Pros and cons of graphite
Graphite electrodes, unlike consumables made from other materials, have a very significant advantage: they transmit electricity without melting. This is the main advantage that predetermines their choice for performing work. Graphite electrodes are produced as regular or copper-plated, with tips of different lengths and shapes.
The most significant characteristics of graphite consumables:
- products are presented in the retail chain in a large assortment;
- the cost of consumables is low;
- low consumption of electrode during use;
- quickly heat up to temperatures at which metals melt;
- When performing welding work with an inverter, a small current of 5-10 amperes is required to ignite the arc.
It must be emphasized that the welding seam formed using graphite electrodes is resistant to high temperatures and resistant to corrosion. In addition, copper wire does not crack during welding. Graphite electrodes make it possible to qualitatively connect not only copper, but also aluminum wires.
However, they have not only advantages, but also disadvantages:
- welding a joint using graphite is a rather complex technological process due to its small diameter - 6 mm;
- the use of graphite consumables increases the carbon content in the workpieces. For this reason, the performance characteristics of the finished connection may deteriorate;
- a specific type of electrode tip is suitable for performing a small list of operations. Therefore, an assortment of consumables is necessary in cases where different types of work are planned.
Scope of use of rods and features of working with them
Graphite electrodes are used not only in cases where it is necessary to connect copper or aluminum wires. The scope of their application is much wider. For example, graphite rods are in demand for surface pre-treatment before welding, edge cleaning, welding of workpieces and a number of other types of processing. Consumables of this type are actively used both in metalworking and in shipbuilding.
Graphite electrodes make it possible to effectively cut rivets and pierce parts made of carbon and alloy steel. They are relevant for heat treatment (fusion) of cast iron and steel. Special nipples allow you to connect the electrodes to each other, which allows you to organize a continuous supply of electrodes to the working area. Thus, it is easy to establish a process for flowing consumables into the furnace.
As practical experience shows, graphite rods when arc cutting metal or welding copper wiring reduce the number of defects. The main requirement when using consumables of this type is compliance with safety requirements and technological process.
In addition, the use of graphite rods is relevant for performing the following operations:
- welding of thin sheet metal or non-ferrous metal blanks;
- elimination of defects formed during casting;
- surfacing of hard-alloy coatings to parts for various purposes.
Often working with graphite electrodes involves the use of an additive. It can be previously laid at certain welding locations or supplied to the working area during the formation of the seam.
It should be remembered that in order to obtain high-quality welded joints using graphite electrodes, you need to take into account the features of working with such consumables:
- It is easier to achieve economical consumption of the rod and at the same time maintain a stable arc for a long period of time with straight polarity. In other words, the minus is applied to the electrode.
- When performing welding work, it is important to take into account the influence of external factors on the stability of the arc. This helps to get a better result.
- When using graphite electrodes, the specialist’s efficiency will be lower than when welding with consumable consumables.
- Welding with graphite makes it possible to obtain welded joints with average ductility.
- The formation of voids inside the seams cannot be ruled out, which negatively affects their strength and durability.
Given the complexity of the technological process, welding work using graphite electrodes is entrusted to experienced specialists. For beginners, it is advisable to practice well for such work.
To work with graphite electrodes, two technological methods are used:
- Feeding material directly into the arc flame. The additive is located between the joint and the electrode at an angle of thirty degrees. In this case, the wire is fed into the working area first and only after it the electrode itself. To speed up the work process, the consumable is held at an angle of 70 degrees.
- First, a bead consisting of the base metal is deposited. After this, filler material is supplied to the melting zone. Unlike the first technological method, here the rod is fed first and only after it the wire.
The biggest disadvantage of the second method is that there is a high probability of a burn-through. Therefore, it is not suitable for working with thin workpieces and is undesirable for use by beginners in this matter. But this technology is suitable for joining workpieces with thick walls.
When working with graphite electrodes, a specialist must remember that the determining parameter for their use is the current density. If, due to any objective reasons, this indicator is higher than acceptable standards, then work should be stopped. Otherwise, with a high degree of probability, graphite will become unusable.
Extending the service life of graphite electrodes is easy. To do this, just screw in special extension nipples on both sides. Thanks to this solution, not only the costs of purchasing consumables are reduced, but their reliability also increases.
Current Adjustment
For welding wiring, the current is adjustable in the range from 30 to 120 amperes. Most inverters on the market have this set of parameters and are suitable for the job.
The specialist selects the exact current value separately in each specific case experimentally. This approach is due to the following factors:
- Each inverter model has its own design features that affect performance characteristics. It is very important to first familiarize yourself with the manufacturers' recommendations set out in the instructions;
- In a household network, the voltage is not always the standard 220 volts. It can be either smaller or larger;
- cable from different manufacturers differs in its composition. Although the differences are minor, they affect the welding process.
The results of welding work using graphite rods are largely determined by the qualifications of the welder. It is necessary to know exactly the optimal current indicators characteristic of conductors of a certain cross-section:
- wiring with a diameter of 1.5 mm is welded with an inverter set to 70 amperes;
- when it becomes necessary to connect three wires of the same size (1.5 mm), the current should be increased to 81-91 amperes;
- when welding three parts of wire with a diameter of 2.5 mm, the current strength is set in the range of 81-101 amperes;
- Current strength in the range of 101-121 amperes is suitable for connecting four copper wires 3 mm thick.
Graphite and carbon electrodes for welding copper wires
- December 08
- 59 rating
Increasingly, electrical wiring installation is not complete without a carbon electrode for welding copper wires. This method is an alternative to soldering copper strands, which requires the use of flux and solder. Like soldering, the task of welding is to ensure reliable contact between the wires, which cannot be achieved by ordinary twisting, because an oxidation film will certainly appear on the copper surface over time. True, after welding, a permanent connection of the twist is not obtained over its entire surface, as with soldering, but only at the tip, which melts within 1-2 seconds, however, such contact prevents overheating of the cables when the load increases.
Due to their technical characteristics, graphite electrodes are consumed more slowly, are easy to cut, and do not crack during welding.
As a rule, welding of wires is carried out in junction boxes. They are located quite high, so for work you need to use portable welding equipment. There are industrial devices for this purpose, the use of which is advisable at a professional level. You can make a homemade welding transformer, but inverter machines, which many people have today, are excellent for welding. They are mobile and also have the ability to adjust the desired welding current.
Types of electrodes for welding copper wires
Classification of electrodes for welding.
Welding of copper must be carried out with specialized electrodes. Coal has already been mentioned. In addition to it, there are graphite electrodes. It must be said that carbon brushes of commutator motors, battery rods and similar products can act in this capacity. They fully replace electrodes from the store, except that they do not have copper plating, but for these devices you will have to design more convenient holders. Homemade alligator clips for both the electrode and ground connection will not be as cumbersome as standard ones, so they are much easier to use when working in junction boxes. Of course, it is necessary to take care of the reliable insulation of their handles.
Carbon and graphite electrodes are similar in the main thing: both have a melting point more than 3 times higher than the melting point of copper. Due to this circumstance, their consumption during installation of electrical wiring is extremely low. At the same time, the electrodes heat up to high temperatures almost instantly, so there is a danger of overheating of the material being welded, which can lead to damage to the insulation in the cables. All these factors must be taken into account by the welder in order to be efficient enough when performing the work, because a few moments will be enough both to reliably fasten the twist and to render part of the wiring unusable.
Return to contents
Welding with a carbon electrode with the supply of filler metal into the arc: a - “left” method; b - “right” method.
Despite the similarity of carbon and graphite rods in the field of application, their characteristics are somewhat different:
- The first difference is the price. Graphite products are more affordable.
- If carbon rods are completely black, then graphite electrodes have a dark gray color with a metallic tint.
- Welding with a carbon electrode requires some experience from the welder, since this rod creates a very high temperature arc, which can cause the strand to break. At the same time, high temperature values are achieved with minimal current, so carbon electrodes are useful for owners of weak transformer devices.
- Owners of inverter devices equipped with current regulators are better off using graphite rods. They are less demanding on the qualifications of the master. In addition, the welded joint after their use is of better quality, greater strength, and increased resistance to oxidation than after welding with coal.
Return to contents
As for adjusting the current, wire welding is carried out in the range from 30 to 120 A (almost all inverter welding machines operate within these limits). In any case, the exact welding current will have to be selected experimentally, since:
Technology of welding copper strands with a carbon electrode.
- Each inverter has its own characteristics.
- The mains voltage may differ from 220 V.
- The chemical composition of copper wires from different manufacturers may vary.
In addition, it doesn’t hurt for the welder to practice so that the work is done as quickly and efficiently as possible.
However, you should be aware of the current values at which wires of different sections are connected:
- When welding 2 wires with a diameter of 1.5 mm2, the inverter is set to 70 A.
- 3 wires of the same cross-section are welded at a current of 80 to 90 A.
- The current for welding 3 wires with a diameter of 2.5 squares is 80-100 A.
- 4 wires of 2.5 mm2 are welded with a current set on the device from 100 to 120 A.
Return to contents
To prevent possible melting of the cable insulation, a metal radiator must be attached to the base of the twist. A clamp with a large surface that improves heat transfer will help remove excess heat from the twist. It is advisable that the radiator be made of copper, as it has high thermal conductivity.
Safety rules for welding work.
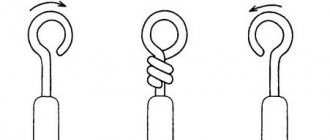
The twist welding process is preceded by a preparatory stage, during which the wires are freed from their sheaths and insulation. The length of the exposed cores must be at least 10 cm, then the twist will be no shorter than 5 cm.
When twisting the wires, you need to ensure that they fit as closely as possible to each other. You also need to ensure that their ends end up at the same level, otherwise some of the wires will end up outside the welded joint. If necessary, the end of the twist is cut off with side cutters.
Near the radiator, a ground clamp is attached to the twist, after which an electrode is brought to the tip of the wires. The contact time should not exceed 2 seconds. After it is interrupted during twisting, a small influx of spherical shape is obtained. The remaining twists are welded in the same way.
Return to contents
When working, you must observe safety precautions:
- The line on which copper wires are welded must be de-energized.
- The use of protective equipment (gloves, overalls, safety shoes, masks) is mandatory.
- The work site must be cleared of objects that could catch fire.
There are at least 2 twists in the distribution box. Don't rush into the next weld.
To avoid getting burned, it is better to wait until the first one cools down.
After welding, the strands should be insulated. This can be done with electrical tape or heat shrink tubing. The latter is put on the wires and heated with a hairdryer. As a result, the tube tightly fits the wiring strands, creating a reliable sheath around them.
expertsvarki.ru
Welding aluminum wiring
The graphite electrode is equally suitable for welding both copper and aluminum wiring. Work on connecting aluminum conductors is carried out under flux - a protective powder, which, when heated, forms a gas protective environment. Thanks to the use of flux, welded joints are protected from contact with oxygen and do not oxidize during work.
The current strength is set to the optimal value. The current is rectified by passing through a diode bridge and a ripple filter. In fairness, it should be noted that some experienced specialists can perform such work with alternating current. They don’t necessarily have to select the right parameters experimentally to get the job done. But the quality of the connection will be worse than in the case of using direct current.
How to properly twist a cable
One of the primary tasks when welding twists is to protect the cable insulation from melting. A universal solution is to connect a metal radiator to the point where the twist leaves the insulation. It is desirable that it be copper, then the maximum possible thermal conductivity and the greatest outflow of excess heat are ensured. Exactly the same effect is guaranteed by increasing the contact area between the radiator and the wiring.
Before starting to weld the twist, a small amount of preparatory work is required. If there is a varnish coating on the insulation, it should be removed. The wires should be twisted together as tightly as possible. It is important that they are in very close contact. The optimal twist length is about 5-6 centimeters. The ends of the wires are cut at the same distance so that both parts of the twist fall into the welding zone.
In the place where the radiator contacts the wiring, ground is connected. All that remains is to bring the electrode to the edge of the twist. Contact should be short. One second is enough for a copper-plated ball of molten metal to form at the edge of the twist. Other sections of the twist are welded in the same way: by briefly closing the circuit using a graphite electrode.
Contact method
In addition to using an inverter for welding copper wires, spot contact welding can also be used, the welding time of which does not exceed 1-2 seconds.
At home, to connect household electrical wiring, you can use a conventional 500 W transformer with a voltage in the secondary winding of 12-36 V. By attaching a holder for the electrode and copper wires to the secondary winding, we get a simple welding machine.
Depending on the cross-section and number of copper wires, it has been experimentally established that the current for welding should be:
- for 2 wires with a cross section of 1.5 mm2 – 70 A;
- 3 sections 1.5 mm2 – 80 A;
- 3 sections 2.5 mm2 – 90-100 A;
- 4 cross-section 2.5 mm2 – 100-120 A.
However, current values can vary greatly depending on the cable used and its manufacturer. The fact is that cable manufacturers use copper wires with various impurities, which affects electrical and thermal conductivity; wire cross-sections sometimes do not correspond to the declared characteristics.
Therefore, spot welding is carried out only after the optimal welding current has been adjusted on scraps of the same cable that is to be welded.
Safety precautions
The use of carbon (graphite) electrodes makes it possible to obtain reliable metal compounds and create durable products. It is important to adhere to safety regulations while performing work. The most significant of them:
- The current supplied to the cables must be turned off when completing operations. This will prevent accidental electric shock if you unintentionally touch an uninsulated section of the wiring.
- Welding work should be performed only in special protective clothing and shoes. In addition, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment - a mask, mitten, lapels, etc., which help protect the eyes and parts of the body from burns.
- There should be no flammable materials present at the welding site. They are the cause of fires at the welding site.
- After completing the twist welding, you need to give the wiring time to cool. After waiting for some time and making sure that the veins have cooled down, you can move on to the next stage of work. If you don’t do this, it’s only a matter of time before you get burned from accidentally touching a hot twist.
- Welded strands must be insulated upon completion of work. For this, insulating tape or heat shrink tubing is used.
Copper technology
Before welding copper, it is necessary to prepare all equipment and components in advance and check their serviceability. To avoid burns, injuries, and visual impairment, welding work must be performed in a special uniform, gloves, and a protective mask.
Have a fire extinguisher at the ready. Only strict adherence to safe welding rules will allow you to obtain the required result. To weld copper, we will use two types of electrodes - carbon and graphite.
Carbon rods from used batteries can be a good replacement. After all the equipment has been checked, we set the current strength we require.
Electrical wires differ in the composition and quality of copper, so it is necessary to select current parameters taking this into account.
If the welding current is selected correctly, the arc will be stable and the electrode rod will not stick. The ability to quickly select current parameters to match the characteristics of the material being welded comes with experience.
Here are approximate current characteristics for different types of wires:
The preparation is complete, you can start welding. First, remove the cable insulation at a distance of 7-10 cm. Then the wires from several cores are twisted.
We carefully trim the resulting twist, leave about 5 centimeters, and place a copper clamp on it. Its function is to remove excess heat. We also connect ground (grounding).
We bring the electrode rod to the twist and cook for several seconds until a copper ball forms at the end of the twist. Welding must be done carefully, without damaging the insulation.
Then we wait until the wires cool down and insulate them using electrical tape or a special heat-shrink tube.
During such work, the copper tip that holds the electrode rod and supplies welding current to it quickly wears out and loses functionality.
Its task is to hold the electrode tightly, the quality of welding depends on this. If worn, it should be replaced.