Design and types of SF6 switches
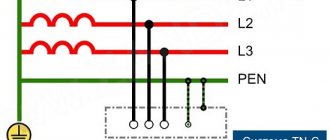
These systems are designed for operational monitoring of the condition of high-voltage power lines. They are very similar to oil ones, but have a different working environment - the principle of operation is based on the properties of gas compounds instead of oil. The medium used is SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride).
The advantage of SF6 gas is its unpretentiousness. If oil models require special care, periodic oil changes and cleaning, then SF6 models do not face such a problem. In addition, the gas is durable: it does not degrade over time and does almost no harm to the mechanical elements of the switch.
Physically, SF6 is a non-flammable, colorless and odorless gas. It is much denser than air, and its molecular weight is 5 times that of air. The gas is resistant to external influences and retains its characteristics: even if an arc occurs in it and decay begins, after some time the state of the mixture will be restored.
There are two types of SF6 circuit breakers (hereinafter referred to as EB):
- tank;
- core EV.
Column electric switches are used in 220 V networks; these are standard single-phase switches. They consist of two interconnected parts:
- arc extinguishing;
- contact part.
Both have the same dimensions and volume.
Tank EVs are smaller. They include one of the types of drives discussed below. The drive is distributed over several phases, due to which the device gently changes the voltage level. Another advantage of tanks is their large load capacity, which is achieved by the presence of a built-in transformer.
The drive here is also a regulator: it provides switching on/off of the flow of electricity and maintaining the electric arc. The following types of EV drives are distinguished:
- spring-hydraulic (PPRG);
- simpler spring ones (PPRM).
Typically the actuator is mounted on a low pedestal or near the ground so that it can be easily reached and adjusted by maintenance personnel. The part consists of:
- turning mechanism;
- release devices;
- locking latch.
Spring ones are reliable and have a very simple design; they use only simple mechanics. During commissioning, a certain compression of the spring is established, and after moving the control lever, it straightens with further opening of the contacts. This type of EV often serves as a stand for presentations of the behavior of sulfur hexafluoride under the influence of an electric field.
Spring-hydraulic SF6 equipment is hydraulically controlled. It is more expensive, but more effective, since it can independently change the position of the latch.
In addition to the design, there are different types of EVs based on the principle of interrupting the electric arc:
- rotating;
- air (autocompression) EVs;
- longitudinal blast;
- similar to the previous point, with gas heating.
All internal components of the EV are placed in a container filled with SF6 gas. Operation control is carried out remotely, using electronics, or mechanically manually. Layout of all components of a typical EV:
Such features lead to rather large dimensions of the devices. Note that purely manual control is relevant for low-power samples; in other cases they resort to:
- mechanical control;
- cargo management;
- spring;
- electromagnetic method;
- pneumatic
But almost everywhere there is an emergency manual lever.
The electromagnetic drive requires external power, so such an EV is connected to a current source of 220 V and 58 A. The system is very reliable and can be successfully operated in adverse conditions. In a pneumatic one, the working unit is a cylinder with a piston. The action of compressed air ensures high response speed.
How does a SF6 switch work and what types are there?
The SF6 circuit breaker itself is designed for systematic monitoring of the functionality of high-voltage networks. It is designed very similar to such an arc extinguishing device only with an oil method of action.
The gas device does not use oil, but sulfur, and its advantage lies in the minimal features of service and casing. The main advantage of the SF6 circuit breaker is its long service life.
There are several types of SF6 gas circuit breaker, for example, depending on the type of design.
- Tank design. It is relatively small in size and necessarily has an additional input for several phases. Due to this feature, any specialist can easily cope with smooth control of switching electrical voltage. And thanks to the built-in transformer, such a switch can withstand even the highest loads.
- Column design. It is larger in size compared to the previous version and is connected to only one phase. The device is equipped with a connection system and an internal arc extinguishing system. In addition, this type of device works both at a distance and on a built-in basis in the network.
Depending on the method of destruction of the electric arc, the circuit breakers are divided into the following subtypes:
- Automatic compression SF6 gas.
- SF6 gas full revolution (or full rotation).
- Longitudinal blowing SF6 gas.
Definition and Application of SF6 Gas
SF6 gas is sulfur hexafluoride, which is classified as an electrical gas. Due to its insulating properties, it is actively used in the production of electrical devices.
In its neutral state, SF6 gas is a non-flammable, colorless and odorless gas. If we compare it with air, we can note its high density (6.7) and molecular weight, which is 5 times higher than air.
One of the advantages of SF6 gas is its resistance to external manifestations. It does not change characteristics under any conditions. If disintegration occurs during an electric discharge, then a full restoration necessary for operation soon occurs.
The secret is that SF6 molecules bind electrons and form negative ions. The quality of “electronegation” endowed 6-sulfur fluoride with such a characteristic as electrical strength.
In practice, the electrical strength of air is 2-3 times weaker than the same property of SF6 gas. Among other things, it is fireproof, as it is a non-flammable substance, and has cooling properties.
When the need arose to find a gas to extinguish the electric arc, they began to study the properties of SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride), carbon 4-chloride and freon. SF6 won the tests
The listed characteristics made SF6 gas most suitable for use in the electrical field, in particular in the following devices:
- power transformers operating on the principle of magnetic induction;
- complete type switchgears;
- high voltage lines connecting remote installations;
- high voltage switches.
But some properties of SF6 gas led to the need to improve the design of the switch. The main disadvantage concerns the transition of the gaseous phase to the liquid phase, and this is possible under certain ratios of pressure and temperature parameters.
In order for the equipment to operate without interruption, it is necessary to provide comfortable conditions. Let’s assume that for the operation of SF6 devices at -40º, a pressure of no more than 0.4 MPa and a density of less than 0.03 g/cm³ are required. In practice, if necessary, the gas is heated, which prevents the transition to the liquid phase.
Application area
The gas-insulated voltage transformer is used in various electrical substations. The device is capable of transmitting a signal to measuring instruments and protective components of switchgear devices. Gas-insulated transformers are connected to a three-phase (industrial) network. Their task is to transform 50 Hz alternating current. Installation is permitted in medium and moderately cold climate zones.
The operation of transformers based on SF6 gas insulation is possible in almost all sectors of human industrial activity. The operation of the equipment allows the processed signal to be transmitted to measuring instruments, security, and safety systems. The installation is used to ensure the operation of various electricity metering devices.
The SF6 current transformer is ideal for closed or underground substations operating within the city. The installations are installed in environmentally critical areas. Oil leakage is not permitted in such areas. Here it is permitted to use only SF6 equipment.
Purpose and principle of operation
An SF6 circuit breaker is a type of high-voltage circuit breaker, a switching device that uses SF6 gas as an electronic arc extinguishing medium; designed for quick connections and disconnections of individual circuits or electrical equipment in the power system.
Figure 1 – Diagram of a SF6 circuit breaker
SF6 circuit breakers have been intensively developed since 1980 and have great prospects at voltages of 110...1150 kV and interruption currents up to 80 kA. In technically developed countries, SF6 gas switches for high and ultra-high voltage (110-1150 kV) have practically replaced all other types of devices.
High voltage SF6 circuit breakers perform their work by isolating the phases from each other using SF6 gas. When a notification is triggered that you need to turn off electrical equipment, the contacts of some cameras (if the device is a speaker device) open. In this way, the built-in contacts form an arc, which is placed in a gaseous environment. It decomposes the gas into different components, but at the same time it itself decreases due to the high pressure in the container.
In the process of using a SF6 circuit breaker, cycles of connecting and disconnecting the switching device are performed. During various operations with the switch for operating purposes, in most cases, the shutdown current is within the limits of the designated values. The number of potentially possible operations, depending on the shutdown current, is set by the manufacturer. In order to find the total number of shutdown operations, it is essential to use a special interconnection diagram, which can be found in the circuit breaker data sheet. The higher the current, the smaller the number of possible on/off cycles of the SF6 circuit breaker. The switch is specialized for installation in a 110 kV outdoor switchgear, since its rated operating voltage is 126 kV. The switch operates in accordance with those declared by the manufacturer under the following conditions:
- installations on a hill above the tier of the sea coast no more than a thousand meters;
- ambient temperatures from -350 C to +400 C;
- installations in accordance with the necessary conditions of the manufacturer;
SF6 circuit breakers are distinguished
- core
- tank
Features of maintenance and operation
Features of the use of remote control switches
During the operation of such switching devices on outdoor switchgear (open switchgear), it is necessary to take into account that condensation can accumulate in the switch drive cabinets, which leads to corrosion of the mechanism systems, as well as secondary control and signaling circuits. For this purpose, the manufacturer provides heating resistors inside the cabinets that operate continuously.
All actions to turn on or turn off the devices are possible only if the gas pressure is not less than the permissible one; if this is neglected, there is a high probability of damage and failure of the relatively expensive switch. For these purposes, a minimum pressure alarm must be installed, as well as control circuit blocking. If the staff notices that the pressure has dropped, the device needs to be taken out for repairs and begin to look for the reasons for the decrease in this vital indicator. Naturally, its removal from operation must be carried out in accordance with all the necessary safety requirements for this electrical installation and set out in local instructions. To control the pressure, there must be a working pressure gauge, and after eliminating the gas leak, it is worth supplementing it through a special connection, which is located inside the drive mechanism.
Inspection of SF6 switches is carried out daily, as well as once every two weeks at night. In damp, humid weather, you need to pay attention to the occurrence of electrical corona. If the value of the disconnected current was the maximum permissible (during short circuits), then high-quality maintenance should be ensured. The number of outages, both planned and emergency, is recorded in logs specially allocated for these needs.
Despite the existing disadvantages, the SF6 circuit breaker has its strengths and is therefore a worthy replacement not only for oil-based, but also for high-voltage air circuit breakers.
Purpose, design and performance indicators of the device
An SF6 circuit breaker (EG) is a switching unit designed for switching in high-voltage electrical installations in order to redistribute currents and voltages in power lines.
The arc extinguishing element (SF6) in the devices is sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), which has the following characteristics:
• High electrical strength;
• Chemical neutrality;
• Increased heat transfer properties;
• Good insulating properties.
All these qualities give the composition excellent arc-extinguishing abilities. The EV design is three-pole. Each of the poles is a sealed container with SF6 gas under a pressure of 0.6 MPa and an arc-extinguishing mechanism.
Design differences between devices
There are three types of high-voltage switches using electrical gas:
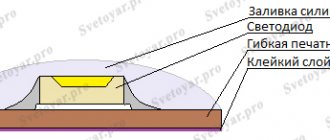
Columnar - have the form of vertical sets of insulators (two or more), representing columns - poles. The upper element contains an arc-extinguishing device, and the lower one is supporting and serves as a dielectric layer between the device and the metal frame. The frame can be individual for each pole, or it can be common for all three. Inside the lower element there is a lever (insulating rod) that transmits movement from the drive system to the moving contact of the switch.
Tank - made in the form of a cylindrical metal container, on top of which two insulators are placed, which are high voltage inputs. The device for extinguishing the electric arc is placed in a metal container filled with SF6 gas.
Combined - combine the two previous models, that is, a metal tank with two rows of porcelain insulators. One of them contains an arc extinguishing device. The second insulator row contains a built-in current transformer.
Electrical arc discharges lead to the appearance of impurities in SF6 gas that are harmful to the human body. Their formation may increase due to the presence of oxygen particles or water vapor. This fact can reduce the electrical insulation parameters of the device, therefore, in the upper part of the first insulating row, a filter is placed to absorb moisture and gas decomposition products.
What does a SF6 circuit breaker consist of and how does it all lead to cutting off the arc?
Since the switches can be tank-type, column-type, or even designed for installation in switchgear. And besides this, there are different types of remote control, then for each switch there will be a separate operating principle and composition of parts.
Consider, for example, in this article, as an example, the popular Schneider electric switch with auto-compression for a voltage of 12 kV type LFP.
The switch is three-pole. Each pole is located in an insulated housing, which is filled with SF6 gas under low pressure. Inside the case there is a remote control, to the contacts of which commands for turning on, turning off or permissible cycles are sent. These commands are supplied from a spring drive located on the front panel or remotely.
The device also includes sensors for monitoring the SF6 gas pressure in the housing and pressure increase sensors. For connection to the power circuit there are special clamps on the back of the case, and there are also terminal blocks for connecting secondary circuits.
The operating principle of the switch is based on the auto-compression method of arc extinguishing.
Let's look at the factory picture above. We have main contacts (letter a, red) and arcing contacts (letter b, dark blue). This means a command is received to turn off the switch. The main contacts open, the arc extinguishing contacts also open. At the moment when the arc extinguishers open between them in the expansion volume (letter c - the area limited by the pink line), an arc is formed. Coils are located on the top of the arc extinguishing contacts. So the electric arc begins to twist under the influence of the magnetic field of this coil. The volume of gas begins to expand under the thermal influence of the arc. The gas pressure increases and it seeks an outlet to an area with lower pressure. This flow of SF6 gas draws the arc into the lower arcing contact (area e in the figure) and the arc stretches. And then, at the moment when the current passes through zero, the arc goes out. At this point, the switch is considered to be open. This time is 70 ms.
The spring drive includes: spring charging motor, trip coils (YO1, YO2), turn-on coil (YF), minimum voltage trip coil (YM), mitop direct-acting relay, B-O cycle counter and other devices necessary for ease of maintenance switch. The coils have a varying number of normally closed, normally open contacts and a changeover contact.
Advantages and disadvantages of SF6 circuit breakers
The devices have undoubted advantages:
- versatility. They can be installed in networks with almost any voltage;
- unpretentiousness - EVs work even in fire hazardous areas and seismic zones;
- response speed. SF6 reacts to the occurrence of an arc in a fraction of a second, resulting in almost instantaneous de-energization of the protected devices;
- durability. Gas does not wear out the elements in contact with it, the gas mixture does not degrade and does not need regular replacement, and the outer shell of the EV is durable and protects well from adverse influences;
- work with both alternating and direct high voltage. This distinguishes them favorably from those that are not capable of functioning in high-voltage vacuum networks;
- explosion and fire safety;
- closed working environment - when triggered, there is no exhaust to the outside.
But there are also design-related disadvantages:
- high price. The SF6 switch is simple in design, but difficult to manufacture; the synthesis of the gas mixture is also quite labor-intensive and expensive;
- cannot be placed in any place. Switches are mounted only on a special electrical panel or a specially prepared foundation;
- demanding temperature conditions - at low temperatures EVs are ineffective (but SF6 gas can be heated);
- maintenance requires specific skills and equipment;
- An electromagnetic drive system requires a high-capacity battery.
The main disadvantage of the mixture is its transition to the liquid phase, which is observed under certain conditions. This occurs at certain temperature and pressure ratios. For example, in cold conditions (minus 40 degrees Celsius) a pressure of no higher than 0.4 MPa is required with a gas density lower than 0.03 kilograms per cubic centimeter - which does not provide proper performance. Therefore, in practice, in order to avoid transition to a liquid state, SF6 gas is heated.
MAIN FEATURES AND ADVANTAGES OF THE SWITCH
- presence of built-in current transformers (with high accuracy classes);
- equipped with a modernized spring drive type PPrK-2000SM, the electrical circuit of which is made on an imported element base: with spring terminal clamps for connecting external circuits; with an increased number of signal contacts (12 NO, 12 NC and 2 pulse), continuously passing currents of a wider range (from 5 to 25 A); with the ability to change the “setpoints” of the temperature, automatically turn on the heating and alarm about a “dangerous” decrease in temperature in the cabinet; with a modified, more user-friendly control panel design;
- the design of an arc extinguishing device operating on the basis of self-generation, unified with SF6 column switches and the VGT series;
- use of pure SF6 gas;
- the use of double seals in connections, as well as a “liquid seal” in the sealing unit of the moving shaft. The natural level of leaks - no more than 0.5% per year - is confirmed by tests of each switch at the manufacturer using methods used in space technology;
- modern technological and design solutions and the use of reliable components, including high-strength insulators from foreign companies;
- high corrosion resistance of coatings (hot-dip galvanizing) used for steel structures of the circuit breaker;
- operation in both temperate and cold climates (down to minus 55°C);
- automatic switching on and off of electric heating of SF6 gas in tanks;
- high mechanical resource;
- small overall dimensions of the switch and weight;
- high switching life specified for each pole, exceeding by 2-3 times the switching life of the best foreign analogues (per each pole) in combination with a high mechanical life, increased service life of seals and components, provides under normal operating conditions no less than 25 -year service life before the first repair;
- the ability to disconnect load currents in the event of loss of excess gas pressure in the switch;
- minimal maintenance between repairs;
- high fire and explosion safety;
- low noise level when activated (meets high environmental requirements);
- delivery of the circuit breaker fully assembled;
- full factory readiness, quick installation and commissioning (under the guidance of the manufacturer’s supervisory staff).
Advantages and disadvantages
Considering the above, the advantages of SF6 type switches include the following:
- the ability to install both closed and open electrical installations of literally all voltage classes;
- the simplicity and reliability of the design in operation is noted;
- high intensity response speed;
- low dynamic loads on foundation supports;
- good breaking capacity;
- small overall proportions and weight amount;
- the presence of two heating stages in the automatic control drive;
- large switching resource of the contact system;
Disadvantages of SF6 switches:
- more careful attention to the use and accounting of SF6 gas is required;
- high necessary conditions for the quality of SF6 gas;
- the need for specially prepared devices for filling, pumping and filtering SF6 gas;
- relatively high cost of SF6 gas;
- complexity and overhead of manufacturing - during production production it is inevitably necessary to maintain the high quality of the device;
- high cost of construction and secondary elements;
- If the switch fails in emergency mode, repairing this device may not be relevant.
Maintenance rules for SF6 circuit breakers
Maintenance of SF6 circuit breakers is regulated by the Electrical Installation Rules (PUE) 1.8.21.
When connecting the system, you should check that there is a minimum pressure in the tank - without this, the device will break. To avoid warnings, the design provides an alarm warning of a critical pressure value. There is also a pressure gauge for visual inspection.
The drive cabinet contains heating elements that prevent condensation from forming on critical mechanisms. The EV operator is obliged to monitor the constant operation of the heaters and prevent them from turning off.
When inspecting an EV you should:
- check the condition of external protection;
- remove contamination if present;
- repair damage;
- find out and eliminate the cause of contact heating, if any;
- if extraneous noises and crackling are detected, identify their source;
- check the integrity of the metal support frame, since it is also part of the ground loop;
- take pressure gauge readings and compare them with the passport data specified by the manufacturer;
- check whether the control and monitoring devices are in working order, repair or replace the faulty ones
When gas pressure drops, its reserves in the chamber are replenished.
Types of drives for SF6 circuit breakers
The rupture of electrical contacts in a sealed EV chamber filled with SF6 gas occurs due to the movement of the moving part of the arc extinguishing device through an insulating rod driven by a special drive. The drive is a complex power mechanism through which the contact group is activated.
There are three main types of drive devices:
Drive devices for SF6 circuit breakers are subject to severe power loads, especially in designs for heavy voltages, in which the weight of the moving part exceeds 100 kg, and the contact movement occurs up to 25 cm, at a speed of 8 m/s, with a load of 80 kN.
Special attention is paid to the quality operation of the drive, since most accidents that occur with electric vehicles are associated specifically with the mechanical part of the devices.
Specifications
The table shows the technical characteristics of VGT circuit breakers - 110 kV. Table 5.1 – Basic technical data of the VGT circuit breaker - 110 kV
| Parameter | Permissible value |
| Rated voltage | 110 kV |
| Shutdown time | 0.035 s |
| Rated current | 2500 A |
| Operating voltage (maximum) | 126 kV |
| Maximum breaking current | 40 kA |
| Automatic reclosure pause | 0.3 s |
| Short circuit current (maximum) | 100 kA |
| Short circuit current flow time | 3 s |
| SF6 gas leak in 12 months | 0,8 % |
| Heating device voltage | 220 V |
| type of drive | Spring |
| Creepage distance | 270 cm |
| Mass of SF6 gas | 6.3 kg |
| Number of drives | 1 |
| Switch weight | 1700 kg |
| Time until scheduled repairs | 12 years |
| Lifetime | 25 years |