What is an AC voltage stabilizer?
An AC voltage stabilizer is a transforming device, the main purpose of which is to protect electrical appliances (for example, a refrigerator, TV, washing machine, split system) from the effects of fluctuations and voltage surges in the supply network, which can lead to their breakdown and failure.
The first stabilizers appeared in the middle of the last century. These were electromagnetic-type devices, the operation of which is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction - the occurrence of electric current in a closed circuit of an autotransformer. They were not distinguished by high values of such performance indicators as accuracy of voltage stabilization, speed of response to changes in the network, efficiency, and overload capacity. In addition, even low-power devices of those times were bulky and heavy.
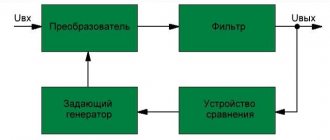
Many modern automatic voltage regulators (AVR - Automatic Voltage Regulator) still use an autotransformer as a conversion device. The most advanced inverter devices of the new generation use the technology of double, transformerless electricity conversion.
Depending on the type of supply voltage for which the stabilizers are designed, there are single-phase, three-phase and devices with a 3:1 configuration (“three into one”). The former are used only to stabilize the power supply of single-phase electrical appliances. Three-phase stabilizers are designed to operate in three-phase networks to power equipment designed for 380 V, but with phase-by-phase load distribution they can also be used to power single-phase electrical appliances.
A distinctive feature of 3:1 configuration devices is the ability to operate in circuits with different types of voltage: the input voltage is three-phase, and the stabilizer output is single-phase. Their use is preferable for connecting high-power single-phase loads - this will ensure uniform distribution of consumption currents across all three phases, eliminating the possibility of phase imbalance.
According to the principle of protection, AC voltage stabilizers can be of a local type (for individual connection of individual electrical appliances) and a main type, designed to connect the entire existing load in the room. The first are, as a rule, low-power devices for installation at the location of the electrical appliance, the connection to the input network and the load of which is made using plug connections (plug-socket). In more powerful main line stabilizers (usually these are devices with a power of over 4000 VA), a terminal block is provided for connection.
What types of voltage stabilizers are suitable for a private home?
Currently, most household stabilizers on the market can be divided into four categories depending on the principle of their operation:
- electromechanical;
- relay;
- semiconductor (triac and thyristor);
- inverter
| Stabilizer type | Description of the operating principle |
| Electromechanical | Devices of this type have a special moving contact. If the input voltage does not correspond to the norm, then it moves along the winding of the autotransformer and changes the number of turns included in the operation to a number that provides a transformation ratio at which the input deviation will be neutralized. |
| Relay and semiconductor | These types of devices are sometimes called step or discrete stabilizers. During their operation, the voltage is not regulated smoothly, but abruptly - with a sharp transition from the rejected value to the nominal value. In these stabilizers, as in electromechanical ones, the autotransformer plays an important role - in case of poor-quality input voltage, its windings are switched so that their output voltage has characteristics as close as possible to the nominal ones. |
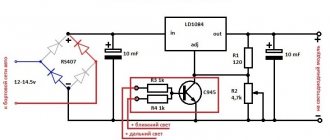
| Inverter | Devices of the fourth category are built on the basis of advanced technology of double-transformerless energy conversion. Such devices change the type of voltage coming from the network twice: first, they convert an alternating input into an intermediate constant, then from an intermediate constant they generate an output alternating, free from network distortions and oscillations. |
As for devices from the above categories, electromechanical and relay models have serious disadvantages: low response speed (for the former) and low stabilization accuracy (for the latter). In conditions of frequent and strong network fluctuations, both will not provide an acceptable level of protection. Therefore, there is a high probability that electromechanical and relay devices will simply be useless in case of power supply problems typical for the private sector.
In semiconductor models, the disadvantages inherent in electromechanical and relay devices are minimized, and in inverter models they are completely eliminated. Products of these two categories should be considered as the primary means for improving the quality of electrical energy in a private home.
Purpose and functions of mains voltage stabilizers
Any electrical device, household appliance or industrial equipment, is designed to be connected to an alternating current network with a standard (nominal) voltage value. The efficiency and safety of operation of the device is guaranteed by the manufacturer, provided that it operates within the declared operating voltage range.
Many readers have probably had to deal with low quality power supplies: increased or decreased voltage of the supply network, its instability, as well as a distorted signal shape and the presence of pulse (switching) and high-frequency interference. This is due to the inadequate technical condition of the networks, their wear and tear, or the discrepancy between the power of today’s outdated equipment of power supply systems and the actual volumes of electricity consumption. Unfortunately, voltage deviations from the norm and instability of its value are not uncommon phenomena not only in rural or country houses, but also in urban electrical networks.
The operation of household electrical appliances or industrial electrical equipment in networks with low quality electricity can lead not only to their breakdowns followed by expensive repairs, but also to complete failure.
An effective solution for organizing high-quality power supply to loads in everyday life and at work is the use of voltage stabilizers. The main purpose of these devices is to correct and constantly maintain the required output voltage level both when its value changes in the supply network and when the load current changes.
Many modern AC voltage stabilizers also have a number of additional functions:
- correction of the output voltage signal shape;
- protection against overheating and short circuits in the load power circuit;
- protective shutdown of the device in case of unacceptable input voltage values (the required threshold for the upper and lower limits can be set by the user independently);
- suppression of RF and impulse noise by the output filter;
- the ability to set the required output voltage values different from the standard ones;
- the ability to implement parameter monitoring and remote control of the stabilizer.
It should also be noted that correction and stabilization of the power supply may be required not only in cases of serious voltage deviations from the norm or in case of unacceptable fluctuations in its values. In accordance with GOST 13109-97, currently in force in the Russian Federation, which determines the quality of electricity, the permissible deviations of the normal voltage in the network are ±10% of the nominal value. Thus, phase voltage in the range of 198–242 V, according to this standard, is considered normal.
Indeed, such a voltage will ensure the normal operation of most electrical appliances. However, to power voltage-sensitive equipment, it is recommended to use stabilizers to avoid failures and errors in operation. For example, to power modern electronically controlled gas boilers, installing a mains voltage stabilizer will definitely not be superfluous. The same can be said for power-sensitive electrical appliances manufactured in countries with more stringent power quality standards.
Main types of AC voltage stabilizers
Depending on the principle of operation, there are the following types of stabilizers:
- ferroresonant;
- electromechanical (servo-drive);
- relay;
- electronic (semiconductor);
- inverter
Their main differences are briefly discussed below. For more detailed information, we recommend that you read the article on the types of voltage stabilizers.
Ferroresonant
The voltage conversion is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic ferroresonance - magnetic saturation of the ferromagnetic cores of the chokes. Due to the static nature and simplicity of their design, these devices are characterized by high levels of failure-free operation and long service life.
Their small distribution in use in our time is due to such disadvantages as low efficiency, modification of the output sinusoid, noise during operation, and a rather narrow range of operating network voltages.
Electromechanical
An alternative name is servo-drive, since their device contains a servo drive that ensures the movement of current-collecting brushes that remove secondary voltage from the turns of the autotransformer winding. The presence of rotating and moving parts in stabilizers represents a certain vulnerability of their design: operation is associated with frequent wear of parts, consumables and the need for regular maintenance.
Having good technical characteristics and being in the lower price category, the devices are in demand as a budget solution to the problems of protecting equipment that does not require power.
Relay
Based on the principle of voltage conversion, they can be classified as analogues of servo drive devices. The difference between them lies in the method of transmitting secondary voltage from the autotransformer. Switching is carried out not by current-collecting brushes from the turns of the transformer, but by power relays installed on the taps of its winding.
Like electromechanical devices, relay devices belong to the budget category of stabilizers. While they are superior in speed and have greater wear resistance, they are inferior to servo drives in accuracy and smoothness of voltage correction.
Electronic
They differ from relay ones in the complete absence of mechanical parts. Switching of the output voltage is carried out by semiconductor power switches - thyristors or triacs. The main advantage of these more advanced devices is their high performance. Unfortunately, stepwise correction significantly reduces the accuracy of voltage stabilization.
Types of stabilizers
All stabilizers are based on the use of transformer coils.
Stabilizers operate based on various physical principles.
Depending on the principle of operation, stabilizers are divided into several types:
- Ferroresonant . They use the phenomenon of ferroresonance that occurs in electrical circuits. If it occurs spontaneously, it can damage equipment. However, if ferroresonance is deliberately provoked and controlled by additional equipment components, it can be used to stabilize the voltage.
- Ferromagnetic . The transformation of electric current in this type of device occurs under the influence of an electromagnetic field arising in coils with ferrite cores.
- Voltage booster . A small-sized stabilizer, the operation of which is based on the properties of an induction coil. Suitable for minor voltage changes, but not suitable for powering several electrical appliances at the same time.
Depending on the type of control unit, stabilizers come in three types.
- Relay . Voltage is supplied to the transformer winding using a relay included in the design.
- Electronic . The current supply in this case is controlled by a “smart” electronic unit.
- Electromechanical . The current supply is regulated by a movable brush contact moving along the transformer winding.
Depending on the area of application, stabilizers are divided into:
- Industrial - capable of powering a large number of electrical appliances at once, and can withstand serious power surges in the network.
- Household - more suitable for home use and significantly inferior in capabilities to industrial ones.
Expert opinion
Torsunov Pavel Maksimovich
You can also purchase an industrial stabilizer for your home. This is relevant if you need to power several electrically demanding devices at once (for example, two or more split systems, refrigeration equipment). The power of an industrial device is quite enough for this. But you will need two or even three household devices, which will ultimately cost more.