Design Features
To better understand this issue, we should take a closer look at what formed the basis of the presented device. The universal commutator motor type is a direct current device that has series-connected field windings optimized for operation on alternating current of a household electrical power supply network. The motor rotates in one direction, regardless of polarity. This is due to the fact that the stator and rotor windings lead to a simultaneous change in their magnetic poles, and due to this, the resulting torque is directed in one direction.
Brushed and brushless motor
What is the difference between brushed motors and brushless motors, the main advantages and disadvantages of both types.
Brush DC Motors
Electric motors operate due to Lorentz forces, which arise when electric current passes through windings located in a magnetic field. The influence of these forces causes the rotor to rotate around its axis. The torque produced by the Lorentz force is a cross product, which means that when the poles of the electromagnets formed by the rotor windings are aligned with the opposite poles of the stator magnets, the force drops to zero and the rotor stops rotating.
No sensor
To determine the rotor position, it is necessary to measure the voltage on the unused winding.
This method is applicable when the engine is rotating, otherwise it will not work. Sensorless travel controllers are easier to manufacture, which explains their widespread use.
The controllers have the following properties:
- maximum direct current value;
- the value of the maximum operating voltage;
- number of maximum revolutions;
- resistance of power switches;
- pulse frequency.
When connecting the controller, it is important to keep the wires as short as possible. Due to the occurrence of current surges at the start
If the wire is long, errors in determining the rotor position may occur. Therefore, controllers are sold with a 12-16 cm wire.
The controllers have many software settings:
- engine shutdown control;
- soft or hard shutdown;
- braking and smooth shutdown;
- advance power and efficiency;
- soft, hard, fast start;
- current limits;
- gas mode;
- change of direction.
The LB11880 controller shown in the figure contains a high-power brushless motor driver, that is, you can run the motor directly to the chip without additional drivers.
Description of VD
This type of motor was created to improve the properties of DC electric motors. High demands on actuators (in particular, high-speed microdrives for precise positioning) have led to the use of specific DC motors: contactless three-phase DC motors (BLDC or BLDC). Structurally, they resemble synchronous AC motors: a magnetic rotor rotates in a laminated stator with three-phase windings. But speed is a function of load and stator voltage. This function is implemented by switching the stator windings depending on the rotor coordinates. BLDC motors are available in versions with separate sensors on the rotor and without separate sensors. Hall sensors are used as individual sensors. If performed without separate sensors, then the stator windings act as a fixing element. When the magnet rotates, the rotor induces an EMF in the stator windings, resulting in a current. When one winding is turned off, the signal that was induced in it is measured and processed. This algorithm requires a signal processor. To brake and reverse the BDPS, you do not need a power reverse bridge circuit - it is enough to apply control pulses to the stator windings in the reverse sequence.
The main difference between a VD and a synchronous motor is its self-synchronization using the DPR, as a result of which in a VD the field rotation frequency is proportional to the rotor speed.
Stator
Brushless motor stator
The stator is of a traditional design and is similar to the stator of an induction machine. It consists of a housing, a core made of electrical steel and a copper winding laid in grooves along the perimeter of the core. The number of windings determines the number of motor phases. For self-start and rotation, two phases are enough - sine and cosine. Usually the HP is three-phase, less often - four-phase.
Based on the method of laying turns in the stator windings, motors with a reverse electromotive force of trapezoidal (BLDC) and sinusoidal (PMSM) shapes are distinguished. According to the power supply method, the phase electric current in the corresponding types of motor also changes trapezoidally or sinusoidally.
Rotor
The rotor is made using permanent magnets and usually has two to eight pairs of poles with alternating north and south poles.
Initially, ferrite magnets were used to make the rotor. They are common and cheap, but they have the disadvantage of a low level of magnetic induction. Magnets made from rare-earth alloys are now gaining popularity, as they make it possible to obtain a high level of magnetic induction and reduce the size of the rotor.
Rotor position sensor
The rotor position sensor (RPS) provides feedback on the rotor position. Its operation can be based on different principles - photoelectric, inductive, Hall effect, etc. Hall and photoelectric sensors have become most popular, since they are practically inertia-free and allow you to get rid of the delay in the feedback channel on the rotor position.
A photoelectric sensor, in its classic form, contains three stationary photodetectors, which are alternately closed by a curtain rotating synchronously with the rotor. This is shown in Figure 1 (yellow dot). The binary code received from the DPR records six different rotor positions. The sensor signals are converted by the control device into a combination of control voltages that control the power switches, so that in each cycle (phase) of engine operation, two switches are turned on and two of the three armature windings are connected in series to the network. Armature windings U, V, W
located on the stator with a shift of 120° and their beginnings and ends are connected in such a way that when switching the keys, a rotating gradient of magnetic fields is created.
Brushless motor
If in a brushed motor everything comes into action due to mechanics, then in a brushless motor it is pure electronics. Also, the positions of some elements in the structure are swapped. In a commutator motor, the windings were on the rotor and the permanent magnets were on the stator. In a brushless type, permanent magnets are transferred to the rotor, and coils with windings are located on the stator. Also, the rotor and stator can change their positions: there are motor models with an external rotor. There are no brushes and a commutator; instead, a microprocessor (controller) and a cooler are added to cool the system. The microprocessor controls the rotor position, rotation speed, and uniform voltage distribution across the winding coils.
Main types of brushless motor:
External rotor motor type
Rotor and stator arrangement in DigiPro brushless motor
Conclusion:
Undoubtedly, brushless motors are aimed at professional work with a decent load. Despite the high performance of the improved engine type, its only drawback hits the wallet. And before purchasing a tool for this or that engine, first of all you need to ask yourself the question: for what purpose is it needed. Make your choice based on the answer.
How many people - so many opinions. The Greenworks company tries to make high-quality products using different types of engines, so that everyone can choose a tool according to their preferences, functionality and required power for specific tasks, which are unique to each client. That is why, for example, in the “Hand Tools” section you can see one type of unit with brushed and brushless motors. Which is better? The choice is yours!
Source
Device, pros and cons
Electric screwdrivers differ from each other in their power supply principle: there are mains ones with a power supply of 220 volts and portable ones equipped with a battery. In addition, models can be equipped with a striking mechanism. No other fundamental innovations have been introduced over the last decade, with the exception of one – a brushless mechanism.
Brush screwdriver
The most common type - a commutator motor - is installed on most models. Its operating principle is simple: the windings are switched mechanically and in the armature chain. The contacts are a collector, and energy is transferred thanks to spring-loaded brushes.
Strengths:
- old, reliable technology;
- low cost of parts;
- simplicity and clarity of repair.
Flaws:
- collector lead to energy losses, which means lower efficiency;
- occurrence of sparks, heating of the motor;
- interdependence of speed and torque;
- power losses during reverse operation;
- rapid wear;
- loss of speed under load.
The brush motor has many weaknesses, but they can be justified by cheap components and ease of repair - this is a more affordable option.
Brushless screwdriver
With inverter models the situation is the opposite. They are more efficient and more suitable for the job. Advantages:
- the ability to control the rotation speed: the user receives a wide range of settings - the rotation can be adjusted, depending on the nature of the work and the surface being processed.
- the engine does not provide a commutator-brush assembly, which means that the tool will break less often (if it is used correctly), and maintenance will not cause problems due to the simplicity of the design;
- models cope more effectively with increased load caused by high torque;
- battery power, if it is a portable screwdriver, is consumed more economically;
- higher efficiency - brushless motor produces 90%;
- the ability to operate the tool in a hazardous environment: near gas mixtures and flammable substances (the inverter motor operates without a spark);
- the same power is maintained in forward and reverse mode;
- increased load does not lead to a decrease in rotation speed.
Weak sides:
- high price;
- the large size of the body, when compared with brush models, makes it difficult to work at arm's length or penetrate into tight spaces.
When choosing, it is important to pay attention to the type of battery inside the screwdriver. If you think correctly, the tool will serve the owner faithfully for many years without loss of performance.
Selecting the type of electric motor for the mechanism
The lower threshold for choosing between any type of component is the type of application and the cost constraint for the end product. For example, a toy robot aimed at six to eight year olds may require four to nine electric motors. They may be brushed or brushless DC machines or a combination of both.
If the robot performs only basic movements or is part of a toy set, there is no need to use brushless BLDC machines, which are more expensive than their brushed counterparts. The toy or set will likely end up in the trash bin long before the brushes on the electric machine fail.
Typical DC motor drives include motorized toys, appliances, and computer peripherals. They are connected to electric drives of windows, seats and other structures in the cabin due to their low cost and simple execution.
Brushless motors are more versatile, mainly due to their speed and torque savvy. They also come in compact packages, making them viable for a variety of small designs. Typical applications include computer hard drives, mechanical media players, electronically controlled fans, cordless power tools, HVAC and refrigeration units, industrial and manufacturing systems, and CD drives.
The automotive industry uses brushless BLDC machines for electric and hybrid vehicles. These electric motors are essentially synchronous machines with permanent magnets in the rotor. Other unique applications include electric bicycles where motors are mounted in wheels or hubcaps, industrial positioning and control, assembly robots, and linear actuators for valve control.
Choosing the right engine
To select a unit, it is necessary to compare the operating principle and features of brushed and brushless motors.
From left to right: brushed motor and FK 28-12 brushless motor
Collector ones cost less, but develop a low torque rotation speed. They operate on direct current, are light in weight and size, and easy to repair to replace parts. The manifestation of negative quality is revealed when a huge number of revolutions are received. The brushes come into contact with the commutator, causing friction that can damage the mechanism. The performance of the unit is reduced.
Brushes not only require repair due to rapid wear, but can also lead to overheating of the mechanism.
The main advantage of a brushless DC motor is the absence of torque and switching contacts. This means there are no sources of losses, as in permanent magnet motors. Their functions are performed by MOS transistors. Previously, their cost was high, so they were not available. Today the price has become acceptable, and the performance has improved significantly. If there is no radiator in the system, the power is limited to 2.5 to 4 watts, and the operating current is limited to 10 to 30 Amperes. The efficiency of brushless electric motors is very high.
The second advantage is the mechanical settings. The axle is mounted on wide bearings. There are no breaking or abrasive elements in the structure.
Let's consider an example of the mechanics of a CNC machine with a spindle.
Replacing a brushed motor with a brushless one will protect against damage to the CNC spindle. By spindle we mean a shaft that has right and left rotations of torque. The CNC spindle has great power. The torque speed is controlled by a servo tester regulator, and the speed is controlled by an automatic controller. The cost of a CNC with a spindle is about 4 thousand rubles.
Surely every beginner at some point in his passion for RC models has a question: what to choose - a brushed or brushless motor ?
Commutator motors have only two outgoing power wires. One of them is “ + ” and the other is “ - ”. In turn, they are connected to the rotation speed controller. Having disassembled the commutator motor, you will always find 2 curved magnets, a shaft together with an armature on which a copper thread (wire) is wound, where on one side of the shaft there is a gear, and on the other side there is a collector assembled from plates, consisting of which are pure copper.
Operating principle of a commutator motor
Electric current (DC or direct current), entering the armature windings (depending on their number for each in turn), creates an electromagnetic field in them, which has a south pole on one side and a north pole on the other. The electromagnetic field that arises in any of the armature windings, interacting with each of the poles of the stator magnets, causes the armature itself to rotate (rotate). Next, the current passes through the commutator and brushes to the next winding and so sequentially, moving from one armature winding to another, the electric motor shaft rotates together with the armature, but only as long as voltage is applied to it. In a standard commutator motor, the armature has three poles (3 windings) - this is done so that the motor does not “stick” in one position.
Disadvantages of commutator motors
By themselves, commutator motors do a good job of their job, but only until the moment when the need arises to get the highest possible speed from them at the output. It's all about the same brushes mentioned above. Because They are always in close contact with the manifold, then as a result of high speeds, friction occurs at the point of their contact, which will subsequently cause rapid wear of both and subsequently lead to a loss of effective engine power. This is the most significant disadvantage of such motors.
Operating principle of a brushless motor
Here everything is the other way around, the motors lack both brushes and a commutator. The magnets in them are located strictly around the shaft and act as a rotor. Windings, which already have several magnetic poles, are placed around it. A so-called sensor (sensor) is installed on the rotor of brushless motors, which will monitor its position and transmit this information to the processor, which works in conjunction with a rotation speed controller. As a result, we get smoother operation of the motor itself with maximum efficiency.
Brushless motors can be with or without a sensor. It is easy to distinguish them from each other. Motors with a sensor, in addition to 3 thick power wires, also have an additional cable of thin wires that go to the speed controller.
Pros of brushless motors
Almost no wearing parts. Almost, because the rotor shaft is mounted on bearings, which in turn tend to wear out, but their service life is extremely long, and their interchangeability is very simple. Such motors are very reliable and efficient. A rotor position control sensor is installed. On brushed motors, the operation of brushes is always accompanied by sparking, and this fact causes interference in the operation of radio equipment, but with brushless motors, as you already understand, these problems are eliminated. There is no friction, no overheating, and this is also a significant advantage. Compared to commutator motors, they do not require additional maintenance during operation.
Cons of brushless motors
Such motors have only one minus - the price . But if you take into account the fact that the operation of such motors immediately frees the owner from problems in the form of replacing springs, armatures, brushes, commutators, then it makes sense to overpay.
Other comparisons
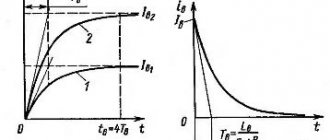
When comparing commutator and asynchronous motors of the same power, regardless of the rated frequency of the latter, different characteristics are obtained. This will be described in more detail below. The universal commutator motor implements a “soft” characteristic. In this case, the torque is directly proportional to the load on the shaft, while the speed is inversely proportional to it. The rated torque is usually 3-5 times less than the maximum. Limiting the idle speed is characterized solely by losses in the engine, and when turning on a powerful unit without load, it can be destroyed.
The characteristic of an asynchronous motor is “fan”, that is, the unit maintains a rotation speed close to the nominal one, increasing the torque as sharply as possible with a slight decrease in speed. If we are talking about a significant change in this indicator, then the engine torque not only does not increase, but also drops to zero, which leads to a complete stop. The idle speed is slightly higher than the nominal speed, but remains constant. A single-phase induction motor has an additional set of starting problems because it does not develop starting torque under normal conditions. The magnetic field of a single-phase stator, pulsating in time, breaks up into two fields with opposite phases, which makes starting impossible without all sorts of tricks:
A container that creates an artificial phase;
Split groove;
Active resistance forming an artificial phase.
Theoretically, a field rotating in antiphase reduces the maximum efficiency of a single-phase asynchronous unit to 50-60% due to losses in the oversaturated magnetic system and windings loaded with counter-field currents. It turns out that there are two electric machines on one shaft, one operating in motor mode, and the second in counter-switching mode. It turns out that single-phase commutator electric motors do not know competitors in the corresponding networks. This is what earned them such high popularity.
The mechanical characteristics of the electric motor provide it with a specific scope of use. Low speeds, limited by the frequency of the alternating current network, make asynchronous units of similar power larger in weight and size compared to universal collector ones. However, when a high-frequency inverter is connected to the power supply circuit, comparable dimensions and weight can be achieved. The rigidity of the mechanical characteristics of the electric motor remains, to which losses due to current conversion are added, as well as an increase in frequency, magnetic and inductive losses increase.
Operating principle of VD
The operating principle of the HP is based on the fact that the HP controller switches the stator windings so that the stator magnetic field vector is always orthogonal to the rotor magnetic field vector. Using pulse width modulation (PWM), the controller controls the current flowing through the HP windings, i.e. vector of the stator magnetic field, and thus regulates the torque acting on the HP rotor. The sign of the angle between the vectors determines the direction of the moment acting on the rotor.
Switching is carried out in such a way that the rotor excitation flux is Ф 0
is maintained constant relative to the armature flux.
As a result of the interaction of the armature flux and excitation, a torque M
, which tends to rotate the rotor so that the armature and excitation fluxes coincide, but when the rotor turns under the action of the DPR, the windings switch and the armature flux rotates to the next step.
In this case, the resulting current vector will be shifted and stationary relative to the rotor flow, which creates torque on the motor shaft.
In the motor operating mode, the stator MMF leads the rotor MMF by an angle of 90°, which is maintained using the DPR. In braking mode, the stator MMF lags behind the rotor MMF; the angle of 90° is also maintained using the DPR.
Advantages and disadvantages
For comparison, the following conditions are used: the devices are connected to a household electrical network with a voltage of 220 volts and a frequency of 50 Hz, the engine power is the same. The difference in the mechanical characteristics of the devices can be a disadvantage or an advantage, depending on the requirements for the drive.
So, an AC commutator motor: advantages in comparison with a DC unit:
Connection to the network is carried out directly, and there is no need to use additional components. In the case of a DC unit, rectification is required.
The starting current is much less, which is very important for devices used in everyday life. If there is a control circuit, its design is much simpler - a rheostat and a thyristor
If an electronic component fails, then the commutator motor, the price of which depends on the power and ranges from 1,400 rubles or more, will remain operational, but will immediately turn on at full power
If there is a control circuit, its structure is much simpler - a rheostat and a thyristor. If an electronic component fails, then the commutator motor, the price of which depends on the power and ranges from 1,400 rubles or more, will remain operational, but will immediately turn on at full power.
There are also certain disadvantages:
Due to losses due to stator magnetization reversal and inductance, the overall efficiency is noticeably reduced.
The maximum torque is also reduced.
Single-phase commutator electric motors have certain advantages compared to asynchronous ones:
Compactness;
Lack of connection to the network frequency and speed;
Significant starting torque;
Proportional reduction and increase in speed in automatic mode, as well as an increase in torque with increasing load, while the supply voltage remains unchanged;
Speed control can be smooth over a fairly wide range by changing the supply voltage.
How does a brushless motor work?
The 1970s saw a breakthrough in semiconductor electronics that eliminated the commutator and brushes in DC motors. In a brushless motor, the amplifier replaces mechanical contact connections. The electronic sensor understands the rotation angle of the rotor and is capable of monitoring semiconductor switches. The elimination of sliding contacts led to a decrease in friction in the mechanism, and therefore an increase in service life.
The brushless motor in a screwdriver is much more efficient and suffers less wear and tear. It is also much quieter and provides high torque. The internal elements are completely closed, so that dirt and water do not get inside. The efficiency of converting energy into force allows for high efficiency.
The rotation speed is affected not by centrifugal force, but by voltage, so the engine can operate in a given mode without interruption. If current begins to leak or the motor becomes magnetized, performance will not be affected and the speed will not lag behind the torque.
When operating the mechanism, there is no need to use a commutator or winding, and the magnet is much smaller, both in weight and in size, when compared with a brush competitor.
This solution is used in screwdrivers whose power does not exceed 5 kW. It is unwise to install them in models with large parameters. The magnets inside the case are sensitive to magnetic fields and strong heat.
The difference between a brushed and brushless screwdriver in the principle of motor operation:
- The current is switched not in the rotor, but in the stator windings. There is no coil on the armature; the magnetic field is formed thanks to special magnets inside the housing.
- The moment when electricity is required is determined by built-in sensors. They work on the principle of the Hall effect. DPR pulses and speed control signals pass through the built-in processor, where they are formed. This is called a PWM signal.
- The generated pulses are sent in order one after another to inverters or, more simply, amplifiers - they increase the resulting current. Their outputs are connected to the winding on the stator. Inverters are needed to switch the current generated in the coils, following the pulses that are supplied from the internal processor node.
As a result of the described process, a magnetic field is formed, which is associated with that around the rotor. The anchor begins to rotate - the tool works.
Making a choice
The decision to choose an engine type is simple and complex at the same time. Even if the basic principles of choice exist, situations may arise that are exceptions to the rule. Each type of engine has different characteristics of speed, turning angle versus torque, and stopping. When choosing, it is necessary to compare the desired functions and limitations of the finished device with the engine parameters.
In most cases, brushed and brushless motors are not suitable for applications that require a stepper option. It is better suited for continuous alternating start/stop/positioning, while the first two are more suitable for continuous operation. When choosing between brushed and brushless motors, consider the following:
- brushed motors have a shorter service life than BLDC motors; in the first case, the service life depends on the wear of the bearings and the brush mechanism; in the second, the service life is limited only by the wear of the bearings. Additionally, brushes that quickly pick up conductive dust can contaminate other surfaces;
- high quality brushed motors can reach speeds of 10,000 rpm, while BLDC motor designs can increase this speed by 5 or even 10 times;
- brushed motors can be operated directly from the power supply and therefore only need two wires, while BLDC motors need electronic commutation, in which case at least three wires plus sensor wires are needed;
- The efficiency of both types is approximately the same, but the sources of losses in them differ. For brushed motors, most of this occurs in the windings and friction associated with the brush mechanism, while BLDC motors experience the same losses in the windings, plus additional losses from eddy currents, which increase with speed;
- the control circuit for stepper motors is initially much more complex than for brushed motors, but new integrated circuits, for example, those developed by STMicroelectronics, practically eliminate these differences;
- A low-power brushed motor, for example for an inexpensive toy, may be the most economical solution in terms of wiring and control electronics (if any), but it may provide very limited performance.
Varieties
Three-pole rotor on plain bearings;
Bipolar permanent magnet stator;
As brushes of the commutator unit.
This set is typical for the lowest-power solutions, usually used in children's toys where high power is not required. More powerful engines include several more structural elements:
Four graphite brushes in the form of a commutator unit;
Rotor with several poles on rolling bearings;
Stator made of permanent magnets with four poles.
Most often, an electric motor device of this type is used in modern cars to drive the fan of the cooling and ventilation system, washer pumps, wipers and other elements. There are also more complex units.
The electric motor's power of several hundred watts requires the use of a four-pole stator made of electromagnets. To connect its windings, one of several methods can be used:
In series with the rotor. In this case, a large maximum torque is obtained, however, due to the high idle speed, there is a high risk of engine damage.
Parallel to the rotor. In this case, the speed remains stable under changing load conditions, but the maximum torque is noticeably lower.
Mixed excitation, when part of the winding is connected in series and part in parallel. In this case, the advantages of the previous options are combined. This type is used for car starters.
Independent excitation, which uses a separate power supply. In this case, characteristics corresponding to a parallel connection are obtained. This option is used quite rarely.
A commutator electric motor has certain advantages: they are easy to manufacture, repair, operate, and their service life is quite long. The following are usually highlighted as disadvantages: efficient designs of such devices are usually high-speed and low-torque, so most drives require the installation of gearboxes. This statement is quite justified, since an electric machine oriented at low speed is characterized by low efficiency, as well as associated cooling problems. The latter are such that it is difficult to find an elegant solution for them.
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)
In the name itself you can already see the fundamental difference between these machines. BLDC machines do not have brushes, which makes their design noticeably more complex. A brushless DC machine has four or more permanent magnets in the rotor.
Efficiency is the main feature of these machines. Since the rotor has permanent magnets, it does not need a voltage source, hence there is no physical connection. No connection - no brush-collector unit, and accordingly, all problems associated with it disappear. But there is also a minus - this type of electric machine must have an electronic system for controlling the position of the rotor in space. A microcontroller is used to analyze the rotation of the machine and generate control pulses at the right moment, and rotary sensors or sensors based on the Hall effect are used to monitor the rotation of the shaft in space.
BLDC motors are synchronous machines, which means that the magnetic fields of the rotor and stator rotate at the same frequency. They can be available in single, two or three phase configurations.
Brushed motor
A commutator motor is an electric machine consisting of several important parts. The main element is the collector - a copper-colored drum. There is a moving (rotor) and a stationary part (stator), an armature winding, a special brush, a fan, a core and a pole winding.
There are also 2 outgoing supply wires (positive and negative). The operating principle of the device is based on the high-quality conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. First, an electromagnetic field is created within the armature windings.
The field generated in the armature begins to interact with the stator poles, which leads to the movement of the armature. Gradually the generated current passes through the brushes and the collector to the next winding. The movement of current causes the shaft and armature to rotate simultaneously. Radio-controlled models with similar units operate on direct current.
Commutator motors are divided into several types. The classification of devices depends on the type of their power supply. Experts distinguish universal and permanent CDs.
Universal units are capable of operating from an alternating and constant power source. Easy to use and compact in size, electric machines are in demand due to their cost.
The second type of commutator motor is famous for its high starting torque. Simple design with smooth speed control. The unit operates using permanent magnets or using special excitation coils.
The advantages of such engines are the dimensions and weight of the structure. The advantages also include the cost of the unit.
The discussed CD is found in various household electrical appliances, such as a washing machine, vacuum cleaners, children's toys, and power plants.
Still, some manufacturers prefer brushless devices.
Commutator type motor
The concept of commutator motors includes various electric machines, where the current switch and rotary sensor are essentially one device. With its help, a high-quality connection of the circuits in the stationary engine compartment with the working rotor is ensured.
Appearance of a commutator motor
The design includes powerful brushes and the collector itself. It is also interesting that the commutator type of motor has the advantage of ease of maintenance and operation, is easy to repair and lasts a long time. But there is also a drawback, which is manifested in low weight with high efficiency. Initially this may seem like an advantage. The high speed coupled with the low weight forces the use of an additional good gearbox, otherwise it will not be possible to operate the motor normally.
If the machines are adjusted to lower speeds, the efficiency will instantly drop. This, in turn, will negatively affect cooling efficiency.
Many people are interested in what a commutator engine means. In fact, it is an alternating current electric machine, capable of easily converting direct current into useful mechanical energy. In this case, at least one winding is connected to the main collector.
Depending on the configuration and the components included in the motor, commutator motors (CM) can be used in toys, radio-controlled models and automobiles, acting as an integral element of the cooling system, ventilation, windshield wipers, windshield washer pumps, etc.
Leading manufacturers have managed to create universal commutator-type motors that are capable of operating on all types of current, that is, alternating and direct. They have found wide application in the creation of electrical tools, household appliances, and in railway transport. Their advantage is their light weight and compact size at a fairly reasonable price.
Regardless of the polarity of the motor, this electric motor will always rotate in only one direction, that is, in one constant direction. This is explained by the series connection of the rotor and stator windings, which provokes a simultaneous change of poles. Therefore, the moment is always directed in the same direction.
The basic components of the design code are:
- A two-pole stator based on permanent magnets. The design uses curved magnets of the appropriate shape;
- The rotor is three-pole type. Specific bearings with a sliding effect are also used here;
- Copper plates. They are used as brushes for a commutator type engine.
The set is really minimal, therefore it is found mainly in the most budget and simple versions of brushed electric motors. These include motors for children's toys that do not require increased power.
If you want to get a higher quality CD, then add to its composition:
- multi-pole rotors with rolling bearings;
- graphite brushes;
- four-pole stator based on permanent magnets.
To achieve high efficiency, several main components were included in the CD. Namely:
- Collector. In fact, the fundamental element of the engine that comes into contact with the working brushes. As a result, these two components begin to distribute electric current across the armature winding coils;
- Stator. Acts as a stationary component of the engine;
- Anchor. A mandatory element of commutator electric motors. An electromotive force is induced inside it and a current flows. It is important to add that the rotor and stator can act as an armature;
- Inductor. A special excitation system that is part of a commutator-type electric motor. Serves to create magnetic flux in order to create torque in time. The inductor must have an exciting winding or permanent machines;
- Brushes. The brushes are part of the circuit that carries electrical energy from the supplier to the armature. The brushes are made of high-strength graphite. Depending on the specific motor, the motor is equipped with 1 pair of brushes or more.
Regardless of the layout and the constituent elements based on certain materials, the operating principle of all commutator types of engines remains the same.
Principle of operation
It will not be difficult for you to imagine 2 magnets that have different advantages. Try placing them next to each other with the same pole and see what happens. You will not be able to connect them, no matter how hard you try. But as soon as you connect magnets with different poles, a high-strength connection is created. It is this effect that forms the basis of the operation and design of commutator motors.
Scheme of a commutator type electric motor
You learned about the CD device. Now, during operation, you will probably want to know how you can check the commutator motor yourself. To do this, you need to understand the principle of its operation. An electric motor of this type operates as follows:
- electric current is supplied to the armature windings;
- depending on how many windings are used on the motor, current is supplied to each of them in turn;
- thereby creating an electromagnetic field;
- on one side is the south pole, and on the other is the north pole;
- the magnetic field appearing in the windings interacts with the poles of the motor stator magnets;
- this allows you to set in motion, that is, make the anchor rotate;
- the current, passing through the collector and brushes, arrives at the next winding;
- this happens sequentially, depending on the number of armature windings;
- moving from winding to winding, the motor shaft together with the armature begin to rotate;
- rotation occurs as long as there is a voltage source.
Standard commutator-type motors require the use of a three-pole armature. That is, it has 3 windings. This prevents the engine from sticking in one of the positions.
Advantages and disadvantages
It cannot be denied that commutator motors or commutator electric motors are actively used in various fields and industries. They are also often used in automotive production.
But for the sake of objectivity, it must be added that DC is not always and not used everywhere, since in specific situations a brushless electric motor will be a more effective and rational solution.
Extensive experience in using DC allows us to identify a number of strong and weak operating qualities of this type of electric motor.
Internal structure of a commutator asynchronous motor
The main advantages include the following:
- Relatively small indicator of starting current parameters. This is noticeably manifested in situations where commutator motors are installed in various household appliances;
- Such electric motors can be connected directly to the energy carrier, that is, to the network. This eliminates the need to use various kinds of additional and auxiliary devices;
- High speed performance;
- Independence from network frequency parameters;
- With a control circuit, the device becomes simpler.
But you shouldn't make hasty conclusions. First you need to look at the existing disadvantages of a commutator motor. Namely:
- Overall efficiency indicators are reduced. This is due to the presence of inductance, as well as losses necessary for reversing the magnetization of the stator;
- Maximum torque figures are far from perfect;
- Relatively low level of reliability;
- Relatively short service life.
Experts identify one key drawback that characterizes commutator types of electric motors. No one argues that it is very convenient to regulate speed in collectors. But if they are tall, the brushes immediately show themselves. And not from the best side. The brushes are always in a state of tight fit to the electric motor commutator itself. At high operating speeds, they begin to wear out quickly. Over time, clogging occurs, resulting in sparks.
The gradual wear of the engine brushes and the entire commutator assembly with brushes contributes to a decrease in the overall performance of the compressor. That is, the commutator-brush assembly can safely be considered the main design flaw. Therefore, manufacturers are increasingly abandoning commutators, choosing brushless analogues instead.
The main competitor of the commutator type electric motor is its brushless counterpart. It has a different operating principle from CD, and is also characterized by its strengths and weaknesses.
What is called a commutator motor?
A commutator motor is an electric machine whose rotor position sensor and current switch are one and the same device, called a brush-commutator unit. You can tell us more about the latter. It provides an electrical connection between the circuits in the stationary part of the machine and the rotor circuits. Structurally, it consists of brushes (they mean sliding contacts that are located around the rotating part of the engine) and a commutator (what is located on the movable element of the mechanism).
The general advantages include the fact that the commutator motor is easy to manufacture and operate, has a significant service life and can be easily repaired. Common disadvantages include the fact that they have low mass and high efficiency. In most cases this is only a plus, but not now. Thus, the combination of low mass and speed (which reaches hundreds and thousands of revolutions per minute) leads to the fact that gearboxes are almost always required for normal operation. And when adjusted to low speed, the machine has reduced efficiency, and cooling problems arise. So far, no elegant solution to this problem has been found.
Brushless motor
Now we can talk about how a brushed motor actually differs from the brushless counterpart under consideration.
Appearance of a brushless motor
An obvious difference can be seen when studying the operating principle of a brushless motor (BCM). Although brushless and brushed motors are often compared to each other as competitors, they are essentially two different motors. Therefore, there are necessarily differences between them.
In fact, BKD works the other way around.
This device and operating principle allows for smoother engine operation at its maximum efficiency.
In the case of brushless electric motors, they can be equipped with sensors or sensors, and can also be operated without them. If there is no sensor, this will to a certain, but insignificant extent, reduce the efficiency of the entire electric motor.
It is quite easy to recognize a BCD with or without a sensor. If a regular engine has 3 power wires, then models with a sensor additionally have a cable consisting of thin wires. It goes from the motor itself to the speed controller.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main and undeniable advantage of brushless electric motors is the almost complete absence of parts that can wear out. It is impossible to talk about their complete absence, since the rotor shaft is mounted on bearings. They can still wear out over time. Although even bearings have a huge resource. Plus, you can always quickly and easily replace the bearing if it wears out.
Brushless electric motor disassembled
These design features give rise to advantages in the form of reliability, high efficiency and long service life. Due to the presence of a rotor position sensor, its performance and accuracy during operation are improved.
Remember the disadvantage of collector analogues, where the brushes spark and wear out quickly, at the same time causing interference during the operation of the unit, mechanism or machine in which the CD is installed. In the case of brushless or brushless motors, this problem was eliminated. There are no sparks observed here.
Brushless motors do not rub or overheat, which is also a significant advantage of the mechanism. Additional maintenance is not required during even very active operation.
If we talk about shortcomings, then out of a significant and still conditional one, only one disadvantage can be identified. This is a higher cost. The disadvantage is conditional due to the fact that at its price it eliminates the need to replace springs, armatures, commutators or brushes. Therefore, the cost is completely justified.
Then you can draw your own subjective conclusions based on the information given above.
Source