EMP (electromagnetic pulse) is quite popular in the world of science fiction. Wouldn't it be cool to have your own EMP gun rig? That's what I thought before I started assembling the electromagnetic emitter with my own hands.
I wanted to make an EMP generator that was portable and could be hidden under my sleeves. If you have the right components, you can assemble it in no time.
WARNING: This project is not for children.
Seriously speaking, you might get a shock. Capacitors are really powerful and therefore please be careful when handling the circuit.
I take no responsibility if you destroy anything with this weapon.
Electronic information systems are widely used on modern battlefields. These systems are constantly moving towards automation and miniaturization, but at the same time their sensitivity to electromagnetic signals and vulnerability to electromagnetic attacks increases.
To combat electronic information systems that can increase combat capability several times, traditional means of fire destruction may be ineffective. The use of powerful energy of electromagnetic pulses makes it possible to hit an intelligent combat platform “to the very heart”, paralyze the “nerve center” of weapons and significantly weaken the effectiveness of the integrated combat system. The electromagnetic bomb, which was accidentally born during nuclear testing in the 1970s and is known as the “second atomic bomb,” is gradually becoming the object of intense interest among world military powers.
The use of electromagnetic technologies makes it possible to create powerful electromagnetic fields in a short time, which are equivalent in intensity to several dozen lightning strikes.
For a long time, electromagnetic weapons, also called “invisible brain eaters,” have been shrouded in mystery and hidden from prying eyes. Only after using this weapon in real combat, where it played a big role, did people suddenly realize that electromagnetic weapons are not a “mythical creature”; in fact, they are rapidly developing and increasing in power.
The high-intensity electromagnetic pulse energy generated by this weapon uses radiation to attack the electronic information system, which makes it possible to instantly disable radars, computers and other electronic equipment located in a certain area, thereby paralyzing the control system and combat system.
Foreign Policy 10/17/2020 Yahoo News Japan 03/11/2021 The National Interest 11/17/2020
According to available data, electromagnetic weapons weighing as little as one kilogram can disrupt electronic equipment, which is comparable to the destructive power of tens of tons of explosives.
So, what is the “true face” of electromagnetic weapons?
There is a narrow and broad understanding of the term “electromagnetic weapon”. In a narrow sense, this weapon refers to a special type of ammunition or equipment that uses ultra-strong electromagnetic radiation to damage the electronic components of an enemy combat platform. In a broad sense, electromagnetic weapons include a larger number of combat platforms, the lethality of which is to create electromagnetic pulses.
In a narrow sense, electromagnetic weapons can be divided into two categories: the first is electromagnetic bombs, missiles and shells that create electromagnetic pulses by bursting. The second category includes combat platforms that generate electromagnetic pulses and attack targets using special launchers.
The most typical example of an electromagnetic weapon is the electromagnetic bomb, known as the “second atomic bomb.” Currently, such bombs have become the object of research by world military powers.
Currently, there are two types of electromagnetic bombs - nuclear and non-nuclear. Nuclear electromagnetic bombs operate in accordance with the principles of nuclear weapons, while non-nuclear electromagnetic bombs compress magnetic flux through an explosive and release powerful microwave energy. Since the latter type of bomb does not cause radioactive contamination, it is the top priority of modern research and development of various countries.
In 2014, Russian media reported that the Alabuga electromagnetic weapon, being tested by the Russian army, exploded in the air at an altitude of 200-300 meters, disabled all electronic equipment located within a radius of 3.5 kilometers, and left military units without means of communication .
Realizing the power of the electromagnetic bomb, the United States once warned other countries not to develop or use electromagnetic weapons, but they themselves had previously used this type of weapon in actual combat.
The 1991 Gulf War, the 1999 NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, and the 2003 attack on a television station in Baghdad all bear the shadow of American electromagnetic weapons.
Several types of equipment are used to create magnetic pulses, such as high-power microwave jammers, microwave guns, and electromagnetic pulse suppression systems.
The creation of electromagnetic pulses through this equipment is carried out not through explosions of ammunition, but using system means. An example is the electromagnetic gun that Russia has been testing since 2015. According to the data, the maximum range of such a gun can reach ten kilometers, which makes it possible to disable electronic equipment located on the ground within this radius, as well as destroy unmanned aerial vehicles.
According to experts, this electromagnetic gun uses ultra-high capacity to instantly release energy and, with the help of a directional antenna, emits powerful electromagnetic waves used for combat purposes.
The United States is actively engaged in research and development in the field of electromagnetic weapons. In 1985, the US military included this type of weapon in the main directions of development of space weapons. In 1993, electromagnetic weapons were tested under the code name "HAARP". In 2004, the United States Army began testing a new generation of electromagnetic weapons to reduce costs. In 2012, a powerful microwave weapon developed by an American company was tested. The aircraft, equipped with microwave missiles, spent an hour in the air at low altitude, knocking out the electronic systems of seven different targets, and all computers located in houses within the range of the weapon.
Compared with conventional electronic weapons, electromagnetic weapons can be called an “invisible killer” in information warfare. From the point of view of hitting targets, unlike electronic weapons, which can only create interference and suppress the operation of electronic equipment, electromagnetic weapons are capable of causing severe damage to the enemy’s electronic equipment, paralyzing it for a long time.
In recent years, with the development of related technologies, electromagnetic weapons have been moving towards increasing power, expanding range and minimizing size, which shows great potential for combating stealth weapons, unmanned aerial vehicles and aircraft carriers.
It is obvious that the main purpose of electromagnetic weapons in the narrow sense of the word is to destroy electronic components of electronic information systems. Therefore, some weapons capable of producing electromagnetic pulses are not included in this category.
The exception is the Russian remote demining vehicle “Foliage”, used by the strategic missile forces. In addition to a mine detector and demining device, the vehicle is also equipped with equipment for creating electromagnetic pulses and suppressing powerful electromagnetic signals. When an explosive is detected, this equipment interrupts enemy signals for an explosion. In addition, the equipment is capable of creating microwave pulses and disabling the electronic components of the explosive device, thereby neutralizing the enemy.
Although the Foliage is capable of generating electromagnetic pulses, the vehicle's primary purpose is mine clearance, so it can only be considered an electromagnetic weapon in the broadest sense.
According to these criteria, a railgun is also an electromagnetic weapon in the broad sense. Although the principle of the railgun is to launch projectiles through the electromagnetic force created by powerful electromagnetic pulses of extremely short duration, its purpose is to launch projectiles and not to destroy electronic components. But despite this, the railgun is still considered one of the new types of weapons that can undermine combat readiness.
Almost all military powers, when developing electromagnetic weapons, attach special importance to means of protection against these weapons. Currently, the methods and measures taken by various countries include electromagnetic shielding, conduction suppression, grounding, etc. To further counter the threat of electromagnetic weapons, some countries have also begun to explore the use of graphene and plasma as shielding materials, as well as microwave photonics technology to improve shielding effectiveness.
At present, in addition to the United States and Russia, Israel, Britain, France, Germany, Japan, South Korea, India and other countries have also made great scientific achievements in the field of electromagnetic weapons. However, the development of this type of weapon is strictly classified in all major countries of the world. On the other hand, this suggests that the position and role of electromagnetic weapons in future combat operations should not be underestimated.
InoSMI materials contain assessments exclusively of foreign media and do not reflect the position of the InoSMI editorial staff.
Electromagnetic weapons. In publications and reality
According to various sources, the leading countries of the world are currently developing promising types of weapons using the so-called. new physical principles. Some successes have already been achieved in certain areas, and in addition, new weapons are becoming a cause for serious concern on the part of the military or analysts. For example, in recent days, with the help of the American press, various countries have started talking about the danger in the form of promising electromagnetic weapons being created in Russia, China and other countries.
It is worth recalling the basic principles of the concept of weapons using electromagnetic pulse (EMP). Such a weapon is a generator of a short-term powerful pulse and is intended to combat enemy electronic systems. A powerful EMP should create interference in the electrical circuits of enemy equipment and literally burn it. After a successful attack using EMP, in theory, the enemy is deprived of the ability to use communications and control equipment, locators, and even on-board equipment systems.
"Mayak" and report
This time a wave of concern was caused by another article in the American publication The Washington Free Beacon. Regular contributor Bill Hertz published a piece on January 24 titled “China, Russia Building Super-EMP Bombs for 'Blackout Warfare'.” “China and Russia are creating a super-EMP bomb for the Blackout War.” The reason for the appearance of this article was the publication of the report “Nuclear EMP Attack Scenarios and Combined-arms Cyber Warfare” (“Scenarios of nuclear and EMP attacks and combined combat operations in cyberspace”).
This 2021 report was prepared for the recently disbanded non-governmental Commission to Assess the Threat to the United States from EMP Attack. The document presented a number of facts and assumptions regarding EMP weapons and their possible impact on the situation in the world. The report was authored by Dr. Peter Vincent Pry.
In his article, B. Hertz cited the most interesting quotes from the report. First of all, he was interested in the capabilities of different countries in the context of EMP systems, as well as the scope of the latter and the results of such attacks. According to a report for a non-governmental organization, several “unreliable” countries are currently developing their own electromagnetic weapons, and in the future they are able to use them to solve their military-political problems. Targets for EMP charges can be objects in Europe, North America, as well as in the Middle and Far East.
P.V. Pry points out that EMP weapons are being developed in Russia, China, North Korea and Iran. Such developments are considered in the context of “sixth generation warfare,” which involves attacking military and civilian targets in cyberspace, as well as using electromagnetic pulses. Due to the possible impact on enemy energy networks, such ideas are also called “Blackout War”.
It is proposed to use nuclear weapons as a source of “combat” EMP. At the same time, different ways of using them with different effects are possible. Thus, detonating a nuclear charge at a low altitude reduces the radius of EMP damage, but increases the power of impact on the enemy. Increasing the height of the detonation leads to the opposite results: an increase in the radius and a reduction in power. In this case, it is possible to obtain outstanding results. Thus, the detonation of a nuclear charge of unspecified power at an altitude of 30 km, according to the calculations of the author of the report, could lead to catastrophic consequences for the infrastructure of North America.
The report “Nuclear EMP Attack Scenarios and Combined-arms Cyber Warfare” also proposed possible scenarios for hypothetical armed conflicts using EMP weapons. According to the authors, Russia can use its systems of this kind against the NATO contingent in Europe, and there is also a threat to the continental United States. China could allegedly hit Taiwan's infrastructure with an electromagnetic pulse. Taiwan and Japan have been designated as targets for North Korean weapons. Iran is capable of using EMP against Israel, Egypt and Saudi Arabia.
Further in the report, even more interesting estimates are given, which are also quoted by B. Hertz. Terrorists from the Islamic State group (banned in Russia) can allegedly purchase EMP charges from the DPRK, as well as receive short-range missiles from Iran. Missiles with unusual warheads could then be used to strike countries in the Mediterranean. P.V. Pry also suggests that Pyongyang is capable of selling its weapons to other terrorist organizations, and this will also lead to attacks on third countries.
For obvious reasons, the Free Beacon cites in particular detail the part of the report devoted to possible EMP strikes on the territory of North America and the United States in particular. In particular, data is provided on the quantitative features of a hypothetical attack. Thus, only 14 nuclear warheads (yield not specified) detonated at an altitude of 60 miles with their electromagnetic pulses are capable of destroying key US infrastructure. The second series of such strikes renders the army's main facilities, including strategic nuclear forces, useless.
The report indicates that the danger to the United States is posed by the activities of several “dictatorial regimes.” American targets can be hit by Russia, China, North Korea and Iran, not counting terrorist organizations. At the same time, there is quite detailed and plausible information about some projects of this kind. For example, Russian military and officials have repeatedly talked about the development of weapons based on electromagnetic pulses.
An article by the Free Beacon, based on a report by P.V. Praya, attracted the attention of readers and became the reason for a number of new publications in various media. For several days now, the discussion of electromagnetic weapons, their capabilities and potential impact on the situation in the world has been ongoing.
Oddities of the report
B. Hertz from The Washington Free Beacon provided only selected quotes from the report “Nuclear EMP Attack Scenarios and Combined-arms Cyber Warfare.” The document itself includes 65 pages and simply does not fit into a small article. In this regard, a lot of interesting information was left outside the article in Free Beacon. For example, it only mentioned the abstracts of the report directly related to the use of EMP weapons, while the original document also discussed threats in cyberspace, nuclear weapons, etc. Also, the report had some features that do not allow us to place any special trust in it.
Contrary to various reprints in the media of different countries, the 2017 report is not directly related to the Pentagon or the US Congress. It was prepared by a “private” expert for a non-governmental organization, which, moreover, recently ceased its activities. These circumstances show the level of the document and its potential in the context of influencing the military policy of the United States. Perhaps congressmen could read the report and learn some facts (or fiction) from it, but they are unlikely to take it seriously.
The document also contains very bold assessments and extremely interesting assumptions. Some of them are based on too loose assumptions, hardly acceptable for a serious report. However, P.V. Pry recalls some past events, takes into account the current political agenda, and then draws conclusions based on them. His fabrications and assumptions may, at a minimum, raise questions, but at the same time they are “politically correct” and meet the interests of some circles in the United States and other countries.
For example, events from twenty years ago are cited as evidence in favor of Russia's ability and desire to use its hypothetical EMP weapons (p. 3). In May 1999, a Russia-NATO meeting was held in Vienna to discuss current events in the Balkans. During this event, the head of the Russian delegation, Vladimir Lukin, made an interesting statement. He proposed to present a picture of events in which Russia really wants to harm the United States and interfere with NATO’s combat work and the solution of the Alliance’s political tasks. In this case, the Russian side could launch an intercontinental missile and detonate its warhead at a high altitude above the United States. The resulting electromagnetic pulse could cripple the state's basic infrastructure. Another Russian delegate noted that if one missile fails, another will follow.
Based on these statements, the author of the report for the EMR Commission draws far-reaching conclusions. In addition, he is inclined to trust not the best sources and take their information on faith. Thus, considering threats in cyberspace (p. 11), P.V. Pry, citing foreign sources, writes that in December 2015 and December 2021. Russia launched information attacks. The consequence of such cyber attacks was a power outage in the western regions of Ukraine and in Kyiv.
The proposed scenarios for the use of EMP weapons may seem plausible or overly bold. However, some of them look extremely strange. Thus, a hypothetical situation in which Middle Eastern terrorists launch a missile attack on Italy and disable its facilities using an electromagnetic pulse is seriously considered (p. 45). Iran and North Korea are indicated as sources of weapons and materiel for such an operation. How and why Pyongyang and Tehran should begin to cooperate with the Islamic State is not specified.
Overall, the report “Nuclear EMP Attack Scenarios and Combined-arms Cyber Warfare” looks very strange. Realistic concerns and assessments in it are accompanied by controversial theses and overly free assumptions. All this sharply reduces its value. In addition, the value of the report is negatively affected by the fact that the media is positioning it as an official Pentagon document presented to Congress. It is unlikely that a serious document needs such false “advertising.”
The document, which attracted the attention of The Washingtin Free Beacon and then other media outlets, raises a lot of doubts and suspicions. Apparently, we are talking about some kind of paper “for internal consumption” related to the interests and objectives of a particular political group in the United States. At the same time, despite the constant mention of third countries, the report is not directly related to them. Foreign developments - both real and supposed - turn out to be just a reason for frightening statements and forecasts. In addition, for some unknown reasons, the report from mid-2021 began to be discussed only in January 2019.
A little reality
It should be recalled that electromagnetic weapons are indeed being developed by several states and may well enter service. However, for obvious reasons, the developers of such systems are in no hurry to disclose all the details, which contributes to the emergence of various versions, assumptions and rumors. It is known that research and development work on the topic of EMP weapons is also being carried out in our country.
Several years ago, information appeared in the domestic press about the development of a promising missile system with a warhead in the form of an electromagnetic warhead. This product became known as “Alabuga”. However, officials later denied the development of such a missile system. At the same time, it was clarified that the “Alabuga” code refers to research work to study the prospects of EMP weapons. In the fall of 2021, it became known that a number of domestic enterprises are now working on the creation of promising weapons suitable for practical use, and this project uses the results of the Alabuga research project. Subsequently, various rumors reappeared, but official reports on this matter were no longer received.
Currently, leading countries are really showing interest in weapons that hit enemy targets using a powerful electromagnetic pulse. There is some information about the development of such systems and their imminent entry into service. Thus, in the near or medium term, the leading countries of the world will indeed be able to obtain fundamentally new weapons with special capabilities. This means that the report from last year for the Commission on EMP Threats and the latest publications in the foreign press still have some relation to real events. However, the realism of individual forecasts is not a worthy justification for overly bold assumptions and implausible scenarios.
Based on materials from: https://freebeacon.com/national-security/china-russia-building-super-emp-bombs-for-blackout-warfare/ https://fantaluciano.altervista.org https://empcommission.org/ https://fas.org/ https://tass.ru/ https://vz.ru/
How it works
How can you create such a powerful electromagnetic field that can have a similar effect on electronics and electrical networks? Is the electronic bomb a fantastic weapon or can similar ammunition be created in practice?
The electronic bomb has already been created and has already been used twice. We are talking about nuclear or thermonuclear weapons. When such a charge is detonated, one of the damaging factors is the flow of electromagnetic radiation.
In 1958, the Americans detonated a thermonuclear bomb over the Pacific Ocean, which led to a disruption in communications throughout the region, there was no communication even in Australia, and there was no light in the Hawaiian Islands.
Gamma radiation, which is produced in excess during a nuclear explosion, causes a strong electronic pulse that spreads over hundreds of kilometers and turns off all electronic devices. Immediately after the invention of nuclear weapons, the military began developing protection for their own equipment from such explosions.
Work related to the creation of a strong electromagnetic pulse, as well as the development of means of protection against it, is carried out in many countries (USA, Russia, Israel, China), but almost everywhere they are classified.
Is it possible to create a working device based on other less destructive operating principles than a nuclear explosion? It turns out that it is possible. Moreover, similar developments were actively carried out in the USSR (they continue in Russia). One of the first to become interested in this direction was the famous academician Sakharov.
It was he who first proposed the design of a conventional electromagnetic munition. According to his idea, a high-energy magnetic field can be obtained by compressing the magnetic field of a solenoid with a conventional explosive. Such a device could be placed in a rocket, shell or bomb and sent to an enemy target.
However, such ammunition has one drawback: its low power. The advantage of such shells and bombs is their simplicity and low cost.
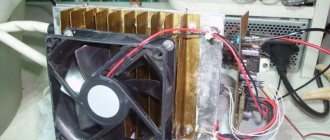
Electromagnetic Pulse Generator – PART 1
This major project shows how to produce a multi-megawatt pulse of electromagnetic energy that can cause irreparable harm to electronic computerized and EMI-sensitive communications equipment. A nuclear explosion causes a similar impulse; special measures must be taken to protect electronic devices from it. This project requires the storage of lethal amounts of energy and should not be attempted outside of a specialized laboratory. A similar device can be used to disable a car's computer control systems in order to stop the car in unusual cases of theft or if a person is drunk at the wheel.
Rice. 25.1. Laboratory electromagnetic pulse generator
and a driver dangerous to surrounding motorists. Electronic equipment can be tested using an electronic pulse generator for sensitivity to powerful pulse noise - lightning and a potential nuclear explosion (this is relevant for military electronic equipment).
The project is described here without specifying all the details, only the main components are indicated. A cheap open spark gap is used but will only give limited results. For optimal results, a gas or radioisotope arrester is required, which is as effective in creating interference as a potential nuclear explosion (Figure 25.1).
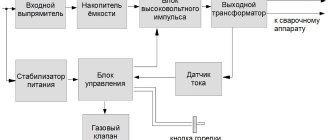
General description of the device
Shock wave generators are capable of producing focused acoustic or electromagnetic energy, which can destroy objects and be used for medical purposes, for example, to destroy stones in human internal organs (kidneys, bladder, etc.). An EMP generator can produce electromagnetic energy that can destroy sensitive electronics in computers and microprocessor-based equipment. Unstabilized LC circuits can produce multi-gigawatt pulses through the use of wire blasting devices. These high-energy pulses - electromagnetic pulses (in foreign technical literature EMP - ElectroMagnetic Pulses) can be used to test the metal hardness of parabolic and elliptical antennas, beeps and other directed remote influences on objects.
For example, research is currently underway to develop a system that would disable a car during a dangerous high-speed pursuit of someone who has committed an illegal act, such as a car thief or a drunk driver. The secret lies in generating a pulse with sufficient energy to burn the electronic control processor modules of the car. This is much easier to accomplish when the car is covered in plastic or fiber optics than when it is covered in metal. Metal shielding creates additional problems for the researcher developing a practical system. It is possible to build a device for this severe case, but it can be expensive and have a detrimental effect on friendly devices, causing them to fail as well. Therefore, researchers are in search of optimal solutions for the use of electromagnetic pulses (EMP) for peaceful and military purposes.
Objective of the project
The goal of the project is to generate a peak energy pulse for strength testing of electronic equipment. In particular, this project explores the use of such devices to disable vehicles by destroying computer chips. We will conduct experiments on destroying circuits of electronic devices using a directed shock wave.
Risk
Attention! The Bottom Project uses deadly electrical energy that can kill a person instantly if contacted incorrectly.
The high energy system to be assembled uses exploding wire which can create shrapnel-like effects. System discharge can seriously damage the electronics of nearby computers and other similar equipment.
Theories
Capacitor C is charged from the current source to the voltage of the power supply over a certain period of time. When it reaches a voltage corresponding to a certain level of stored energy, it is given the opportunity to quickly discharge through the inductance of the resonant LC circuit. A powerful, undamped wave is generated at the natural frequency of the resonant circuit and at its harmonics. The inductance L of the resonant circuit may consist of the coil and the inductance of the wire associated with it, as well as the capacitor's own inductance, which is about 20 nH. The circuit capacitor is an energy storage device and also affects the resonant frequency of the system.
The emission of the energy pulse can be achieved through a conductive conical section or a horn-shaped metal structure. Some experimenters may use half-wave elements with power supplied to the center by a coil connected to the coil of the resonant circuit. This half-wave antenna consists of two quarter-wave sections tuned to the frequency of the resonant circuit. They are coils whose winding has approximately the same length as the quarter wavelength. The antenna has two radially directed parts parallel to the length or width of the antenna. Minimal emission occurs at points located along the axis or at the ends, but we have not tested this approach in practice. For example, a discharge lamp will flash brighter at a distance from the source, indicating a powerful, directed pulse of electromagnetic energy.
Our test pulse system produces several megawatts of electromagnetic pulses (1 MW of broadband energy) that are propagated by a conical sectional antenna consisting of a 100-800 mm diameter parabolic reflector. The 25x25 cm widening metal horn also provides a certain degree of impact. Special
Rice. 25.2. Functional diagram of a pulse electromagnetic generator
Note:
Basic theory of the device:
The LCR resonant circuit consists of the components shown in the figure. Capacitor C1 is charged from a DC charger with current lc. Voltage V at C1 opg*a' ouivwrcs. ratio:
V=lt/C.
The GAP spark gap is set to start at a voltage V just below 50,000 V. At start-up the peak current reaches:
di/dt-V/L.
The response period of the circuit is a function of 0.16 x (LC)5. Kj jhj />»–гп ц > then i ternoe hea in the inductance of the circuit behind VaX, and the peak value of the current leads to an explosion of the wire and interrupts this current yo» s{Nolstshnno before it reaches the peak value. Itc' .^sp*»*»^ energy (LP) via*/»–“is given in the form of the stomach and jftpcxa tl^htiggguktosgo electromagnetic radiation. Peak power iprmol*tz1 in the manner described below and "**i*gg many megawatts!
1. Charge cycle: dv=ldt/C.
(Expresses the charge voltage on the capacitor as a function of time, where I is direct current.)
2. Accumulated energy in C as a function of voltage: £=0.5CV
(Expresses energy in joules as voltage increases.)
3. Peak current cycle response time V*: 1.57 (LC)0–5. (Expresses the time for the first peak of the resonant current when starting the spark gap.)
4. Peak current at point V* of the cycle: V(C/ Ts05 (Expresses the peak current.)
5. Initial response as a function of time:
Ldi/dt+iR+ 1/C+ 1/CioLidt=0.
(Expresses voltage as a function of time.)
6. Energy of the inductor in joules: E=0.5U2.
7. Response when the circuit is open at maximum current through L: LcPi/dt2+Rdi/dt+it/С=dv/dt.
From this expression it is clear that the energy of the coil must be directed somewhere within a very short time, resulting in an explosive field of energy release E x B.
A powerful pulse of many megawatts in the low frequency range can be obtained by destabilizing the LCR circuit, as shown above. The only limiting factor is the inherent resistance, which is always present in different forms, for example: wires, pivirhnistny effect, losses in dielectrics and switches, etc. Losses can be minimized to achieve optimal results. The electromagnetic wave must be emitted by an antenna, which can be in the form of a parabolic dish of a microwave oven or a tuned one. iM. <gp1gch electromagnetic wave will depend on the geometry of the structure. A large length r* X'bodz will provide better characteristics of the magnetic field B, and short arrivals to a greater extent form the electric field E. These parameters will be included in the equations for the interaction of the radiation efficiency of the antenna. The best approach here is to experiment with antenna design to achieve optimal results, using your mathematical knowledge to improve the basic parameters. Circuit damage is usually the result of a very high di/dt (B field) pulse. This is a subject for discussion!
A 0.5 µF low inductance capacitor is charged in 20 s using the ion charge device described in Chapter 1, Anti-Gravity Project, and modified as shown. Higher charge rates can be achieved with higher current systems, which are available by special order for more advanced studies through www.amasingl.com.
A high-energy RF pulse can also be generated where the output of the pulse generator is coupled to a full-size, center-fed half-wave antenna tuned to frequencies in the 1-1.5 MHz range. The actual range at a frequency of 1 MHz is more than 150 m. Such a range may be excessive for many experiments. However, this is normal for an emissivity of 1; in all other circuits the coefficient is less than 1. It is possible to reduce the length of the actual elements by using a tuned quarter-wave section consisting of 75 m of wire wound at intervals or using two to three meter PVC tubing PVC. This circuit produces a pulse of low frequency energy.
Please be aware, as previously stated, that the pulse output of this system can cause damage to computers and any devices with microprocessors and other similar circuitry over a significant distance. Always be careful when testing and using this system, it may damage devices that are just nearby. A description of the main parts used in our laboratory system is given in Fig. 25.2.
Capacitor
The capacitor C used for such cases must have a very low self-inductance and discharge resistance. At the same time, this component must be able to accumulate sufficient energy to generate the required high-energy pulse of a given frequency. Unfortunately, these two requirements conflict with each other and are difficult to fulfill simultaneously. High energy capacitors will always have higher inductance than low energy capacitors. Another important factor is the use of relatively high voltage to generate high discharge currents. These values are necessary to overcome the intrinsic complex impedance of the series-connected inductive and resistive resistances along the discharge path.
This system uses a 5 µF capacitor at 50,000 V with an inductance of 0.03 µH. The fundamental frequency we need for the low energy circuit is 1 MHz. The system energy is 400 J at 40 kV, which is determined by the ratio:
E = 1/2 CV2.
Inductor
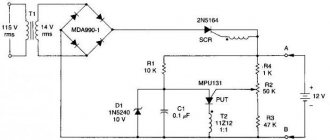
It is easy to make a coil for receiving a low-frequency radio pulse. The inductance, designated L1, is the sum of the parasitic inductance of the wires, the spark gap, the wire blasting device, and the capacitor's own inductance. This inductance resonates over a wide frequency range and must withstand a high-frequency discharge current pulse I. The value of the total inductance is 0.05-0.1 μH. The size of the conductors must take into account the pulse current, which is ideally equal to Vx(C/L)1/2. During a transient process, current tends to flow along the surface of the conductor due to the high-frequency skin effect.
You can use a multi-turn coil for low frequency experiments with a dual antenna. The dimensions are determined by the air inductance formula:
Rice. 25.7. Installing a spark gap for connection to the antenna for low frequency operation
Application device
This system is designed to study the sensitivity of electronic equipment to electromagnetic pulses. The system can be modified for field use and runs on rechargeable batteries. Its energy can be increased to pulses of electromagnetic energy of several kilojoules, at the user's own risk. You should not attempt to manufacture your own version of the device or use this device unless you have sufficient experience in using high energy pulsed systems.
Pulses of electromagnetic energy can be focused or fired in parallel using a parabolic reflector. Any electronic equipment and even a gas-discharge lamp can serve as an experimental target. A burst of acoustic energy can cause a sonic shock wave or high sound pressure at the focal length of a parabolic antenna.
Sources for purchasing components and parts
High voltage chargers, transformers, capacitors, gas spark gaps or radioisotope gaps, MARX pulse generators up to 2 MB, EMP generators can be purchased through the website www.amasingl.com[21].
Tweet Like
- Previous post: Tesla Coil with a spark discharge length of 30 cm – PART 2
- Next entry: Signal conditioning techniques to increase the efficiency of a switching power supply
- Inductance (0)
- LITHIUM-NON CELL CHARGER CHARGER CONTROLLER (0)
- SYNCHRONIZER WITH SETTING TIME INTERVALS (0)
- PC PROTECTION DEVICE WITH PASSWORD (0)
- MICROPROCESSOR CONTROL DEVICE MATCHING DEVICE AND SIGNAL INPUT DEVICE RTS (0)
- VIDEO LINE DECODER I (0)
- VIDEO LINE DECODER Il (0)