What is selectivity
Selective residual current devices perform the same tasks and operate on the same principle as simple ones. The devices compare the current values in the phase and neutral wires and, based on the measurements, calculate the leakage current. If it exceeds the set point, the power supply to the apartment is turned off.
Leakage current occurs in 2 situations:
- Wiring insulation is damaged. There is a risk of fire or electric shock to persons.
- The risk described above paid off. The person touched either the body of an electrical appliance that came under the phase potential, or directly the bare wire from the socket.
Important! The residual current device has one big drawback. If a person simultaneously touches the phase and neutral wires, but does not make good enough contact with the ground, the RCD will not work. The protective device responds to current leakage to ground.
Selective RCD - what is it?
Many people are familiar with the residual current device (RCD). A modern electrical network cannot do without this element of protective automation. The main purpose of its installation is to protect people from exposure to electricity and from fires caused by current leaks.
Such emergency situations can arise due to worn-out old conductor insulation or poor-quality electrical wiring connections. In order to detect such accidents in time and prevent them from developing into a fire or electrical injury, protective shutdown devices are installed. When installing two-level protection, a selective RCD is used.
What is this device? How is it different from ordinary? What other types and types of RCDs are there? Below we will answer all these questions.
Operating principle of selective RCD
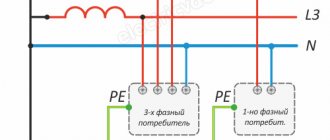
The operating principle of selective protection is based on the difference in shutdown time. For example, consider a typical apartment. There is one common input RCD. It is installed in the electrical panel. Configured to turn off 0.5 s after leakage current occurs. The phase wires from this protective device are distributed among group RCDs. They have a shutdown time of 0.25 s. Through them, sockets in the bathroom, kitchen, living room and other rooms are powered.
If a phase wire in the bathtub shorts to the body of the washing machine, the RCD will trip with a shutdown setting of 0.25 s. It is this room that will shut down. The incoming RCD with a setting of 0.5 s will not work and will leave the apartment energized, since enough time has not passed for it to turn off. That is, an RCD of 0.25 s will work faster than 0.5. The bath will turn off, but not the whole apartment.
Selective power network protection circuit
Features of selective protection
Selective devices, unlike conventional ones, have the ability to select the protection current and response time. The corresponding values are indicated on the device body. By combining the protective system according to these parameters, it is possible to give the protection the property of selectivity.
As a result, if a leakage current occurs in one of the rooms, only the emergency room will turn off, and not the entire electrical wiring. As a result, the time for troubleshooting and troubleshooting is reduced significantly.
Timing characteristics of RCD type S
Devices from different manufacturers have different properties. The differences lie in the leakage current and the dwell time at which shutdown occurs.
Therefore, devices of this type are usually divided into 2 groups:
- ordinary;
- type S.
Selective RCD from ABB: F202 AS, 63A
A comparison of their timing characteristics is given below.
| RCD type | Shutdown time with leakage current equal to Idn | 2*Idn | 5*Idn |
| Regular device | 0,3 | 0,15 | 0,04 |
| RCD type S | 0,13-0,5 | 0,06-0,2 | 0,05-0,15 |
Operating modes
During operation, the residual current device can be in one of two operating modes:
- normal;
- emergency;
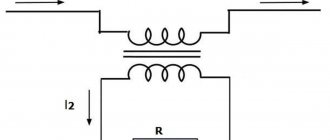
Normal operating mode means equality of currents passing through L and N wires. In a differential transformer, magnetic fluxes of equal magnitude but opposite in vector are induced. They compensate each other. The RCD concludes that there is no current leakage. The electrical wiring continues to operate as normal.
In emergency mode, the current in one of the wires is less (more) by the amount of leakage. Usually it does not exceed 100 mA. But even this deviation is enough to disrupt the equality of magnetic fluxes in the device’s transformer and trigger the RCD. The electrical wiring is turned off.
Purpose and principle of operation
Relay devices for electrical networks, designed to provide protection from direct contact in hazardous areas, as well as equipment protection, are available in a variety of designs.
Features of selective devices
A distinctive feature of a selective device is the presence in the circuit of a time delay function for turning off the circuit that powers the load.
Typically, this parameter exceeds 40 ms - this means that selective devices are not designed to protect against damage from direct contact.
The range of devices used for protection during the operation of electrical networks provides a wide choice. Almost all types of RCDs can be used in single-phase or three-phase networks
Also among the features of selective devices, it should be noted their good stability in response to current and voltage surges. Thanks to this property, the risk of false alarms and, accordingly, circuit shutdowns is almost completely eliminated. What selectivity of circuit breakers is is described in detail in this material.
As a rule, in practice, devices are used whose rated current is in the range of 25-100 A. In this case, the value of the differential leakage current is in the range of 0.1-0.3 A.
Two-pole and four-pole versions of the device are manufactured. Each type is actively used as part of branched cascade circuits.
Operating principle and design of RCD type S
The distinctive features of selective devices are limited only to those indicated above.
In all remaining design functionality, there is virtually no significant difference between selective devices and general-purpose devices.
The operating principle of the modules has the sole purpose of preventing possible current leaks, which poses a potential threat to users of various electrical equipment. Selective type RCDs also act to prevent damage to equipment.
The principle of operation, accordingly, remains standard - applicable to all protective devices from the RCD group:
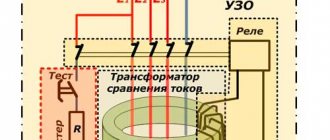
- There is a differential transformer in the design.
- Thanks to the transformer, a comparison of the control currents is carried out.
- The difference is transmitted to the sensing element.
- If the difference exceeds the set control parameter, a cutoff occurs.
That's the whole operating principle in general terms. However, it is also worth noting such a feature as the dependence of the devices on power supply.
In practice, two design options for selective-type RCDs (and general ones too) are used. One of the options involves external power supply, while the other excludes it completely.
Four-pole module integrated into a single-phase voltage network. The switching is carried out on the basis of a traditional solution, when an input machine, an electrical energy meter and then a selective RCD are used
It is clear that protective device designs that do not use an external power circuit appear to be more reliable than those that require an energy source for operational efficiency.
Since the differential transformer is, in fact, the dominant design element, special requirements are imposed on this part of the RCD circuit.
The magnetic core of the DT must have a strict linear magnetization characteristic.
This is approximately how the processes occur inside the magnetic core of a selective type RCD and the flow of currents through the existing working windings. By changing the current indicators of each line, the leakage factor is controlled
The temperature properties of the magnetic core should ensure high-quality operation over a wide temperature range. Therefore, to manufacture this element, a special material is used - amorphous iron or the like.
Other parts of the design of a selective RCD device are sensitive magnetoelectric relays - direct-acting elements, often called threshold elements.
In some designs, relays are replaced by electronics, but the principle remains the same.
Normal and emergency modes
When operating an S-type RCD, until the presence of a leakage current (differential current) is detected, the conductors forming an electrical circuit in the magnetic field of the core pass equivalent rated load currents.
A diagram clearly showing the internal processes of a selective-type module when operating the device in operating mode. The required level of sensitivity is ensured by setting it according to the cutoff current
These currents, equal in magnitude, induce magnetic fields of multidirectional action inside the core.
Their total flux turns out to be zero, which explains the absence of current on the secondary winding of the diesel generator. Its zero current has no effect on the cutoff sensing element. The RCD remains on.
Otherwise, when the described circuit is disturbed, the balance of currents is also disturbed. As a result, a current of a certain magnitude is generated on the secondary winding of the DT.
As soon as this value exceeds the threshold value of the trigger element of the selective protective device, it will operate. Which will activate the executive blocking system - cutting off the load power circuits. The RCD will turn off and cut off the load circuit.
Types of selective RCDs
Typically, for domestic needs, an alternating voltage of 220 V and a current frequency of 50 Hz is used. However, in the world of electrical engineering, everything is not so monotonous. Some consumers are powered by voltages of other values. The current consumption can be constant. Therefore, RCDs are produced in a wide variety of ways:
- Category AC. Used in alternating current circuits. Insensitive to DC leakage. Example - (ABB FH202)
- Cat. A. Universal. Used in networks with direct and alternating current (IEK VD1-63)
- Cat. S. Used to build selective protection with long time delays (ABB F204 A S-63/1).
- Cat. G. They are used for selective protection, but have long time characteristics (Eaton Electric model PFIM-G).
RCD category AC
Note! A 4-pole RCD is separately distinguished. It is used to power three-phase consumers (frequency drive, motor). This type of protective device requires the connection of 3 phases and zero.
Types of selective RCDs
The main types of RCDs are represented by the classification of devices according to their current indicators at which the device is triggered. In accordance with the basic parameters, fire protection devices of the protective type can respond to current strength equal to 100 and 300, as well as 500 mA.
The classification of protective selective devices can also be carried out according to the number of poles. Standard RCD devices have a pair of poles and are widely used in single-phase electrical networks. Devices used in three-phase electrical networks have four standard poles.
RCD selective
Depending on the method of operation of protective selective devices, devices of this type are divided into certain categories:
- “AS” - mounted in electrical networks with variable current values, for which these devices are designed;
- “A” - can be installed in electrical networks with alternating and direct current values;
- “B” - characterized by operability under conditions of three types of current, therefore it can easily interact with constant and variable quantities, as well as with rectified differential current indicators;
- “S” - refers to selective protective devices that have a certain shutdown delay;
- “G” - selective RCDs with a minimum delay in shutdown time.
Depending on the type and characteristics of the technical design, all selective types of RCDs are represented by electronic and electromechanical models.
The first type of such models requires a separate power source, which determines some limited distribution.
The second option does not require electrical power and is capable of responding to differential current values.
RCD option
The electronic protective device is connected both to external sources and to the protected power network. Such RCDs are capable of automatically disconnecting the network when the additional power source is turned off.
The restoration of the electrical power supply is accompanied by automatic switching on of the network. However, you need to remember that for some types of protective devices, this function is not available.
Not all types of selective devices are used to protect people from electric shock, therefore, for such purposes, it is recommended to install devices that can turn off the voltage when there are indicators of 10-30 mA.
Time selectivity
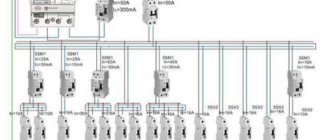
The time selectivity of the protection is based on the response delay. You must use at least 2 devices. They should differ several times in response time. To achieve selectivity, it is important to follow the sequence of arrangement of the RCD. The closer the power source (electrical panel), the longer the shutdown time of the protective device.
An RCD with a maximum time delay is installed at the entrance to the apartment. Typically this is a single phase S type device. This is followed by conventional RCDs with a shorter shutter speed.
Important! The general input protective device is subject to increased reliability requirements. If it fails, downstream consumers will be disconnected or left without protection. Therefore, it is desirable that the input device be from a quality manufacturer. For example, ABB or Schneider.
Leakage current selectivity
Current selectivity works on a similar principle. But the value used for selectivity is not time, but leakage current.
A minimum of 2 safety devices are also used. What is located closer to the apartment panel has a higher operating current value. Typically, for such tasks, fire protection RCDs with a shutdown current of about 100 mA are used. For example, IEK 2p 63A 100mA VD1-63 AC.
Next, devices with a lower leakage current of 5-30 mA are placed in consumer groups (individual rooms). If a fault develops in one of the rooms, then only the low-current 30 mA relay is more likely to operate. And the 300 mA fire protection device installed at the input will remain in operation. Thus, only the emergency room is switched off.
Response delay
The RCD response delay is one of the most important aspects of its operation. Especially if we talk about selective protective systems, the operation of which is impossible without different time characteristics.
The shutdown time is indicated on the device body. Typically it ranges from 0.001 to 0.5 s, which is enough to build most selective protections. The delay itself is provided using a compact electronic board included in the device.
Applications of selective protection
The main task of selective RCDs is to build selective protection. Therefore, such devices are used in a wide range of electrical systems:
- The simplest thing is to use it in an apartment. A selective protective device is needed to turn off the emergency room or outlet specifically.
- Construction of complex electrical circuits with consumers that differ greatly in power. Used for separate power supply of a private house, garage and garden lighting. Typically, in such cases, a three-phase RCD is used.
- In relay protection and automation systems. The selective device allows you to organize time delays and delays for switching between the main and emergency power sources.
Automation relay protection system
Selective RCD: technical characteristics
Residual power supply devices come in different types and operating principles. Electromechanical selective RCD is considered one of the most practical, because it allows you to disconnect a certain group of electrical consumers.
What is selective RCD
Selective RCDs differ from conventional protection devices in their long response time. This implementation makes it possible, in the event of any interruptions in the electrical circuit with series-connected protection devices, to disconnect not all wiring, but only a certain part of it.
Photo - principle of connecting a selective RCD
Since the protective devices responsible for a certain part of the electrical network operate before the selective RCD, the process of troubleshooting is greatly simplified.
To ensure selectivity, you need to do the following:
- Set the response time of the protection device (if such a function is available in a certain model);
- Set shutdown parameters for leakage current or short circuit (they must exceed those of other non-selective options).
Both of these parameters must be three times higher than the corresponding characteristics of other RCDs in the system, otherwise the device will not operate effectively.
Models are divided into the following types:
The first one is triggered at the slightest change in the supply current. It also instantly reacts to its smooth increase and exceeding the leakage current threshold. This option can be used both in an apartment panel and to ensure the safety of industrial or office electrical networks. This is the most accessible and popular type.
Photo - device connection diagram
The second type is triggered when the load is pulsating, as well as when the threshold leakage current value is exceeded. It is more expensive than AC, but its functionality is much higher. Scope of application: connecting a washing machine, power plants, refrigerators and other electrical appliances that require increased control.
The type B fire protection device allows monitoring of constant leakage current even at low ripple levels. This device is considered special, which is reflected in its scope of application (bridge circuits, industrial equipment, medical equipment, etc.).
Considering that the main task of operation is to maintain a certain time interval (it is by this parameter that the main classification is made), protection devices are:
The S marking is used for protection and shutdown devices that have a delay time interval of 0.15 to 0.5 seconds. This is an excellent choice for electrical networks where several protection devices are installed simultaneously and rapid shutdown of the current is required when necessary. For example, if in an apartment or private house there are several groups of loads, say 2, then a separate RCD (by type) is installed for each of them, and a selective RCD is installed at the input of the supply cable.
Connecting an RCD with selective cut-off
A selective protective device is connected according to the same rules as a regular one. Difficulties arise if it is necessary to build more complex protection with the simultaneous use of S-type devices with other automation devices.
When assembling the circuit, you should be guided by the following principles:
- Initially, the machine is set to input. It will protect subsequent circuits from short circuits and allow you to quickly remove voltage during repairs or maintenance.
- After the machine, an S-type RCD is connected. Sometimes a fire-fighting device is installed in its place. EKF VD-100 2P with a leakage current of 300 mA is suitable.
- Next come consumers or other RCDs with lower current and response time. If selective protection is required, then additional protective devices are indispensable.