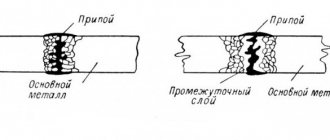
Terminal blocks
The list of electrician tools and consumables includes terminal blocks.
Terminal blocks are copper or brass coated with a layer of nickel, designed for wires of a certain cross-section and covered with a layer of insulating plastic. The wires are secured with 2 small screws. When connecting copper and aluminum terminal blocks, the locking screws must be properly tightened. If you tighten them, you can damage the aluminum conductors, which will not have a very good effect on the further operation of the electrical wiring. Therefore, it is necessary to find a middle ground: not tighten too tightly, but achieve high-quality contact.
Wire Specifications
The characteristics of the cables vary. Both metals have strengths and weaknesses. These parameters must be known for the correct selection, installation and maintenance of wiring in the apartment. To compare them, a number of criteria should be taken into account.
Electrical resistivity
This value shows the relationship between the conductor material and electrical resistance. This parameter determines what maximum current the cable can pass without overheating and melting the insulation.
| Metal | Electrical resistivity, Ohm*mm2/m |
| Copper | 0,017 |
| Aluminum | 0,028 |
From the table it follows that with equal lengths and cross-sections, the resistance of aluminum wires will be 1.67 higher. Hence the heating will be higher at equal currents.
Copper has less resistance, so you can get by with a smaller cross-section cable
Thermal conductivity
This parameter characterizes the ability of the conductor to dissipate excess heat. This property is important to take into account, because there should be no local overheating on the cable. To take this parameter into account, the thermal conductivity coefficient is used. The higher it is, the better the metal dissipates temperature.
| Metal | Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m*°C) |
| Copper | 389,6 |
| Aluminum | 209,3 |
It is clear that copper's superiority continues. It dissipates heat 1.86 times more efficiently.
The high thermal conductivity of copper allows the passage of higher power currents
Temperature coefficient of resistance
Wiring temperature affects electrical resistance. Hence, the voltage drop in the electrical network will also change. The relationship between heating and cable conductivity is characterized by the temperature coefficient of resistance.
| Metal | Temperature coefficient of resistance |
| Copper | 0,043 |
| Aluminum | 0,042 |
The table shows that the resistance of metals behaves almost identically when heated.
Weight of aluminum and copper cables
The ease of installation and cost of wiring will depend on this parameter. The weight of a substance primarily depends on density.
| Metal | Density, kg/m3 |
| Copper | 8900 |
| Aluminum | 2700 |
With equal volumes, the mass ratio of copper and aluminum is 3.3 times. For residential wiring, this factor is not critical. But for the installation of overhead power lines, the weight of the current-carrying core plays a significant role. In this case, aluminum wins. Its mass is noticeably less.
Due to its lighter weight, aluminum wire is used on overhead power lines
Tensile strength
This property applies to overhead lines. The conductor must withstand its own weight and year-round strain due to summer heat and winter frost. The strength of metals is determined by their temporary mechanical resistance.
| Metal | Tensile strength, MPa |
| Copper | 200-250 |
| Aluminum | 80-120 |
The table shows that copper is 2 times stronger at tensile strength.
Operating period
The operating time of the cable depends on the environmental conditions. If we talk about residential wiring, the service life of the cables in question has significant differences.
Aluminum wiring
This type of wiring became widespread in residential buildings and apartments throughout the country back in Soviet times. You can still find aluminum today, in any house older than 15-20 years. This was due to such alloy parameters as:
- light weight;
- cheapness.
Since aluminum weighs much less than copper, it is more often used when laying power lines, which reduces the load on the supports and, accordingly, saves on their manufacture and installation. According to the PUE, when installing a new network, aluminum cables with a cross-section of less than 16 mm2 are not used. Don't discount the cheapness either, since copper is more expensive.
Minuses
However, even high-quality aluminum wire has more disadvantages than advantages. Negative points include:
- lower electrical conductivity than copper (2 times difference);
- the ability to oxidize upon contact with air (as a result of oxidation, a layer is formed on the surface of the wire that does not conduct electric current, which reduces the useful cross-section and increases resistance);
- shorter service life (20-25 years, after which the probability of fire increases sharply due to oxidation and subsequent heating of the contacts);
- weak mechanical strength (after several bends, the aluminum cable breaks easily);
- complexity of installation (in this case, you will have to ensure the necessary conductivity by choosing cables with a larger cross-section, which are extremely inconvenient to work with. Such cables are produced only as single-core cables).
This is interesting: Protection against zero loss in an apartment - let’s look into it in detail
Conductivity and resistance
U.S. shows the ability of a substance to prevent the passage of current. But in physics there is also an inverse quantity - conductivity. It shows the ability to conduct electric current. It looks like this:
σ=1/ρ, where ρ is the resistivity of the substance.
If we talk about conductivity, it is determined by the characteristics of charge carriers in this substance. So, metals have free electrons. There are no more than three of them on the outer shell, and it is more profitable for the atom to “give them away,” which is what happens in chemical reactions with substances from the right side of the periodic table. In a situation where we have a pure metal, it has a crystalline structure in which these outer electrons are shared. They are the ones that transfer charge if an electric field is applied to the metal.
In solutions, charge carriers are ions.
If we talk about substances such as silicon, then in its properties it is a semiconductor and works on a slightly different principle, but more on that later. In the meantime, let’s figure out how these classes of substances differ:
- Conductors;
- Semiconductors;
- Dielectrics.
Conductors and dielectrics
There are substances that almost do not conduct current. They are called dielectrics. Such substances are capable of polarization in an electric field, that is, their molecules can rotate in this field depending on how electrons . But since these electrons are not free, but serve for communication between atoms, they do not conduct current.
The conductivity of dielectrics is almost zero, although there are no ideal ones among them (this is the same abstraction as an absolutely black body or an ideal gas).
The conventional limit of the concept of “conductor” is ρ<10^-5 Ohm, and the lower threshold of that for a dielectric is 10^8 Ohm.
In between these two classes there are substances called semiconductors. But their classification into a separate group of substances is associated not so much with their intermediate state in the “conductivity-resistance” line, but with the features of this conductivity under different conditions.
Dependence on environmental factors
Conductivity is not a completely constant value. The data in the tables from which ρ is taken for calculations exists for normal environmental conditions, that is, for a temperature of 20 degrees. In reality, it is difficult to find such ideal conditions for the operation of a circuit; actually US (and therefore conductivity) depend on the following factors:
- temperature;
- pressure;
- presence of magnetic fields;
- light;
- state of aggregation.
Different substances have their own schedule for changing this parameter under different conditions. Thus, ferromagnets (iron and nickel) increase it when the direction of the current coincides with the direction of the magnetic field lines. As for temperature, the dependence here is almost linear (there is even a concept of temperature coefficient of resistance, and this is also a tabular value). But the direction of this dependence is different: for metals it increases with increasing temperature, and for rare earth elements and electrolyte solutions it increases - and this is within the same state of aggregation.
For semiconductors, the dependence on temperature is not linear, but hyperbolic and inverse: with increasing temperature, their conductivity increases. This qualitatively distinguishes conductors from semiconductors. This is what the dependence of ρ on temperature for conductors looks like:
The resistivities of copper, platinum and iron are shown here. Some metals, for example, mercury, have a slightly different graph - when the temperature drops to 4 K, it loses it almost completely (this phenomenon is called superconductivity).
And for semiconductors this dependence will be something like this:
Upon transition to the liquid state, the ρ of the metal increases, but then they all behave differently. For example, for molten bismuth it is lower than at room temperature, and for copper it is 10 times higher than normal. Nickel leaves the linear graph at another 400 degrees, after which ρ falls.
But tungsten has such a high temperature dependence that it causes incandescent lamps to burn out. When turned on, the current heats the coil, and its resistance increases several times.
Also y. With. alloys depends on the technology of their production. So, if we are dealing with a simple mechanical mixture, then the resistance of such a substance can be calculated using the average, but for a substitution alloy (this is when two or more elements are combined into one crystal lattice) it will be different, as a rule, much greater. For example, nichrome, from which spirals for electric stoves are made, has such a value for this parameter that when connected to the circuit, this conductor heats up to the point of redness (which is why, in fact, it is used).
Here is the characteristic ρ of carbon steels:
As can be seen, as it approaches the melting temperature, it stabilizes.
Properties of aluminum wiring
Aluminum wiring is resistant to mechanical stress
Aluminum is not the best option for indoor wiring, but the material has several advantages over its analogues. We are talking about low weight, which greatly simplifies installation work, provided that a large amount of aluminum cable is required. The cost is lower compared to copper. These two main advantages became decisive when choosing types of wiring during the construction of structures in the USSR.
Another important feature of the material is its resistance to corrosion. However, aluminum is highly oxidized when exposed to air. As a result, a film is formed that serves as protection against further damage to the wiring. This film has poor conductivity, which can be attributed to another disadvantage.
- When oxidized, copper does not lose its conductive properties.
- Has a long service life.
- The material is more resistant to mechanical stress, for example, bending, twisting, etc.
During oxidation, films are formed in both cases, but each has different conductive properties.
Aluminum fluidity
Aluminum is several times softer than copper
First of all, you need to know about the physical and chemical properties of aluminum. The substance belongs to the group of fluid metals; it is several times softer than copper. This is a significant drawback, since homeowners need to regularly check and, if necessary, tighten all screw contact points, for example, in sockets, automatic machines and terminal blocks. This is very inconvenient if there are 10 or more sockets in the house, which need to be disassembled, tightened and installed in their original place every six months.
Flexibility and fragility
The second feature of aluminum cores is fragility and fragility. If you bend them several times, they will break off without much effort. It takes a lot of effort to deform copper.
Connecting aluminum to machines
Aluminum and copper are not galvanically compatible
The third feature of the material is the contacts of switching equipment. For RCDs, switches, voltage relays, contactors, terminal blocks and starters, they are initially made of copper or brass.
If you directly connect brass-aluminum = copper-aluminum contacts, a galvanic couple is formed, accompanied by strong heating of the junction and the formation of oxides.
Core cross-section
Another feature of aluminum wiring is the need to increase the cross-section of the wiring strands. If previously it was enough to use cables with copper conductors of size 2.5 mm2, now there is a need to lay at least 4 mm2.
Differences between copper and bronze
The two species are similar in color. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to make distinctions. This is not so difficult to do if you know the features of the bronze composition. You can find out what exactly is in front of you using the following characteristics.
- Things made of more plastic material are characterized by the presence of a reddish-brown color. But bronze is characterized by a yellow-pink tint. Even by this feature you can distinguish copper from bronze.
- Products can also be distinguished by the nature of their interaction with the saline solution. If it is spilled on a copper object, a color change will be observed. The color of bronze will remain unchanged. This is also a characteristic difference.
- Both types differ in elasticity properties. If copper wire is easily bent with one hand, then bending a bronze product is very problematic.
- Copper items are subject to a natural patination process. With prolonged interaction with air, they become covered with a greenish coating. Bronze items do not have this feature.
Rules, orders and PUE for aluminum and copper wiring
Aluminum wiring
In accordance with the amendments adopted in 2021, wiring in residential premises can be made from aluminum and copper cables.
However, it is not aluminum wires from the 60-70s that are suitable for use, but modern alloys with some iron content. The main thing is to comply with the requirements given in the table.
| Line name | Smallest cross-section of cables and wires, mm.kv | |
| With cores made of aluminum alloys | With copper wires | |
| Group network lines | 2,5 | 1,5 |
| Distribution network lines for supplying residential premises (risers) | 6 | 4 |
| Lines from floor to apartment boards and to the settlement meter | 4 | 2,5 |
Prohibition of aluminum wiring in the apartment
Old-style aluminum wiring is prohibited from being used due to its recognition as a potential fire hazard.
In accordance with international standards, old-style aluminum wiring is recognized as a potential fire hazard and is therefore prohibited. Several facts that confirm this:
- There have been numerous cases of fires around the world caused by aluminum wiring. As a result, more than a dozen people were killed.
- According to statistics, in apartment buildings and country houses with an aluminum electrical network, the frequency of spontaneous combustion is 55 times higher than the number of fires in rooms with electrical wires made of other materials.
- According to chapter 7.1. PUE. Clause 7.1.34 this type of wiring is permitted for use only in structures that were built before 2001.
- To prevent fire? It is prohibited to connect copper and aluminum wiring, for example by twisting.
Dependence of resistance index on temperature
The temperature coefficient is a value that is equal to the change in the voltage of a part of the circuit and the resistivity of the metal as a result of changes in temperature. Most metals tend to increase resistivity with increasing temperature due to thermal vibrations of the crystal lattice. The temperature coefficient of resistance of copper affects the resistivity of copper wire and at temperatures from 0 to 100°C is 4.1 10− 3(1/Kelvin). For silver, this indicator under the same conditions is 3.8, and for iron it is 6.0. This once again proves the effectiveness of using copper as a conductor.
We advise you to study How to make a battery
The concept of “specific copper” is often found in electrical engineering literature. And you can’t help but wonder, what is this?
The concept of “resistance” for any conductor is continuously associated with an understanding of the process of electric current flowing through it. Since the article will focus on the resistance of copper, we should consider its properties and the properties of metals.
When it comes to metals, you involuntarily remember that they all have a certain structure - a crystal lattice. Atoms are located in the nodes of such a lattice and move relative to them. The distances and location of these nodes depend on the forces of interaction of atoms with each other (repulsion and attraction), and are different for different metals. And electrons revolve around atoms in their orbits. They are also kept in orbit by the balance of forces. Only this is atomic and centrifugal. Can you imagine the picture? You can call it, in some respects, static.
Now let's add dynamics. An electric field begins to act on a piece of copper. What happens inside the conductor? Electrons, torn from their orbits by the force of the electric field, rush to its positive pole. Here you have the directed movement of electrons, or rather, electric current. But on the way of their movement they come across atoms at the nodes of the crystal lattice and electrons that still continue to rotate around their atoms. At the same time, they lose their energy and change the direction of movement. Now does the meaning of the phrase “conductor resistance” become a little clearer? It is the atoms of the lattice and the electrons rotating around them that resist the directional movement of electrons torn from their orbits by the electric field. But the concept of conductor resistance can be called a general characteristic. Resistivity characterizes each conductor more individually. Including copper. This characteristic is individual for each metal, since it directly depends only on the shape and size of the crystal lattice and, to some extent, on temperature. As the temperature of the conductor increases, the atoms vibrate more intensely at the lattice sites. And electrons rotate around nodes at higher speeds and in orbits of larger radius. And, naturally, free electrons encounter greater resistance when moving. This is the physics of the process.
For the needs of the electrical engineering sector, widespread production of metals such as aluminum and copper, the resistivity of which is quite low, has been established. Cables and various types of wires are made from these metals, which are widely used in construction, for the production of household appliances, busbars, transformer windings and other electrical products.
One of the most popular metals in industries is copper. It is most widely used in electrical and electronics. Most often it is used in the manufacture of windings for electric motors and transformers. The main reason for using this particular material is that copper has the lowest electrical resistivity of any material currently available. Until a new material with a lower value of this indicator appears, we can say with confidence that there will be no replacement for copper.
Useful tips
The wire connection must comply with safety regulations
The cable layout in the apartment consists of an upper and lower level. The lower one has sockets designed to power consumers, the power of which can reach 2 kW: washing machines, boilers, microwave ovens. In order not to expose the lines to the risk of overheating and burning, it is advisable to install a copper cable with the maximum cross-section of conductors allowed for household outlets.
The upper level is used to power doorbells, ceiling and wall lamps. These products consume a minimal amount of electricity, especially if they are equipped with modern LED lamps. You can run a thin and inexpensive aluminum cable on top, the power reserve of which is sufficient with a large reserve. With this solution, a separate issue arises of a safe way to join two incompatible metals.
Conductive paste
To avoid problems with contacts after installation, you can use one of the following devices:
- Clamp. The product consists of 3 steel plates. The cores are inserted between them, after which the plates are tightened with bolts.
- Bolt with 2 iron washers. The ends of the cores are twisted into rings and placed on the axle, and washers are installed between different materials. Tightening the nut ensures reliable contact.
- Spring switch. Its terminals are treated with a special anti-corrosion lubricant. The cores are inserted into the grooves and secured with spring levers.
- Pads. They are a steel strip with contacts pressed into a plastic case. The ends of the cable are inserted into the holes where they are tightened with bolts. The products can be used to connect 2-10 pairs of wires.
Copper. Its characteristics and properties
Description of substance and properties
Physical properties of copper:
- melting point - 1084 degrees Celsius;
- boiling point - 2560 degrees Celsius;
- density at 20 degrees - 8890 kilograms divided by cubic meter;
- specific heat capacity at constant pressure and temperature 20 degrees - 385 kJ/J*kg
- electrical resistivity - 0.01724;
Copper grades
This metal can be divided into several groups or grades, each of which has its own properties and its own application in industry:
- Grades M00, M0, M1 are excellent for the production of cables and conductors; when remelting, oversaturation with oxygen is eliminated.
- Grades M2 and M3 are low-cost options that are designed for small-scale rolling and satisfy most small-scale technical and industrial tasks.
- Brands M1, M1f, M1r, M2r, M3r are expensive copper grades that are manufactured for a specific consumer with specific requirements and requests.
The brands differ from each other in several ways:
- type of delivery;
- oxygen saturation;
- difference in resistance indicator;
- presence of impurities;
- degree of thermal conductivity;
The influence of impurities on the properties of copper
Impurities can affect the mechanical, technical and performance properties of products.
- Mechanical properties. Substances such as iron, bismuth, lead or oxygen affect the ductility of copper. Some poorly soluble impurities affect the preservation of the structure of a substance with increasing temperature. For example, lead or bismuth makes copper very brittle, but the addition of even a small amount of silver (five hundredths of a percent) significantly increases the fusibility of copper, that is, even at high temperatures its crystal lattice remains unchanged, and there is no loss of thermal or electrical conductivity.
- Technical properties. These include pressure treatment at different temperatures and fusibility (welding) of the substance. In the presence of poorly soluble impurities in copper, zones of special brittleness appear at high temperatures, this makes pressure treatment very difficult, however, in grades M1 and M2, the required ductility is achieved due to the low content of impurities. If we talk about pressure at low temperatures, then this technology is used in the production of wire rod (wire) and the ability to draw is also different for different brands.
- Operational properties. Under standard operating conditions, different brands behave quite similarly, but due to the hydrogen and oxygen content of different brands, the conditions apply as the temperature increases. In particular, oxygen begins to negatively affect copper when the ambient temperature rises, and hydrogen when the substance itself is heated to two hundred degrees.
In conclusion, it should be emphasized that copper is a unique metal with unique properties. It is used in the automotive industry, the manufacture of elements for the electrical industry, electrical appliances, consumer goods, watches, computers and much more. With its low resistivity, this metal is an excellent material for making conductors and other electrical devices. In this property, copper is surpassed only by silver, but due to its higher cost, it has not found the same application in the electrical industry.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=SlxOEEaQ4Cg
Advantages
From the very beginning, it should be noted that aluminum wiring is not the most reliable and high-quality and cannot boast of any outstanding merits compared to other types. But, nevertheless, it is precisely this type of electrical wiring that is installed in most old houses and apartments (Khrushchev). So, let’s start with the advantages of this type:
- lightness (aluminum has less weight compared to other metals that are used in electricity as conductors);
- resistance to corrosion (metal when exposed to air instantly oxidizes, forming a film that protects the rest of the wire from further corrosion).
According to chapter 7.1. PUE, clause 7.1.34. Electrical wiring must be carried out using cables with copper conductors. Aluminum cables and wires with core cross-section from 2.5 sq. mm can be used when connecting individual electrical appliances that belong to engineering electrical equipment or when connecting powerful electrical equipment with an aluminum cable with a core cross-section of 16 sq. mm.
In accordance with the above, today aluminum in electrical wiring is used most often in power cables of large cross-section (tens and hundreds of sq. mm.), where the weight and cost of the material are very important factors. The savings in this case can be very significant - aluminum is a cheap metal, and the amount of material used will still allow you to spend less compared to other types of wires. A true example of this is the enormous popularity of SIP wires, the cores of which are made of aluminum. For aerial cable laying, this conductor is one of the most suitable. Moreover, according to the PUE chapter 2.1. clause 2.1.14 and chapter 7.1. clause 7.1.131, the cross-section of the aluminum cable for branching through the air must be at least 16 square meters. mm.
However, aluminum wiring has not been used in new buildings for a long time, and there are reasons for this.
How to distinguish copper from aluminum
Naturally, metals are easy to distinguish by color. The situation becomes more complicated when it is necessary to determine what the cable cores are made of. Tinned copper takes on a silvery tint, while copper-plated aluminum takes on a yellow tint. The result is that it is extremely difficult to distinguish metals from each other by color.
Tinned copper in cables
The best option is to measure the resistance. For a copper twisted pair cable about 100 meters long, the parameter value reaches 4–8 ohms. The resistance of a similar aluminum cable is significantly higher: 12 – 20 Ohms. This method is good because there is no mechanical impact on the metal.
The second method is bending/extension of the vein. The aluminum conductor will break quickly. The next option is a flame test. The melting point of aluminum is 600 °C, that of copper is much higher.
Connecting aluminum and copper wires: what are the risks?
Sometimes it happens that when laying aluminum wires it is not possible to avoid connecting with copper wires. But, as you know, direct contact connection of copper and aluminum in electrical wiring is not recommended and even dangerous. What to do?
It is impossible to twist wires made of two different metals together, because aluminum and copper differ in their properties, chemical structure, and current conductivity, and the resistivity of an aluminum wire differs from that of a copper wire.
This also applies to the protective film that forms after oxidation: on copper products it conducts electric current, but on aluminum the film has such a strong resistance that it practically does not allow current to pass through and, accordingly, is practically resistant to heating. And after heating and cooling occurs several times in a row at the junction of copper and aluminum wires, they are greatly weakened, which can lead to overheating, sparking and even fire.
Also, in places where copper and aluminum wiring are connected, a galvanic couple can occur. It causes dissociation of the oxides of electrical conductors, contributes to the destruction of the metal structure and the formation of voids and cavities in it, which in turn contribute to a reduction in their cross-section and a deterioration in their ability to pass electric current.
In a word, the connection of aluminum conductors with copper leads to electrocorrosion of the metal and its destruction.
But if you need to connect different wires, then in this case you should not use soldering of aluminum and copper wires, but bolted connections and terminals. Thanks to this, higher security can be achieved than using the conventional twisting method.
Comparison of conductivity of different types of steel
The characteristics of steel depend on its composition and temperature:
- For carbon alloys, the resistance is quite low: it is 0.13-0.2 μOhm/m. The higher the temperature, the greater the value;
- Low-alloy alloys have a higher resistance - 0.2-0.43 μOhm/m;
- High-alloy steels have high resistance - 0.3-0.86 μOhm/m;
- Due to the high chromium content, the resistance of chromium stainless alloys is 0.5-0.6 μOhm/m;
- Chromium-nickel austenitic steels are stainless and, thanks to nickel, have a high resistance of 0.7-0.9 μOhm/m.
Galvanized braiding is often made from steel.
Copper is in second place in terms of electrical conductivity: it perfectly passes electric current and is widely used in the manufacture of wires. Aluminum is also used no less often: it is weaker than copper, but cheaper and lighter.
Terminal block
A cheap and simple solution to the question of how to connect aluminum wires to copper wires is the use of terminal blocks. Buying them now is not a problem at all; moreover, you can buy not a whole section, but ask the seller to cut off the required number of cells. Terminal blocks are sold in different sizes, depending on the cross-section of the conductors connected to them.
What is such a block? This is a transparent polyethylene frame designed for several cells at once. Inside each cell there is a brass tubular sleeve. From opposite sides, the ends of the wires to be connected must be inserted into this sleeve and clamped with two screws.
The use of terminal blocks is very convenient because you can always cut off exactly as many cells from it as there are pairs of wires that need to be connected, for example, in one junction box.
Using the terminal blocks is very simple:
- Unscrew one clamping screw, thereby freeing one side of the sleeve for the conductor to pass into it.
- On the cores of the aluminum wire, strip the insulation to a length of 5 mm. Insert it into the terminal, tighten the screw, thereby pressing the conductor to the sleeve. The screw should be tightened firmly, but do not force it too hard, so as not to break the core.
- Do the same operations with the copper wire, inserting it into the sleeve from the opposite side.
Why do you have to do everything one by one? You can immediately unscrew two screws, insert the wires and tighten them. This is done to ensure that the copper and aluminum wires do not touch each other inside the brass sleeve.
As you can see, the advantages of terminal blocks are their ease and speed of use. This connection method is a detachable one; if necessary, you can remove one conductor and replace it with another.
Terminal blocks are not entirely suitable for connecting stranded conductors. In order to do this, you must first use ferrules that will crimp the bundle of cores.
There is one more feature in the use of terminal blocks. Under screw pressure at room temperature, aluminum can flow. Therefore, periodic inspection of the terminal and tightening of the contact connection where the aluminum wire is fixed will be required. If this is neglected, the aluminum conductor in the terminal block will become loose, the contact will weaken, begin to heat up and spark, which may result in a fire.
How to connect wires using a terminal block is shown in this video:
How to distinguish copper from other metals by eye?
Visual perception is the simplest, but not always quite accurate method. However, in most cases it works and it is not difficult to distinguish copper scrap from other non-ferrous metal scrap. Indeed, despite the name of the category non-ferrous metals, only the following are equally colored:
The remaining metals are characterized by a gray tonality and differ mainly in the intensity of their shine. Therefore, color is an excellent “means of identification” in such matters as distinguishing copper from aluminum, zinc or nickel.
Pure copper with a characteristic copper color
The natural color of the pure element Cu is red-pink. It is recommended to look at metal in natural light. Artificial lighting, with the exception of LED lamps with warm color temperatures, changes the hue towards a yellow-green tone.
The second rule for visual identification of copper is that the surface oxide film must be removed. Oxidation creates a greenish-blue coating on the metal surface. Therefore, to determine by color that you have copper, preferably by fresh sawing or by processing the material with a file. The situation with copper alloys: brass and bronze is much more complicated. It is also visually difficult to distinguish between Cu and copper-plated aluminum.
Which wiring material is better?
Types of copper wire connections
With all the advantages of aluminum, one should not forget about its disadvantages. The main one, apart from mechanical characteristics, is low conductivity. It is impossible to endlessly increase the diameter of the cable, since household appliances and channels laid in the walls are not designed for this. We should not forget about such a factor as the fragility of the metal. After several years of use, it may burst when replacing an outlet or meter. It is not advisable to twist it in the socket box, as it will not last long. Choosing aluminum will provide good savings on the purchase of materials, but subsequent repair costs may negate this.
Copper also has its disadvantages, but they are offset by a large number of advantages. Even the process of pulling the cable through the channel is easier, since it bends well without any tendency to break or break. It is worth remembering about low resistance. By installing a line with 2.5 mm² conductors, you can use as powerful consumers in your home as the common house line allows.
To summarize, we can recommend that craftsmen make their choice in favor of copper products. If the budget is limited, you can combine materials using modern switching means.
Application of electrical conductivity of materials
The presence of the noted properties is used not only in engineering energy networks. Good electrical conductivity allows information signals to be transmitted over long distances without distortion. Maintaining a high amplitude reduces the requirements for amplification paths and reduces the overall cost of systems. Minimizing losses is useful in electrolysis installations, when creating contact groups and motor windings.
Important! In all of the above examples, in addition to a general increase in efficiency, you can count on preventing overheating.
Features of connecting wires on the street
When installing a cable line along the street, all connection elements are exposed to external negative factors, such as snow, icing, rain, etc. Therefore, to perform such work, only a hermetically sealed structure that is resistant to ultraviolet rays and low temperatures is required. When making connections on a pole, roof or other open place, piercing clamps are most often used. You may be interested in learning in more detail how to connect SIP with copper cable on the street, because... in this case, the connection of aluminum and copper occurs in the open air.
In rooms, when laying a cable in a wall under plaster, the cable is laid in one piece in the groove, and any connection of even homogeneous metals is undesirable. All connections in a socket or junction box are made in any of the ways described above, suitable for each individual situation.
What is the resistance of copper and aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal that can be easily machined and cast. It has high electrical conductivity: it ranks 4th after silver, copper and gold.
Important! Despite a number of advantages (low cost, light weight, ease of processing, and others), in the long term, aluminum wires are less profitable than copper wires.
In electrical engineering, 2 terms have meaning:
- Conductivity: Responsible for the transfer of current from one point to another. The higher the conductivity of a metal, the better it transmits electricity. At +20 degrees, the conductivity of copper is 59.5 million siemens per meter (S/m), aluminum - 38 million S/m. The conductivity of a copper cable is practically independent of temperature.
- Electrical resistance: the higher this concept, the worse the substance will pass current. The resistivity of copper is 0.01724-0.0180 μOhm/m, aluminum - 0.0262-0.0295.
You might be interested in this Description of the junction box
Aluminum cables are in demand no less than copper ones
In other words, copper has higher conductivity and lower resistance than aluminum.
Flaws
There are quite a few disadvantages to this type of wire:
- Metal fluidity. Aluminum tends to stretch, this has a negative consequence in the case of screw connections of wires. Wire connections weaken over time, begin to heat up, oxidize and burn, until contact is completely lost.
- Aluminum fragility. During the process of aging and long service life, the wires will simply break, especially with frequent loads and overheating. This also needs to be taken into account when you re-terminate old strands - when unwinding and re-twisting them, there is a high risk that the core will break.
All of these shortcomings, to one degree or another, ultimately lead to the fragility of the entire power supply system and a short service life. When asked how long aluminum electrical wiring lasts, you will receive a comprehensive answer - as long as its insulation lasts. Depending on the conditions and installation method, the service life is 5-25 years.
Other cases of fire and acid testing
Exposure to flame is used not only to identify metal relative to aluminum. For these purposes, a gas stove, lighter or fire is sufficient. Heating copper leads to the formation of its oxide, which affects the color change. The surface of the metal gradually becomes dull until it acquires a completely dark shade.
Nitric acid is another identifier for copper at home. It is also important to be careful here. It's better to just drip the liquid onto the metal. Pure copper at the point of contact will turn blue-green.
Video - how to distinguish aluminum from copper:
Which wiring material is best?
Now let's look in more detail which wire is better, copper or aluminum. In this regard, many stereotypes and misconceptions have appeared, which we will discuss below:
Durability. It is believed that the lifespan of copper wire is longer than aluminum. This is a misconception. If you look at a special reference book, you can make sure that the service life of cables made of both types of metal is identical. For products with single insulation it is 15 years, and for products with double insulation - 30. Tendency to oxidation. When using an aluminum cable, it is worth remembering its tendency to oxidative processes. Back in school, we were told that Al (aluminum) is a metal that actively interacts with oxygen, which is why a thin film appears on its surface. The latter protects the metal from further decay, but impairs its conductivity. If the wire is isolated from the environment, the risk of oxidation processes is minimized. The best option is to use special terminal blocks with conductive paste. The peculiarity of the latter is to improve the quality of the contact connection between two wires and remove the oxide film from the metal. In addition, a special lubricant prevents aluminum from coming into contact with the surrounding air. Strength. Copper wiring is considered more durable and can withstand repeated bending. GOST states that a wire made of copper must withstand 80 kinks, and one made of aluminum - 12. If the wiring runs in the wall, floor, or is hidden under the ceiling, this feature is not so important. Price. The price of aluminum wire is 3-4 times lower
But when choosing, it is important to remember that a copper wire with a cross-section of 2.5 sq. mm is designed for a current of 27 Amperes. If you give preference to aluminum wiring, the wire thickness should be 4 kW
mm (rated current 28 Amps). Resistance. When deciding whether to choose aluminum or copper wires, it is worth considering different resistivities. For copper, this parameter is about 0.018 Ohm*sq.mm/m, and for aluminum - 0.028. But it is worth considering that the total resistance (R) of the conductor depends not only on the mentioned parameter, but also on the length and area of the conductor. If we take into account that aluminum wires of a larger cross-section are used for the same load, the final R of copper and aluminum products will be approximately identical. The greatest resistance occurs at the joints, but if you follow the tips discussed above, you don’t have to worry about this. Ease of installation. It is believed that connecting aluminum wires is a more difficult task. This is only relevant for the usual connection of wiring, by twisting. In the case of using end caps, terminal blocks or bolts, this problem disappears.
A situation involving contact between two different metals deserves special attention. When copper and aluminum combine at the point of contact, various processes occur, due to which the resistance increases. As a result, the junction of the two wires overheats, the insulation is destroyed and the risk of fire increases.
The feature discussed above is characteristic of all metals having different resistivities. In addition, many manufacturers do not use “pure” metals, but their alloys, which also leads to a change in the resistance parameter. To avoid problems in the future, it is better to connect the wires correctly and avoid twisting them.
Differences between copper and aluminum
The question of how to distinguish copper from aluminum often becomes relevant.
In terms of electrical conductivity properties, it is 1.5 times higher than that of aluminum. Such items are stronger than aluminum items. If you bend the aluminum wire several times, it will break, but the red wire rod will remain unharmed. You can even distinguish these species by weight. Aluminum products are much lighter. Aluminum has a much lower melting point. If at a temperature of 660 degrees it begins to melt, then this temperature is clearly not enough to melt copper.
The red wire is easy to solder and the contact will be very reliable. But soldering an aluminum wire using the usual method is very problematic.
He is a younger representative in terms of receiving it. It does not occur in nature in its pure form, but when interacting with oxygen in the air, it is capable of forming a stable compound. They began to obtain it only in 1825, while copper was smelted already in ancient times. Since it is much lighter, it is actively used in the production of aircraft. That is why it received the name “winged metal”. By adding copper to aluminum, an alloy called duralumin is obtained, which has higher strength characteristics.
We also recommend reading:
Chemically pure copper has three distinctive characteristics. It is a colourful, ductile and corrosion resistant metal. The latter property is due to the formation of a thin oxide film. This layer makes the copper chemically inert in a non-corrosive environment and also adds a red tint to its golden pink color.
The best way to accurately identify copper is spectral analysis, which requires expensive equipment - a metal analyzer, while identifying copper at home is a task with a limited set of tools. Here the best instruments are the senses, easily accessible chemicals, fire and improvised devices.
Is it possible to replace old aluminum wires in an apartment?
Old cables include an aluminum core that is not suitable for modern power
The steel-aluminum wire must be replaced. One of the most significant reasons is the maximum load that it can withstand. Even fully functional and efficient wiring installed several decades ago will not be able to withstand the loads of modern times. This is due to the large number of household appliances installed at home. And additionally equipping electrical wiring with a large cross-section is strictly prohibited, as this can cause overheating and result in a fire.
It is recommended to give preference to copper cables because they are more fire-resistant and reliable and can withstand heavy loads.
Despite the requirements of the PUE for the operation of copper wiring in apartment buildings and private buildings, on October 16, 2017, Order No. 968 of the Ministry of Energy was issued to allow the use of aluminum wires again. However, we are not talking about the material that was used in the 60s of the last century, but about more advanced cables that consist of conductors of an aluminum-iron alloy.
Comments:
Stanislav
Unfortunately, even now developers do not hesitate to use aluminum cables. I saw in one new building an incoming aluminum cable from the meter to the consumer. At the same time, the construction company showed documents that, according to the rules, this is allowed...
Yurievich
Stanislav, the fact of the matter is that, according to pre-revolutionary rules, in some cases this is actually allowed, but people who invest money in these apartments even before construction expect that at least in this they will not be deceived, but aluminum is input is a very common practice.
Michael
And for me, one master connected aluminum with copper in a junction box with twists. The apartment almost burned down. And most importantly, at first everything works as it should, and only six months later it begins to spark, hiss and melt...
Oleg
In low-voltage and low-current networks, wiring made of copper, oxygen-free copper, silver or gold makes sense. And your networks have 220 V. Don’t fool around and don’t litter our people’s heads with garbage. They are already very weak. 16 sq. section - you have to be a complete fool to invent this nonsense. In power shields, the risers are laid thinner. Factories have produced and will continue to produce aluminum wires, regardless of your stupid articles.
Anton
Regarding the fragility of aluminum wire: I hung a chandelier in an old house built by captured Germans in the first years after the war - the soft aluminum wires bent so easily that it seemed as if under their own weight. This is the aluminum wire of the post-war years. And now in wires and cables it’s not aluminum, but duralumin; if you bend it, it even cracks, sometimes cracking at the bend.
irakli
moemu domu 46 let i aluminumevaia provodka rabotaet dosixpor bez problem 2.5mm a ne 16
Sergey
And my apartment burned down from overheated oxidized aluminum contacts. House 74 years old, Moscow. Luckily no one was hurt. Now only copper and arc-flash circuit breakers.
Sergey
Poor boy! Did he read this nonsense or memorize it?
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Similar posts
Features and some secrets of installing open wiring in a wooden house with your own hands Correctly replacing wiring in an apartment of a panel house - what you need to know and be able to Correctly connect phase-zero-ground wires. Do-it-yourself wiring in a country house - features of organization and installation sequence
What is the resistivity of steel
Steel is a metal alloy of iron with carbon and other elements. It contains at least 45% iron, the carbon content ranges from 0.02% to 2.14%. Depending on the exact composition, steel is used in construction, mechanical engineering and instrument making, as well as in many areas, for example, in transport, the national economy, and in the production of household appliances.
The conductivity of steel is only 7.7 million S/m, the resistivity is 0.13 μOhm/m, that is, it is quite high. Steel conducts electricity poorly and is not used in the production of cables. However, you can often find an outer galvanized steel braid that protects the wires from mechanical stretching. Such protection is needed if the cable runs under a road or on unstable ground, if there is a risk of sharply pulling the wire.
PNSV is also made from steel - a heating wire with a steel core and vinyl insulation. It is placed inside the structure before concrete is poured and is subsequently used for electrical heating of the finished block. The cable practically does not conduct electricity.