In industrial and domestic conditions, there is a need to control the level of liquid in containers. For this purpose, special measuring devices are used - liquid level sensors. They can be contact or non-contact. Both options are located at a given height of the container and, if the water rises above the set point, the sensor is triggered, signaling this to the user. There are several types of devices that differ in functionality and operating principle. The article will discuss the types of sensors that monitor water levels. The topic of how to make a liquid level sensor with your own hands will also be discussed.
Classification
All manufactured sensors are divided into two classes: level meters and alarms.
The task of the former is to constantly measure the liquid level in the present time. Their design includes sensors that receive the signal. The data is processed by analog or digital electronic circuitry included in the sensor. The indicators are displayed on the display elements.
Alarms have a different task - they signal when the water level in the tank has reached a predetermined value. Such liquid level sensors, when triggered, transmit data about the cessation of water supply. The output signal in them is discrete. Alarm - sound or light.
How is the level measured?
There are several measurement methods. It all depends on what properties the liquid in the tank has:
- Contact. In this case, the level sensor directly interacts with the water in the container.
- Contactless. No direct contact with liquid. Devices of this type are used to measure the level of a viscous medium or one with aggressive properties.
Contact meters are installed in the container itself: on the surface (float), in depth (hydrostatic sample pressure gauges) or mounted on the wall (plate). Non-contact sensors for measuring liquid level should not come into contact with water, so they are placed in such a way that it is possible to “observe” the surface of the medium.
Float meters
The most common, reliable and affordable measuring instruments are made in the form of a float (better known as remote control). Depending on the design, they can be vertical or horizontal.
A vertical float sensor for measuring water level is so called because its stem is located vertically. Its body contains a round magnet. The rod is a hollow plastic tube with reed switches inside.
Float devices are placed on the surface of the measured water. When the magnetic field approaches the reed switch, the sensor contacts are activated - this is a signal that the container has been filled to the indicated volume. Contact pairs can be connected in series with each other using resistors. This will make it possible to monitor the liquid level based on the total resistance of the circuit. The standard signal parameter in this case is 4–20 mA. Typically, float-type water level sensors are used in tanks up to 3 m long.
Even if the meters are visually similar, they may have different electrical circuits with reed switches installed. Sensors are placed at different levels of the container to receive a signal as it is filled. There are linear devices that transmit a signal continuously.
It is not always possible to implement surface installation. In such situations, float sensors are used to measure the liquid level, but in a horizontal position, which are mounted on the wall. The magnet and float are located on a lever with a hinge, and the reed switch is “hidden” in the housing. When the liquid level rises, a magnet begins to act, approaching the contacts, which causes the sensor to operate.
If the liquid is contaminated or subject to freezing, use “reinforced” float meters on a flexible cable. Design: a sealed container located at depth, containing a toggle switch or a metal ball with a reed switch. When the liquid level coincides with the position of the sensor, the container turns over and at the same time the contact is activated.
The most accurate and reliable float devices are magnetostrictive. They are equipped with a float and a magnet that slide along a metal rod. The working principle boils down to changing the duration of passage of the ultrasonic pulse through the rod. Since there are no electrical contacts in the design, the ultrasonic level sensor operates more clearly.
Capacitive
The capacitive liquid level sensor has the form of plates located on both sides of the tank. Alarms of this type can determine the maximum fill level. The technological medium is water or loose, mixed substances.
A capacitance meter works in a similar way to a capacitor: the capacitance is measured between the plates. When the water in the tank reaches the threshold level, a signal is sent to the controller. A “dry contact” can also be used - the sensor is triggered through the wall of the container, being isolated from the working environment.
Capacitive level gauges operate in different temperature ranges, operate even over long distances and are not affected by electromagnetic fields. Thanks to these characteristics, the scope of application is expanding. That is, the sensor can be used even in difficult conditions.
Electrode
These meters are used to monitor the level of electrically conductive liquids. Working principle: using an alternating voltage, one monitors how the resistance of water changes between immersed single-pole electrodes.
Sensor design: one small and two long electrodes fixed in a terminal box. The smaller one is the contact of the upper water level, the longer ones are the contact of the lower one. The electrode level sensor is connected to the relay and pump circuit by wires.
When water comes into contact with the small electrode, the pump turns off. And it turns on when the level drops to long electrodes.
Depending on the design there are:
- Single-rod. They are used in situations where the tank, container or tank for storing the working medium has conductive walls. The role of the wall is the control electrode. Such devices monitor one level value.
- Multi-rod. They have multiple electrodes in their design, allowing them to track multiple control points.
If the tank walls are not conductive, then a level gauge with an additional control electrode is used. Device contacts located in water may oxidize. To reduce this effect, stainless steel or graphite rods are used.
Hydrostatic
The operating principle of these level meters is to measure pressure or pressure drop in a liquid. There is hydrostatic pressure in the working environment, and it varies depending on the immersion. One membrane of the device is placed on the tank, and the second is placed at the point of excess pressure (closed tank) or at the atmospheric supply (open). The hydrostatic sensor is suitable for monitoring the level of viscous liquids. In this case, the sensitive element of the device comes into contact with the measured medium.
There are two types of design:
- Submersible pressure transducer. It looks like two blocks connected by a compensation cable. The meter is a immersion probe. Such a water level sensor is used in a well, a well, a reservoir and other open sources. Manufacturing materials: body - polymer or steel, membrane - steel or ceramic. The compensation cable contains a support pressure tube made of Teflon, polyurethane or PVC.
- Inserted pressure transducer. Installed on the tank wall in a horizontal position. There are contact and non-contact sensors for measuring liquid level, with an open end membrane.
Submersible devices are based on the measurement of hydrostatic pressure. Using this method, the height of the water column is determined depending on the pressure acting on the walls of the vessel or its bottom.
A hydrostatic level gauge is used if you need to measure a liquid column up to 250 m deep. There are special devices for deep-sea measurements.
Radar
Universal alarm devices that are used to measure the level of any technical media. The liquid can be aggressive and explosive, but neither pressure nor temperature affects the readings.
The principle of operation is not complicated. Narrow-range radio waves (several GHz) are emitted from the sensor, at which time the receiver catches the signal and, based on the delay time, determines how full the tank is. Pressure, temperature and properties of the working environment do not affect the meter. The same goes for dust. Radar sensors are high-precision devices with an error of no more than 1 mm.
Today this is one of the most technologically advanced and advanced measurement methods, as evidenced by its advantages:
- there are no moving elements;
- non-contact measurement method;
- universal (for almost any environment, regardless of conditions);
- high precision.
But such level meters are not cheap.
Ultrasonic
An ultrasonic liquid level sensor operates using a return signal method, like a radar sensor. It is installed in the upper part of the tank, parallel to the surface of the working medium. The device sends and receives pulses, measuring how long it takes for the signal to travel. Further calculation of parameters is based on the data obtained.
Ultrasonic devices are used to monitor water levels in industrial environments where large tanks are installed. With their help, the exact number of sewage and wastewater is determined remotely. When the liquid reaches the maximum level, the device signals a problem via SMS, GSM or GPS.
Designed to work with water and other liquids. They will not be able to measure the level of solids. In order for the device to work more accurately, compensation for external influences (wind, water with a foam layer) is required.
Conductometric
Conductometric sensors are designed to measure the level of an electrically conductive liquid with a conductivity of more than 0.2 S/m. We are talking about drinking and industrial water, weak alkaline solutions, acids, waste water and drinking liquids (kvass, beer).
The principle of their operation: liquid that has reached a certain level leads to a short circuit of the sensor electrode to the container body or the electrode of the meter itself. As a result, an electric current is generated in the sensor circuit. Due to the closure of the circuit, the relay that controls the circuit is activated.
The conductometric level sensor is capable of operating at operating medium temperatures up to +350 degrees Celsius and pressures of no more than 6.3 MPa, it all depends on what material the electrode insulator is made of. These meters are used to monitor one or more levels (single- or multi-electrode). Their principle boils down to the fact that the liquid has a different electrical conductivity than air, which is what the electrodes record.
The simplest type of such a sensor is stainless steel electrodes, one of which is placed in a container in contact with the liquid, while the others are used as signal electrodes.
Optical
These meters rely on visible infrared or laser light to detect liquid levels. The basis of their work is that the substance being measured transmits, reflects and refracts light rays.
There are contact and non-contact devices. Non-contact systems work like this: light is directed onto the surface of the liquid, and the reflected rays are captured by a photocell. If the system consists of several photocells, this makes it possible to detect the working environment at different levels. Optical instruments are popular due to their high accuracy and almost instantaneous response.
They are used to detect high levels of foam or specific materials. They also make it possible to determine whether the observed medium has reached the required viscosity, density, transparency or level of thermal conductivity.
Types of level sensors
Depending on the principle of operation, alarms are usually divided into the following types:
- float type;
- using ultrasonic waves;
- devices with a capacitive level detection principle;
- electrode;
- radar type;
- working on the hydrostatic principle.
Since these types are the most common, let's look at each of them separately.
Float
This is the simplest, but nevertheless effective and reliable way to measure liquid in a tank or other container. An example implementation can be found in Figure 2.
Rice. 2. Float sensor for pump control
The design consists of a float with a magnet and two reed switches installed at control points. Let us briefly describe the principle of operation:
- The container is emptied to a critical minimum (A in Fig. 2), while the float drops to the level where reed switch 2 is located, it turns on the relay that supplies power to the pump pumping water from the well.
- The water reaches the maximum level, the float rises to the location of reed switch 1, it is triggered and the relay is turned off, accordingly, the pump motor stops working.
It’s quite easy to make such a reed switch yourself, and setting it up comes down to setting on-off levels.
Note that if you choose the right material for the float, the water level sensor will work even if there is a layer of foam in the tank.
Read also: How to properly install a pump in a heating system
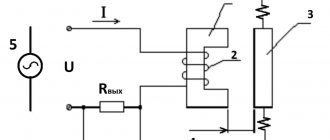
Ultrasonic
This type of meter can be used for both liquid and dry media and may have an analogue or discrete output. That is, the sensor can limit the filling upon reaching a certain point or monitor it continuously. The device includes an ultrasonic emitter, receiver and signal processing controller. The operating principle of the alarm is demonstrated in Figure 3.
Rice. 3. Operating principle of ultrasonic level sensor
The system works as follows:
- an ultrasonic pulse is emitted;
- the reflected signal is received;
- The duration of signal attenuation is analyzed. If the tank is full, it will be short (A Fig. 3), and as it becomes empty it will begin to increase (B Fig. 3).
The ultrasonic alarm is non-contact and wireless, so it can be used even in aggressive and explosive environments. After initial setup, such a sensor does not require any specialized maintenance, and the absence of moving parts significantly extends its service life.
Electrode
Electrode (conductometric) alarms allow you to monitor one or more levels of an electrically conductive medium (that is, they are not suitable for measuring the filling of a tank with distilled water). An example of using the device is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Liquid level measurement with conductometric sensors
In the example given, a three-level alarm is used, in which two electrodes control the filling of the container, and the third is an emergency one to turn on the intensive pumping mode.
Capacitive
Using these alarms, it is possible to determine the maximum filling of the container, and both liquid and bulk solids of mixed composition can act as the process medium (see Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Capacitive level sensor
The operating principle of the alarm is the same as that of a capacitor: the capacitance is measured between the plates of the sensitive element. When it reaches the threshold value, a signal is sent to the controller. In some cases, a “dry contact” design is used, that is, the level gauge operates through the tank wall in isolation from the process medium.
These devices can operate over a wide temperature range, are not affected by electromagnetic fields, and can operate over a long distance. Such characteristics significantly expand the scope of application up to severe operating conditions.
Radar
This type of alarm device can truly be called universal, since it can work with any process environment, including aggressive and explosive ones, and pressure and temperature will not affect the readings. An example of how the device works is shown in the figure below.
Level measurement with radar sensor
The device emits radio waves in a narrow range (several gigahertz), the receiver catches the reflected signal and, based on its delay time, determines how full the container is. The measuring sensor is not affected by pressure, temperature or the nature of the process fluid. Dustiness also does not affect the readings, which cannot be said about laser alarms. It is also necessary to note the high accuracy of devices of this type; their error is no more than one millimeter.
Hydrostatic
These alarms can measure both maximum and current filling of tanks. Their operating principle is demonstrated in Figure 7.
Figure 7. Fill measurement with gyrostatic sensor
The device is built on the principle of measuring the level of pressure produced by a column of liquid. Acceptable accuracy and low cost have made this type quite popular.
Within the scope of the article, we cannot examine all types of alarms, for example, rotary-flag ones, for identifying granular substances (a signal is sent when the fan blade gets stuck in a granular medium, after first tearing out the pit). It also makes no sense to consider the principle of operation of radioisotope meters, much less recommend them for checking the level of drinking water.
How to choose a meter
A variety of sensors are used to monitor the level of water and aqueous solutions, petroleum products and lubricants, food drinks and juices. If the device housing is sufficiently protected or non-contact measurement is used, then levels of alkali, acid, viscous or aggressive media can be monitored. One type of sensor can be used in different conditions.
To measure the level of water and any non-viscous liquids, it is better to use ultrasonic, float, vibration, optical, capacitive and hydrostatic alarms and level gauges. Capacitive, vibration and reed switch devices are suitable for acid solutions. Foamy and sticky media can be conveniently monitored with capacitive RF instruments. If the working environment is highly viscous, use vibration or ultrasonic non-contact varieties.
What and in what order should be taken into account to select a specific device:
- Composition and physico-chemical properties of the working environment.
- Features of the storage tank (volume, shape, what the walls are made of). There are sensors that require insertion into walls, but not every container is suitable for such purposes.
- Constant monitoring is required or an alarm will suffice when a predetermined level is reached.
- Will the device be integrated into the overall control system?
Non-volatile devices, unpretentious, reliable and long-lasting, successfully cope with everyday tasks. If the goal is to monitor the water level of a pump, well, decorative pond or swimming pool, a float sensor is suitable. If it is necessary to constantly measure the water level in the well, hydrostatic type level meters are installed.
Scope of application of water level sensors
- Advanced country houses and farms engaged in growing fruits and vegetables use drip-type irrigation systems in their work. To ensure automatic operation of watering equipment, the design requires a large capacity for collecting and storing water. It is usually filled with submersible water pumps in a well, and it is necessary to monitor the level of water pressure for the pump and its quantity in the collection tank. In this case, it is necessary to control the operation of the pump, that is, turn it on when a certain water level in the storage tank is reached and turn it off when the water tank is completely filled. These functions can be implemented using float sensors.
Rice. 1 Operating principle of a float level sensor (RPL)
- A large storage tank for water may also be required for water supply at home if the flow rate of the water intake tank is very small or the performance of the pump itself cannot ensure water consumption corresponding to the required level. In this case, liquid level control devices for automatic operation of the water supply system are also necessary.
- The liquid level control system can also be used when working with devices that do not have protection against dry running of the well pump, a water pressure sensor or a float switch when pumping groundwater from basements and rooms with a level below the ground surface.
How to make a water level sensor with your own hands
If necessary, you can make a water level sensor yourself. A homemade device is inferior in terms of accuracy to modern manufactured devices, but is much cheaper. Assembly:
- Rectifier diodes are taken, the upper bulb is carefully cut off from them and a tubular connection is obtained.
- Using a 1.5 mm drill, a hole is made in the connection body.
- Take the wire and thread it into a fluoroplastic tube (its thickness should be equal to the diameter of the hole - 1.5 mm).
- One terminal of the cord is soldered, and the second is sealed with glue. A “loop” is formed.
The inner conductor can be increased in size. The finished device is connected to the circuit and connected to the indicator. It can be a dial or a compact monitor.
There is another way to make a water level sensor, for example, to control a pump. Since water accumulates in a well, well or any other reservoir, the pump should be automated - so that it turns off itself after filling. A level meter is assembled from a magnetic starter with a 220 V coil and two reed switches: the minimum one goes to close, the maximum one goes to open. How it works:
- Water is collected, at which time the float with a magnet rises.
- The liquid reaches the reed switch, which is set at the maximum level. Under the influence of a magnetic field, it opens, the starter coil is turned off and, as a result, the pump motor is de-energized.
- This also works in reverse. The tank runs out of water, at this time the float drops and, when it reaches the minimum level, the reed switch contacts close. Voltage is applied to the coil and the pump is turned on.
Such a simple sensor can last for years. The necessary parts can be found in almost any city, not to mention Moscow.
Self-manufacturing of the sensor
Suppose the task is to automate the use of a “Malysh” type pump to provide water to a summer house or country house. As a rule, water is pumped into a storage tank, and it is necessary to ensure timely, automatic shutdown of the pump when the tank is sufficiently filled. There is no need to install complex and expensive sensors for this. You can make a device based on a reed switch that will perfectly perform the task with your own hands. Let's call this device: an electric float valve for the water level in a tank based on a reed switch.
Reed switch
A reed switch is a switch that is the main performing part in the device of a reed switch water level sensor for controlling a pump. It looks like a small sealed glass container with a vacuum or inert gas inside. Inside there is a closed or open contact group, in other words, two closed or open contacts made of ferromagnetic material with a gold or silver top coating. When exposed to a magnetic field, the contacts of the part are magnetized and repel each other, opening the circuit in which they are connected, stopping its operation, or, conversely, they close and turn on the circuit. Reed switches are divided into two types:
- Reed switch with normally closed contacts.
- Reed switch with normally open contacts.
The environment inside the glass bulb prevents oxidation of contacts and the formation of sparks when shorted.
Sensor device based on a reed switch
To manufacture the device, you will need a 220-volt magnetic coil starter and a pair of reed switches, one of which is closed in the normal state, and the second is open. And you will also need a float for the water tank, which is made of foam plastic, a rod, a tube and three wires of small cross-section and thickness.
The operation of the device is simple and, most importantly, safe. The operating principle is as follows:
- In the process of collecting liquid, the float with a magnet, having reached the maximum level of the reed switch, which is in a closed state, opens under the influence of the magnetic field, commutating the power triggering coil, which turns off the pump.
- As the water from the reservoir decreases, the float lowers and when it reaches the lower reed switch, which is triggered by a short circuit under the influence of a magnetic field, the starting coil is switched to start the pump.
- A sensor made according to this principle can operate for many years without complaints, unlike electronic control systems for monitoring the filling of containers. Making a float water level sensor with your own hands is not difficult, and it does not require any special knowledge in the field of electrical engineering.
Scheme for controlling water pumping by a drainage pump
Based on the principle of vertical operation of the float mechanism, it is possible to propose a sensor connection diagram for switching the drain pump start relay with an additional 12 volt power supply.
It is worth noting that reed switches are not capable of handling high currents and cannot turn the pump on or off directly. Therefore, they are used in low voltage circuits to switch high-power relays to start or stop a pump. When the level is high, liquid is pumped out until the minimum set level is reached. The operating principle is as follows:
- When the liquid in the container rises to the upper level, the float with a magnet closes the upper reed switch SV 1, and current begins to flow to the relay coil P1. The contacts close in parallel with the connected reed switch, which puts the relay into a self-capturing state. This function does not allow the coil supply voltage to be switched off when the reed switch SV 1 is opened. This is achieved by connecting the relay load and its coil in one circuit.
- The power coil of relay P2 in the electric pump power circuit is switched on and liquid pumping begins.
- When the liquid level decreases, the float with a magnet reaches the lower reed switch SV 2, closing its contacts. A positive voltage potential begins to be supplied to the relay coil P1 from the other side as well. This leads to the removal of the self-capture function and the relay being turned off, which switches off the power coil P2, which provides power to the electric pump.
- By swapping the reed switches SV 1 and SV 2, the sensor will turn off the pump when the container is filled to the set level and turn it on when the liquid level drops.