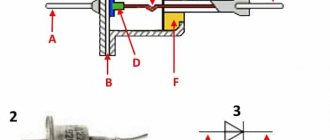
Changing the icon
To ensure that the shortcut is recognizable and visually matches the action being performed, it would be wise to change its icon. The latter can be selected in the appropriate system folder or created manually.
To change the icon as standard, you need to:
- Right-click on the created shortcut and find “Properties” among the context menu items.
- Go to the “Shortcut” tab and click the change icon button.
- Select the one you like among the proposed icons and click OK.
You can create an icon for the shortcut yourself by drawing a picture or editing the image you like in the Paint application. For those who do not know how to draw, the second option is preferable:
- Open the graphic editor, click on the “File” button and open the selected image.
- On the Resize and Skew tab, set the aspect ratio to 16x16, 32x32, 64x64, or 128x128 (in pixels).
- Save the result as an image in BMP format by clicking on the save button in the top panel.
- Right-click on the created file and change its extension from .bmp to .ico.
In addition, you can download your favorite icons from the Internet. Absolutely any image with the .ico extension will do - from a road sign to an image of a tropical forest. There are also special utilities that contain ready-made icon packs and change the design of folders at the user’s request, but most of them are paid or have very limited functionality.
Conventional functional symbols on equipment of all types
Reading alphanumeric designations of electrical circuit elements
On all types of circuits, any element - a resistor, contactor coil, measuring device, etc., has an alphanumeric designation.
This designation consists of one or two letters and numbers. The letter(s) denotes-
They indicate the code of this element, and the numbers (digits) indicate the serial number of this element in this scheme.
For example, the alphanumeric designation KT2 means the following: KT - time relay, 2 - second in order in this circuit.
In the case of depicting on the diagram the components of electrical circuit elements
After the main digital designation, an additional one is placed through a dot, indicating
general serial number of this component.
In this case, deciphering the designations of numbers and letters is performed in the reverse order, i.e. alphabetic characters and numbers are read from right to left.
For example, the alphanumeric designation KM5.4 means the following: KM – electromagnetic contactor coil, the serial number of the contactor in the circuit is 5, the serial number of the contactor contact in the circuit is 4.
This designation is read as follows: the fourth contact of the fifth electrical
magnetic contactor.
Rice. 1. Plus, positive polarity . To identify positive polarity connectors connecting a DC power source
Rice. 2. Minus, negative polarity . To designate negative connectors
significant polarity connecting the DC source
Rice. 3. Direct current. To designate connectors connecting the device -
ru to a direct current source, as well as to indicate that the equipment operates only on direct current
Rice. 4. Alternating current. To designate the connectors connecting the device
ru to the alternating current source, and also to indicate that the equipment operates on alternating current only
Rice. 5. AC to DC converter. To denote pre-
AC to DC transformer and corresponding connectors
Rice. 6. DC to AC converter. To denote pre-
DC to AC generator and corresponding connectors
Rice. 7. Body, chassis. To identify connectors connected to the chassis or chassis
Rice. 8. Grounding, ground. To identify ground connectors
Rice. 9. Grounding, protective . To designate grounding connectors, I create
providing protection against electric shock
Rice. 10. Device of protection class II . To designate equipment, the corresponding
meeting the safety requirements specified for class II equipment (protective
You )
Rice. 11. Fuse. To identify fuse boxes and indicate their location
Rice. 12. Signal lamp. To designate a switch with which
turn the warning light on and off
Rice. 13. Lighting lamp, backlight . To designate switches, controls
shining a light source
Rice. 14. Included. To indicate the switching on of the network, power switches or their position corresponding to the switching on of the network
Rice. 15. Off. To indicate turning off the network, network switches or their position corresponding to turning off the network
Rice. 16. On/Off, push-button switch with two fixed
bathroom provisions . To indicate a switch that turns on or off
network. Each switch position is fixed.
Rice. 17. Ready to turn on, standby mode . To indicate switch-
body (or its position), with the help of which part of the equipment is brought into
“Ready to turn on”. On ships, the standby mode is called “stand-by.”
Rice. 18. Foot switch, pedal . To designate connectors to which
eye connects foot switch
Rice. 19. Program channel switch . To designate switches that control channel selection, program
Rice. 20. Start, launch, activation. To designate start, start, actuation switches
Rice. 21. Quick start. To designate a switch or control element
ment by which the operating speed (normal mode) is achieved without signi-
expected delay
Rice. 22. Stop, block. To denote a switch by means of which movement, for example, the movement of a tape, is stopped
Rice. 23. Quick stop, stop . To designate the control elements with the help of which the process, programs, or belt progress is stopped without significant delay
ki
Rice. 24. Pause, break . To designate a switch whose action is re-
the movement (e.g. of a belt) is interrupted by the braking system and shutdown
Rice. 25. Effect or action in the direction of the starting point, normal mode . To indicate effect or action switches in the direction of action
real or imaginary starting point, sign, mark, for example, simultaneous reduction of several equipment parameters to pre-selected values
Rice. 26. Automatic control . To designate the switch (or its position) by which the equipment is brought into automatic control mode
Rice. 27. Manual control . To designate the switch (or its position) by which the equipment is put into manual control mode
Rice. 28. Remote control . To indicate a switch (or its position
Rice. 29. Regulation. To designate an element to be regulated, setting the corresponding value of the quantity. The value of the quantity increases with the height of the figure
Rice. 30. Adjusting high sound frequencies . To indicate adjustable
main elements of high sound frequencies
Rice. 31. Regulation of low sound frequencies . To indicate adjustable
main elements of low sound frequencies
Rice. 32. Music. To indicate the "music" position of the "speech/music" switch
Rice. 33. Sound. To designate switches, controls and connectors related to audio information
Rice. 34. Balance. To indicate stereo channel balance adjustment
Rice. 35. Synchronization. To designate connectors, switches and controls
synchronizing elements designed to control equipment operating synchronously
but, for example, connecting a film projector synchronizer
Rice. 36. Filter (pass) high frequencies . To designate a high-quality filter
high frequencies, as well as associated switches and control elements
Rice. 37. Filter (pass) of low frequencies . To identify a low-pass filter and its associated switches and controls
Rice. 38. Band-stop filter, notch . To indicate stripes
barrier filter, as well as associated switches and control elements
Rice. 39. Mid-pass filter, bandpass . To designate a bandpass filter
ra, as well as associated switches and control elements
Rice. 40. Tuner, radio receiver . To designate connectors, switches and control elements of a radio receiver, tuner
Rice. 41 . Entrance. To designate input connectors when a distinction between inputs and outputs is needed
Rice. 42. Exit. To designate output connectors when necessary
between inputs and outputs
Rice. 43. Loudness compensation. To designate switches and control elements
cops that allow you to compensate for the physiological hearing curve
Rice. 44. Amplifier. To designate connectors, switches and adjusters
main elements of the amplifier. To designate an amplifier enclosed in a protective housing
Rice. 45. Clock, time relay . To designate switches and control elements in clocks, time relays, timers
Rice. 46. Monophonic, mono . To indicate monaural playback
recording (recording) sound. To indicate the "mono" position on the "mono/
stereo". Also used on record labels
Rice. 47. Stereophonic . To indicate stereophonic playback (recording) of sound. To indicate the "stereo" position on mono/stereo switches. Also used on record labels
Rice. 48. Tape recorder. To designate connectors, switches and adjustments
ing elements intended for a tape recorder
Rice. 49. Stereo tape recorder . To designate connectors, re-
switches and control elements intended for stereo magnetic
backgrounds
Rice. 50. Headphones . To designate connectors, switches and control elements intended for headphones
Rice. 51. Stereo headphones . To designate connectors, switches and control elements intended for stereo headphone
ical phones
Rice. 52. Headphones with a microphone. To designate connectors, transfer
switches and control elements intended for headphones with a microphone
Olfon
Rice. 53. Microphone . To designate connectors, switches and adjusters
building elements intended for microphones
Rice. 54. Stereo microphone . To designate connectors, switches
drivers and control elements designed for stereo microphones
Rice. 55. Earphone. To designate connectors, switches and adjusters
main elements intended for the earphone
Rice. 56. Loudspeaker. To identify connectors, switches and control elements intended for a loudspeaker
Rice. 57. Recording (registration) on a storage medium . To denote re
switch its position in which the equipment is turned on for recording
Rice. 58. Playing a recording from a storage medium. To denote re-
switch or its position in which the equipment is turned on for playback from a storage medium
Rice. 59. Erasing a recording from a storage medium . To indicate switch
la or its position in which information recorded on the media is erased
le
Rice. 60. Control of input data during recording or registration on the wearable
body of information. To designate a control element by which input data is controlled during recording or recording
Rice. 61. Control of input data after recording or registering them on a device
body of information. To designate a regulatory element by means of which control of input data is carried out after recording or registering them
Rice. 62. Control of input data during playback. To denote
the value of the regulatory element by means of which the input is controlled
data during playback
Rice. 63. Write blocking . To designate the control element, I block
circuit designed to prevent accidental playback of a recording.
Rice. 64. Marker (marker) . To designate a control element, using
whose mark (for example, signal, perforation, special code) can be reserved
registered on storage media
Rice. 65. Media cutoff. To designate the control element of the system from -
cutting, for example, in devices for copying and mounting paper, magnetic, perforated
roved tape
Rice. 66. Direct and alternating current . To designate connectors, connect
connecting equipment to a source of direct or alternating current, as well as to indicate
understanding that the equipment operates on direct and alternating current
Rice. 67. Quartz. To designate controls for quartz resonators
Rice. 68. On/off, push-button switch with one fixed
bathroom position . To designate a switch that turns on or off
go network. Off position is fixed, "On" position carried out only when the switch is pressed
Rice. 69. Call. To indicate the switch that controls the bell
Rice. 70. Horn. To indicate the switch that controls beeps, sound
with alarms
Rice. 71. Fan . To indicate the switch that controls the fan
rum
Rice. 72. Silent grounding . To indicate grounding connectors, both
ensuring minimal equipment noise from grounding
Rice. 73 . Equipotentiality . To designate connections intended to bring several pieces of equipment to a single potential
Rice. 74. Rectifier (without specifying type). To identify connectors and control elements associated with rectifier devices
Rice. 75. Transformer . To designate connectors, switches and adjustments
lyrating elements designed to control power transformers
Rice. 76. Movement in one direction . To designate the regulating element
ment, as a result of which the object moves in the specified direction
Rice. 77. Movement in two directions . To designate the regulating element
ment, as a result of which the object moves in two specified directions
Rice. 78. Movement restricted in two directions . To designate elements
one, as a result of which the object moves in two directions in a certain
within limits
Rice. 79. Action from the starting point . To designate the regulating element,
through which an object (effect) moves from the original (real or imaginary) point
Rice. 80. Action towards the starting point. To indicate regulation
element through which the object (effect) moves to the original (real or imaginary) point
Rice. 81 . Action in two directions from the starting point. To denote regu
lyrating element through which the object (effect) moves from the original (real or imaginary) point
Rice. 82. Sequential action from the starting point and back . To denote
of the regulating element through which subsequent movement occurs
transfer of an object (effect) from a starting point (real or imaginary) and back
Rice. 83. Simultaneous action from the starting point and back . To denote
tion of the regulatory element, through which simultaneous change occurs
moving an object (effect) from the starting point and back
Rice. 84. Setting the minimum . To designate the regulating element, in the middle
which sets the minimum value of a quantity, for example, the balance of a bridge circuit, the minimum deviation of a measuring device, indicator, etc.
Rice. 85. Setting the maximum. To designate a regulating element,
by means of which the maximum value of a quantity is set, for example,
construction, maximum deviation of the measuring device, indicator, etc.
Rice. 86. Notch resonant filter (wave trap). To indicate
values of the regulating element that controls the notch resonant filter
Rice. 87. Band-stop filter with variable stop band
(bandwidth). To designate a regulatory element that controls
Variable bandpass filter
Rice. 88. Bandpass filter with variable average frequency. To designate the control element that controls a variable center frequency bandpass filter
Rice. 89. Bandpass filter with variable bandwidth (selective control). To designate the control element that controls a variable-bandpass filter