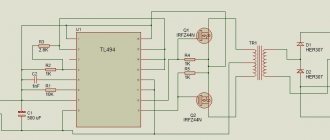
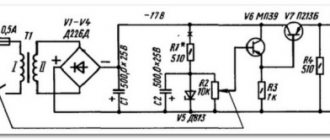
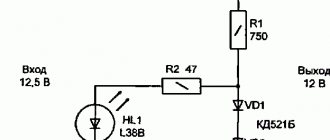
Design and operating principle
A pulse transformer, by analogy with other identical devices, consists of the following elements:
- primary and secondary windings;
- core.
When unipolar pulses “e(t)” are applied to the input coil, the time interval between them is quite short, it causes an increase in inductance during the interval ti, after which its decline is observed in the interval (T-ti). Due to the difference in the number of turns on the input and output coils and the pulsed nature of the current supply, it is possible to achieve a high transformation ratio with a reduction in the overall dimensions of the device.
At the same time, the tasks of measuring the level and polarity of a current pulse or voltage characteristics, matching the resistance value of the device that creates signals with consuming equipment, creating feedback circuits, etc. are solved.
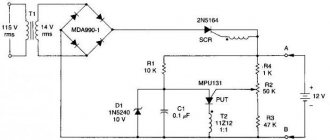
Pulse transformer connection
Examples of calculations
To calculate the width of a strip capacitor for a Kuldoshin transformer, you need to understand what capacity is required, the power of the device and the number of turns. If you use a small number of turns, the capacitor strip will be wider, and vice versa. This indicator for such transformers is determined taking into account the same principles as when creating a winding from wire.
The displacement current vibrates on the primary winding. Using the equation, you can calculate the amplitude voltage value, as well as find out what capacitance and frequency of alternating voltage is required. To carry out calculations, it is necessary to multiply the amplitude value of the voltage between the tapes by the number Pi, the frequency of the voltage and the capacitance of the capacitor.
It is important that the turns and capacitance of the capacitor are sufficient for zero voltage and current shift.
The correct elements provide sufficient process for converting reactive current into the opposite one. This type of current is concentrated in the windings.
The Kuldoshin transformer has a great economic prospect. Thanks to this invention, it became possible to further create small transformers for electronic devices. But a good effect can only be achieved if the calculations are performed correctly.
For small transformers, it is necessary to select an appropriate strip capacitor. Its width should be sufficient to cover the entire surface of the reels with tape.
The use of ribbon capacitors is practiced for radios, ignition coils, televisions, and other devices.
Similar windings of tape capacitors are used in the energy and electrical industries.
The peculiarity of Kuldoshin’s invention is that the primary winding of the transformer is wound as a tape condensate, and the secondary winding is made as a standard winding using a round wire. But this is not the only possible option. The transformer is also used when the secondary winding is made in the form of a strip capacitor.
There are also transformers in which mixed winding and conventional winding are used. The option is chosen based on the goals set and the required power level. All calculations should be checked several times so as not to spend a lot of materials on the production of the transformer.
Application area
For the most part, these transformers are used in pulsed devices:
- gas lasers;
- triode generators;
- differentiating modules;
- magnetotrons, etc.
Types of transformers
These devices are used in modern electronic equipment, for pulse-type power supplies, televisions, computers and other equipment.
Another area of use for devices is as protective elements in the event of a short circuit under no-load conditions, excessive load or excessive heat.
Varieties
Depending on the design features, the following types of pulse transformers are distinguished:
- rod;
- armored;
- toroidal, with wire wound on an insulated core, which does not require the use of coils;
- armored rods.
Types of magnetic cores
The cross-section of the core in most devices is in the shape of a circle or rectangle, by analogy with power devices.
Also read: Three-phase oil transformer - TMF
The main characteristics of the devices are marked on the case, so from the symbol you can glean information about the main parameters of the equipment.
Transformer cost
The price per unit of product can range from 50 to 700 rubles and more, depending on the characteristics of the device. When purchasing, the manufacturer of the product and the size of the purchased batch are taken into account. The cheapest products are made in China and are widely available on the market.
Pulse transformers are devices without which it is impossible to imagine modern household appliances and industrial production. These devices have a number of advantages compared to similar equipment, but in some cases the associated disadvantages do not allow their use.
How to choose materials
When making a step-down transformer from 220 to 12 Volts, it is important to use high-quality materials - this will ensure high reliability of the device that you will subsequently assemble on it. It should be noted that the transformer allows for decoupling from the network, so it can be installed to power incandescent lamps and other devices that are located in rooms with high humidity (showers, basements, etc.). When making your own coil frame, you need to use durable cardboard or textolite.
It is recommended to use domestically produced wires; they are much stronger than their Chinese counterparts and have better insulation. You can use wire from old transformers, as long as there is no damage to the insulation. To isolate the layers from each other, you can use either plain paper (preferably thin) or FUM tape, which is used in plumbing. But to insulate the windings, it is recommended to use fabric impregnated with varnish. It is necessary to apply insulation on top of the windings - varnish cloth or cable paper.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of pulse transformers has the following advantages:
- high output power;
- small weight and overall dimensions;
- high efficiency due to reduced energy losses;
- lower price with comparable characteristics;
- high reliability due to the presence of protection circuits.
Disassembled pulse transformer
Low mass is achieved by increasing the pulse frequency. This leads to a reduction in the volume of capacitors and simplicity of the rectification circuit.
An increase in efficiency is ensured by reducing energy losses.
The reduction in size is associated with a reduction in the amount of materials used. This is the main reason for the reduction in price of these products. Another advantage of its small size is the possibility of using the device in small-sized electrical products.
The disadvantages are associated with difficulty in repair due to the absence of high-frequency interference in the galvanic isolation circuit, due to the design features and operating principle of the device.
To prevent the influence of high-frequency interference, it is often necessary to resort to the use of special protective equipment if equipment is used for which such factors are undesirable. In some cases, due to interference, the use of pulse transformers is impossible.
Procedure for checking serviceability
To check the health of the pulse transformer, use an analog or digital multimeter. A digital device has advantages due to its ease of use. There is no need to further adjust it, just make sure that there is power and the integrity of the connection wires.
Also read: Single-phase cast current transformer - TSL
The analog multimeter is configured as follows:
- the operating mode is selected by switching to the area of the minimum resistance value during measurement;
- the wires are inserted into the contacts of the device and come into contact with each other;
- with a special adjustment the needle is set to zero;
If you cannot align the arrow with zero, this indicates problems with the batteries that need to be replaced.
If the transformer is an integral part of some apparatus, it is advisable to separate this element from the rest of the structure in order to eliminate the impact of associated interference during diagnostics.
Checking with an oscilloscope:
The malfunction of the device may be due to the following problems:
- damaged core;
- burnt compounds;
- violation of wire insulation, causing a short circuit in the winding;
- wire break.
In addition to instrumental measurements, it is necessary to pay attention to the appearance of the device. A malfunction may be indicated by a burnt winding, traces of burning and a corresponding smell.
Tools and materials for making the device
To make it you will need the following tools:
- Core (can be taken from an old TV).
- Lakotkan.
- Thick cardboard.
- Boards and wooden blocks.
- Steel rod.
- Glue and saw.
Making this transformer is not difficult. A transformer for halogen lamps can also be made using these tools. Remember that there is no need to deviate from winding technology. If all the rules are followed, then it will work for many years. These tools and materials are enough to make a transformer with your own hands.
Winding procedure
If the wire of the input or output coil is not suitable for further use, the transformer can be rewound. To do this, select a wire with double or triple insulation, which must be wound around the core.
The operation is performed in the following order:
- the wire of the primary coil is wound, after preliminary soldering of the input contact. The turns are wound evenly and tightly;
- the output end of the wire is soldered in the right place;
- insulation is applied in several layers;
- the secondary winding is wound, with the input and output ends soldered.
For the device to work properly, the wire is wound evenly, eliminating knots and twists. The number of turns is determined based on a calculation based on the characteristics of the device.
Connection process
When considering how to wind a transformer, it is necessary to study the process of connecting the wires. If the core breaks during winding, the soldering process should be performed. This procedure may also be required if you initially plan to create a circuit from several separate pieces of wire. Soldering is performed in accordance with the thickness of the wire.
For wire up to 0.3 mm thick, the ends need to be cleared to 1.5 cm. They can then simply be twisted and soldered using the appropriate tool. If the wire is thick (more than 0.3 mm), you can solder the ends directly. In this case, twisting is not required.
If the wire is very thin (less than 0.2 mm), it can be welded. They are twisted without undergoing a stripping procedure. The connection point is brought into the flame of a lighter or alcohol lamp. An influx of metal should appear at the junction. The junction of the wires must be insulated with varnished cloth or paper.