Greenhouse on wooden beams
A greenhouse eventually appears on every private plot, if there is at least a little free space. The main thing in greenhouses is the accumulation of heat from the sun's rays; most often the walls and roof are built from polycarbonate. The use of heat-resistant plastic materials leads to a low weight of the structure, which makes it possible to make a foundation for the greenhouse from timber. This method of construction is the simplest, most economical, making it possible to quickly create a greenhouse.
Functions, requirements, features of the foundation
Due to the fact that greenhouses are lightweight and do not sag under their own weight, many people think that it is not necessary to build a foundation. This belief leads to the instability and fragility of greenhouses.
Advantages:
- The walls of the greenhouse, attached to the base, can withstand stronger side winds due to the even distribution of loads.
- An air or sand layer between the ground and the floor serves as thermal insulation, minimizing the heat that goes into the ground by 10-15%.
- Protection against underground pests - insects, rodents, as well as bacterial plant diseases that can come from open ground.
- Preventing the greenhouse from getting cold or increasing humidity during heavy rainfall.
Foundation requirements:
- Strength. The more stable the support of the greenhouse, the longer the service life and the less likelihood of breakdowns and destruction in the off-season.
- Resistance of materials to aggressive environmental influences; if low quality raw materials are selected, or not suitable for wet and cold exposure, the greenhouse will turn out to be unreliable, with a maximum service life of 2-3 seasons.
- The design corresponds to the structure being built; to avoid deformation of plastic sheets and load-bearing floors, the support must have technical characteristics suitable for the greenhouse.
Portable greenhouse made of polycarbonate, on a wooden base.
A timber foundation meets all the requirements for greenhouses built from lightweight materials.
Economical and easy to install or move, it requires certain preventive actions, otherwise it will quickly collapse.
Timber foundation for a greenhouse
A timber foundation for a greenhouse is the simplest and cheapest option for constructing a foundation. However, despite its simplicity, it extremely reliably performs the task of distributing the weight of the greenhouse over as large a surface as possible.
Also, a foundation made of timber will serve as a kind of “anchor” that will not allow your greenhouse to fly away to a neighboring area at the first gust of wind. A wooden foundation is a good barrier to prevent heat leakage from the greenhouse premises and, vice versa, cold penetration from the ground during spring frosts.
Also, a wooden foundation, especially one deepened into the ground, will not allow a variety of field rodents to get close to greenhouse plants.
Let us consider in detail the procedure for constructing a timber foundation for a greenhouse with our own hands and the materials and tools used.
Advantages, disadvantages of wooden supports
On a wooden base, you can build both small greenhouses, used for beds and flower beds, which are easy to move without disassembling, and large stationary greenhouses. It is necessary to analyze the advantages of timber-based greenhouses.
The main advantages of lumber:
- low price compared to other building materials;
- speed of assembly and dismantling;
- mobility of small structures;
- availability of materials and basis for repairs;
- simplicity in calculations and construction;
- the ability to move the greenhouse to maintain crop rotation;
- spring cultivation of seedlings, after which the greenhouse is dismantled or transferred to the next section of the garden;
- does not emit toxic compounds that affect grown plants.
Despite all the positive aspects of a wooden support, it has a number of disadvantages that affect the construction and use of finished greenhouses. Such greenhouses require special protective measures against fungal infections of wood, insects that feed on wood fibers, as well as insulation from moisture, which causes rotting of the material.
If the wood is not treated with the necessary additives, this can affect the crops being grown, spreading pathogens among them, or poisoning the air in the greenhouse with their waste products, which will lead to a slowdown in growth, or the accumulation of toxic compounds in the fruits.
Timber foundation for a greenhouse
A timber foundation for a greenhouse is the simplest and cheapest option for constructing a foundation. However, despite its simplicity, it extremely reliably performs the task of distributing the weight of the greenhouse over as large a surface as possible.
Also, a foundation made of timber will serve as a kind of “anchor” that will not allow your greenhouse to fly away to a neighboring area at the first gust of wind. A wooden foundation is a good barrier to prevent heat leakage from the greenhouse premises and, vice versa, cold penetration from the ground during spring frosts.
Also, a wooden foundation, especially one deepened into the ground, will not allow a variety of field rodents to get close to greenhouse plants.
Let us consider in detail the procedure for constructing a timber foundation for a greenhouse with our own hands and the materials and tools used.
Types of wooden bases
The foundation for a greenhouse is made of timber of the strip type. Differences arise due to the adaptation of the base to different types of soil, which affects the depth of installation and additional supports.
The recessed strip base is used for greenhouses built on soils with low moisture content, rocky or sandy, with deep groundwater.
Raised foundation due to soil moisture
If a strip foundation on supports is used, then the base is raised above the ground, and waterproofing material is placed under the non-buried supports. This type also includes a wooden grillage mounted on piles. It is used on flooded or unstable soils.
Combined strip base, this type of construction is used for difficult terrain building areas, when part of the greenhouse is located below the soil level, and the other is raised by supports. Thanks to this construction, the greenhouse has a horizontal floor.
Protection of timber from damage
The timber in the greenhouse is in contact with soil and water, so certain protective measures are required to ensure that it lasts a long time. Thus, the main destroyers of wooden supports are insects, rotting, and fungal colonies. In order to secure the foundation, you can use both special industrial and home-made impregnations. The better the substance is suitable, the less often repair work will be required.
Of the factory ones, non-washable antiseptics are most suitable for treating greenhouses for outdoor use. Non-washable impregnations are used when wooden supports are exposed to aggressive environmental influences. Due to their composition, they remain in the wood and prevent mold and rot from appearing. Antiseptics for external use penetrate into the timber to a shallow depth, which is why if the top layer is damaged, fungus and mold may appear in scratches, which will spread under the treated layer.
For self-made protection, copper sulfate, used machine oil or firing and coating with bitumen are used.
The simplest homemade impregnation is a solution of copper sulfate, with the proportions of substance and water 1 to 100. You can apply it after the powder has completely dissolved; for this, the liquid is heated to 40-45 °C.
Mastic coated base
Used engine oil must be heated before being applied to the wooden frame. This method can be dangerous due to the substance getting into the products grown in the greenhouse, which will lead to deterioration of the harvest and harm to health.
Burn the base with a gas burner until charred. After completion of the heat treatment, bitumen or bitumen mastic is applied to all surfaces in 2-3 layers.
Once the wood is soaked, it must be allowed to dry completely before continuing with construction work. It is very important to cover the places where the greenhouse walls are attached to the base so that moisture does not get through them. This can be done either with bitumen or silicone sealant.
Recessed option
A greenhouse or greenhouse is built on a wooden foundation even if it is necessary to grow vegetables and seedlings in the winter. It is usually buried 1 meter. This makes it possible to save on resources, taking advantage of the warmth of the earth. Despite the fact that the area of the walls transmitting light is reduced, this option allows you to save fuel.
The technology of the polycarbonate surface version differs not only in the design of the frame, but as for the base, it is created much more powerful. Using logs or semi-tips, semi-logs. Having removed the bark and carried out pre-treatment.
In these basics, the work goes like this:
- They excavate the soil to a given depth and level the walls. Lay a waterproofing layer of roofing felt on the outer wall.
- Drive the pointed end of the log into the ground around the perimeter. Pre-treating them with bitumen or mastic.
- Along the lower and upper parts of the finished log walls, staples 40-50 cm long are driven in and tightened.
- Level the top edge using a chainsaw. Then they place the top beam, screwing it to the ends of the logs.
- They compact the base near the pillars.
Tip: Every 5th log should be 50-60 cm longer than ordinary ones. For example, the burial height is 1000 mm. The row post is 1400 mm long, and the corner and intermediate post is 1800 mm long.
To build greenhouses made of wood or polycarbonate, you can use any of these technologies. The main thing is to determine the direction and purpose of the greenhouse. And to build a base from wood means choosing the optimal ratio of price and service life.
Making your own wooden foundation
In order to create a timber foundation for a greenhouse with your own hands, you need to select a construction site and create a plan that will indicate the size of the greenhouse and the depth of the base. After planning, preparatory work begins. In the selected area, the top layer of soil containing plant roots is removed, after which they begin to mark the territory.
For marking, use pegs stuck in the corners of the future structure and a cord stretched between them. The most important thing at this stage is to check how correctly the stakes are installed. The cord should form right angles. If the proportions are not maintained, then the beams will not be able to be connected, this will lead to the redoing of all earthworks, or the calculations of the greenhouse will have to be completely changed, which will reduce its reliability.
Ready trench for filling sand
The second preparatory stage is the excavation of the soil, which occurs in two ways, depending on the cost of construction. For a better foundation, it is necessary to create a pit 10-15 cm deep, which will be filled with sand. Trenches must be dug under the timber, deepened by another 15 cm. A cheaper method is to dig a trench 15-20 cm deep and 7-10 cm wide, into which the timber is laid, and the sand floor is not created or is no more than 5 cm thick .
A 5 cm layer of sand is poured into the dug trench and compacted. The finished sand cushion is checked with a level for horizontality; the difference between the two angles should not exceed 3 mm, otherwise the base will lie unevenly, which will lead to warping of the greenhouse, the formation of cracks and drafts. This situation will require frequent repair work due to breakdowns. After this, you can begin laying and securing lumber.
Laying beams
Prepared beams are laid on the prepared bottom, checked to see if the trench fits exactly and whether any changes are needed. At the next stages it will be difficult to produce them. If all is well, the base is fastened together. When the greenhouse base has a large area, internal crossbars that do not protrude from the ground are used to impart rigidity to the structure. You can watch the workflow for assembling the foundation in the video. There are three methods of fastening:
- simply attaching one end to the other and screwing screws into the side is the easiest and most unreliable method;
- half-wood connection, when a section of half its height is removed from the end of the beam and made with the width of the second lumber, on which the same is done, only in a mirror form, after which the halves are placed on top of each other and secured with self-tapping screws;
- The most reliable method of fastening “into the paw” is when a piece is cut at the bottom at a downward angle to the edge of the block being applied, and an acute angle is made at the top.
Type of fastening “in the paw”
After adjusting all the beams, they must be fastened with corners mounted on screws or nails. To prevent moisture from entering, the attachment points must be treated with mastic. The finished frame is placed in a trench, covered with sand on the sides, and the backfill is compacted well. If the base is created on a sand cushion, then before filling the floor, you need to lay geotextiles.
To preserve the wood, some craftsmen recommend laying roofing material in the hole, which is wrapped around it after laying the beams. This is a dubious method of protection, which does not completely protect even from moisture, since it has open joints. It also does not prevent the development of mold and mildew, so it is better to spend more time on waterproofing, but get a reliable base.
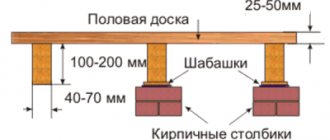
If you plan to partially or completely build the greenhouse on stilts, then you will need a beam of a larger cross-section, with mandatory partitions supporting the floor. It may be suitable to mount shields on a wooden grillage that will hold the sand poured inside. This will serve as support for the floor and insulate against moisture and heat loss. It is advisable to do this when the greenhouse rises above the ground by 20-25 cm maximum. If the difference is greater, sand is not poured, but shields are mounted so that the floor of the greenhouse is not blown with cold air, cooling the entire structure.
Timber for building a foundation is a popular material, easy to install, and does not require specific knowledge or additional costs for building materials. Due to its properties, greenhouses built on it have more functions and capabilities than heavier ones built on stationary supports.