TICKET No. 1
1. Scope of safety regulations for the operation of electrical installations
Safety rules for the operation of electrical installations apply to employees of organizations, regardless of ownership and organizational and legal forms, engaged in the maintenance of electrical installations, performing adjustment, repair work, testing and measurements.
The rules apply only to existing electrical installations.
Parts of electrical installations to be grounded, grounding installation
Parts to be grounded or grounded include:
Housings of electrical machines, transformers, apparatus, lamps, etc.;
Drives of electrical devices;
Secondary windings of instrument transformers;
Frames of distribution boards, panels and control cabinets;
Metal sheaths of power cables, steel electrical wiring pipes and other metal structures associated with the installation of electrical equipment;
Metal cases of mobile and portable electrical receivers.
Grounding installation
1 It is necessary to install grounding connections on live parts immediately after checking the absence of voltage.
2 Portable grounding must first be connected to a grounding device, and then, after checking that there is no voltage, installed on live parts.
The portable grounding must be removed in the reverse order: first remove it from live parts, and then disconnect it from the grounding device.
3 Installation and removal of portable grounding connections in electrical installations with voltages above 1000V must be carried out wearing dielectric gloves using an insulating rod. The portable grounding clamps should be secured with the same rod or directly with hands wearing dielectric gloves.
4 It is not allowed to use conductors for grounding that are not intended for this purpose.
Requirements for the table for commissioning work
Must be made of non-conductive material (wood, plastic, etc.).
There must be shelves to accommodate instrumentation and power supplies;
Must be equipped with a separate electrical panel with a general switch, fuses, warning lamp or voltmeter, recessed plug sockets and protective grounding;
It is strictly forbidden to make a metal edging of the working surface of the table, made of dielectric material, to avoid touch voltage in the event of an insulation breakdown or malfunction of the grounding conductors (breakage more than 5%, poor contact).
What should a person providing assistance to a victim know and be able to do?
Must know:
The main signs of a violation of the vital functions of the human body;
General principles of first aid and its techniques in relation to the nature of the injury received by the victim;
Basic methods of carrying and evacuating victims.
Should be able to:
Assess the condition of the victim;
Determine the sequence of first aid;
Perform artificial respiration and chest compressions;
Stop bleeding by applying a tourniquet, a pressure bandage, or pressing the vessels with a finger;
Apply a bandage to a wound, burn, or bruise;
Immobilize (create rest) the injured part of the body;
Provide assistance with heat stroke, sunstroke, etc.
TICKET No. 2
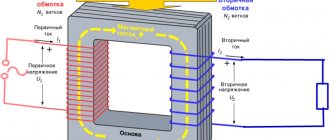
What electrical installations are called active?
Operating electrical installations are considered to be those installations that contain sources of electricity (chemical, galvanic and semiconductor elements) that are fully or partially energized, or which can be energized at any time by turning on switching equipment.
Current and voltage levels dangerous to life. Step voltage.
The amount of current dangerous to humans is 50 mA or more.
The magnitude of the current lethal to humans is 0.1 A.
The AC voltage is 50 V or more.
The DC voltage is 120V or more.
Step voltage is the voltage between two points on the surface of the earth, at a distance of 1 meter from one another, which is taken to be equal to the length of a person’s step. It is caused by the spread of electric current over the surface of the earth or a conductive floor in the event of a single-phase wire ground fault. The magnitude of this voltage depends on the step width, soil resistivity and the location of the person (the closer the person is to the fault point, the greater the voltage). The wider the step, the more current flows along the leg-to-leg path.
When you come under step pressure, convulsive involuntary muscle contractions occur and, as a result, a person falls to the ground. The current begins to pass along a new path, more dangerous (for example, an arm-leg), which is fraught with death.
To protect against step voltage, additional protective equipment is used - dielectric boots, mats. In cases where the use of these means is not possible, you should leave the danger zone with a “goose step” - the heel of the walking leg, without leaving the ground, is placed against the toe of the other leg.
It is also safe to move on dry boards and other non-conductive objects.
If the victim himself cannot leave the danger zone, he should
remove by isolating the feet and boots using rubber boots, dry woolen cloth, etc.
Voltage over 50 V is life-threatening, and under unfavorable conditions - 12 V (humidity, etc.). Dangerous current 0.05A (50 mA). The degree of electric shock is influenced by a person’s electrical resistance, contact area, type of current, its frequency, flow path, duration of exposure, as well as air humidity, skin condition and well-being.
Electrical protection means on rolling stock and requirements for them.
These include: dielectric gloves, pliers with insulated jaws, shorting. All of them must have a tool mark and a stamp indicating the expiration date and permissible voltage.
Short-circuit
must have the mark of the tool depot and the numbering assigned to this composition. A flexible cable with a cross-section of at least 16-25 mm 2 must be well tinned and soldered at the ends. The clamp screws must move freely along the threads. Breakage of no more than 5% of the cores of a flexible cable is allowed.
Before using dielectric gloves
it is necessary to clean them from dirt and dust, check for punctures by twisting them towards the fingers, and check on the stamp whether the periodic test period has expired. Gloves must be replaced several days before the next test date indicated on the stamp. This is due to the fact that some trains remain overnight on the line, without the possibility of changing gloves. It is prohibited to use gloves with external damage, punctures or expired periodic testing.
When using gloves, they must be worn over the sleeves without tucking them up. Their length must be at least 35 cm. Dielectric gloves are tested once every 6 months with a voltage of 6 kV for 1 minute (produced in the electrical measurement laboratory of the Electricity Supply Service).
Wearing gloves should be carried out: replacing VTsVn fuses, red headlight lamps, installing and turning the reversing handle in the switchgear and setting the short circuit.
Pliers with isolated jaws are inspected visually to check their functionality.
Often, electric shock occurs due to the fact that the rules for working with high voltage are violated or a person does not know how to properly handle electrical appliances. In any case, the main reason is human carelessness.
How can current affect the human body?
Electric current can instantly spread upon contact throughout the body. In order for it to pass through the body, it needs an “entry” place, and then the current, passing through the entire body, has an irritating effect on it. For example, the effect of current on the human body is divided into several types:
- Thermal, when you get a burn.
- Mechanical, when soft tissue ruptures.
- Chemical is directly electrolysis itself.
As a result of an electric shock, a person’s muscles may involuntarily contract, breathing may be paralyzed, and the heart may stop.
What voltage is considered dangerous for humans?
If a person is in a dry room, then the voltage for him is dangerous, which turns out to be over 36 volts. Death can occur with a shock of 0.1 ampere. A current of 0.05 amperes is also dangerous to life. The fact is that with such a current strength, convulsions occur that do not allow you to move away from the source of the lesion.
If we are talking about static electricity, then such electricity does not pose a danger to human life. The maximum that the human body can feel from the impact of a spark discharge is an injection. Alternating current poses a great danger. Dangerous voltage for humans is over 50 V, and under unfavorable conditions (humidity, for example) – over 12 V. Dangerous current – 50 mA. It is the current of this force that can cause damage, and its effect on the human body within 5 seconds can become fatal.
Difference between direct and alternating current
According to the school physics course, electric current is the directed movement of charged particles. In metal wires these are free electrons, but in the human body, which is 55-70% water, this role is played by ions of various elements, mainly table salt.
There are two types of electric current:
- Alternating current (from the English Alternative Current - AC). The direction of movement of electrons in the wires and the polarity at the terminals changes periodically.
- Direct current (from the English Direct Current - DC). Its peculiarity is that the polarity and direction of movement of the electrons remain unchanged.
At the beginning of the twentieth century, there was much debate between proponents of constant and alternating voltage. The AC concept won. It is easier to transfer it from the power plant to the consumer, to change the voltage value, and AC electric motors are simpler and cheaper.
Despite the fact that the magnitude of the alternating voltage with a frequency of 50 Hz rises to a maximum and decreases to “0” 100 times per second, incandescent lamps shine with an even light.
This is due to the fact that the eye does not notice such a flickering frequency, and the heated filament does not have time to cool, which reduces their amplitude. LED and energy-saving light bulbs are powered by a built-in driver (power supply), which eliminates fluctuations in luminosity.
Factors that affect the body during electric shock
It is necessary to take into account not only the strength of the electric shock, but also what path it will take through the body. It is worth remembering that the longer the current path through the human body, the more severe the consequences will be. As we have already said, alternating current is considered life-threatening; direct current does not have such a destructive effect on the human body. There are a number of additional factors that may increase the danger:
- High current strength.
- Passing it through the body. It should be noted that different tissues of the body have different resistance abilities; in most cases, the current passes through the blood vessels. The worst thing is when the path of the current runs along the entire body, for example, this can happen if the arm and legs are involved, then the current can pass through the heart, spinal cord or brain. But sometimes death can occur when current passes from hand to hand, it all depends on how high the dangerous voltage was.
- Exposure time. The time interval allowed for exposure to current should not exceed 2 seconds.
- Conductivity.
- The area where the electric shock occurs.
It is impossible to calculate exactly how the current will affect the body. Human attention plays an important role, therefore, in dangerous places, it is necessary to provide a special safety sign, which is called the “high voltage” sign.
Why is this or that current dangerous?
The severity of damage to the human body depends on many factors:
- Current and voltage;
- Duration of exposure;
- Type of current and frequency;
- The resistance of the human body is a variable value, depending on many factors.
Various injuries due to electric shock are caused by the nature of the movement of particles: alternating causes chaotic convulsions of internal organs, constant – heating, burns, destruction of body tissues.
Current and voltage
An important parameter that determines the danger of injury is the current strength. An alternating current of 10–15 mA and above is considered dangerous, and a constant current of 50–80 mA.
You may be interested in: Formulation and definition of Ohm's law
For humans, alternating current is more dangerous than direct current at the voltages that people most often encounter in everyday life. A direct electric shock occurs at a voltage of 120 V; for alternating current, a similar shock occurs at U = 42 V.
At high voltages (500 V and above), direct current poses the same danger to the body as alternating current. At a higher U, it becomes even more dangerous to humans.
Ammeter measurement
Damage duration
With increasing exposure time, the epidermis is destroyed at the site of contact, the resistance of the human body decreases, and the strength of the flowing electric current increases. Increased sweating at this moment can reduce resistance tenfold. Prolonged contact with electricity causes the accumulation of negative effects on body tissues.
Human body resistance
The law of physics says: the higher the resistance, the lower the current in the circuit. The condition of the epidermis largely determines the amount of general resistance of the human body (up to 90%). Intact, dry, rough skin has dielectric properties. The resistivity of the human body in this case is 40,000–100,000 Ohms.
Reasons for reducing the resistance of the human body
The value is not constant. Depends on the area of influence and density of contact, the duration of current passage through the body. The thickness of the skin is important - in women and children it is thinner and is more susceptible to damage.
Reasons for decreased resistance:
- High temperature, sweating;
- Damage to the epidermis;
- Increased humidity in the room.
Important! Persons who are intoxicated are at particular risk of electrocution due to a sharp drop in resistance.
Current type and frequency
The number of pole oscillations in a power supply network is called frequency. In Russia and the CIS countries, the standard value is 50 Hz, which means that every second the direction of the alternating current changes 50 times. This unit of measurement has nothing to do with direct electric current; electrons move in one direction.
Reference! The greatest danger is caused by lesions with frequencies in the range from 50 to 500 Hz.
Frequency 50 Hz
At a frequency above 20 kHz, thanks to the skin effect, alternating current does not cause harm to a person, passing over the surface of the skin and without penetrating into the body. Nikola Tesla proved this experimentally by touching electrodes with his bare hands with a potential of 100 kV with a frequency of 100 kHz.
You may be interested in this Features of the ripple coefficient
What role does body resistance play?
The resistance of the body depends on the condition of its skin; the following factors can have an influence:
- What condition is a person’s skin in? For example, it can be clean, it can be dirty, wet, damaged.
- What was the area of contact of the current with the skin?
- The magnitude of the applied voltage.
- What frequency current passed through the body.
- General condition of the human nervous system.
If the skin has been scratched or abraded, the dangerous stress may be minimal for death to occur because the body's resistance is reduced. The ability to resist is lost in a person who has a sweaty or dirty hand. For example, a voltage of 30 volts with dry hands does not cause severe pain, but if you touch it with a wet hand, a person will not be able to unclench his fingers and will feel severe pain. In such cases, it is customary to say that a breakdown of skin resistance has occurred.
Skin resistance can decrease even when a low voltage is applied, 20-40 volts.
What voltage is considered acceptable?
Statistics indicate that most electrical injuries occur as a result of touching There are three safe voltages:
- In rooms where there is no increased danger, 65 volts are allowed.
- In a room where there is danger - 36 volts.
- In high-risk areas - 12 volts.
In premises of the second and third types there must be a “high voltage” sign, which will warn of danger. Often, injuries occur to employees who, by the nature of their employment, are required to work with voltages up to 1000 V, but neglect safety precautions and do not use protective equipment.
The answer to the question of what voltage is considered dangerous can be quite simple: any electric shock can cause damage, but the most dangerous is considered to be voltage from 60 V, when respiratory paralysis and cardiac arrest can occur. But this may not happen if you pay close attention to everything that surrounds a person and in some way relates to electricity. Personnel who work with high voltage and electric current must always remember safety rules and be on high alert.
So, from this article you learned what voltage is life-threatening. We hope you find this information useful.
Testing knowledge of the Rules. Types of checks. Frequency of inspections Testing the knowledge of employees is divided into primary and periodic (regular and extraordinary). An initial knowledge test is carried out for workers who first entered a job related to the maintenance of electrical installations, or if there is a break in knowledge testing for more than 3 years; next - in the order established in clause 1.4.20; and extraordinary - in the manner established in clause 1.4.23. The next inspection must be carried out within the following periods: - for electrical personnel directly organizing and carrying out work on servicing existing electrical installations or performing adjustment, electrical installation, repair work or preventive tests in them, as well as for personnel who have the right to issue orders, orders, conduct operational negotiations - once a year; — for administrative and technical personnel not belonging to the previous group, as well as for labor protection specialists authorized to inspect electrical installations — once every 3 years. The time of the next test is set in accordance with the date of the last knowledge test. For employees who receive an unsatisfactory assessment during the next knowledge test, the commission assigns a repeat test no later than 1 month from the date of the last test. The validity of the certificate for an employee who has received an unsatisfactory assessment is automatically extended until the period appointed by the commission for the second inspection, unless there is a special decision of the commission recorded in the knowledge test log on the temporary suspension of the employee from working in electrical installations. An extraordinary knowledge test is carried out regardless of the period of the previous test: - when new or revised rules and regulations are introduced into the consumer; — when installing new equipment, reconstructing or changing the main electrical and technological circuits; - upon appointment or transfer to another job, if new responsibilities require additional knowledge of rules and regulations; — in case of violation by employees of the requirements of regulations on labor protection; — at the request of state supervisory authorities; — according to the conclusion of commissions that investigated accidents with people or disruptions in the operation of an energy facility; - when increasing knowledge to a higher group; — when testing knowledge after receiving an unsatisfactory grade; - if there is a break in work in this position for more than 6 months.
Question 2: When is it necessary to immediately turn off the electric motor?
The electric motor must be immediately (emergency) disconnected from the network in the following cases: 1) in case of accidents with people; 2) when smoke and fire appear from the electric motor, as well as from its ballasts and excitation devices; 3) failure of the drive mechanism, the appearance of an abnormal knock; 4) a sharp increase in vibration of the unit bearings; 5) heating of bearings above the permissible temperature established in the manufacturer’s instructions.
Question 3. What voltage is considered dangerous to human life?
There is still no established point of view regarding the amount of “permissible” or “safe” voltage, since human electrical resistance varies widely depending on specific conditions. Therefore, different countries regulate their own standards. For example, in France the standard is 24V for AC and 50V for DC. In our practice, depending on the environmental conditions, the permissible voltage is up to 50V AC. However, these voltages cannot be considered as providing complete safety. For example, the literature describes cases of fatal injury to a person with voltages of 12V and below. The dangerous value of current flowing through the human body should be considered 10 mA, lethal - 100 mA.
What is touch voltage
The benefits of electricity can hardly be overestimated - it is the source of “life” for almost everything that surrounds us, from basic lighting to the operation of powerful technological equipment. However, electricity poses a serious threat to humans, because electric shocks can cause:
- pain;
- body burns;
- death of a person.
Electrical safety deals with the issues of limiting human interaction with electricity, or more precisely with its dangerous consequences; among its terminology you can find such a thing as touch voltage - let’s try to figure out what it is.
The essence and danger of touch tension
In fact, this term is considered to be voltage, characterized by the potential difference between two points that are accessible when simultaneously touched by a person and form an electrical circuit. In our case, this is a piece of ground underfoot and part of the body of electrical equipment (electrical installation) with which there is contact. The concept of touch voltage must be considered taking into account:
- step voltages;
- current spreading zones.
These definitions allow us to conclude that the highest value of the touch voltage (magnitude of the damage current) will correspond to the maximum possible distance due to accidental touch.
State standard GOST 12.1.038-82 regulates the values of permissible touch voltage, provided their total daily exposure to a person is no more than 10 minutes:
- 2 V for AC 50 Hz;
- 3 V for AC 400 Hz;
- 8V for DC.
The photo shows the reading of the measuring device, 121 volts, between the grounded outlet and the body of the refrigerator, which is plugged into an ungrounded outlet.
Higher voltage drops are generally considered harmful.
Ways to protect against touch voltage
The main protection against electric shock is reliable electrical insulation of wires. If a person accidentally touches live parts, the greatest electric current will flow through his body, equal to the quotient of the voltage divided by the body resistance. With proper insulation, its resistance is at least 1 mOhm (for circuits up to 1000 V) and 0.5 mOhm (220/380 V).
Considering that the value of the insulation resistance connected in series with the human resistance is disproportionately higher, it limits the currents flowing through the human body to safe values, almost equal to zero. The insulation of live parts must be regularly checked for compliance with standards; resistance measurements are made with a megohmmeter.
An effective remedy is protective grounding, with a resistance of the transition contacts not exceeding 0.01 Ohm. The connection between the AC electrical installation and the ground must be provided by a welded or bolted connection.
For TN-CS or TN-S grounding systems, an effective protection measure is the use of residual current devices or differential circuit breakers. Other methods of protection against touch voltage include:
- location of dangerous equipment at an inaccessible height;
- installation of protective barriers in hazardous areas;
- equipped with a warning alarm;
- use of posters and signs.
An important point is the mandatory use of personal protective equipment.
See also other articles:
Why is grounding needed?
Voltage itself does not pose a danger to human life - you can be under the potential without harm to health, the threat arises when an electric current passes through the human body. A current not exceeding 1 milliampere is considered safe, but a current of 50 mA can lead to cardiac arrest.
Read more…
What is RCD used for?
The protective shutdown in the event of the appearance of differential currents equal to the leakage current is carried out by a residual current device (RCD).
In this case, the controlled leakage current depends on the type of device and can start from 10 mA. The protective device must be installed in series with the input circuit breaker. Read more…