Waterproof cement
A number of concrete structures, in accordance with their special purpose, must have varying degrees of water resistance. Among the “structures for special purposes”: all types of hydraulic structures, basements, cellars, water storage tanks, etc., waterproof cement is used for this.
- How to make cement waterproof
- Types of waterproof cements
- Vibration
- Maintenance of concrete structures
- DIY waterproof cement
By using waterproof cement for the manufacture of concrete and mortars, it is possible to ensure guaranteed protection of structures from the penetration of moisture into the thickness of their structure. And also significantly reduce or completely eliminate expensive waterproofing measures.
Work options
They can be carried out in two ways:
- at shallow depths, where there are no tides and there are minor waves, the solution is lowered through a funnel into cavities fenced with special jumpers, or concrete is poured into the water;
- at quite impressive depths, in places where the waves can be very strong, caissons become a reliable assistant in concreting work. The concrete mass is moved into such caissons through shafts or pipes. It’s better not with your own hands, but with concrete pumps.
In the photo - hydraulic structures
How is pouring carried out, what is the GOST for water for concrete and mortars? Let's take a closer look at this process.
Method No. 1
The instructions are as follows:
- It begins with the fact that in the place where the proposed structure will be erected, rows of piles are driven (sheet piles are used). This makes it possible to avoid drainage works.
- Then concrete is thrown between them through a funnel.
Advice: if the base under the concrete solution is of insufficient density, for example, from thrown stones. In this case, it must first be densely crushed, and then covered with a cloth, the edges of which will be curved upward. Thanks to such measures, the solution will not be able to seep into the crushed stone, and concreting will be much better.
How to concrete in water using a concrete pump
Preparing concrete
After the base is ready, you need to prepare the solution. It is important to remember that it needs some time to mature. At the same time, it should not be exposed to direct sunlight or moisture.
If the solution is kept for the required period, then it will reach the desired consistency for immersion in water: it will set a little and will not erode much in water. This method of preparing a solution was first used by Kinipple, an engineer from the UK.
In this way, he managed to avoid unnecessary costs for installing a system to protect the concrete solution from erosion. Kinipple dipped the solution, which was already half-hardened, under water.
Table of proportions
In addition, the engineer provided technology to protect it from the force of waves and underwater currents. To do this, he covered the outside of the concrete surface with thick linen fabric (canvas).
Advice: for the core of such a structure, use an unsaturated solution, while the outer part requires a saturated solution, and its thickness should be at least 1 m.
The compositions are as follows:
| Core (saturated solution) | Mix crushed stone together - 6 parts; cement - 1. It is required to leave it to harden in air for about 5 hours. |
| Shell (unsaturated solution) | Recipe: crushed stone - 7 parts, Portland cement - 2, must be kept in air for 3 hours. |
Recommendations:
- Depending on the characteristics of the rate of hardening of the concrete mass, it is necessary to distribute the time between mixing it and moving it into water . It is important to calculate the timing in the most optimal way so that the concrete does not erode too much when immersed. Otherwise, some of the cement will be lost, which will negatively affect the quality of the structure.
- It is also important to ensure that the concrete mass does not become too hard, because in this case it will not bind tightly to the solution that was previously immersed and will not become monolithic . In those underwater areas that are subject to powerful waves and strong currents, a small portion of quick-hardening cement is added before placing the concrete in the water.
- Among other things, concrete submerged in water needs compaction. To ensure this, it is compacted. The top of the tamper is above the water level, taking the blows of the tool used for tamping. Remember that tamping must be done very carefully, because if you overdo it, then too much vibration and waves will inevitably lead to erosion of the concrete.
To obtain such concrete, you will need to mix cement with pure pitch in a ratio of 1 to 2.5.
Advice: the answer to the question - does concrete allow water to pass through can be answered - it depends on the composition, so it can be used to build water tanks.
Reinforced concrete water tanks in production
Method number 2
- Near the area where it is planned to build the necessary concrete structure, for example, a dam, it is necessary to dig two ditches at the bottom using dredging machines. Semi-hardened concrete should be poured into them, directly into the water. The result will be two shafts that will reach the low water level.
Advice: before you start laying them, evaluate the condition of the reservoir in the selected area and the quality of the cement. The price of the latter cannot be low.
- To remove these shafts, the concrete mass is lowered into water in sacks. This idea is not accidental; their value is that in the process they are able to form a monolith. After pouring cement for the shafts, iron piles are driven. Do this at an angle to create slopes.
Underwater concreting using the rising solution method
- Connect the piles to each other with special iron rods with eyelets. To keep them at the desired angle, place a steel cable on top and attach it to the dead anchors.
Tip: to prevent concrete from being washed away during strong waves, place boards covered with canvas on the inside of the piles.
- Install concrete partitions along the entire length of the building. The material for them should already be at the stage when it begins to dry out and harden. This will allow you to form a monolithic part with the lower layers.
This technique allows you to save money, since monolithicity is guaranteed even with the use of low-saturated concrete. However, when working with low-saturated concrete, it is important to know that its constituent parts must mix very well and form a homogeneous mass. In addition, be aware that if there is a lot of water in concrete, its “setting” will be greatly impaired.
Advice: it is necessary to immerse it in water after this mass has begun to set. If weather conditions are unfavorable (wind, strong waves) or concreting is carried out at great depths, work is carried out inside the caissons.
A clear example of why you should pour water on concrete - this way you allow it to harden properly
After the soil for the base has been prepared, install partitions 1-1.2 m thick around the chamber - from the roof to the very bottom. Make the walls from vertical boards, which are then removed as the concrete hardens. Under the ceiling, treat the solution with a flat tamper.
Advice: it is best to lay concrete in layers, but you should not begin the process of laying a new layer until the previous one has dried.
It takes 5-6 hours for one to harden. The concrete solution is lowered through special pipes, which are equipped with valves at the top and bottom.
Pipe
In underwater concreting, a very important device is the pipe. By opening the top valve, you ensure that some of the concrete gets into it, after which it should be closed.
Moving pipe method
The air pressure in the device and in the chamber is equalized using a tap that connects them. Then you need to open the valve located below so that the concrete sinks under the water until its layer is sufficient to resist the water pressure.
Advice: if you don’t know how much water you need to spend per cube of concrete, take the average value - 125 liters.
After this, the solution is lowered through the shafts. To reduce the consumption of material for filling the caisson, you can use stones from the bottom where the work is being carried out, simply pouring them from above. At the moment, the maximum depth of underwater concreting work is no more than 30 m.
What is non-shrinkage and fast-hardening concrete?
In recent years, non-shrinkable concrete has gained great popularity in construction and reconstruction work. The material was developed by a Russian scientist at the end of the 20th century, and the composition is still being refined and improved. Read about the technical characteristics of ShB-5 brick here.
Unlike traditional types of concrete, it is characterized by increased strength, minimal risk of cracks and a rapid shrinkage period. This property is possible due to the addition of a large number of superplasticizers to the composition. They increase the strength of cement during compression and demonstrate a rapid reaction with water before hardening begins.
Non-shrinkage concrete, which can be purchased in a store or in production, is conventionally divided into repair and construction. The first type sets faster when diluted and hardens almost instantly.
Composition in bags
Concrete that does not require shrinkage is supplied in bags ranging from 3 to 30 kg. When choosing a specific mixture for construction or repair, you should determine the specifics of the work. Non-shrink mortar can be dry or cast. To fill pre-prepared cracks, it is best to choose the second type. It has the ability to expand, high adhesion, due to this it quickly sets with nearby elements (reinforcement, stone, cement). Such concrete is capable of filling space, strength and sealing efforts. The main area of application is the restoration of horizontal surfaces.
Technical characteristics and GOST
Non-shrinkage concrete is widely used in construction due to its excellent physical characteristics. The table shows the main properties of the material. Find out about fiberglass putty for cars here.
| Characteristic | Meaning |
| Color | grey |
| Fraction size | up to 0.63 mm |
| Preservation of the consistency of the solution | up to 40 minutes |
| Maximum compression density after 28 days | 40 MPa |
| Density | 1400 kg/m 3 |
| Adhesion strength to concrete (after 28 days) | 2.0 MPa |
| Frost resistance grade | F300 |
| Waterproof | W 14 |
| Material consumption per 1 m 2 (layer thickness – 10 mm) | 15-18 kg |
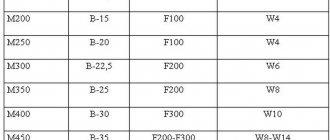
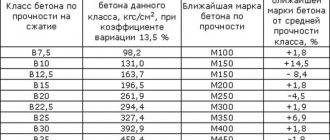
For the production of non-shrinking compositions, traditional cement grades from B7.5 (M100) to B45 (M600) are used; they are produced in accordance with GOST 7473-2010.
Brands and characteristics of non-shrink cement
Table 1 - The most popular brands of cement
| Brand | View | Additive content, % | Characteristic |
| M 400 | VBC | D 0 | One of the most widely used cements, it is durable, impervious to moisture, and hardens quickly. It is sealed, durable, corrosion resistant and reliable. |
| D 20 | |||
| VBC B | D 0 | ||
| D 20 | |||
| M 500 | VBC | D 0 | |
| D 20 | |||
| VBC B | D 0 | ||
| D 20 | |||
| M 600 | VBC | D 0 | |
| D 20 | |||
| VBC B | D 0 | ||
| D 20 |
- M 400, 500, 600 - this is the marking of cement, it means the strength of the finished material, measured in kg per square meter. cm.
- VBC – waterproof non-shrinking cement, B – quick-drying.
- D – characterizes the content of additives in the cement composition, which affect the characteristics of the product. D0 means that there are none, D20 means that 20% of the product was replaced with additives.
Characteristics of non-shrinking material
Modern construction even includes objects whose operating conditions require the construction and location of objects in a humid environment (or completely in water). For example, dams, dikes, bridges, lining of river canals, and so on. Naturally, the material used in the construction or finishing of such objects must meet the requirements of water resistance.
This is precisely why types of waterproof material have been developed. One of them is waterproof non-shrink cement or WBC.
This composition is based on aluminous cement, which meets the characteristics of a fast-hardening binder using aluminum oxide.
Scheme of cement production.
As for the raw materials for the production of this composition, these are limestone and bauxite, the extraction of which is carried out on Russian territory.
- The principle of operation of VBC provides for the crystallization of calcium aluminates during the hardening of the solution in compliance with the conditions of counteracting free expansion, which in turn contribute to a strong degree of compaction of the stone. It is in this regard that concrete acquires the properties of water resistance and high waterproofing;
- Factory-produced VBC is made by grinding cement (alumina) together with components such as gypsum and calcined lime;
- the basic requirement for the amount of cement is 85%, but the proportions of gypsum and lime may vary. Sometimes asbestos is used in an amount of 5%.
The waterproof properties of such cement are achieved an hour after preparing the solution, and final hardening and acquisition of all qualities by the solution occurs after 28 days.
Self-production
As an additive to the composition of the concrete mixture, a substance such as dehydrol “lux” grade 10-2 called “Liquid waterproofing hyperconcentrate” is used. Using such an additive, it is possible to produce concrete with hydraulic properties with your own hands using a conventional type of concrete mixer.
- the average dosage of the composition corresponds to the ratio of 4 liters per 1 m 3 of concrete. This means that in a concrete mixer with a volume of 100 liters (somewhere from 200 to 240 kg) you will need only 0.4 liters of dehydrol;
- here are the approximate proportions: cement in the amount of 50 kg, sand - 60 kg, crushed stone - 110 kg, dehydrol - 0.4 l, water - about 20 l;
- To achieve the desired consistency and plasticity, water is first poured into the concrete mixer, followed by dehydrol, and only then the remaining components are gradually added in the required proportions. After 5 minutes of mixing, the concrete mixture will be ready for use.
Don't forget about important nuances. For example, the amount of water component cannot exceed the amount of cement by more than 40%. This means that when using one bag of cement weighing 50 kg, the water will be no more than 20 liters.
Another important point is that it is not allowed to use clay or clayey sand to prepare the concrete mixture. And yet, the amount of cement used per 1 m 3 cannot be less than 350 kg.
Necessity of material
Waterproof cement is most often used to create foundations that are not subject to seasonal impregnation with moisture. This is especially important in areas where groundwater lies close to the surface of the earth. In such conditions, the base of a building made of standard cement requires additional waterproofing to prevent structural failure.
Waterproof cement is used both in civil construction and for the construction of massive industrial buildings.
Cement works well for swimming pools. It can not only withstand the influence of water that will be in the bowl, but also prevent the destruction of the structure by groundwater. The hydrophobic composition is widely used to create artificial reservoirs and ponds.
Thanks to special additives, you can make cement mortar waterproof with your own hands, which has expanded the scope of use of this material.
Nowadays it is often used to connect and seal rings during the construction of wells and well construction.
In addition, this material can be used to fill the bottom and walls of cesspools to prevent soil and groundwater from being polluted by runoff. The moisture-resistant material is also recommended for use in the construction of basements and cellars, construction of tunnels, bridges, dams, etc.
Pile method
This technique involves the use of special piles that are driven directly to the bottom of a pit with water. Piles - strong reinforced concrete columns - are connected by a tongue-and-groove lock. Similar connections are used when joining laminate and a number of other floor coverings. Such a lock does not completely seal the joint, and moisture can leak through it. However, concreting in water can be carried out, because special semi-finished concrete is used for this technique.
Pile foundation on a floating surface
Proper preparation of concrete
For pouring, 2 types of concrete mortar are used - saturated and unsaturated. The difference between them lies in the proportions of the components. The first solution involves the introduction of 7 parts of crushed stone and 2 parts of cement, and the second - 6 parts of crushed stone and 1 part of cement. Both solutions are kept in air until partially hardened, which allows them to resist the action of water and reduces the risk of erosion of the mass.
The saturated solution is kept outside under a canopy and tarpaulin for about 3 hours, and the unsaturated solution for 5 hours. During the aging period, the compositions must be protected from wind and sun. They are considered ready for pouring when they stop spreading in liquid and lie quite tightly. After compacting the solution, a dense monolith is formed, which is not afraid of the effects of precipitation and groundwater.
Fill rules
A saturated and unsaturated solution has a significant difference - unequal strength. Since saturated concrete is the strongest and most reliable, it is used for laying near the formwork. The middle of the structure is made from an unsaturated solution.
The process is divided into several stages, each of them being strictly controlled. The concrete mass that is poured first should still be semi-liquid, not completely hardened. The solution that is poured from above must adhere securely to the bottom. If the latter has already become a monolithic stone, then any vibration can cause cracks to appear along the joining line. They will gradually expand, and the structure will sooner or later become unusable.
Preparatory work
Concreting in a humid environment necessarily involves certain preparation, without which the quality of the result will decrease. Before starting work, it is important to examine the bottom of the reservoir (ditch, pit) that will be concreted. The base must be strong and free of stone inclusions. If there are still stones, they are completely covered with a thick layer of crushed stone.
In addition, as preparation measures, the bottom is covered with a special dense fabric (tarpaulin, canvas), which will prevent the solution from leaking through the crushed stone layer. Part of the fabric is placed on the formwork, covering it. This technology is well suited for areas where there is no strong water flow.
Application area
Waterproof cement is usually used in conditions of high humidity, risk of destruction of concrete by water, where waterproofing measures cannot be carried out or would be too expensive.
Scope of application of waterproof cement:
- Conditions of high humidity from 75% and above - in dry conditions after using a solution with such properties it will shrink significantly
- Construction of foundations, plinths, load-bearing structures
- Construction of wells of various designs at great depths
- Waterproof expanding cement is actively used in the restoration of destroyed reinforced concrete and concrete objects
- Waterproofing of mine shafts, tunnels
- Underground and underwater construction, installation of waterproof joints
- Construction of insulating shells in various designs of reinforced concrete structures
- Waterproof cement for swimming pools is used when laying tiles on the bottom of the bowl
- Installation of floor screed in the basement, cellar, garage
- Filling the bottom and walls of septic tanks
- Construction of water pipelines, decorative ponds
- Creating a waterproof screed on the roof of underground garages
The use of the material is relevant wherever there is a need to increase the resistance of a concrete structure to moisture and protect it from destruction.
Non-shrink
Non-shrinking waterproof cement is created using aluminate in a small volume. A crystalline cement stone is created, strengthening and compacting the structure. Composition of the mixture: aluminous Portland cement (about 85% of the volume), asbestos (up to 5%), semi-hydrous gypsum and calcium aluminate (up to 10%).
The material is used for the construction of structures that are constantly exposed to water. Therefore, a mixture of calcium nitrate, aluminum powder and ferrosilicon is often added to the solution for an anti-corrosion effect and to protect the reinforcement from moisture.
Expanding
Expanding type WRC is made by adding hydroaluminate to the composition. Most often, the composition is as follows: 70% aluminous cement, 20% semi-hydrous gypsum, 10% calcium hydroaluminate. The mixture is prepared as follows: mix the dry ingredients and grind. Thanks to the active reaction between the components, the mass expands during the process of rapid hardening, sets within a few minutes after laying, and the process is completed within 10 minutes.
Moisture-resistant expansive cement expands more the higher the humidity. The process of internal expansion takes a long time. After 3 days, the cement corresponds to the strength of grade M300, after 28 – grade M500. The solution has high waterproofing properties that improve in water. This characteristic allows the use of concrete in the construction of swimming pools, dams, and dams.
Fast-hardening
Waterproof fast-hardening cement hardens faster than all others. Its composition helps to increase strength already on the third day after pouring. Tricalcium silicate is added to the composition in a volume equal to at least 50% of the total mass of the solution.
Fast-hardening waterproof cement is used in the creation of ultra-strong concrete, to speed up the laying time, in the production of reinforced concrete structures that are not afraid of moisture, to create paving slabs and curbs.
Expanding cement
Table of proportions for preparing concrete.
Waterproof expansive cement is made by introducing a hydroaluminate-based mixture. The most common composition is the following: aluminous cement (70% by weight), semi-hydrous gypsum (20%), calcium hydroaluminate (10%). This mixture is mixed dry and crushed. Due to the active interaction of the components, the mass expands while simultaneously rapidly hardening. When water is added to the cement mixture, setting of the mass begins within a few minutes and is completed within 10 minutes.
The degree of expansion of the material increases with increasing humidity. Internal expansion continues for quite a long time. After 3 days, the cement should correspond to the M300 grade, and after 28 days - M500. If necessary, increase the hardening time, you can add borax or acetic acid.
Waterproof expanding cement has fairly high waterproofing properties, which increase when the solution is in water. This condition makes it possible to use the material even for dams, dams, and swimming pools.
Scope of cement application
The material is used in conditions of high humidity or contact with water if there is a risk of structural failure. It is well suited when it is impossible to carry out waterproofing measures. Usually, waterproof cement is used to make foundations on wet soils, to build structures where groundwater levels are low, to construct basements, cellars, wells, and tanks. Other areas of its application:
- structures at great depths;
- insulating shells in reinforced concrete structures;
- water filtration devices;
- tunnels (underwater and underground);
- plinths;
- mine shafts;
- concrete objects requiring restoration;
- waterproof seams;
- pool bowls;
- garages;
- septic tanks;
- water pipelines and decorative ponds.
Non-shrinking cement mortar. Waterproof cement
First you need to decide what kind of concrete you need: waterproof or frost-resistant.
Where is waterproof concrete needed?
If you want to make sure that water can't get through the concrete you use, then you need waterproof concrete.
For example, waterproof concrete is needed if you decide to pour:
- foundation slab or other concrete foundation structures that are not subject to water filtration;
- concrete floor, walls of the basement, cellar, garage, insulating from ground moisture;
- walls and bottom of the cesspool that prevent sewage from entering groundwater;
- water-tight walls and bottom of a decorative pond, water conduit;
- waterproof screed on the roof of an underground garage, basement.
Where is frost-resistant concrete needed?
Frost-resistant concrete is needed if you want to be sure that moistened concrete, when the temperature drops to negative (especially after numerous cycles of transition through zero temperature in the off-season), will not be destroyed by freezing water after exposure to rain and other precipitation, groundwater, high water, melt water and flood. So that neither the ice inside the concrete nor the frost outside provokes its destruction. For example, if you decide to make:
- concrete path or blind area, paving slabs;
- a wall above the ground in contact with the blind area;
- concrete enclosing structures (fence, walls, fences, curbs);
- concrete decorative elements (pedestals, figures, decorative items imitating natural stone);
- concrete load-bearing structures (columns).
Choosing material
| Additive for producing waterproof concrete (frost resistance as an additional effect) | Additive for obtaining frost-resistant concrete (water resistance as an additional effect) |
| Dehydrol lux brand 10-2 “Liquid waterproofing hyperconcentrate” | Betonoprav luxury brand 2 “Liquid additive for producing corrosion-resistant concrete” |
Why is water in concrete dangerous and how to protect it?
Any building requires reliable protection from groundwater, atmospheric moisture, rain and melt water. Due to dampness, building structures quickly lose their strength, as a result of which their durability rapidly decreases. It is very important to know which processes lead to premature aging of buildings. Knowing their nature, you can competently eliminate the cause of their occurrence.
How water affects building structures
Water intensively destroys concrete, brick, and metal elements of a building. Even clean water that does not contain caustic chemicals is itself a solvent and can wash out the binding components from concrete. But in the soil, water is often contaminated with impurities that enter the environment along with exhaust gases and leaks from enterprises. In many cottage areas, the water in the soil is so highly acidic that when it comes into contact with a brick, it dissolves salts and then evaporates, taking with it everything that was dissolved. As a result, efflorescence appears on the walls of brick houses, which cannot be removed.
Wooden houses deteriorate not so much due to the effects of water itself, but because of microorganisms that successfully reproduce in humid conditions. Log and timber structures rot and are affected by mold and mildew. The result of this biological effect is a decrease in decorative qualities and loss of strength. In addition, pathogenic microbes and bacteria appear in a damp wooden house.
Another reason for water damage to building structures is that when water freezes it turns into ice, which literally destroys the materials from the inside. Freezing and thawing processes are repeated several times throughout the year, causing brick and concrete walls to become less durable.
How to choose water protection methods
To rid the house of these problems, all kinds of waterproofing methods are used. They are quite diverse, so you need to understand the principle of operation of one or another method in order to choose the most suitable solution. When choosing a waterproofing technology, professionals take into account the material from which the structure is made, the purpose and specific operation of the surfaces being treated. It is also important to understand the source of moisture penetration into building structures (moisture from interior spaces, water from the ground, rainwater). Since the foundation walls are mainly influenced by groundwater, the methods for waterproofing them will differ from those used for waterproofing walls.
Moisture that penetrates the foundation gradually rises to the walls and seeps into the house. Therefore, builders lay waterproofing roll products on top of the foundation, preventing further rise of moisture. Violation of this layer of waterproofing leads to the fact that water rises higher through the capillaries and is absorbed into the wall material with all the ensuing consequences.
Exterior wall decoration to protect from rain
Finishing materials are used to protect external walls from rain and dew. The waterproofing layer must also perform decorative functions. For example, thanks to plaster, you can create a vapor-permeable layer that can remove moisture from the walls and prevent water from being absorbed. At the same time, the plaster can have a beautiful appearance. To prevent moisture absorption, plastered walls are painted with special paints and varnishes. Concrete enclosing structures are treated using penetrating waterproofing technology, due to which the capillaries of the wall material are clogged. Subsequent cladding of concrete walls gives them reliable protection from rain and improves their appearance.
Use of water repellents
To create high-quality protection against moisture, a variety of water repellents are used. Some compositions after treatment do not impair the decorative characteristics of the walls. These products include impregnations containing moisture-repellent components. They are selected individually depending on the wall material (wood, brick, concrete). All porous materials can be treated with such impregnations. The essence of this technology is very simple: the active component penetrates the material several centimeters, seeping through capillaries and pores. Remaining inside, this component prevents moisture from penetrating into the capillaries. And at the same time, the treated structure does not lose its ability to “breathe”.
Economic effect of introducing waterproofing
Waterproofing technologies require small financial investments, the amount of which is much less than the costs associated with major renovations of the building. Even expensive waterproofing methods ultimately pay off by extending the service life of structures and maintaining an optimal microclimate in the premises.
Contact the Rembeton Team at the initial stage of construction and receive professional support and comprehensive support for waterproofing work at all stages of the new building. When faced with the appearance of moisture, active leaks and any filtration manifestations in concrete - call Rembeton Concrete Rescuers! Professionals trust us!