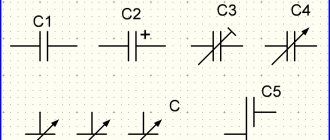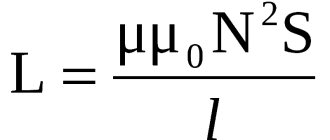What will be the maximum charge of the capacitor?
An oscillating circuit consisting of an inductor and a capacitor is tuned to a wavelength m.
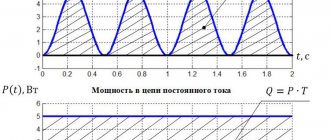
If the maximum current in the circuit I = 0.02 A, then the maximum charge of the capacitor is ———————————————————————————————— ——————- where: — the speed of propagation of the electromagnetic field (as far as I understand in this case in a vacuum) — the inductance of the circuit — the capacitance of the circuit
where: I is the maximum current in the circuit w is the cyclic frequency q is the amplitude value of the charge
from formula 1) can be found knowing you can find “q is the amplitude value of the charge” “q is the amplitude value of the charge” this will be the “maximum charge of the capacitor”?
What is Young's modulus ? A tape has a thickness of d=5 µm and a width of b=5 mm. If you hang it from a tape with a length of L=0.7 m.
What is the maximum potential ? What is the maximum potential acquired by a negatively charged metal plate?
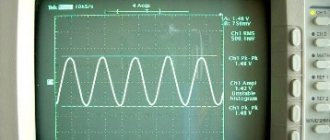
What is the period of oscillation of the particle? Please describe how to solve these problems, I just can’t solve them. Problem 1 Particle doing.
What is the radius of the disk if its oscillation period is 2 s? a disk hangs on a nail driven into the wall so that the hanging point is at a distance of 1/6 of the radius from.
Source
Capacitor
A capacitor is an electronic component designed to store electrical charge. The ability of a capacitor to accumulate electrical charge depends on its main characteristic - capacitance . The capacitance of a capacitor (C) is defined as the ratio of the amount of electrical charge (Q) to voltage (U).
The capacitance of a capacitor is measured in farads (F), a unit named after the British physicist Michael Faraday. A capacitance of one farad (1F) is equal to the amount of charge of one coulomb (1C) creating a voltage across the capacitor of one volt (1V). Recall that one coulomb (1C) is equal to the amount of charge passing through the conductor in one second (1sec) with a current of one ampere (1A).
However, a pendant is a very large amount of charge relative to how much charge most capacitors can store. For this reason, microfarads (µF or uF), nanofarads (nF) and picofarads (pF) are commonly used to measure capacitance.
- 1nF = 0.000000001 = 10-9 F
- 1pF = 0.000000000001 = 10-12 F
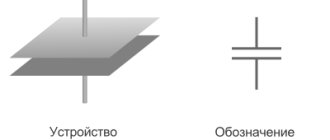
Flat capacitor
There are many types of capacitors with different shapes and internal structures. Let's consider the simplest and most fundamental - a flat capacitor. A flat capacitor consists of two parallel conductor plates (plates), electrically insulated from each other by air or a special dielectric material (for example, paper, glass or mica).
Capacitor charge. Current
In terms of its purpose, a capacitor resembles a battery, but it is still very different in its operating principle, maximum capacity, and charging/discharging speed.
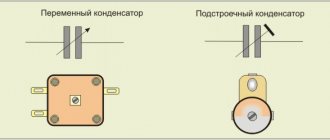
Series and parallel connection of capacitors
A capacitor (from Latin - “seal”) is a passive element designed to accumulate charge in an electrical circuit, consisting of two plates that are separated by a dielectric layer. Capacitance is measured in Farads - F.
Series connection of capacitors
Figure - Series connection of capacitors
When capacitors are connected in series, the voltage is summed, the charges are equal, and the capacity is determined by the formula, that is:
Parallel connection of capacitors
Figure - Parallel connection of capacitors
When connecting capacitors in parallel, the capacitance and charge add up, and the voltages are equal to each other, that is:
The electrical capacity of the capacitor is calculated by the formula:
Formula for the capacitance of a flat capacitor: Formula for the energy of a charged capacitor:
C – electrical capacity, F; q – charge, C; U – voltage between plates, V;