundation made of blocks has the following advantages:
- High construction speed. The block system does not require time to gain strength, like monolithic analogues, so you can proceed to the construction of the building frame 1.5-2 weeks earlier.
- The ideal geometry of the elements not only speeds up installation, but also facilitates the process.
- Thanks to the presence of technological grooves and special loops, it is possible to move heavy products using lifting equipment with minimal time.
- The cost of construction is lower than the price of a monolithic tape.
- During construction, an order of magnitude less concrete solution is required, so there is no need to order a concrete truck; you can mix the composition in a manual concrete mixer.
- High flexibility and mobility of the structure. A strip foundation made of blocks maintains its integrity on unstable soil, while a monolithic foundation may crack due to its movements.
- Installation can be carried out in almost any weather; such a base can be installed even in winter.
- If all technological requirements are strictly observed, the service life exceeds 100 years.
However, this type also has disadvantages, these include the following points:
During construction, it is impossible to do without heavy lifting equipment.- It is necessary to waterproof the base and carry out thermal insulation.
- If the soil at the construction site is heaving, a reinforced concrete base is required.
- Brick and stone buildings on prefabricated strip foundations can only be erected on stable soils.
- Compared to a monolithic base, the load-bearing capacity is slightly lower.
Application area
Most often, prefabricated strip foundations are installed for industrial and commercial buildings:
- Warehouses.
- Shopping centers, shops.
- Production facilities.
- Farms, granaries.
In addition, it is used in the construction of multi-storey residential buildings and tall cottages for permanent residence.
It is optimal to equip such a structure on dry ground; Clay soils and areas with high groundwater levels are not as suitable for this type.
Device
Depending on the depth, there are two types of structures:
- Recessed. They are usually made for large objects.
- Shallow. This is the best option for outbuildings and technical facilities.
In any case, installation includes the same set of works: a cushion is placed in the prepared trench, after which the blocks are installed, fixing them together using a cement-based mortar.
Seams and joints are carefully protected from moisture, then the structure is thermally insulated. The system must be reinforced without fail. It takes an average of 2-4 days for arrangement.
Types of strip foundations according to construction method
Depending on the design features, strip foundations can be monolithic or prefabricated. They, in turn, can be divided into monolithic foundations with vertical supports and prefabricated strips made of brick or foam block.
Monolithic strip foundation
When installing a monolithic strip foundation, reinforcement and pouring of the foundation are carried out directly at the construction site. As a result, the overall integrity and continuity of the carrier tape is achieved.
A monolithic strip foundation is a continuous reinforced concrete strip along the entire perimeter of the building
Monolithic types of foundations, regardless of technology, are used for the construction of objects for various purposes on heaving and moving types of soil. The solidity of the structure ensures high strength and reliability of the load-bearing base.
Pile and columnar strip foundation
Pile-tape and column-tape foundation types are a monolithic strip of reinforced concrete located on supports buried in the ground. In fact, these types of foundations are nothing more than a modernized version of pile or columnar foundations with a grillage.
Pillars or piles are located along the perimeter of the foundation in increments of 2 m
In the first case, steel products in the form of piles of various lengths are used as supports, which are screwed into the ground manually or automatically. In the second, the supports are made from the same concrete mixture that is used to fill the supporting tape.
The arrangement of pile and columnar strip foundations is justified only when constructing objects in areas with a large depth of soil freezing. Steel piles or reinforced concrete pillars, buried below the freezing level of the soil, will distribute the load that is transmitted from the reinforced concrete strip.
Prefabricated strip foundation
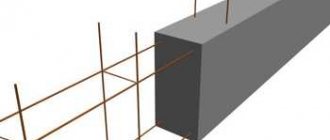
The main material for the construction of a prefabricated strip foundation is reinforced concrete foundation blocks (FBC), made from heavy grades of concrete. The blocks form a load-bearing foundation strip, which is located along the perimeter and area of the future structure. To connect the blocks to each other, concrete grade M350 and steel reinforcement Ø15 mm are used.
After assembling the foundation, the outer surface of the load-bearing base is treated with waterproofing materials. The most commonly used are bitumen mastic and special bitumen membranes that have a self-adhesive base.
Prefabricated strip foundation consists of reinforced concrete foundation blocks connected by concrete
The main advantage of a prefabricated strip foundation is the short construction time. Unlike a monolithic base, you do not have to wait for the concrete mixture to reach the minimum strength. You can start building a house within a few days from the moment the tape is assembled.
Despite this advantage, prefabricated strip foundations are used for the construction of private houses a little less frequently than a monolithic concrete foundation. This is largely due to the fact that the prefabricated structure is not suitable for use on moving types of soil. With the same thickness, the strength indicators of a prefabricated structure are 20–30% lower than a monolithic one.
Brick strip foundation
Brick strip foundations are a prefabricated structure and are often used for the construction of one-story houses using frame technology. Burnt solid brick is used to make the tape. Laying depth - 40–50 cm.
A brick strip foundation is highly repairable, but requires high-quality waterproofing
After assembly, as in the case of blocks, it is necessary to install a full waterproofing layer. The advantages of this foundation include:
- structural rigidity;
- high maintainability;
- simplicity of arrangement.
If we make a more detailed comparison of bricks with reinforced concrete blocks, then foundations made of blocks are less hygroscopic and have higher strength. Brick is more fragile, which affects not only the frequency of repairs, but also the service life of the structure as a whole. Taking this into account, it is recommended to build a brick strip foundation in areas with dry and hard soil, as well as in areas with low groundwater levels.
Types of foundation blocks
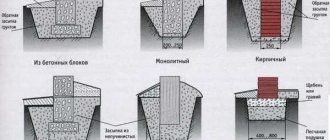
Depending on the type of concrete used and the structure, there are three types of products used for arranging a prefabricated base:
Monolithic. This is the most popular variety, which has a solid structure. The marking of such blocks is FBS.- Monolithic blocks with a groove are another popular type.
It differs from the previous one in the presence of special cutouts, which serve for quick and convenient installation of engineering systems, including the electrical network, low-current systems, etc. These blocks are sold under the name FBV. - Hollow blocks, or FBP. They are used primarily for the construction of buildings made of wood or frame materials, since the load-bearing capacity is significantly reduced.
Classification is also possible according to other criteria, for example, the presence or absence of a reinforcing frame. Thus, FBS blocks are not reinforced, since they can withstand compressive loads without additional devices, and FL products have an armored belt. Reinforced BF blocks made of heavy concrete can also be used to construct the foundation.
Design and drawings
When choosing the type of strip base, experts take into account many factors, including the following nuances:
- The degree of soil freezing.
- Load level from the future building.
- Height of groundwater location.
- "Ribbon" design.
- Seismic activity in the location chosen for construction.
- Relief features.
- Soil composition, properties of individual layers.
The slightest errors in calculations are fraught with serious consequences , from distortions during the shrinkage of the building to premature destruction of the integrity of the foundation and the structure itself.
That is why the preparation of the project should be entrusted to engineers with extensive experience. The set of papers includes drawings of the future foundation with markings of the main elements, dimensions, relationship with other parts of the structure and other data.
The design drawing is included in the documentation for the entire building. You can see what different installation schemes for foundation blocks look like in the illustrations below.
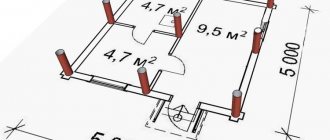
Foundation plan from FBS
This is a separate part of the project, which represents a horizontal section of the future structure at the level of the upper part of the foundation system.
The plan includes the following information:
- The depth of the pillow and blocks.
- Dimensions and configuration of individual elements.
- Images of cross sections from different angles.
- Layout of blocks.
- Location of openings for communications.
- Explanatory note.
The photo shows an approximate plan of the foundation from FBS:
The plan must also indicate such parameters as the load on the base, design features (for example, the presence of a basement), and the total weight of the building. If it is necessary to level the area for installation, this fact must be indicated in the document.
More details about the prefabricated strip foundation made from FBS blocks in the video:
Construction of a prefabricated strip foundation from FBS blocks
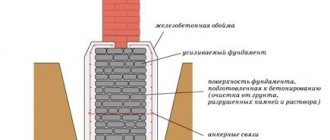
Design of prefabricated strip foundation:
- priming;
- sand cushion;
- foundation slab;
- FBS blocks;
- reinforced reinforced concrete belt;
- waterproofing;
- blind area;
- basement wall.
Construction of a prefabricated strip foundation
Application area
Prefabricated strip foundations are used for the construction of private buildings. One-story and two-story houses made of brick, foam blocks and gas blocks. The base can withstand heavy buildings. If you choose the right block size.
Used on stable and low-heaving soils. Clay or loamy soils can lead to subsidence of the foundation.
The advantage of a prefabricated foundation is that it is quickly assembled. The blocks allow you to assemble the structure in a few days. Provided that a pit is dug and a concrete pad is made.
The disadvantage is that it can only be used on dry and stable soils.
Calculation criteria and rules
The calculation of a prefabricated strip reinforced concrete foundation is carried out taking into account the following factors:
- Soil type and composition.
- Depth of groundwater.
- The degree of soil freezing.
The minimum requirement for most buildings is to lay the blocks in 2 rows; other parameters are determined taking into account the characteristics of a particular object. So, the width of the base should be greater than the thickness of the walls; the latter factor is influenced by the material of their manufacture and finishing methods. For a deep foundation, you will need to install 3 rows of blocks.
Material should be purchased with a reserve of 10%; If at the end of the work it turns out that there are extra blocks left, they can be used for other purposes or resold.
Strip base design
A strip foundation is a closed reinforced concrete strip that supports the load-bearing walls of a house, both external and internal. It is a supporting structure that takes on the weight of the building, evenly distributes and transfers it to the ground. The tape must have sufficient strength and load-bearing capacity to withstand the weight of the house, taking into account the operational load (furniture, appliances, things, people or animals), snow and wind loads, plus a safety margin in case of unforeseen external influences.
The design of the strip base consists of a strip of reinforced concrete of rectangular cross-section (sometimes an expanded concrete pad is made at the base, which reduces the specific pressure on the ground). Such foundations are built on stable soils with low or no heaving (expansion and change in topography due to winter freezing of soil water). Optimal soil option:
- sand;
- sandy loam;
- loam with a high sand content;
- sandy and rocky soils.
It is impractical to build a belt on clay soils, since soil moisture is locked in an impermeable layer, which causes severe frost heaving and high loads on the concrete belt.
The concrete strip is a monolithic casting with a metal (or fiberglass) reinforcing frame inside. It is a mandatory element that takes on multidirectional loads. Concrete can withstand high pressure, but it cannot withstand tensile forces. With lateral or vertical loads on an unreinforced strip, fracture and loss of bearing capacity are inevitable, therefore, the frame increases the service life and ensures the safety of the foundation.
The construction of a strip foundation is a sequence of several stages:
- Digging a trench.
- Laying a sand cushion and drainage.
- Formwork assembly.
- Knitting of reinforcement frame.
- Pouring concrete.
- Keep the casting for 28 days with daily watering (the first 2 weeks water at least 2 times a day), with protection from direct sunlight.
- Stripping is carried out after 2 weeks of curing; further work is allowed only after a 28-day period of concrete crystallization.
There are several types of strip foundations, but the general construction scheme remains the same.
Recessed belt type
A recessed version of a strip foundation for a house made of aerated blocks is a concrete strip immersed in the ground below the freezing level in winter. this is a way to protect the foundation from ground influences - frost heaving, changes and movements due to hydrogeological processes in the off-season. When the lower part of the belt rests on stable ground, excess loads cannot be expected. Loads due to heaving are possible at the upper levels of the belt, but they can be compensated for by an increased layer of dry sand backfill. The recessed strip foundation has many advantages:
- high load-bearing capacity;
- the ability to use the inside of the tape for a basement;
- absence of soil influences on the foundation;
- the occurrence of excess loads that appear due to the redistribution of soil water is easily carried by buried belts - they have a large height and width, which allows them to carry significant loads.
Disadvantages of a buried strip foundation:
- large volume of earthworks;
- high consumption of building materials (boards for formwork, reinforcement, concrete);
- significant labor investment;
- difficulty in maintaining a buried tape, the need for constant monitoring, the risk of cracks;
- high cost of foundation.
The disadvantages are serious, so buried strip foundations are rarely used for the construction of light buildings.
Shallow strip foundation
A shallow strip foundation (MSLF) is a reinforced concrete strip immersed in the ground above the freezing level in winter. It is built for relatively light buildings - low-rise private houses or small public buildings, production workshops, etc. As a rule, MZLF is used on strong soils with high drainage capacity (sandy) with a low groundwater level (GWL). The absence of factors that cause heaving or seasonal movements allows you to save on the height and thickness of the foundation, which significantly reduces the cost of construction.
A shallow strip foundation for a house made of aerated concrete is a common option, since the weight of the walls is low and the load on the foundation is significantly reduced. Only the usual types of influence remain:
- snow and wind loads;
- operational (weight of furniture, equipment and other things);
- weight of people or animals.
As a rule, MZLF under a house made of aerated concrete is immersed in the ground to a depth of 1-1.2 m. However, other options are possible, since the depth of immersion depends on a combination of different factors:
- soil composition;
- weight of the house, number of storeys;
- building area;
- ground water level;
- amount of snow in winter;
- abundance of precipitation, possibility of squally gusts of wind, etc.
When designing a shallow foundation for a house made of aerated concrete, the possibility of flooding of the site is also taken into account. To protect against excess moisture from heavy rains or melted spring waters, a system of drainage pipes and storm sewers are used, discharging wastewater to a collector or to a discharge point. This is an important point, since the trench cannot be allowed to fill with water. Otherwise, there will be a serious danger for the tape, and the supporting structure will begin to erode.
Tools and materials
For installation you will need the following set of devices:
Buckets for construction mixture.- Scrap.
- Shovels.
- Plumb and building level.
- Pegs, rope.
- Hammer.
- Level.
- Concrete mixer.
As for consumables, in addition to block products, you will need:
- Sand.
- Cement.
- Gravel.
- Materials for hydro- and thermal insulation.
Step-by-step installation instructions
Before starting construction work, you will need to complete a set of preparatory measures:
- geological surveys;
- preparation of drawings;
- applying markings in compliance with the proportions of the design values.
After this comes the stage of excavation work on the ground.
Preparing the trench
First, workers remove the fertile layer of soil, after which they build a pit or trench, the depth of which should be greater than the freezing level of the soil.
As a rule, a prefabricated strip foundation requires 2-2.5 m of depth , unless it is a shallow variety. The bottom is leveled, after which they move on to the next stage.
The edges of the trench should not crumble, otherwise the quality of the installation will suffer.
Pillow
A sand-gravel mixture is poured onto the prepared bottom of the trench, forming a cushion 30-40 cm thick. Backfilling is done in parts: first a 15-20 cm layer of river sand is placed, then the same amount of crushed stone is laid (middle fraction material is used for the work).
Every 10 cm is compacted using a vibrating screed , in some cases the work is carried out manually.
Forming the sole and laying the blocks
A FBS sole can be installed under the foundation;
its variety depends on the type of soil. For example, on dense soil you can make it prefabricated, but in heaving or weak soil it is better to give preference to a more expensive but reliable monolithic structure.
To construct buildings from frame-panel materials, you can do without a sole, but then you will need to lay a masonry mesh on the sand bed.
After arranging the sole, the stage of directly laying the blocks begins. They are mounted at the corners of the building, and a rigid cord is pulled between the slabs to level the masonry.
The blocks are fastened together with cement mortar, the upper and lower elements must be strapped. To fill vertical joints, use concrete M-100 or the same solution.
The next row should always go in the opposite direction from the corners and external masonry to the internal partition structures.
All blocks must be leveled so that the base is of the correct geometric shape.
Final stages
After masonry, waterproofing is required: for such work, liquid mastic-based compounds are usually used.
The product is applied to the outer surfaces of the base, evenly coating the structure, special attention should be paid to the joints. If the waterproofing layer is too thin or uneven, the concrete surface will begin to absorb soil moisture , which will lead to premature destruction of the foundation and the building itself.
In addition, thermal insulation of the structure may be required, especially if it is planned that the building will have a basement. Installation of insulating material is most often carried out from the inside; for this, rolled products or expanded clay are usually used.
Step-by-step instructions for creating a strip block foundation
- At the first stage, a pit is dug to the depth of soil freezing. The size of the trench for the FBS foundation should be greater than its width for ease of laying the blocks, and the depth of the pit should not hide the supporting structure. Even before starting work, you need to determine the location of the crane - it is necessary that the boom reach is sufficient to reach any point of the supporting structure.
- At the second stage, the sole is created. A prerequisite for building a foundation for a FBS house from blocks is a tape - a cushion filled with concrete. In rare cases, a masonry mesh is used to create a cushion so that there are no gaps between the blocks. To make the sole, you need materials such as sand, crushed stone and reinforcement. The markings in the trench are made exactly according to the level, the bottom is filled with sand and compacted. Then it is filled with crushed stone and this layer is also compacted. Then you need to attach reinforcement and install the formwork.
- At the third stage, the formwork is assembled. When assembling the formwork, a 25 mm board is used. This structure needs to be assembled as evenly as possible, for which it is necessary to mark the depth using a water level, and then, using the marks, you need to pull the cord inside the formwork and align it with the cord. After pouring the reinforcement frame, it is left for two weeks to shrink. To assemble the formwork, you need rods 60 cm long and 4 meters long, plus you will need about 10 kg of knitting wire. The reinforced belt has standard dimensions (width 30 cm, thickness 20 cm).
- At the fourth stage, the pillow is filled. A faster and more reliable way is to use a mixer. The pillow is filled with a mixture of concrete to a depth of 10-15 cm. Then the structure is covered with burlap or plastic film and dries for a week under the condition of 20 degree air conditions and 90% humidity. After drying, the pillow is waterproofed, this is done with roofing felt or other similar material. In this case, an overlap is made on the walls on the outside and is joined to the waterproofing material of the walls. A concrete screed is made onto the roofing felt layer, which will later become the basement floor. The remaining space of the trench is filled with soil and compacted. Sometimes pillows are made into prefabricated ones, but they are not suitable for all types of soil, but monolithic structures are considered to be universal.
- At the fifth stage, the blocks are installed. To install the blocks faster, you need to use a crane, because the material is heavy. If the size of the blocks is small, then installation can be done using the old method. The installation of FBS foundation blocks is carried out simultaneously with ligation of the vertical seams. The blocks are laid on cement mortar, and the vertical joints are filled. Communication sleeves are installed between the blocks in the places indicated in the drawing.
- At the sixth stage, another waterproofing is done and the remaining space of the trench is filled. This time the waterproofing is done with bitumen lubricant. More carefully, you need to coat with lubricant those places that are in contact with the ground; this needs to be done to the entire depth of the pit from the outside of the foundation. In cases where the house is made of beams, an additional reinforced belt is made. Installing a block foundation for a house is not an easy process, but it is very reliable, and therefore worth the effort and money spent.
Basic mistakes and tips for construction
Most often, the following mistakes are made in the process of arranging a prefabricated belt:
Incorrect determination of the load-bearing load or weight of the building.- Lack of geological surveys.
- Construction on excessively mobile soil without a monolithic base.
- Leaving the dug trench for several days. In this case, the earth may crumble and the bottom may be washed away by water.
- Changes in the bottom of the trench will lead to uneven distribution of the load.
- Lack of cushion or careful compaction on soft soils.