Correct arrangement of expansion joints
Calculation of the exact number of seams required should be carried out by an experienced surveyor. To correctly construct a seam that protects the foundation from deformation, you must adhere to certain rules:
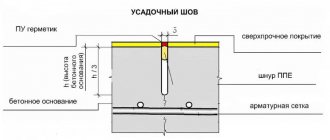
- The height of the expansion joint for the foundation must be equal to the height of the base itself,
- The pitch between the seams is determined based on calculations. The average indicators are as follows: if the house has walls made of wood, the step will be 0.6 m, brick walls - 0.15 m,
- The structure of the future building also plays an important role. If the house has an extension, then expansion joints are also required along the corner boundaries,
- The width of each seam is on average 10 to 12 cm,
- The choice of thermal and waterproofing insulators for each type of foundation will be different: it is better to protect a slab foundation with tarred tow, and a strip foundation – with a separate thermal insulation and waterproofing layer,
- When constructing a blind area, one or more wooden slats are used, which are filled with bitumen,
- A seam between the blind area and the foundation structure is not required if the base is already insulated from moisture and cold.
The tips listed above are universal and apply to all types of expansion joints. Following these tips will allow you to build a strong and reliable foundation that will last for decades.
Basic rules for constructing compensation gaps
For foundations, it is important how this or that seam will be made. There are some nuances that should be taken into account when designing it.
- Firstly, the height of the vertical gap must be equal to the height of the foundation, otherwise the whole point of carrying out the work is lost. Often the base is included in the linear dimension.
- Secondly, the distance between the structural gaps is taken depending on the material of construction of the ground part of the structure. For a wooden house, the optimal step is sixty meters, and for a brick house - fifteen meters. The soil heaving index is also taken into account. The higher it is, the smaller the distance between expansion joints.
- Thirdly, the expansion joint is made about 10cm wide for ease of insulation and waterproofing.
- Fourthly, a gap should always be provided at the boundary of extensions, even if the nearest seam is nearby.
- Fifthly, after insulation and waterproofing work, the gap must be sealed with an elastic and weather-resistant compound.
The above rules are considered universal. But for each foundation there are additional nuances that are laid out in the project. For example, it is recommended to seal the seam between concrete slabs with tarred tow, but for a strip monolith, insulation and waterproofing will have to be purchased separately. The future fate of the foundation and, as a result, the entire house largely depends on the quality of materials, as well as the endurance and elasticity of polymer sealants.
Construction of a seam that protects the foundation from deformation
The difference between expansion joints and each other determines the scope of their application. For example, the installation of a seismic seam on foundations is justified in areas of increased seismic activity. It takes on the load during ground vibrations and protects the building from deformation. If it is necessary to make a seam between the main structure and the extension, the foundations of these structures must be separated by a layer of penplex, styroform or armoflex 2 cm thick. This measure will smooth out possible fluctuations.
Foundation pairing: 1. House. 2. Old foundation. 3. Pins. 4. Fittings. 5. Base. 6. Foundation base.
The areas for installing expansion joints on foundations are regions where the air temperature throughout the year has a wide range. To smooth out soil movements due to temperature changes, the foundation area under the house is divided with wooden slats into separate sectors (maps). Such seams are more popular when protecting unheated rooms.
Shrinkage expansion joints are installed between the layer of foundation blocks and the concrete poured on top. The reason for such operations is to take into account the ability of concrete to decrease in size when water evaporates.
The construction of a sedimentary protective seam is shown during the construction of the foundation under a multi-story building. This allows you to evenly distribute the total load and prevent all kinds of destruction.
Installation of seams against deformation of buildings is carried out using various profiles. In other words, modern builders select the optimal profile option and make an expansion joint for the foundation from it.
Profile for creating an expansion joint on the foundation
Important: all expansion joints installed at the base of the building must be clearly stated in the design documentation.
The purpose of installing foundation joints is to protect the structure from deformation and ensure its stability.
Types of foundation expansion joints
Expansion joints are designed to separate the foundation slab or strip into separate sections (blocks). Thanks to their presence, the tension between adjacent, contacting zones is minimized, so during soil fluctuations or when temperature changes affect any compartment located next to it, the areas will not suffer from deformation processes.
By their design, seams are cuts that act as compensators that soften negative impacts.
Types of expansion joints and their purpose are presented in the table below.
| № | Types of cuts | Purpose |
| 1 | sedimentary | designed to reduce the risk of foundation failure on heaving, mechanically unstable soil types; they compensate and distribute in the foundation slab or strip the loads from the erected structure, contribute to the normal course of the settlement process of the building |
| 2 | shrinkage | used to prevent cracking of massive monolithic bases of strip or slab type when concrete dries |
| 3 | seismic | protect buildings from weak seismic ground vibrations |
| 4 | temperature | protect the base from deformation movements arising from compression and expansion of its sections under the influence of temperature changes |
Compensation cuts are located from each other at the distances specified in the building codes. The frequency of their location is determined by the following factors:
- the material from which the base is built;
- type of soil at the construction site;
- parameters and weight of the structure being erected.
Compensation cut
The standards determine the greatest distance between adjacent seams, which can be taken without performing preliminary calculations. To carry out accurate calculations, the standards provide appropriate formulas.
Expansion joints are used in the construction of slab, strip and prefabricated foundations. Their design is selected according to the conditions existing at the construction site.
Settlement and shrinkage seams
There are various reasons for foundation settlement. The main ones are the following:
- uneven load on foundation sections;
- the presence of soil layers of different properties at the construction site.
Uneven load distribution is often caused by placing different numbers of floors on separate sections of the 1st foundation.
If the structure being erected occupies a significant area, then the soil underneath is rarely of a uniform structure and type. The layers have different load-bearing capacities, so the foundation and the constructed building are deformed, up to irreparable destruction.
The sedimentary seam protects the structure from vertical movements and prevents subsidence of both the problem area and the adjacent sections. In this case, the structure does not warp.
The construction of an expansion joint is necessary at the point of contact between buildings with different numbers of floors. An example would be a house with a garage or terrace attached to it. In this case, adjacent foundations are not rigidly connected to each other. The loads are distributed separately, so the foundations can be laid at different depths.
Shrink seam
As concrete hardens, it loses water. Moisture is of paramount importance in the process of strengthening a material. During its evaporation, concrete decreases slightly in size. The result of this is contraction, leading to the formation of cracks. This phenomenon is especially strong for large volumes of poured solution.
To prevent such negative processes, a shrinkage seam in a monolithic slab or tape is designed. Compensation cuts eliminate the formation of fractures and tears.
Settlement and shrinkage joints are located along the area of the foundation according to the calculations performed. At the same time, the features of the above-ground and underground parts of the structure being built are taken into account.
Features of temperature and seismic joints
Building material changes its dimensions under the influence of temperature. The negative consequences of “compression-expansion” manifest themselves especially quickly in regions with significant seasonal fluctuations. Tension inside the foundation is created due to the temperature difference between the outside of the building and the inside:
- in winter, cold street air cools the outer sections of the walls (resulting in compression), and the heat of the rooms heats them from the inside (promoting expansion);
- In summer, everything happens the other way around: the foundation is heated outside, and inside, a circulating, cooler air mass inhibits the expansion process.
The result of the stresses that arise is the destruction of the above-ground parts of the foundation. Its elements located in the soil do not experience significant changes. A separate case is basements with a heating system located in regions with deep soil freezing. But at the same time, the resulting deformation stresses are less than in the above-ground parts of the building.
Creating an expansion joint minimizes the negative effects of temperature fluctuations. Joints of this type are made only in structures located above the ground, in the basement.
Seams under significant loads
The construction of expansion joints is a building norm in areas with possible seismic activity. The foundation is divided into separate compartments. They are arranged in the required manner around the entire perimeter. The cuts prevent the structure from collapsing in the event of waves generated by an earthquake.
Temperature and shrinkage joints are quite often combined with each other. This combination makes it possible to increase the reliability of protecting the building from destruction and extend its service life.
How to fill expansion joints
If the seam at the base of the structure is installed incorrectly, it may collapse. It is very important to use only high-quality sealants, the elasticity of which is suitable for sealing this kind of seams. The material for the manufacture of such sealants are polymers (butyl rubber, silicone, polyurethane, etc.).
Filling the seam with sealant
The most popular when working on expansion joints is polyurethane sealant, which provides greater endurance and long-term operation of insulated structures. The cost of this material differs from other proposals, but it is worth it.
Profile adhesion to each other
Preparation for sealing is aimed at cleaning the seam from dust and dirt. This way the treated seam will receive a high-quality and durable coating. Sealants based on polyurethane, in addition to high elasticity, have a high level of adhesion to the surface, are heat-resistant and can withstand temperature fluctuations from -100°C to +100°C.
Expansion joints for foundations
Expansion joints for the foundation
The foundation of any building of any size is the main load-bearing structure, which bears the entire mass of the building. That is why its quality has always been considered one of the most important features in construction. When constructing a foundation, the concept of expansion joints deserves special attention. These are specially constructed places that protect the foundation from movements of the earth’s crust and from temperature fluctuations. They are most commonly used for buildings that are being built in seismically hazardous areas. As for the type of foundation, an expansion joint is most often used with the strip type. Today, there are several types of such seams: temperature, sedimentary, seismic and shrinkage. The specific type of device directly depends on the quality of the soil on which the house stands and on the temperature conditions of the external environment.
Seismic joints between foundations are usually installed in potentially seismically hazardous areas. Their presence can prevent, to some extent, the vibration of the earth’s crust and prevent the foundation and walls of the house from cracking. To arrange them correctly, first of all it is necessary to divide the foundation into several cubes with identical sides. It is along all the edges of these conditional cubes that the seams should be made. Moreover, they should look like small compartments, reliably protected by waterproofing materials from moisture and temperature. It is advisable to install sedimentary joints for the foundations of buildings that will have a variable number of storeys. Indeed, in this case, the part of the building with fewer floors will put less pressure on the foundation than the part with more floors. And the seams are able to even out such a load. In addition, their installation can compensate for problems that arise in the event of soil settlement. The principle of the device is that both the foundation and the building itself are divided into certain units. In this case, each node must be protected by a seam. Accordingly, they need to be installed on the slab of the building. Although this will take more materials and time, in the future a high-quality expansion joint will greatly reduce the likelihood of wall cracking.
Temperature expansion joints between the foundation are best installed in areas that have a very changeable climate. That is, temperature will have a strong impact on the quality of the structure. This applies to both cold and hot climates. Based on the technology for installing expansion joints, the entire building is divided into certain square compartments, the size of which is determined by calculations. It is most convenient to do this on a stove, where the measurements will be clearer. This takes into account the geographical location, seismic conditions of the area, the dimensions of the building and the depth of soil freezing. And although such seams are usually not made on foundations, experienced builders believe that it is better to do them anyway, since the depth of freezing can vary significantly in different periods. But as for shrinkage joints, it is advisable to use them for foundations and buildings in the construction of which there is a large amount of concrete, especially if it is poured over a monolithic foundation frame.
This can be explained very easily. After all, over time, concrete tends to release moisture, thereby decreasing slightly in size. But even a slight decrease can lead to large deformations and the appearance of cracks in the foundation and walls. Therefore, their installation is mandatory in places where a lot of concrete is used.
But meanwhile, builders consider the best option to combine temperature and shrinkage type seams. This option gives the best effect, moreover, their device is considered the simplest. A combination of these types can be used for buildings of any number of floors and for any type of foundation.
RULES FOR CONSTRUCTION OF EXPANSION JOINTS
Let us now consider the basic rules for arranging any type of such seams. First, make a preliminary calculation with a surveyor, on the basis of which you can determine the exact amount required for the foundation of your house. Then get to work on the device. Please keep these basic rules in mind:
The height of any seam must correspond to the full height of the foundation. It is forbidden to make it smaller than the foundation. The horizontal distance between the seams is determined from calculations. The optimal average option is considered to be: 60 meters, if the walls in the house are supposed to be built of wood; 15 meters if you plan to make brick walls of the house.
With all this, it is still very important to take into account the heaving of the soil. So, for highly heaving soil, a distance of 15 meters between the joints is considered ideal, and for slightly heaving soil - about 30 meters.
Be sure to consider the structure of the building. If you are planning to build a large house that will have at least one extension, then do not neglect additional seams at the corner borders. As for the width of the seams, on average it is 10-12 cm. This is usually a constant figure. Seams must be made both in the foundation strip and in the foundation slab itself (depending on the type of foundation). In this case, it is best to choose tarred tow for a slab foundation as insulation and waterproofing. And for a strip foundation it is better to buy separately waterproofing material and special insulation. Don't forget about the blind area. Only here a prerequisite is the presence of a wooden slat filled with bitumen. If the space is large, you can use several of these slats, the distance between which should be no more than 2 meters. The presence of a seam between the blind area and the base of the foundation is not necessary if a sufficiently thick layer of material with high waterproofing and thermal properties has already been laid on the base slab of the future house.
Such tips are designed for making any types of seams, as they are general and universal. When performing the work, you will only need to take into account the characteristics of the soil and the building, but still adhere to the same tips. Completing them will make the foundation of your future home as strong as possible. At the same time, the house will serve you for a long time without causing major problems.
Expansion joint in the foundation: types and their structure
A seismic expansion joint in foundations is created in an area that is subject to earthquakes of varying strengths. Thanks to the construction of expansion joints, it is possible to minimize the consequences of shocks to the earth's surface.
When constructing them, the foundation is conventionally divided into separate cubes with identical sides. The expansion joint of the foundation is made along the edges of these cubes. Once organized, the structure appears divided into compartments. To protect against the harmful effects of ambient temperature, the seams are covered with waterproofing materials.
A popular option in construction among expansion joints is the sedimentary type. This type is relevant for buildings with variable number of storeys. As the number of floors increases, the load on the foundation will increase and it will experience subsidence into the ground. Thanks to the presence of special seams, the structure will not crack and will maintain its integrity.
Such a seam represents a division of the foundation into several nodes. Each seam must be protected by a special design unit. Arranging a sedimentary joint will require additional funds and take significant time - but in the future you do not have to worry about the integrity of the walls.