Columnar foundations are used during the construction of frame and low-rise buildings without basements.
It is also constructed if a large foundation depth is expected - 4–5 m. In this case, a strip foundation is unprofitable due to the high consumption of building materials.
We'll talk about how to build a columnar foundation for columns in the article.
Varieties
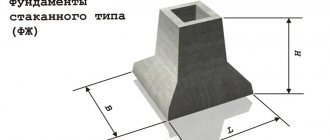
A columnar foundation consists of a slab part of 1–5 steps and a column base, solid or hollow - glass. Its type depends on the type and material of the column.
Column is a part of a supporting structure. It absorbs the load between floors and at the foundation level. Can serve as a decorative item. Columns are produced in standard sizes and made to order.
There are 2 types:
Metal - consists of a head to which crossbars and beams are attached, a rod and a base - the part in contact with the foundation.
There are solid and through columns - lattice, perforated. The latter weigh less and are easier to install. The structures are made from beams and rolled profiles.- Reinforced concrete – made from reinforced concrete grades M300, M400, M600. The design is standard. With a small cross-section, it can withstand a high load-bearing load and, unlike metal, is not afraid of water. The shape is round, square and rectangular. Round is more common in decorative elements.
The column continuously interacts with the base; violation of the position of at least one support leads to the collapse of the house. Therefore, it is not recommended to use piles under columns.
There are 2 types of columnar foundation:
- Monolithic - a finished structure in which the pillars are installed according to a certain pattern. The columns are secured to the foundation with bolts.
- Prefabricated - each base is manufactured separately, on the construction site or in a factory, and installed separately. The top of the supports is concreted to avoid the appearance of cracks.
The material for a columnar foundation is selected based on the load and column material:
- Concrete foundations – or rather, reinforced concrete. They are made of heavy concrete and reinforced with special reinforcement. Only monolithic concrete is installed under metal columns; a prefabricated option is allowed under brick columns.
- Brick - withstand less load and are used for low-rise buildings.
- Wooden - suitable only for wooden or frame buildings.
- In private construction, supports made of concrete or asbestos pipes are found.
Features of foundations for steel columns
There are a number of buildings where there are special requirements for the type and strength of foundations. In most cases, these are industrial facilities, as well as various enterprises in the energy industry.
Such buildings are often erected on frame-type foundations, where the main load is taken by a metal column installed inside a special concrete bowl or recess.
All foundations for steel columns are distinguished by a special design, because initially a rectangular or square concrete pad with a recess is created, where the column is installed and fixed with the help of anchors.
In addition to buildings with anchor connecting elements, it is also possible to provide in such foundations:
- pipelines of various types and diameters;
- sewer systems with anchor fasteners;
- Electricity of the net;
- special supporting elements and structures.
Taking into account the high strength requirements for such structures, all calculations and further construction are carried out as accurately as possible, quality control is carried out at each stage of construction, and the building materials fully comply with the standards.
Preparation for construction
Preparation includes:
layout - supports are mounted in the corners, in areas where walls adjoin and intersect, along the load-bearing wall every 3–6 m and under each column;- marking and excavation of earth to the required depth;
- if the burial depth is great, then a sand or concrete substrate is laid at the bottom of the pits;
- construction of formwork.
The depth and height of the concrete base is determined by the weight of the building and the looseness of the soil.
Tools and materials
For construction you need:
- board or plywood for formwork;
- sand, broken brick, gravel for a pillow;
- concrete grades M300, M400, M600;
- roofing felt or other film material for waterproofing;
- anchor fasteners for metal columns.
To work you will need the following tools and devices:
- nylon cord and wooden stakes for marking;
- shovels and bayonet shovels;
- plumb line, building level, tape measure;
- manual rammer.
If you make concrete yourself, you need a concrete mixer or a container to mix the solution.
How to calculate?
The initial data for the calculation is the load exerted by the column and the results of geotechnical research.
The first include:
Vertical load - the weight of the column and the magnitude of the load transmitted to it by the walls and roof.- Bending moment.
- Transverse - attributable to the support from the base of the column.
- Load under the action of torques in 2 planes.
- Total wind and snow – calculated based on regional weather data.
Engineering-geological data include:
- soil properties;
- ground water level;
- depth of soil freezing.
Based on the data obtained, the size of the support pillars for the columns is calculated.
Calculation example for a monolithic column
Calculate the depth and cross-section of the base. In simple cases, the parameter determines the maximum freezing depth.
For more accurate calculations, use the formula: df=kh*dfn, where:
- kh – coefficient adopted for the foundation of a heated house;
- dfn – freezing depth.
The dimensions of the base are calculated using the formula: A=N/(R0-ȳd), where:
- N – vertical load, it is obtained when calculating the building frame;
- R0 – soil resistance – the value is presented in the reference book SNiP 2.02.01-83;
- ȳ – average specific gravity of the foundation;
- d – depth.
For buildings above 3 floors, the calculations are more complex, taking into account the edge load.
Calculation example for a metal column
The material does not affect the calculation method .
You need to take into account the depth of the column itself. Therefore, the same calculation methodology is used. For ease of calculations, it is better for non-professionals to use online calculators on the Internet.
They indicate all the required parameters for calculations. The calculation is done automatically.
What data needs to be collected to correctly calculate the foundation for columns?
Connection diagram of a metal column with foundation reinforcement
Calculation of a column foundation is quite difficult, because many factors are collected at once. It is clear that it is almost impossible to do such complex calculations on your own; you need special education and skills. Therefore, before starting to calculate a column foundation, you need to obtain the following data:
- features of climatic conditions in the region of the construction site, the type and power of winds, as well as the frequency of rainfall;
- create a detailed geodetic map, and it is better to do borehole analysis in order to obtain data on the structure of the soil, the thickness of soft and hard rocks. You also need to obtain data on the occurrence of groundwater and its seasonal movement;
- the mass of the building itself. The larger it is, the more powerful the columns should be. It is clear that glass-type foundations are used for reinforced concrete columns, and completely different ones for metal ones;
- type of column, its load-bearing characteristics, degree of tension and compression when exposed to high and low temperatures;
- type of concrete, its grade, composition and performance characteristics;
- the structure of the future structure, the material of load-bearing walls and ceilings, the height of the structure.
Previously, the calculation of a column base was done by eye, using standard indicators of permissible loads. For example, the standard immersion depth of the cushion was up to 200 mm, and its upper part protruded from the ground to a height of up to 50 mm.
Such columns are not able to withstand soil movements, because the cushion was quickly washed out and the base was destroyed. Now the calculation clearly indicates the maximum permissible immersion depth of the cushion; it should be below the freezing depth of the soil, where there are practically no loads.
Stages of construction for a monolithic column
When constructing a private cottage or dacha, a monolithic foundation is constructed. To save materials, support pillars are made in the form of steps . The height and number of steps depends on the load.
For the foundation, dig a hole of the required size and lay a 20 cm thick layer of sand and crushed stone on the bottom. If the depth of the foundation is large, install a concrete pad. Then formwork is erected from plywood or wood.
If the dimensions of the base are significant, steel formwork is used. Asbestos-cement or concrete pipes can be used as permanent formwork.
Reinforcement of supports
Reinforcement is carried out as the foundation is erected.
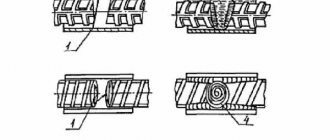
For this purpose, rods with a diameter of 12–16 mm are used, knitted or welded into finished frames. Steel mesh with cell sizes from 5–6 mm, but not more than 12 mm is used as horizontal elements:
- After compacting the sand and gravel cushion, pour at least 10 cm of concrete and lower the prepared structure into the hole.
- The cross-section of the frame is only slightly smaller than the cross-section of the well. The frame fits tightly.
- The middle of the column is not reinforced, since the load here is minimal.
- The reinforcement outlets are bent horizontally - 30–40 cm each. If the column support is made of brick, at least one reinforcing rod must be anchored in the brickwork.
The size of the column can coincide with the cross-section of the column. If a glass is required, formwork of a complex shape is constructed.
You can watch the making of the frame in this video:
Shoe installation
To evenly distribute the load from the building, it is recommended to make a shoe - expanding the lower part of the well:
- Formwork is made, the diameter of which is 1.5 times larger than the cross-section of the future pillars and installed on a sand cushion.
- Only the shoe is poured with concrete grade M300–M400.
- Concrete hardens for at least 10 days.
After the mortar has set, the construction of the foundation continues.
Installation of columns
Work begins with the construction of a reinforcing frame:
The monolithic column is reinforced with rods. With a large cross-section, the rods are additionally reinforced with horizontal clamps.- For formwork, wooden boards of the required length are used. They are fastened with clamps. It is recommended to cover the inside of the formwork with roofing felt to make it easier to remove later. The surface of the column will be smooth.
- For pouring, use concrete grade M200 or higher. To remove air, the solution is pierced with a metal pin. The formwork is removed only after complete drying.
The optimal construction temperature is above +15 C. If a building is constructed in winter, plasticizing additives are added to the concrete in order to speed up hardening.
Grillage
A monolithic grillage is erected under reinforced concrete columns; essentially, it is a concrete strip reinforced with steel rods. Used in the construction of frame and panel buildings, wooden log houses:
- Formwork of the required dimensions is made.
- The fittings are laid. To strengthen the slab part, a reinforcing mesh is used, which is placed in 2 layers. There must be an insulating layer of concrete between them - at least 20 cm, so pouring is carried out in 2 stages.
- Horizontal meshes are connected by vertical fragments of rods. The length is as short as possible so that the frame does not lose stability over time.
The binding of the frame is carried out in the formwork or on the base, and not on the ground.
Initial conditions
The dimensions of the sole for the standing support are chosen so that the load on the plane of contact with the ground does not exceed its load-bearing capacity. Typical indicators for shrinkage of each individual loaded element in the foundation did not exceed the permissible values specified in the standards.
The column can stand on a separate foundation or be located in a group for which there is a single base (strip or slab type).
Group of columns on a single base
Releases of reinforcement for future columns in a monolithic concrete slab.
When calculating a columnar foundation for a column, the area of the base of 1 column is taken as the starting value. The required number of such supports must be taken with a margin of at least 50% in strength for each element being installed.
The materials for the manufacture of single foundations are:
- reinforced concrete products;
- rubble stone;
- brick;
- poured concrete.
Rigid types of foundations include structures made of monolithic branded concrete and made of brickwork.
Columns installed on a prepared foundation differ in the type of material they are made of: metal, reinforced concrete products. Each variety has its own method of attachment at the lowest point. Column supports for them are manufactured in the factory (standard type) or directly at the construction site at the installation site (design calculation).
The monolithic self-fabrication method has the advantage that it is universal, regardless of whether the steel or reinforced concrete product will be mounted on top of the base.
Stages of construction for a metal (steel) column
Metal columns are mounted in glass bases or using an anchor method. The procedure is similar, but excludes some steps:
Mark the position of the wells and dig holes of the required depth.- A sand and gravel cushion is laid at the bottom. Constructing formwork. The structure is reinforced with rods and mesh in the manner described above.
- The prepared wells are filled with concrete of a grade not lower than M300. Before pouring, geodetic levels and elevation signs are installed in the cavities. They serve as indicators of the location of the steel support.
- Anchor bolts are installed into the surface of the concrete foundations for fixation. A metal column is attached to them. They are connected to each other by beams.
Leaning can be done using another method. Instead of anchors, metal plates are mounted on the surface of the support and filled with concrete mixture. The filling level is below 5–8 cm of the design mark of the sole. A column is installed in the resulting recess.
Installation on anchors can be seen in this video:
Installation of metal columns
Installation of a metal support
Metal columns are mounted on bases in which anchor bolts are installed in advance to secure them. After design, the standard position of the supports is ensured by the precise placement of anchor bolts at the fixation points. In this case, the accuracy of installation is ensured by serious preparation of the base plane.
The columns are supported as follows:
- On the surface of the base, which is mounted to the required level of the supporting sole, without subsequent addition of the cement mixture. Used for supports with milled shoe soles.
- Metal slabs are installed in pre-calibrated locations and filled with concrete mixture. The base is concreted to a level 5-8 cm below the level of the base of the support, which is indicated during the design.
- After that, the installation of support columns is carried out, combining the axial marks of the alignment axes on the elements built into the foundation with their marks. The set screws adjust the position of the individual support in height, taking into account that the top surface of the slab will be located at a given level of the support plane of the shoe. The supporting planes of the pillars must be planed in advance.
- The base is concreted to a level 0.25−0.3 m below the surface of the shoe, marked during its design.
After completing this work, the embedded elements and components of the supports are installed. The upper part of the base is cemented to a level 4-5 cm below the upper plane of the supporting elements. The supporting surface of the shoe is made at right angles to the axis of the pillar itself.
Mistakes during construction and ways to avoid them
Building a foundation is a rather complex job that requires calculations and qualifications. Novice builders most often make the following mistakes:
- the load distribution is incorrectly calculated, and the foundation begins to sag and the walls of the building begin to crack;
the depth is incorrectly determined - too large a value only leads to the consumption of materials, but an insufficient value leads to deformation of the walls;- install supports at different depths;
- they use low quality material - the grade of concrete must be at least M200;
- incorrectly assess the soil resistance - consultation with a specialist is necessary;
- do not center the frame during installation - this has a particularly destructive effect on the grillage;
- assemble the frame on the ground - centering is automatically eliminated;
- Connect the rods and mesh at the corners by welding - this is prohibited.
Supporting bases and columns are vertical elements. During the construction of formwork, reinforcement, and fastening of pillars, verticality must be constantly checked.
You will find a lot of important and useful information about columnar foundations here.