Thoughtful design and no secret
The foundation is the safety cushion of a building, without which the service life of the structure is doomed to short-lived. Any type of foundation is a carefully calculated technology with features that provide the benefits of support in certain conditions.
Screw piles are installed along the perimeter of the building, at the intersection of load-bearing partitions and every 2-3 meters from each other. These are metal pillars, mostly buried in the soil and connected to each other by a grillage to evenly distribute the load. At the end of each support there are screws - blades that perform 2 functions:
- facilitating the immersion of the pile into the ground;
- compaction of rock to increase traction and load-bearing capacity.
The trick of the technology is to pass through the upper, capricious and frost heaving-prone layers of soil to a stable ground.
What parameters affect the depth of driving piles
To build a pile foundation, it is necessary to carry out engineering-geological surveys, since the length and diameter of the pile are selected depending on the type of soil, freezing depth, as well as the area of the house and the design load.
Basic geological parameters needed to calculate the screw-in depth
- groundwater level, as well as the characteristics of these waters;
- the depth of solid soil with sufficient load-bearing capacity: the piles must be supported and “fixed” in a solid foundation;
- depth of soil freezing in the construction area: it is important to position the pile blades lower so that in the event of frost heaving, the reliability of the foundation is not affected. The depth of soil freezing in the Leningrad region does not exceed 1.5 meters.
The basic rule for constructing a pile foundation: the deeper the pile is screwed, the more reliable the foundation. Here it is also important to determine the appropriateness of the depth of twisting - this influences the choice in favor of manual labor or the use of special equipment.
Depth of screwing in piles depending on soil type
Screw piles are used in almost any type of soil (exception: rocky rocks). By choosing the depth and diameter of the piles, it is possible to choose the best option even for sandy, unstable or underwater soils.
The driving depth depends on the soil on which the pile foundation is placed. When building a foundation on peat bogs and loose soil, the pile must be screwed in until it reaches a solid base. Available data show that the dense layer of soil in most cases is located at a depth of 1.5-2 meters, but in each case the exact distance is determined by test screwing and geological research.
Soils of different composition also differ in their freezing index: for example, sandy soil freezes deeper than loam and clay. If, for example, we take the Leningrad region, then in the case of clay soil the depth of screwing in the pile will be: 120 cm (freezing depth) + 30 cm (diameter of the pile blade - according to the rules it is necessary to deepen at least this amount after) = 150 cm. And if If you have sandy soil on the site, then the calculation for the freezing depth will be as follows: 135 cm + 30 cm = 165 cm.
If you have rocky (boulder, pebble, etc.) soil, the best option would be a bored foundation with high-strength, factory-quality piles.
Simplicity of design, speed of installation and flexibility in terms of solving non-standard problems have influenced the prevalence of pile foundations. If you correctly calculate the depth of screwing in the piles and build the foundation according to the technology, the foundation will serve you for many years.
Immersion depth depending on purpose
Piles are used to construct a supporting foundation for various buildings, as well as to reconstruct an old foundation that requires repair or increasing the capabilities of the existing one.
Since improving the adhesion of a screw column directly affects the load-bearing capacity, the immersion depth of large-sized buildings is usually greater than for lighter structures - sheds, fences, sheds. However, this factor is determined individually at the design stage, taking into account the characteristics of the built-up area.
The more complex the soil, the deeper
On sand, clay and other similar types of soil layers, as well as wetlands, it is very difficult to install a structure, since the soil is mobile. The solid foundation bulges, collapses unevenly and pulls parts of the building along with it, destroying it. The use of piles solved this problem, because it became possible to secure the supports in the firmament, bypassing the problematic soil. A variety of standard sizes allows you to select support posts of suitable length.
Geological research or information from the urban planning organization at the construction site will help determine the composition of the soil and the depth of hard rocks of the earth.
Frost heaving is a trifle for piles
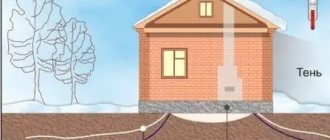
Before the onset of winter, a lot of moisture usually accumulates in the soil due to autumn rains and the first melted snow. During the period when negative temperatures are established, a process called frost heaving occurs. At this time, the liquid in the upper layers of the soil turns into ice, and therefore increases in volume. The soil protrudes by about 5-10 cm, pushing out everything that is in it, including the foundation on piles, located at insufficient depth.
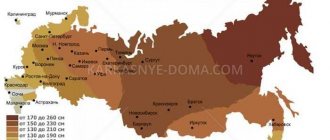
This parameter varies in different regions. For example, in the southern regions the freezing depth is 70-80 cm, and in colder regions it can reach 4 meters. To bypass freezing soil, select the appropriate length of screw piles. For the Moscow region, these are most often supports of 2.5 m. You can view the frost heave depth indicators in a specific region in SNiP 01/23/99.
Depth of soil with sufficient bearing capacity
For proper perception of design loads, the lower blade of the pile (if we are talking about modifications with two blades, more about which in the article Features of calculating two-blade screw piles) must be fixed in the soil with sufficient bearing capacity. In this case, the thickness of the layer of dense soil under the pile, as a rule, should be at least 1 meter.
According to statistics, soil layers with sufficient bearing capacity, as a rule, lie at a level of 1.8 meters from the ground surface. And only in 5-7% of cases they are located higher. That is, the depth of the pile-screw foundation cannot be less than 1.8 meters.
The level of soil with sufficient bearing capacity can be determined using a procedure adapted for low-rise construction - geological and lithological surveys (more details Express geology (geological and lithological surveys) and measurements of corrosion activity).
Express geology also allows you to determine:
type, properties of soil;
groundwater level;
difficult ground conditions;
potentially hazardous geological objects and processes, etc.
To ensure that the structure of the base is minimally disrupted during the process of driving the pile, and that its load-bearing capacity does not decrease, it is necessary to select a rational blade configuration at the design stage (more information in the material Key principles for selecting blade parameters).
Soil freezing depth
Some soils are susceptible to frost heaving. In autumn, the pores of such a base begin to fill with water, and then the ice formed during freezing begins to displace it upward (during crystallization, water increases in volume by an average of 12%).
If you leave the lower blade of the pile in such a layer, it will inevitably begin to rise along with the base. Even if the structure is not pulled out of the soil, the structure will still shift or become deformed. This may not be noticeable to the eye, but windows and doors will inevitably open and close in the spring not as well as in the fall. And this situation will repeat from year to year, forcing you to endlessly adjust or repair something.
This requirement does not mean that you can neglect the need to locate the blade in a layer of soil with sufficient load-bearing capacity. In this case, the screw pile should pass the mark of the standard freezing depth, after which it should continue screwing until the blade is fixed in the soil with sufficient bearing capacity, and the thickness of the layer of such soil under the pile is at least 1 m, as we have already discussed spoke earlier.
Do not forget that it is the blade of the pile that should be located beyond the freezing level, and not the tip of the cone. For example, for the piles of the GlavFundament company this distance is 0.2 m. Therefore, when calculating, this indicator must be summed up with the rest.
Calculation of the depth of a pile foundation
Thus, the following formula can be derived:
Blade depth + Soil level with sufficient bearing capacity/Soil freezing level = Foundation depth
Central and southern regions (Moscow, Penza, St. Petersburg, Krasnodar, Rostov-on-Don, etc.):
0.2 m + 1.8 m (soils with sufficient bearing capacity) = 2 m;
Ural-Volga region (Ekaterinburg, Izhevsk, Yoshkar-Ola, Kazan, Kirov, Magnitogorsk, Naberezhnye Chelny, Nizhny Novgorod, Nizhny Tagil, Orenburg, Perm, Saratov, Ufa, Chelyabinsk, etc.):
0.2 m +1.8 m (soils with sufficient bearing capacity and freezing level) = 2 m;
Western Siberia (Barnaul, Kemerovo, Krasnoyarsk, Novokuznetsk, Novosibirsk, Tomsk, Tyumen, etc.):
0.2 m + 2.3 m (freezing level) = 2.5 m;
Eastern Siberia (Irkutsk, etc.):
0.2 m + 2.8 m (freezing level) = 3 m.
It is worth considering that in the south of Russia the depth of freezing is either insignificant or absent altogether, but there is a large thickness of a weakly bearing layer of chernozem. When calculating the length of piles in this region, it is also necessary to rely, first of all, on the level of soil with sufficient bearing capacity.
To determine the soil conditions of your site, sign up for a geologist visit.
Base height above ground level
This indicator does not relate to the screw-in depth, but is important when choosing the length of the pile.
From an aesthetic point of view, cladding is less important than the detrimental effects of snow cover and wetlands on the walls of a building. Prolonged exposure to a liquid environment destroys building materials, even those with low hydrophobicity.
Therefore, when you order piles, please note that you should purchase them not only taking into account soil freezing and the depth of the solid layers, but also by adding the height of the base.
In each region of Russia, special attention should be paid to the quality of the foundation. If you doubt that you can independently choose the desired length of supports and to what depth to screw them, contact a city planning organization or consultants of companies that install piles.
How deep to dig the foundation
Foundation depth
Armed with these numbers and the results of the site survey, you need to select several foundation options. The most popular are strip and columnar or pile. Most experts agree that with normal bearing capacity of the soil, their base should be 15-20 cm below the freezing depth. We described above how to calculate it.
Please keep the following recommendations in mind✍
- The sole should rest on soil with good bearing capacity.
- The foundation should be immersed in the load-bearing layer by at least 10-15 cm.
- It is desirable that the groundwater be located lower. Otherwise, it is necessary to take measures to drain the water or lower its level, and this requires very large amounts of money.
- If the load-bearing soil is too deep, it is worth considering the option of a pile foundation.
Having selected several types of foundations and determined their laying depth, an approximate calculation of the cost of each is carried out. Choose the one that will be more economical.