Which UPS to choose? We raised this topic in the previous article and looked at the types of uninterruptible power supplies that manufacturers offer. Today we’ll talk about how to choose an uninterruptible power supply depending on your tasks and the type of your equipment, and also calculate the required UPS power.
What kind of uninterruptible power supply you need depends on several main points:
- What kind of network problems do you want to protect your equipment from?
- Design features of the equipment you want to connect to the UPS.
- Planned load power on the UPS.
- Required battery life.
So, in this article we will look at choosing an uninterruptible power supply, taking into account the following questions:
- Why do you need a UPS?
- What equipment are you buying a UPS to protect?
- How to calculate the power of a UPS?
- Power in volt-amperes and watts - what's the difference?
- Calculation of power in volt-amperes.
- Calculation of power in watts.
- We calculate the battery capacity for a known battery life.
- We calculate the battery life, knowing the capacity of the UPS.
Why do you need a UPS?
The answer to the question: which uninterruptible power supply to choose depends primarily on why you need it.
| For what? | What to buy |
| Correctly turn off the computer and have time to save data during a power outage. | In this case, feel free to take an inexpensive off-line or line-interactive UPS with a battery life of 5-15 minutes. |
| Provide power to equipment in the event of a long power outage. | If your equipment is suitable for a non-sinusoidal waveform, buy an off-line or line-interactive UPS, but with increased capacity, with the expectation of long battery life. You can read below how to calculate capacity. The largest reserve of battery life is available for UPSs with external batteries, due to the ability to increase the capacity with additional batteries (connected in parallel). Such uninterruptible power supplies are most often from the expensive category, with double conversion. If you need a really long run time, tens of hours, perhaps purchasing a generator is the best option. |
| Protect equipment from overvoltage or undervoltage, dips, and equipment-dangerous shutdowns for a few seconds (our electricians like to pull the switch back and forth). | For these purposes, you need a UPS with AVR (automatic voltage regulation) function: a line-interactive UPS or a more expensive double conversion UPS. Voltage stabilization in linear-interactive UPS is most often implemented in a stepwise, rough form; in online models the stabilizer operates smoothly. |
| Protect sensitive equipment from as many electrical interruptions and disturbances as possible. | For these purposes, only an on-line uninterruptible power supply is suitable. |
Note that if you only need power stabilization and do not need to ensure autonomous operation of the equipment during a power outage, it is more advisable to buy a separate stabilizer.
Also, quite often they use a combination of a stabilizer + an inexpensive UPS (the uninterruptible power supply is connected to the network AFTER the stabilizer). Such a tandem not only allows you to regulate the voltage if this is not provided in the UPS, but also extends the life of the UPS batteries.
Differences in power plan
The use of uninterruptible power supplies solves several problems - provides the computer with uninterruptible power supply, increases the sinusoidality of current and voltage, cuts off unnecessary harmonics, and filters network noise.
The use of a UPS solves several problems - provides the computer with uninterruptible power supply, increases the sinusoidality of current and voltage, cuts off unnecessary harmonics, filters network noise
This has a positive effect on the durability of the system unit’s capacitors, which extends the time of its trouble-free operation.
Passive filters of modern UPSs include varistors, which filter out surges and switching surges. Often such interference occurs when there are devices in the circuit with large starting currents (+)
For alternating current, there are three types of household UPS:
- Reserve (off-line). The computer is powered directly from the mains. When the voltage goes beyond the permissible range, it switches to batteries within 6-10 ms. Such uninterruptible power supplies are equipped with the simplest passive filters against impulses and interference.
- Interactive or line-interactive. Functions similarly to the backup type. There is a voltage stabilizer at the input.
- Online or double-conversion. The incoming current is converted into direct current and powers the batteries, and from them, through the inverter, the reverse transformation occurs into alternating current, which goes to the output of the device. Therefore, the switching time to battery operation for this type of UPS is zero.
UPS operating on a backup circuit are the cheapest and almost silent. Interactive devices have slightly shorter switching times and are slightly more expensive. Since switching power supplies for computers are not very demanding on the quality of electricity, the use of uninterruptible power supplies of the first two types is acceptable for them.
Online devices are much more expensive. They are used for high-performance stations and file servers with heavy loads. They are characterized by high heat generation and significant noise levels.
Powerful uninterruptible power supplies make a lot of noise, so they are often placed in closets or utility rooms - closets and non-residential rooms
The efficiency of backup and interactive devices is very high (95-99%). For UPS operating using a double conversion scheme, this parameter is much lower (80-96%), but there are also expensive models with the ability to use intelligent modes, in which the efficiency increases to 98-99%.
What equipment are you buying a UPS to protect?
Which UPS to choose also depends on the design features of the connected equipment.
The general rule is this: you can connect almost any equipment to a UPS with the correct sine wave at the output; you just need to correctly calculate the power. Not all equipment can be connected to other UPS, especially the offline type.
| Peculiarity | Optimal UPS type | Explanation |
| Elements sensitive to non-sinusoidal waveforms. | Linear interactive with regular sine wave, Double conversion UPS (online). | The most common case is devices with an electric motor, pump, compressor, including gas boiler pumps, as well as almost all household appliances: refrigerators, hair dryers, washing machines, electric drills, etc. A stepped sinusoid or, especially, a meander has a negative effect on an electric motor: eddy currents arise, inductive reactance drops, As a result, the engine overheats to the point of combustion. Read more about the correct sine wave here. Some devices, such as laser printers and photocopiers, may also contain components that require a sinusoidal voltage to operate, and when operated from a UPS with a square wave or step waveform, they will last much less. |
| Inductive elements (inductors, chokes). | UPS on-line type. | Quite often the question arises: is it possible to connect devices with an inductive load, for example, fluorescent lamps, to a regular cheap uninterruptible power supply? In practice, they connect it, and everything seems to work. But it should be borne in mind that many manufacturers categorically do not recommend this and classify cases of uninterruptible power failure after connecting an inductive load as non-warranty. In addition, there have been cases where a reactive load damaged a UPS that was not designed for it. |
| Transformer (linear) power supply. | UPS on-line type. | When choosing a UPS for devices with transformer power supplies, you need to be wary of a UPS that does not produce a pure sine wave output. When powered with voltage in the form of a meander or stepped sinusoid, losses in the transformer increase, which, if it is heavily loaded, will lead to a decrease in the transformer’s resources by tens of times. Also in practice, there have been cases when the UPS itself, to which such a load was connected, burned out. On the other hand, quite often equipment with low-power transformer power supplies, for example, radiotelephones, works quietly in tandem with an off-line UPS. However, many manufacturers, as in the case of inductive loads, most often do not recommend connecting transformer power supplies to conventional UPSs. How to distinguish a transformer power supply from a regular switching power supply? If we are talking about an external power supply, then a pulse power supply is usually light and small, while a transformer power supply is heavier and larger, due to the fact that the transformer itself is located inside it. The type of built-in power supply is more difficult to determine; here you need to rely on the manufacturer’s documentation. The good news is that in most cases, switching power supplies are now used in electronic equipment such as modems, switches, routers, and computers. |
| Structural elements sensitive to power quality. | Only on-line UPS type. | Almost everyone knows that equipment is sensitive to voltage drops in the network, or constantly under (over) voltage. However, the quality of power supply is determined not only by voltage. Sensitive telecommunications, audio-video, measuring, and medical equipment also react negatively to:
All this can not only distort the operation of equipment, but also shorten its service life. |
| Starting currents. | On-line UPS with power corresponding to the load. | Equipment with electric motors, pumps, compressors and other structural elements that consume a large amount of electricity at the time of start-up cannot be connected to low-power UPSs. Inrush currents can exceed standard consumption by 3-7 or more times. |
What parameters to focus on when choosing a UPS
One of the main characteristics by which you need to choose a UPS is the maximum permissible power of the connected devices. Uninterruptible power supply can be used for a PC (system unit and monitor), router, office equipment, set-top boxes and other devices. The electricity they consume must be summed up.
The power of the UPS is indicated in VA (volt-amperes) or in W. When selecting a device, it is important not to confuse these indicators.
It is best to have a power reserve of 30-40%. Firstly, the computer can be upgraded to increase performance or additional peripherals can be connected to it.
And secondly, the battery life of household batteries (this is the second most important indicator) at maximum load is small and is usually 1-3 minutes.
At a consumption level of 50-70% of the maximum, batteries can power devices for much longer: 6-20 minutes for household models.
Some UPSs allow the connection of external batteries. This significantly extends battery life. A low-power computer can work for several hours
The input voltage range determines to what values the uninterruptible power supply will not power the computer from batteries. If the voltage drops frequently, you should not use devices whose lower limit of this interval is greater than 180 V. Otherwise, frequently turning the batteries on and off will lead to a rapid loss of their capacity.
The number of output connectors does not at all guarantee the connection of the corresponding number of computer peripheral devices - the UPS is capable of carrying a certain power. It is always recommended to estimate the total volt-amperes of devices.
Many UPSs have an LCD display and/or a connection to a computer via a USB port. This allows you to program their actions in case of problems with power supply, as well as inform the computer operating system about this.
When placing uninterruptible power supplies in residential or office premises, their noise level is important. Devices operating on a backup power circuit do not emit much heat and do not have coolers, so they are the quietest.
If the UPS is paired with a computer and its fan is working properly, then it produces a sound comparable in power to the noise of the system unit. Sometimes, when overloaded, the uninterruptible power supply can produce high-frequency irritating sounds.
And the last parameter that needs to be taken into account is the weight of the device. Especially if its place will be on the shelves of a computer desk or there are plans to mount the device on the wall.
UPSs are often installed for other household appliances; read more about choosing such devices in the articles:
- Uninterruptible power supply for TV: ten best UPS models + valuable tips before purchasing
- UPS for gas heating boilers: purpose, review of models, maintenance tips
How to calculate the power of a UPS?
In order to choose the right uninterruptible power supply, you need to calculate the total power of the equipment that you are going to connect to it. Power values can be clarified in the technical specifications (data sheet or instructions for the equipment).
Let's look at a hypothetical example.
We want to connect to the UPS:
- 250 W computer,
- 60 W LCD monitor,
- 2000 W air conditioner (cos φ = 0.8).
There is one point here: even if the power of all devices is expressed in one unit, in this case in W, you need to calculate two powers: in volt-amperes and watts.
Power in volt-amperes and watts - what's the difference?
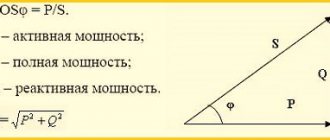
Power, which is expressed in volt-amperes (VA, VA) is called apparent power. It shows the actual load of the equipment, taking into account active and reactive ones.
Power, which is expressed in watts (W, W), is called active power.
These are two different quantities, and both need to be taken into account when choosing a UPS with the power you need. This is especially important if you are going to connect a reactive load to the UPS, since in such equipment the apparent and active power can differ significantly.
Calculation of power in volt-amperes.
To convert active power (in watts) to total power in volt-amperes, we use the formula:
Where:
- VA - total power,
- W - active power,
- P is the power factor of the equipment.
If the equipment belongs to the active load, and this is almost all network, telecommunications equipment, lighting and heating devices, that is, equipment without inductance, without reactive power, as well as computer equipment with power supplies with power factor control (APFC), then the coefficient can be accepted equal to 1, or better with a small margin - 0.95.
If you are going to connect a laser printer, air conditioner, fluorescent lamps - equipment that has electric motors and the like, everything that has inductance and reactive power, as well as computers with power supplies without APFC, to the UPS, then you need to look at the power factor in the device passport or on a sticker on the back wall. For this technique it is most often indicated. The power factor is designated as Power Factor (PF) or cos φ.
In the case where the manufacturer has not indicated the power factor value, but the load is clearly not fully active, you can take the most common value: 0.7.
Let's return to our example.
The power supply in the computer does not have power factor adjustment, so we take the P value equal to 0.7. It's the same on the monitor. In total we get the full power:
- for a computer with a monitor: (250+60)/0.7 =442 VA,
- for air conditioner: 2000/0.8 =2500 VA,
- Together: 2942 VA.
So, should we buy a 3000VA uninterruptible power supply? Take your time, it's not that simple.
Calculation of power in watts.
Most often, the simplest case occurs - when the power in watts, also called active power, is already indicated in the documentation for the equipment. If not, you can convert the power from volt-amps to watts using the same methodology as for total power.
Let's calculate the power of our equipment in watts:
- computer with monitor - 310 W,
- air conditioner - 2000 W,
- Together: 2310 W.
In our online store, among the 3000 VA UPSs, for example, there are the following:
ProLogix Professional 3000 LB USB UPS - 1800 W active power.
Logicpower LPM-PSW-3000VA - active power 2100 W.
PowerCom VGS-3000 - active power 2700W.
In terms of full power, all three are suitable for our conditional example, but in terms of active power, only one is suitable - PowerCom VGS-3000.
Shall we buy it? Not so. Let's count further.
Power reserve
Firstly, you need to take into account that the UPS should not operate at maximum load. Different manufacturers recommend different power reserves; on average, the uninterruptible power supply should not be loaded more than 70-80% of the maximum. This means that we need to add at least another 20% to the estimated consumption of the connected equipment.
You also need to take into account a possible upgrade of equipment (at least 10%). Installing a more powerful video card in a computer, replacing a monitor with a larger diagonal model - all this will entail an increase in power consumption, both active and total.
Let's calculate the reserve for our equipment.
Total power: 2942+20% + 10%= 3883 VA.
Active power: 2310+20% + 10% = 3049 W.
So, the UPS model we selected before is not suitable, because it only has 3000VA and 2700W.
But that's not all.
Starting currents
Equipment with electric motors, pumps, compressors differs from conventional equipment in that at the moment of switching on it consumes 3-7 or more times more power than usual. These are the so-called starting currents. If you do not take their presence into account when calculating the power and take a UPS that cannot withstand this load, then at best the uninterruptible power supply will turn off when such equipment is turned on, at worst it will burn out.
Inrush currents also exist in devices that contain inertial elements or inductors. For example, regular incandescent and fluorescent light bulbs consume much more power when they are turned on than when they are running. Another thing is that initially these are small values, and if we are talking about several lamps, such a starting current can be ignored. If we are talking, for example, about a huge room with hundreds of lamps, then the power jump can be quite noticeable.
Most UPS models are designed to withstand overload, but rarely more than 150%. Again, it is better to play it safe and focus on less than what is indicated in the passport, for example, 120-130%.
In our example, the starting currents of the air conditioner are of greatest importance. Let's say they are 3.5 times the normal power, then we have 7 kW active and 8.75 kVA full load at start.
We will not consider the starting currents of the computer and monitor in this example, since the probability of simultaneous start of all equipment is extremely small (or this situation can be purposefully avoided).
Total estimated power of the UPS we need:
Full:
8750 (air conditioning) + 442 (computer and monitor) + 10% for upgrade + 20% reserve = 1,2133 VA (12.1 kVA) .
Active:
7000 (air conditioner) + 310 (computer and monitor) + 10% for upgrade + 20% reserve = 9650 W (9.6 kW) .
Let's drop 30% on the overload capacity that the UPS should take on.
So, instead of a 3000 VA , which we needed at first glance, we actually need to buy a powerful UPS of at least 9300 VA/7420W.
Such uninterruptible power supplies can only be found in the expensive line.
And at this point it’s worth thinking about the advisability of purchasing a UPS with an approximate cost of more than 80,000 UAH for an air conditioner with a price tag of, for example, 5,000 UAH
It is precisely because of the large inrush currents that few people buy UPSs for refrigerators, washing machines and other similar equipment. It's simply not economically feasible.
Taking away the air conditioner from our example, we get a much more adequate load value: ≈ 580 VA (400W) (we do not count the starting currents for the computer and monitor, since they are most often covered by the overload capacity of a standard UPS).
For these purposes, for example, APC Back UPS ES 700VA is quite suitable.
How to calculate the required capacity of an uninterruptible power supply?
Usually, when choosing an uninterruptible power supply, we have some specific requirements for the time during which it will support the operation of the equipment connected to it in the event of a power outage. Many manufacturers indicate an approximate range, for example, they write that depending on the load, the battery life will be 4-20 minutes. Or they indicate that when working at maximum load this time will be 5 minutes.
But this is approximate, and we need to be absolutely sure that the UPS we purchased will provide battery operation for a certain list of equipment. Or calculate how long our chosen UPS model will hold our load.
We calculate the battery capacity for a known battery life
For calculations we need:
- The total active power (in watts) of the equipment that we are going to connect to the UPS (W).
- Battery life (T).
- UPS efficiency (approximately 0.85).
- Rated battery voltage.
We use the formula:
Where:
- T — time of planned autonomous operation (h),
- P is the power of the connected equipment (W),
- KPD - efficiency of the uninterruptible power supply (you can take about 0.85).
And the formula for converting capacity in Wh to capacity in AH:
Let's say we need the computer and monitor from the example above to work for 2 hours after a power outage.
Capacity (Wh) = 2 * 310 / 0.85 = 730 Wh.
However, battery capacity is usually indicated in ampere-hours. To convert watt-hour capacity to amp-hours, you will need to specify the rated voltage of the batteries.
For 12V batteries:
Capacity (A*h) = 730/12 = = 60.83 ≈ 61Ah.
For 24V batteries:
730/24 = 30.42 ≈ 30Ah.
Since most often a UPS uses 1-2 batteries, less often 4, with a capacity of 7-9AH, it will be difficult for us to select a standard UPS for such total capacity values. It is best to buy an uninterruptible power supply with the ability to connect external batteries and select the capacity according to your needs.
UPS catalog with the ability to connect external batteries.
For example, the following models may be suitable:
- ProLogix Optimum 500 500VA-300W,
- ProLogix Professional 1000 LB USB,
- Logicpower LPM-PSW-1000VA (700W),
- Logicpower LPY-PSW-500VA (350W) (UPD Discontinued).
The advantage in this case is also that if the load connected to the UPS increases, it will be possible to buy and connect another additional battery.
We calculate battery life, knowing the capacity of the UPS
For calculations we need:
- The total active power (in watts) of the equipment that we are going to connect to the UPS (W).
- The total capacity of all UPS batteries in watt-hours (Wh).
- UPS efficiency (approximately 0.85).
We use the formulas:
Where:
- V - rated battery voltage (V),
- AH - capacity of one battery (AH),
- N is the number of batteries.
And
Where:
- E - total capacity (Wh),
- KPD - efficiency of the uninterruptible power supply (by default you can take 0.85,
- P is the power consumption of the connected equipment.
Let's take the PowerCom BNT-800AP USB UPS as an example. The manufacturer claims a battery life of 5 minutes at maximum load. How long can our computer and monitor work with a power consumption of 310 W?
Total capacity (Wh) UPS = 12V * 7.2AH * 1 = 86.4 Wh.
Time = 86.4*0.85 / 310 = 0.237 hours ≈ 14 minutes.