What is a gel battery?
A gel battery is a lead-acid direct current source designed for installation in cars and stationary units. The difference is the abandonment of the liquid electrolytic composition in favor of a thickened substance consisting of sulfuric acid and distilled water.
Filling option for other types of batteries. In helium batteries, it was replaced with a mixture with a thicker consistency, which made it possible to avoid carrying out some maintenance activities.
The use of the gel made it possible to avoid periodic maintenance of the device associated with measuring density and adding water to the electrolyte. The sealed housing allows power supplies to be transported on airplanes or charged indoors.
Design
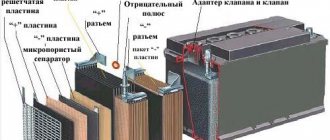
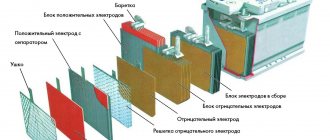
The design of the battery cell includes the following elements:
- terminals or pole pins that are used to connect a load or charger;
- negative electrode flat configuration;
- tubular type positive plate;
- a separator made of a special material, impregnated with a thickened electrolyte.
The main structural elements of a helium-type battery.
The plastic housing of the current source is made of impact-resistant polypropylene; the sealed design prevents the leakage of electrolytic substances during long-term operation of the product at an angle. The electrolyte located inside the housing retains the gases generated during operation; a safety valve is provided to relieve excess pressure.
To reduce the mobility of the electrolyte, silicon dioxide is used, which does not change the electrochemical characteristics of the solution.
Characteristics of Gel batteries
When purchasing a gel battery, you need to consider the following characteristics:
Appearance of the Delta GX 12-55 battery.
- Rated capacity, measured in A*h (amps per hour). The parameter indicates the time interval during which the battery is capable of delivering a current of 1 A. For example, the Delta GX 12-55 battery has a capacity of 55 Ah. There are products with a capacity of 230 Ah or more, designed for installation on trucks.
- Cold cranking current, indicating the maximum voltage in the circuit for several tens of seconds. The ability of the battery to start the power unit depends on the parameter. The Delta GX 12-100 battery provides a current of 900 A at an air temperature of 25°C.
- The permissible current in the charging circuit, which determines the time to restore functionality. For the Delta GX 12-100 battery, a current of up to 20 A is considered the norm.
- Self-discharge rate at a temperature of +20…+25°C. For example, the Sonnenschein a512/40 A product is discharged by 9% for every 3 months of storage in a warehouse.
- Battery operating voltage. For cars, 12-volt batteries are used; it is possible to connect 2 sources in a series circuit to increase the voltage (used on trucks).
- The weight and dimensions of the product allow you to select a power source for a car or a stationary installation.
- Polarity and type of attachment to the battery pad.
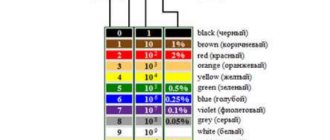
Marking of gel batteries
On the top cover of the case there is a label on which the characteristics of the power source are indicated and the date of manufacture is written. Each manufacturer uses its own date encoding system. For example, Optima products are marked with 4 digits of the form ABCD, where A indicates the year of manufacture, and BCD informs the buyer about the day of production (counting from the beginning of the year). The inscription of the form 7156 indicates the 2021 release, the battery was assembled on the 156th day of the year.
Labeling of helium-type batteries from Optima.
Delta products use a 2 letter, 2 number code. The letters indicate the year and month of manufacture, and the numbers indicate the day of assembly. For example, the code AA11 indicates a product released on January 11, 2011. For subsequent months and years, the Latin letters are used in alphabetical order. Varta uses 4-6 digits for coding in the designation printed on the battery casing. The numbers indicate the year and month of assembly, respectively.
Life time
Developers of gel batteries claim a maximum service life of up to 10 years, but operating conditions can reduce this figure by 2-3 times. When using the product at low temperatures (-30°C and colder), accelerated destruction of the electrodes and electrolyte is observed. Elevated temperature (more than 50°C), which promotes the evaporation of water from the gel electrolytic composition, also has a negative effect.
Dependence of the service life of a gel battery on temperature.
To ensure the service life declared by the manufacturer, it is necessary to comply with the operating conditions of the gel battery:
- use in the temperature range -30…+50°С;
- carry out charging with a special device;
- avoid regular deep discharges;
- install the product in an area with low humidity;
- Avoid overcharging and undercharging the battery.
Overheating further accelerates corrosion processes that destroy the surface of the positive and negative plates.
Gel batteries. Features of operation
Many users believe that the gel battery cannot boil. It is a myth. A gel battery can boil, but visually it happens a little differently. Due to the fact that in gel batteries the electrolyte is in a gel state, it is difficult to observe strong gas evolution on the surface of the electrolyte. However, if the load on the gel battery is higher than the nominal value, then the process of boiling the battery begins. At the first stage, gas bubbles form at the points of contact with the metal plates. Unlike batteries with liquid electrolyte, in these batteries the bubbles cannot immediately rise to the top; they begin to gather in groups and grow. At the same time, the pressure inside the gel battery increases. When the critical pressure is exceeded, the safety valve is activated and excess gas escapes with a characteristic loud sound. For gel battery models without a protective gas valve, this situation can result in an explosion. For this reason, it is necessary to monitor the battery charge level and battery charging modes.
Second distinctive feature
operation of gel batteries is the high sensitivity of the battery to violations of charging conditions. Exceeding the charge current or exceeding the charge voltage leads to rapid failure of gel batteries. For this reason, to charge gel batteries, special chargers are required that take into account the structural features and operating modes of such batteries. As a rule, such chargers use a multi-stage battery charging mode. We recommend using the special SKAT-UTTV device to effectively charge, restore and train gel batteries.
Third distinctive feature
gel batteries provide the ability to operate at low temperatures. At low temperatures, gel batteries can hold a charge for a long time. However, the ability to immediately deliver high current at low temperatures drops sharply. Therefore, when working with high starting currents, special devices for heating batteries should be used.
Fourth distinctive feature
Gel batteries are able to operate for a long time, have a long service life, and can carry out a large number of charge and discharge cycles. In order for your gel battery to last for many years, you need to keep it completely clean and exercise the battery in a timely manner. For training, you can use forced discharge of the battery by forcibly turning on the load or use special equipment for training the battery.
Fifth distinctive feature
gel batteries are highly sensitive to short circuits. Even a very small short circuit can completely destroy a gel battery. Therefore, when using such batteries, it is necessary to reliably protect the battery from short circuits. If gel batteries are used in uninterruptible power supplies, such UPSs must have effective electronic protection against short circuits.
Pros and cons of gel batteries
The advantages of gel-type batteries include the following:
A substance used to fill plates.
- The device does not require replenishment of electrolyte or water under normal operating conditions. It is only necessary to open cans and refill with distilled water when trying to restore the battery.
- The gel poured between the plates acts as a dielectric spacer between the positive and negative electrodes. The substance additionally prevents chipping of the active mass, which allows the battery to be used under conditions of increased vibration loads.
- No aggressive sulfuric acid vapors enter the engine compartment. The evaporated substances and gaseous reaction products remain locked in the gel and are then used during battery operation. Since the battery does not emit hydrogen (which forms explosive mixtures with oxygen in the air over a wide range of concentrations), the device can be used in household uninterruptible or emergency power supplies.
- The device can be operated in an inclined position; the battery can withstand a short-term rotation of 180°.
- The plate is made of chemically pure lead, which helps reduce internal resistance and speeds up charging.
- High starting current (depending on ambient temperature).
- Extended service life. Unlike a battery with liquid electrolyte, which lasts 2-4 years, a gel device lasts up to 10 years (subject to the manufacturer's recommendations).
- The battery can be deeply discharged without the risk of structural damage.
Equipment disadvantages:
Controller circuit for current regulation.
- Increased cost, 2-3 times higher than the price of a standard liquid electrolyte power supply.
- Charging requires setting the exact current and voltage values. When the voltage in the power circuit increases (for example, when the regulator on a car generator malfunctions), irreversible destruction of the battery structure occurs. A difference of 1-2 V compared to the required voltage value leads to a drop in capacity by 30-40%.
- When the temperature decreases to -30°C and below, the gel freezes, which turns into a brittle material. Liquid electrolyte begins to flow from the hardened shells into the lower part of the battery case.
- It is necessary to use an additional controller that regulates the current parameters in the power circuit. The device is placed on a terminal and is adjusted depending on the battery capacity.
Pros of GEL batteries
There are really a lot of advantages of this technology, I would even say that this is a “really breakthrough”, I have already listed some positive aspects several times, but I will repeat once again, it should still stick in your brain:
- Absolutely maintenance-free technology - no need to go there, it’s fine there without you.
- The gel between the plates, which holds the electrolyte, is a dielectric and protects against shedding.
- There is no evaporation of the electrolyte, it is always in the gel - as the manufacturers write, the gas recombines back inside.
- Therefore, it can be used even inside a car or at home in alternative energy supply systems, because hydrogen and oxygen do not evaporate.
- Robust design - can be placed on its side or even upside down (although manufacturers do not recommend it).
- Another plus is the pure lead in the design, it has lower internal resistance, which means fast charging.
- But the discharge is also fast and can produce large starting currents. The advantage of this is that in winter the car almost always starts (if the engine and battery are in good condition).
- Increased service life - let's say, if compared with a conventional acid battery, the difference can be up to three times. That is, a regular one works on average for two to three years, a gel one for 6 to 10 years.
- Resistant to deep discharges, withstands up to 400 zero cycles (discharged to zero), for comparison, a regular one - no more than 20 - 30 cycles.
- And in general, the number of discharge-charge cycles is 5-10 times greater than standard “acid tanks”, when compared with AGM it is 2-3 times.
- In idle mode, it can retain its charge for a very long time, for example, it discharges by 15 - 20% in a year.
If we translate the advantages into ordinary language, it turns out - “seems to be reliable”, does not require knowledge of batteries, set it and forget it! It's like that? But not really - there are disadvantages and some can simply kill your super battery in a matter of months.
The difference between gel batteries and acid and AGM batteries
Standard batteries use a liquid electrolyte consisting of distilled water and sulfuric acid. To increase operating efficiency and reduce water consumption, antimony was introduced into the plate material, which was subsequently replaced by calcium. To increase resistance to deep discharges, silver is added to the electrode material.
The resulting batteries are classified as low-maintenance; topping up with distilled water during operation is not required.
The gel device differs from the AGM series devices (also lead-acid) with a voltage of 12 Volts in the fluidity of the electrolyte. In AGM products, the liquid is located in the pores of separators made of special acid-resistant fiberglass. The structure of the elements ensures liquid retention due to the capillary effect.
There are special cavities of increased size designed to collect gaseous products formed during the electrochemical reaction.
Gas and moisture removal system for AGM batteries.
The advantage of AGM devices is their resistance to electrode and electrolyte degradation during deep discharges. The effect is achieved by compacting the package assembled from lead plates and fiberglass separators. Tightly contacting surfaces prevent water evaporation and precipitation of the active mass.
Charging gel batteries
A gel-type battery for a car is sensitive to the parameters of the electric current supplied to the terminals. Do not use standard chargers for conventional lead-acid devices. It is necessary to purchase special equipment that allows you to manually adjust the characteristics of the electric current.
The design of the device includes a controller that automatically regulates charging parameters depending on the temperature of the battery.
An additional device designed to monitor the battery charge level. It is not purchased separately, but is installed in specialized charging equipment.
Sequence of actions when servicing a gel battery:
- Remove the power source from the machine, and then connect the cables from the charging unit, observing the polarity (a red plastic clip is used for the positive terminal).
- Manually set the current in the charging circuit, which should be 10% of the rated capacity (for example, for a product with a capacity of 54 A*h, the value must be set to 5.4 A). To control the parameter, a digital or analog device mounted on the housing is used. If it is necessary to perform accelerated capacity restoration, the current strength is increased to 30% of the rated capacity. Often using the accelerated algorithm is not recommended (the current threshold in the charging circuit is indicated on the case, the Max Initial Current parameter).
- Adjust the voltage in the power circuit to 14.5 V (the exact value is indicated on the manufacturer's label in the Cycle Use column). As the parameter increases, the gel softens, which leads to a loss of electrochemical characteristics.
- Charging the car power supply takes up to 12 hours. If the battery is not in use or is installed in an emergency power source, the device must be recharged. The permissible voltage in the circuit is indicated on the manufacturer's label in the Standby Use column.
Cons of gel batteries
Price
A significant disadvantage of the GEL battery is its price. With comparable capacity, it is approximately 3 times more than an AGM and 5 times more than a traditional lead-acid battery. But this disadvantage is fully compensated by a higher service life.
Sensitivity to overvoltage
A disadvantage associated with the operating principle of a gel battery is its sensitivity to voltage exceeding a certain level when charging. For example, a battery with a nominal voltage of 12.6 V cannot be charged at a voltage higher than 14.5 V. With a significant increase in voltage during charging, a change in the structure of the electrolyte towards greater fluidity is observed. For this reason, you cannot install, for example, car gel batteries in older models, where the on-board voltage varies within a wide range. Such batteries are suitable only for modern car models where the on-board voltage is stabilized. And, of course, it is unacceptable to charge a gel battery from a charger that is not specifically designed for such batteries.
Charging current limits
The need to maintain the jelly-like structure of the electrolyte also limits the charging current of GEL batteries. And, although such batteries surpass traditional lead-acid batteries in charging speed, they lag behind AGM batteries. There is a simple rule for GEL batteries - the optimal charging current in amperes is numerically equal to 10% of the capacity expressed in ampere-hours. The maximum permissible charging current is indicated in the technical specifications of the battery; it is usually about 3 times greater than the optimal one.
A long-term short circuit can lead to “swelling” of the gel battery case and its complete failure. However, short circuits are also contraindicated for other types of lead-acid batteries.
Do-it-yourself charging for gel batteries
A homemade charger for a gel-type car battery is built on the basis of a step-down transformer, working in conjunction with a semiconductor rectifier unit. A current and voltage regulator built on a microcircuit is introduced (for example, the L200CV product from ST Microelectronics).
The design provides additional resistance that allows you to regulate the current in the output circuit. To monitor the parameters, an ammeter and a voltmeter are installed, all parts are placed in a closed housing.
The popularity of gel batteries is growing
Currently, the popularity of using gel batteries has grown significantly. A significant number of advantages of this type of battery have led to the use of gel batteries in various types of devices. Gel batteries are used in automobile and railway transport, in power supply systems for security and fire systems, to power surveillance equipment and computer equipment. The effectiveness of using gel batteries to ensure uninterrupted power supply to heating and water supply systems is also high.
Battery Maintenance
The device does not require periodic maintenance during operation. If there is a drop in the capacity, accompanied by swelling of the body, then it is necessary to remove the plastic plugs and inspect the cans. If electrolyte has fallen off due to lack of water, further use of the battery is not recommended.
It is not possible to restore the product by adding an electrolyte; there are no special reagents for reactivating the substance.
Is it possible to fill a gel battery with electrolyte or water?
To restore the operating parameters of the battery, it is allowed to add distilled water to the jars (it is not recommended to introduce electrolyte). Before starting topping up, you must disconnect the power source from the external circuit. Then you will need to remove the plastic lid and remove the rubber plugs covering the jars.
The liquid is applied with the nozzle of a syringe or a rubber bulb, 2-3 ml each, onto the surface of the separators, and then the device is left for 8-10 hours (to saturate the separating plates with the solution).
Syringe for adding water to the battery.
If all the liquid has been absorbed, then you need to add another 2-3 ml of water.
The procedure is repeated until the absorption of the solution stops; excess liquid is removed with a syringe. Measure the voltage at the terminals, and then connect the external power supply. After charging with low current, the battery parameters are partially restored, but the capacity is reduced by 30-50%. Long-term use of the product is not recommended, since the battery will not ensure reliable starting of the engine.
How are gel batteries charged?
GEL battery
Those motorists who decide to purchase gel batteries for installation in their “iron horses” must keep in mind that special chargers should be used to charge them. Their distinctive feature is a very precise value of the output voltage: the fact is that for a battery of this type it should in no case exceed the limit strictly defined for each of the models. As a rule, it is around 14.5 V, and if the voltage is higher, the battery will simply fail.
As is the case with conventional acid batteries, gel batteries are charged with a current that is 10% of the capacity. As for the frequency of recharging, experts recommend doing it once or twice a year. To determine the period of time during which recharging should last, it is necessary to divide the battery capacity by the charging current.