How the device protects electrical appliances
Our homes are filled with household appliances and equipment that are connected to the power grid. Electrical appliances themselves are safe to use, which is ensured by manufacturers during their manufacture and is guaranteed by appropriate quality certificates.
However, a number of unfavorable factors affecting devices and network wiring in each individual room can worsen their insulation and create conditions for the passage of current through the human body, which will lead to electrical injury. These factors include:
- heat;
- humidity in the air and in the places where the wiring passes;
- the presence of metal products with unstable grounding;
- mechanical damage to the insulation.
Compact isolation transformer.
When an electric current leaks, voltage appears on the metal surfaces of not only the devices themselves, but also on pipelines or other metal objects surrounding the user.
The highest risk of electric shock is in the bathroom. Because it contains all the negative factors affecting insulation.
Electric shock can be avoided by using protective measures. This is a reliable grounding of the housings of electrical appliances, so that in the event of accidental insulation breakdowns, dangerous currents pass through the grounding circuits.
They are also protected by the use of RCDs or differential circuit breakers in the input load connection circuits, which disconnect the network in the event of ground leaks.
Such protection measures are based on the fact that the ground for all electricity consumers is part of the electrical circuit. Protective electrical grounding simply bridges the circuit that may arise between a phase accidentally falling on the electrical equipment body and the ground through the human body in case of accidental contact.
Interesting read: how to assemble a Tesla coil yourself.
Another method of protection would be to exclude the connection of the earth with the electrical network and this can be achieved through complete galvanic isolation of the primary and secondary electrical networks. This is achieved by using safe isolation transformers, the devices of which will be discussed below.
The specific nature of some household appliances, such as a washing machine or hair dryer, requires them to be constantly connected to the power grid in conditions of high humidity, which increases the risk of electric shock from a faulty appliance or broken wiring.
Accidental touches to the conductive phases and the neutral wire will lead to tragic consequences. The 220 V voltage from the power supply network is formed according to the connection scheme of all three circuits with a potential difference of 380 V between them with a neutral wire, which is connected (grounded, as they say in everyday life) to a potential in the ground.
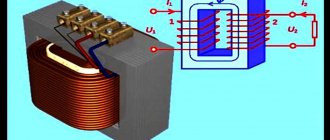
Connection diagram of the isolation transformer and devices to it.
This scheme predetermines the presence of phase voltage between each of the three network linear wires (colloquially referred to as phases) and zero (neutral) - ground. If the conductor insulation is broken, the phase voltage passes to the housing of the household appliance.
Simultaneous contact by the user of such a “broken” case and grounded metal objects such as heating radiators, faucets or water taps provokes the passage of electric current through the human body with all traumatic consequences.
Operating principle of the device
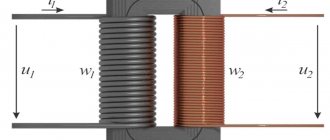
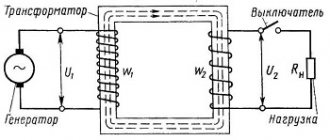
The operation of a low voltage isolation step-down transformer is based on the galvanic isolation effect. Technically, this is implemented in the form of autonomous operation of both coils. The coils of the device are physically separated, that is, they do not touch each other.
This ensures safe operation provided that the circuits are not short-circuited due to mechanical stress. To completely eliminate the possibility of contact, the windings are insulated with several layers of high-quality insulation.
Isolation transformer circuit.
Passing through the primary winding, the current induces electricity in the secondary coil, to which circuits with consuming equipment are connected. The secondary winding of the RT or devices connected to it cannot have contact with ground or neutral.
It will be interesting➡ Idle mode for transformers
Significant increase in operational safety even in the event of a breakdown in the housing. With this scheme, a breakdown will not cause a current overload in the circuit, and the device itself will remain fully functional.
If a person comes into contact with an electrical appliance under emergency voltage connected through an isolation transformer, there will be no fatal injury from leakage current. Since it will not exceed a life-threatening level.
One of the operational features of isolation voltage transformers is the conversion coefficient equal to unity for most used models. Thus, both the input and output voltage are equal to the same value - 220 or 380 V.
When making calculations, it is necessary to take into account the energy costs for the operation of the device, since the efficiency of most models is in the range of 70-85%.
Isolation transformer - operating principle and purpose
An isolation transformer is a device that is designed for the so-called galvanic separation of electricity consumers and the electrical network supplying them.
The main objective of such a device can be called increasing safety due to the fact that equipment such as an isolation transformer does not have electrical connections in the secondary circuits with the ground or with voltage sources made in the form of a solidly grounded or effectively grounded neutral at transformer substations.
In this situation, even the occurrence of a possible electrical breakdown on the housing will not cause an electrical overload. The device itself will remain in absolutely good working order. If a person accidentally touches a part of the device, which, accordingly, is under emergency voltage, the leakage current will not exceed a life-threatening level for the person, and as a result, a tragedy can be avoided.
An isolation transformer will come in handy not only in industrial enterprises, but even at home. Especially if you have a home workshop.
The basis of such a device as a separating transformer is the so-called TS (unified transformer). Since modern household electrical appliances come in different energy intensity and power, unified transformers are also taken with the expectation of a wide variety of load types and load power values.
The effect of separation and absence of electrical communication (which leads to the so-called galvanic isolation of the voltage that powers the device and the voltage that is supplied from the electrical supply lines) is achieved quite simply. The isolation transformer has two windings in its design - secondary and primary. Between them, reinforced (no less than double) insulation or a metal grounded tap is installed, which ensures the avoidance of breakdown. Since the isolation transformer is not designed to convert voltage, its transformation ratio is usually equal to unity. In this case, the input voltage will differ from the output voltage.
However, what is the point of using such a transformer then? This can be easily demonstrated with an example if there is an electrical point without galvanic isolation in a damp place, for example in a bathroom. If moisture gets into such a point, an insulation breakdown will occur. As a result, some section of the wall and ungrounded electrical appliances next to it will be exposed to voltage.
If there is an insulation breakdown with an isolation transformer, then the same part of the wall may also be energized, but in this case the current will be minimal. And if there is no insulation breakdown, the design of a device such as an isolation transformer is chosen correctly, then there will be no current or voltage at all.
Such a device is often used in medicine. It is possible to use it as an output transformer or as a coupling transformer to match the circuit resistance.
Types of devices
At the moment, in electrical engineering, most transformers provide galvanic isolation of input and output circuits. Despite the fact that the “classical” definition of an isolation transformer implies the invariability of the value of the transformed parameter (voltage), in fact all types and types are isolation. Depending on the purpose, there are several types of transformers.
Current
Most often used to connect circuits on which measuring and recording devices (electricity meters, ammeters) and protective relays are installed.
Pulse
Converts the received signal into a rectangular pulse. Used to prevent high frequency interference.
Power
The design, most often, consists of several secondary windings that convert an incoming electrical impulse with one voltage system into several outgoing ones with other parameters of the voltage system.
Peak transformers
Used to convert the sinusoidal voltage component. The main purpose is to prevent interference in circuits with digitizing equipment.
Some sources list portable isolators as a separate category. It should be noted that the overall dimensions in the technical design of devices of various types do not play a key role.
Classification
Currently, several types of isolation transformers are commercially produced, designed for the safe operation of electrical installations. The following types of such devices are distinguished:
- current - the primary coil is used to connect a current source, the secondary is sent to an electric meter or similar device. Installed in a measuring or relay electrical network;
- peak - for converting sinusoidal voltage, in most cases used in digitizing devices;
- pulse type – convert the received signal into a pulse, smooth out high-frequency interference;
- automatic - the design connects the input and output windings together, which forms an electrical connection, together with a magnetic one;
- power ones - with several windings, allowing the characteristics to be transformed simultaneously with transmission;
- portable – used for organizing lighting systems outdoors or indoors.
Also read: Three-phase power transformer - TMG
Devices can provide for highly specialized application conditions. Such devices are installed in medical institutions to supply power to operating rooms, inpatient departments and other important departments where high safety requirements are imposed.
Isolation transformer
Design features
Different types of isolation transformers can be either stationary or portable. Most often, portable devices have additional protection from external influences and are used in extreme operating conditions, in open areas.
Automatic transformers are not isolation transformers, since their design uses a different principle of arrangement of the primary and secondary windings.
They are combined into one, which forms, in addition to electromagnetic, a direct electrical connection. RTs for narrowly targeted use are being developed. For example, for hospitals and laboratories.
So-called medical isolation transformers are used to provide power supply with precisely defined parameters to sensitive devices installed in intensive care units, operating rooms of various biological, chemical and medical laboratories.
Material on the topic: interesting information about step-down transformers.
Varieties
Today, several main types of devices are used that increase the safety of operation of household appliances and fixed assets of the enterprise. The following types are distinguished:
- Current transformer. Its primary winding is connected to a source of electricity, and its secondary winding is connected to a meter or other measuring device. It is used in measuring or relay circuits.
- Peak transformer. Converts sinusoidal voltage. Most often used in devices with digitization.
- Pulse. Receives and converts the received signal, and then transmits a rectangular pulse. Prevents high frequency interference.
- Auto. The principle of connecting the primary and secondary windings into one is used, which allows the formation of not only a magnetic, but also an electrical connection.
- Power. The design has two or more windings that convert one voltage system to another through the process of electromagnetic induction.
- Portable. Used for street and tunnel portable lighting. It has compact dimensions. The device is also used in open areas or under extreme working conditions.
Isolation transformers can be highly specialized. For hospitals, for example, special units are used. They are responsible for providing electricity to such important facilities as intensive care, operating rooms and inpatient departments. Separating materials prevent the decoupling from becoming phase-to-ground. This allows you to prevent electric shock to medical personnel and patients.
For domestic purposes, both single-phase and three-phase units are used. Most often it is used for boilers, electric heated floors, etc.
Purpose of household transformer separators
Design of a medical isolation transformer.
A cardinal solution in terms of ensuring electrical safety in rooms such as bathrooms or basements is to prohibit the installation of sockets in them that connect directly to the power supply network.
In this case, an isolation transformer (IT) is installed near the outlet, the task of which is not to convert the voltage up or down, but only to isolate the device using mains electricity from the network itself.
For the purpose of safe use of the same outlet in the bathroom, the RT is powered by its primary winding from a 220 V power network, and its secondary winding is connected to the outlet. In this way, galvanic isolation of the power supply system and the device of use is carried out. The principle of operation of the RT is illustrated by a schematic diagram of its connection and devices for use.
It is prohibited to ground the secondary winding of the RT and connected devices! Only the casing (housing) of the transformer is grounded.
Application of transformer separators
Design of an isolation transformer.
The design of the isolation transformer is made in complete analogy with the layout of the main functional elements in voltage converters of a step-up or step-down type of operation.
Also, primary and secondary windings with identical winding characteristics are installed on the magnetic circuit; according to the same laws of electromagnetic induction, alternating current electricity is converted from the primary winding to the secondary.
Since the voltage parameters of the output circuit repeat the same characteristics of the mains voltage applied to the primary, the voltage vectors in the circuits are practically the same.
The main design difference between RT and other transformers is the careful electrical insulation of the windings from each other. The connection between them is only magnetic due to the magnetic flux in the magnetic circuit.
It will be interesting➡ Design and circuit of a three-phase transformer
This method of transferring energy between circuits without direct electrical contact is called galvanic isolation. In this case, the secondary circuit of the transformer is not grounded! A sudden electrical breakdown will not cause an overcurrent; the leakage current in the event of accidental contact of a person with equipment under load will not exceed dangerous threshold values.
Features of transformers
One of them is the presence of double insulation and/or a protective shield, which provides galvanic isolation, unlike a conventional device . This means that electrical energy is transmitted without direct contact between the windings. The isolator provides protection against serious electric shock . If the insulation on the housing inside the energy consumer breaks through, then the risk of electrical injury when a person simultaneously touches the device and a grounded object will become much lower.
Another feature of isolation transformers is that their conversion coefficient is most often equal to unity . Thus, the output voltage will be equal to the input - 220 volts. This variety is the most common. Transformers introduce some losses into the energy transmitted through it, since the efficiency is in the range of 70 to 85 percent.
Device characteristics
At its core, an isolation transformer resembles a step-down transformer of an ordinary electrical device, consisting of a primary and one (several) secondary windings. The turns of the primary windings of such transformers are separated by galvanic insulation from the secondary ones, however, in the event of emergency situations, for example, overheating, destruction of insulation or short circuit of the windings, the appearance of a phase in the secondary circuits could not be excluded. The main characteristics of isolation transformers are shown in the figure below.
Main technical characteristics of isolation transformers.
Isolating transformers have a transformation ratio equal to unity, provided by windings with identical parameters. And its main feature is the reliable galvanic separation of the windings.
This is realized by using reinforced or double insulation; the most reliable option is considered to be the decoupling of the primary and secondary windings by winding on different coils mounted on a single magnetic core. The efficiency of isolation transformers approaches 85%, but this is a worthy price to pay for electrical safety; it is not for nothing that such devices are called safety transformers.
The likelihood of suffering from secondary voltages in a network operating from an isolation transformer is minimized. Of course, the danger of electric shock remains if you touch both wires of the network (the concept of zero or phase in this circuit is not applicable), but each individually is neutral with respect to the ground and therefore does not pose a danger to human life.
An industrial isolation transformer in a housing is a complete panel structure with a transformer (or several transformers), an input switch, circuit breakers, a network indicator, and a terminal block for connecting a cable.
The galvanic isolation created by the RT between the incoming power system and the consumer load circuit provides reliable protection for users at home and maintenance personnel in production. The model range includes as basic designs:
- single-phase isolation transformer;
- three-phase dry isolation transformer.
Which model to choose for installation in your apartment or in a separate building is already chosen by the homeowner in accordance with the recommendations of experts. Transformers are produced for various types of voltage. Among others, the most common typical combinations are:
- isolation transformer input 380/220V – output 380/220V
- isolation transformer input 380/220V – output 220/127V
- isolation transformer input 220V – output 220V
- isolation transformer input 220V – output 36V
- isolation transformer input 220V – output 24V
- isolation transformer input 220V – output 12V
Tables 1 and 2 show the main characteristics of three-phase isolation transformers 380/380V and 380/220V and single-phase isolation transformers 220-220V.
Table 1. Main characteristics of three-phase isolation transformers 380/380V and 380/220V.
Table 2. Characteristics of single-phase isolation transformers 220-220V.
Winding connection diagrams for three-phase transformers in input/output combinations:
- star
- triangle
- zigzag
During operation of the transformer, a situation may arise where the thermal switch is triggered when the temperature of the transformer exceeds 125 degrees C. In this case, the transformer is turned off. This situation can occur when the transformer is overloaded or the input network voltage is exceeded. With proper operation, the transformer resumes operation after approximately 20 minutes.
What is an isolation transformer
When creating electrical networks, electrical safety issues always come first. The voltage level of 220 V is extremely dangerous for human life, but this is present in any household electrical outlet. Electric shock can be avoided by using protective measures:
- reliable grounding of the housings of electrical appliances, so that in the event of accidental insulation breakdowns, dangerous currents flow through the grounding circuits;
- using RCDs or differential circuit breakers in the input load connection circuits, disconnecting the network in the event of ground leaks.
Such protection measures are based on the fact that the ground for all electricity consumers is part of the electrical circuit. Protective electrical grounding simply bridges the circuit that may arise between a phase accidentally falling on the body of electrical equipment and the ground through the human body in case of accidental contact.
Another method of protection would be to exclude the connection of the earth with the electrical network and this can be achieved through complete galvanic isolation of the primary and secondary electrical networks. This is achieved by using safe isolation transformers, the devices of which will be discussed below.
Design and principle of operation of isolation transformers
At its core, an isolation transformer resembles a step-down transformer of an ordinary electrical device, consisting of a primary and one (several) secondary windings. The turns of the primary windings of such transformers are separated by galvanic insulation from the secondary ones, however, in the event of emergency situations, for example, overheating, destruction of insulation or short circuit of the windings, the appearance of a phase in the secondary circuits could not be excluded.
Isolation transformers have a transformation ratio equal to unity, provided by windings with identical parameters, and its main feature is reliable galvanic separation of the windings. This is realized by using reinforced or double insulation; the most reliable option is considered to be the decoupling of the primary and secondary windings by winding on different coils mounted on a single magnetic core. The efficiency of isolation transformers approaches 85%, but this is a worthy price to pay for electrical safety; it is not for nothing that such devices are called safety transformers.
The likelihood of suffering from secondary voltages in a network operating from an isolation transformer is minimized. Of course, the danger of electric shock remains if you touch both wires of the network (the concept of zero or phase in this circuit is not applicable), but each individually is neutral with respect to the ground and therefore does not pose a danger to human life.
Examples of using
The use of isolation transformers is mandatory in high-risk areas. A typical example is the bathroom, where the use of conventional electrical power is limited:
- high air humidity;
- the possibility of water getting into live parts;
- the presence of metal objects with unstable grounding.
When carrying out temporary work in particularly hazardous areas, the use of portable safety transformers is allowed.
Thanks to the medical isolation transformer, it becomes possible to create special IT networks that are required for powering Group 2 premises (intensive care units, operating rooms), completely safe for both patients and medical personnel. The rated power of single-phase transformers for such networks can range from 0.5 to 10 kW.
If necessary, three-phase isolation transformers are used.
See also other articles:
What is RCD used for?
The protective shutdown in the event of the appearance of differential currents equal to the leakage current is carried out by a residual current device (RCD).
Read more…
What is touch voltage
Electrical safety deals with the issues of limiting human interaction with electricity, or more precisely with its dangerous consequences; among its terminology you can find such a thing as touch voltage - let’s try to figure out what it is.
Read more…
Advantages and scope
Isolating transformers are widely used in almost all areas of electrical engineering. They provide the user with a wide range of specific benefits depending on the industry in which they are used:
- devices with a transformation ratio of 1:1 are used in AC power networks without the need for additional grounding and insulation of peripheral equipment;
- isolation of DC circuits in communication lines. If it is necessary to use signal amplifiers, the use of RT makes it possible to separate the direct current for connecting the amplifier from the components of the information electrical pulse;
- increasing the safety of electrical equipment operation. Minimizes the risk of fatal electrical shock by isolating the user or operator from high-power sources;
- when testing, servicing or repairing equipment, it makes it possible to carry out work on devices that are turned on. In this case, isolation transformers are used with a ratio of 1:1, but having a low voltage power of the secondary circuit;
- filter out (cut off outside the operating range) the distorted sinusoidal voltage waveform, bringing it to the correct one. Reduce the negative impact of pulse width modulations;
- neutralizes a wide range of noise generated when connecting audio devices (amplifiers) to speakers.
It will be interesting➡ Oil transformers - what they are, device and principle of operation
The use of isolation transformers is determined by the operational requirements and specific application of electrical networks:
- High humidity or the presence of water in the room, the presence of metal products without grounding or with weak grounding: bathrooms and shower rooms, power switching cabinets located on the street, cable wells, basements and semi-basements.
- Remote tracking, measurement and control posts in medical institutions, data and call centers, as well as other institutions where it is necessary to increase the level of personnel protection and the safety of equipment operation.
- Operation of power tools and equipment belonging to the first safety class.
Installation of operation of electrical appliances through an isolation transformer is necessary in the following cases:
- when connecting power consumption devices that do not have grounding potential;
- in pulsed power networks that require increased insulation performance. Especially in medical and laboratory equipment;
- during laboratory testing of electrical and electronic devices to ensure personnel safety.
When using an isolation transformer, it is also necessary to use a residual current device (RCD) for the operated circuit. Despite the high reliability and safety, cases of insulation damage are possible.
In this case, the potential can be brought to the body of the device and there is a possibility of electric shock if you touch the body and the metal conductor connected to the ground. That is why it is recommended to connect isolation transformers through an RCD. A single-phase isolation transformer, depending on its design, can be used in the following cases:
- With mounting plates and exposed terminal blocks. Installation in an installation cabinet. In this case, a vertical or horizontal installation scheme or special fasteners for mounting on a DIN rail can be implemented.
- If there are no terminal blocks, remove the secondary winding through a cable branch. It is used as a component of electrical equipment and installations for any purpose.
- Portable option with a housing, socket and switch. Additionally, it can be equipped with a cable (extension cord).
A three-phase isolation transformer is actually three single-phase devices installed on one mounting plate:
- open option in both horizontal and vertical arrangement with star or triangle connection;
- arrangement of elements in the housing, including sealed housing.
- An isolation transformer is a necessary and useful device, especially in a home workshop. It can be used in reduced AC voltage mode to test high voltage devices.
Three-phase isolation transformers.
For example, connecting a 220 V circuit to a 36 V power source will allow you to safely monitor the flow of current in the tested circuits.
In this case, the use of any unified isolation transformers is allowed, since modern electronic devices do not have high consumption.
Useful to know: how to assemble a step-up transformer yourself.
How to make your own isolation transformer
It is not difficult to make a low-power device yourself, if you have similar skills and basic knowledge in the field of electrical engineering.
Sequence of operations:
- two half windings are made on two identical cores - the coils are divided in half;
- a pair of half windings are connected in series;
- Additionally, you can equip the device with a throttle or stabilizer.
A more detailed diagram of the device and the order of connecting the half-windings is shown in the diagram:
The device can be used to power a workshop or other auxiliary room. Before connecting to a stationary power supply, the device must be tested with a small electric current. An ordinary low-power lamp is suitable as a consuming device.
But if the home handyman does not have enough electrical knowledge and no experience in such work, it is recommended to contact a specialist of the appropriate profile.
Examples of using
The use of isolation transformers is mandatory in high-risk areas. A typical example is the bathroom, where the use of conventional electrical power is limited:
- high air humidity;
- the possibility of water getting into live parts;
- the presence of metal objects with unstable grounding.
When carrying out temporary work in particularly hazardous areas, the use of portable safety transformers is allowed. Thanks to the medical isolation transformer, it becomes possible to create special IT networks that are required for powering Group 2 premises (intensive care units, operating rooms), completely safe for both patients and medical personnel.
The rated power of single-phase transformers for such networks can range from 0.5 to 10 kW. If necessary, three-phase isolation transformers are used. The video provides information about a self-assembled isolation transformer.