How are PB and PC boards produced?
The markings PC and PB indicate floor slabs with voids. It is thanks to these voids located along the entire length that the weight of the slab is reduced compared to monolithic floors.
The main difference between PB and PC boards:
- PB - the manufacturing process takes place on a special machine without the use of formwork.
- PC - formwork is used during manufacturing, this is an old technology.
PC slabs are made from concrete grades from M200 to M400. Reinforcement marked AIII is used. If slabs longer than 4.3 meters are made, then stressed reinforcement is used. As we said, the slab is made in formwork, and compaction is carried out by special vibrators.
For PB slabs, more durable concrete marked M400 or M500 is used. In such slabs, regardless of their length, prestressed reinforcement is used. Thanks to this tension, the plates bend less.
Reinforced concrete solid floor slabs for large-panel buildings.
Lecture. Floors and floors for multi-storey panel residential buildings
(16.04.2013)
.In large-panel residential buildings, prefabricated reinforced concrete floors of the following types are used:
- from solid reinforced concrete slabs;
- made of solid slabs with edges along the contour (Fig.);
- two-layer ribbed slabs (slabs with false ceiling);
- from hollow-core floorings (fig.)
Multi-hollow floor panels: a - with round voids; b - produced on installations with concreting combines (1 - top layer; 2 - bottom layer; 3 - middle layer); c - with oval voids
In industrial housing construction, solid-section floor panels with a thickness of 140, 160 mm and hollow-core panels with a thickness of 220 mm are used.
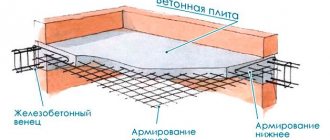
Reinforced concrete solid floor slabs for large-panel buildings.
The panels are used in a cross-wall structural system of buildings with a pitch of transverse walls (multiple of 300 mm) of 2.4 - 4.2 m, the length of the slabs reaches 7.2 m (multiple of 600 mm), thickness is taken from 100 to 200 mm.
Reinforced concrete solid floor slabs for large-panel buildings are divided into types according to their thickness and the pattern of support on the wall panels:
- 100 mm thick, supported on 4 sides;
- 120 mm thick, supported on 2 or 4 sides;
- thickness 140, 160, 180, 200 mm, supported on 2, 3 or 4 sides.
160 are most widespread .
The slabs are supported on the walls along the contour (4 sides) with a small pitch of the transverse walls, on three sides - with a small pitch of the transverse walls, or on two opposite sides with a large pitch of the transverse walls. Thus, the working reinforcement of the slabs is placed in two or three directions.
Slabs with a length of L≥ 4.8 m are designed to be supported on 2 sides and have prestressed reinforcement.
Coordination slab dimensions:
- length - 3.0 - 7.2 m (every 0.3);
- width – 1.2 – 6.6 m (every 0.3).
The length of the slab is taken to be:
- the smaller size of the slab in plan when supported on 4 sides,
- the size of the side of the slab that is not supported by supporting structures when supported on 2 or 3 sides.
According to operating conditions, one of the dimensions should not exceed 3.6 m.
The plates have:
- steel embedded parts, reinforcement outlets and other structural elements for connection with other building structures;
- channels for hidden electrical wiring, sockets for boxes and sockets, plastic boxes with anchors for fastening lamps;
- holes and openings for the passage of utilities.
The side faces on the sides of the slabs, intended for connection in the span (without resting on the walls), are made with closed or open recesses, the shape of which ensures the joint operation of the connected slabs for shear in the horizontal and vertical directions after grouting the seams between the slabs. The slabs may have recesses to form dowels on the sides that rest on the wall panels.
The depth of the platform for supporting the slabs on the external walls is 90 mm. The nominal size of the depth of the support area on the internal walls is half the thickness of the wall panel minus 10 mm. Supporting the slabs on the walls of the staircase - the entire thickness of the wall. The floor slabs are supported using cement-sand mortar. All steel connections between the floor slabs and the external wall panels are welded. There are at least two connections on each side of the floor slab.
The panels are made from heavy concrete of class B15 or higher, or from lightweight concrete with porous aggregates of class B12.5. The protective layer is at least 15 mm.
The 120 mm thick floor panel has two lifting loops on one long side, and on the other side there are embedded parts for welding to the lifting loops of the panel, which is laid side by side in the floor. At each beveled corner of the panel there are reinforcement outlets connected by welding to the outlets of adjacent floor panels. The lifting loop, placed parallel to the surface of the panel, protrudes 70 mm beyond the edge of the panel. Accordingly, the embedded part from the steel angle is recessed by 80 mm. The reinforcement outlet at the corner of the panel is curved at an angle of 90˚.
Solid panels have cutouts or recesses to form dowels. Channels with a diameter of 25 mm are installed in solid panels for hidden replaceable electrical wiring.
Solid floor panels with a thickness of 160 mm are used for residential buildings with small and large spacing of transverse walls. The panels are used in conjunction with thermal insulation floors. These panels in Kyiv have 6 lifting loops and 2 embedded parts on each side.
PC and PB boards, technical characteristics
The most important parameter of floor slabs is load-bearing capacity. This parameter expresses how much load the slab can withstand without collapsing. The standard load-bearing capacity of PC slabs is 800 kilograms per square meter, sometimes you can see slabs with characteristics of 1250 kilograms per m2. PB slabs have a wider range of characteristics, from 30 to 1600 kilograms per square meter. Despite the large selection of values, 800 kilograms is considered the standard.
Let's consider the geometric characteristics of the slabs:
- For each type of slab, the standard is 22 cm.
- Length. The maximum length of PC slabs is a little more than 7 meters, and PB is almost 11 meters.
- Surface. In this indicator, PB slabs win because, thanks to modern technology, they have a smoother shape, which will allow for significant savings on finishing work.
It is also worth noting that PB slabs are more accurate in their geometry, which is due to the technology of continuous formation.
Fastening and anchoring floor slabs
Overlap
- a horizontal structural element that divides a building into floors and transfers the load from its own weight, people and equipment to walls, beams and columns.
By location in the building:
- prefabricated reinforced concrete;
- monolithic reinforced concrete;
- laid on steel or wooden beams.
- strength;
- rigidity;
- soundproof;
- industrialism;
- efficiency.
Special requirements for floors
- waterproof;
- incombustibility.
The floor structure consists of floor slabs and a floor laid on them. Hollow-core reinforced concrete slabs are manufactured at the factory with a length of 2.4-7.2 m, a width of 1-1.8 m, and a thickness of 220 mm. The slabs come with round
,
oval
and
polygonal
voids, more often used with round ones. These slabs rest on two sides. They are laid on load-bearing walls along a layer of mortar.
Support depth of floor slabs
- on brick walls 90-120 mm; support of up to 250 mm is allowed on external walls;
- on panel walls 50-90 mm.
Slabs with a span of 9-12 m, 300 mm thick are used in the floors of public buildings (rarely).
Anchoring
- fastening floor slabs to each other and to external walls.
Anchoring and sealing the joints between the slabs with M100 cement-sand mortar creates a hard drive that turns the building into a spatially unchangeable system. The anchors are placed across the slab, but no more than 3 meters from each other.
Marking PK60.12 (length 6000 mm, width 1200 mm, multi-hollow).
Hollow-core slabs are used in buildings with either longitudinal or transverse load-bearing walls, because The slabs rest on two sides.
Solid, flat single-layer reinforced concrete slabs are slabs of constant cross-section with the lower surface ready for finishing, and the upper surface ready for flooring. They are used in panel buildings with a cross arrangement of load-bearing walls. Length 3.6-6.3 meters, width 2.4-7.2 meters, thickness 100 mm (for multi-layer flooring), 160 mm. Flat slabs are supported along the contour (on 3-4 sides), the support depth is 50-90 mm, i.e. the slab does not reach the axis of the wall by 10 mm.
Anchoring - fastening the slabs to each other and external walls with anchors in the form of rods, brackets (6-12 mm in diameter) or metal plates.
Marking P36.24 (length 3600 mm, width 2400 mm). The letter designation P is a solid slab, PC is a multi-hollow slab.
They separate heated rooms from basements and technical underground. The load-bearing part is a hollow-core or solid floor slab, on top of which thermal insulation from loose, slab or monolithic insulation is laid. A cement-sand screed is placed on top - preparation for the floor.
They separate the premises of the upper floors of the building from unheated (cold) attics.
A vapor barrier (rolled materials or bitumen mastic) is installed along the top of the ceiling, which protects the overlying insulation from moisture from the warm room. Insulation made from any materials (loose, slab, monolithic) is covered with a protective screed on top.
The protective screed protects the insulation from atmospheric moisture.
Floors in sanitary facilities and wet rooms are waterproofed - 2-3 layers of rolled materials on mastic. In places where the surface of the waterproofing carpet adjoins the walls, strips of waterproofing are glued and raised 150-200 mm higher.
The waterproofing is protected from above with a cement-sand mortar screed.
In buildings with longitudinal load-bearing walls
slabs
of a solid section
with a thickness of 160 mm, supported on 2 sides or hollow-core slabs with a thickness of 220 mm are used.
In buildings with cross load-bearing walls
Use
solid-section
the size of a residential cell (room), supported on three to four sides.
P 63.42 - solid; PC 63.15 - multi-hollow.
4 - standard size; P - floor slab; 63 — nominal length, dm.; 30 — nominal width, dm.; 16 — thickness, cm; 5.8 - the value of the design load without taking into account the dead weight of the slab, 100 kgf/m² L - from lightweight concrete; 1 - abbreviated brand of slab.
The slabs are anchored to each other and to the external walls. For this purpose, they provide special editions. For electrical wiring, the slabs have channels with a diameter of 20 mm.
Positive qualities of technology without formwork
Pb slabs have the following positive qualities:
- You can cut the ends at any angle.
- Good manufacturing accuracy helps to reduce gaps between slabs when laying on a building.
- Since there is no mesh of reinforcement inside the slab, it is easier to make holes for chimneys or communications.
Since there are no special brackets, this creates some problems during the loading, unloading and installation process.
What are the differences in the installation of PB and PC slabs?
There are no differences in installation, everything is absolutely the same. The only difference is in the gaps between the plates, which are subsequently covered over.
However, a couple of differences can be noted:
- Slabs made with formwork are lifted and installed using special brackets, and PB slabs are moved using rigging devices.
- The slabs, which were made without the use of formwork, rest on the walls on both sides, but without a protrusion.
How to make
Hollow-core floor slabs are manufactured using different types and series of concrete. Among them:
- Silicate.
- Lungs.
- Heavy.
When producing hollow structures based on the listed types of concrete mixture, different technologies and methods are used:
- Without formwork. For the manufacture of such products, automated equipment is used that supports the vibration compaction function. The workpiece gradually passes along the line and is processed using automation, which gives it the correct geometry and overall dimensions of the hollow core slabs. In order to increase the density, the structure is equipped with reinforcing ropes.
- With formwork. The concrete mixture is placed in a standard metal formwork with metal rods and reinforcement. When hollow core slabs undergo the compaction procedure, they are treated in hydrothermal chambers. Upon completion of the steaming process, the products are removed from the formwork and left to harden.
The second method is considered more popular because it is performed without the use of complex equipment and technologies. In most cases, it is used in industrial enterprises where reinforced concrete hollow-core slabs are produced. The presence of reinforced elements increases the strength properties.